Generally accepted norms of indicators
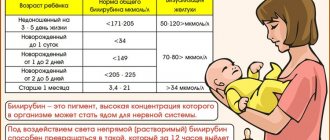
The acceptable level of bilirubin concentration for each age is different. The highest concentration of the substance in the blood is observed in newborns, in the initial stages of life, up to 200 µmol/l, this is due to the period of adaptation of the newborn’s gastrointestinal tract to the digestion of mother’s milk. The acceptable level of bilirubin concentration for each age will be different. The highest concentration of the substance in the blood is observed in newborn children, in the initial stages of life. In one-year-old children and children under 13 years of age, a satisfactory indicator of the concentration of indirect pigment is considered to be up to 20.3 µmol/l, for direct pigment up to 5.2 µmol/l.
The degree of concentration of the substance for adults should not cause concern if the survey analysis shows a level of up to 19.9 µmol/l for indirect, and 4.9 µmol/l for direct bilirubin, since such measurements are satisfactory for people of the adult age category.
Diagnosing infants
If in adults jaundice means the presence of diseases, then in children hyperbilirubinemia can be physiological or pathological. In the first case, it is noted by the 4th day of life, in Asian children by the 7th, it goes away on its own, without reaching critical levels of bilirubin.
The pathology may be a consequence of liver dysfunction, high concentrations of beta-glucuronidase in breast milk, or occur with a low-calorie diet or dehydration. Both the baby himself and his mother are subject to examination.
Anamnesis and external signs are studied. It is important to rule out or diagnose kernicterus as soon as possible. Warning signs include: jaundice on the first day of life and after 2 weeks, increased total bilirubin and the rate of its rise, respiratory distress, the presence of bruises or hemorrhagic rash. The child's bilirubin level and blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid cultures are measured. It is necessary to exclude the presence of TORCH infections in the mother.
Causes of increased bilirubin in the blood
The source of the pathological condition is caused by disruption of the liver, resulting in improper outflow of bile, which causes the occurrence of viral lesions and hepatitis.
symptoms of increased bilirubin
The cause of increased bilirubin in the blood may be:
- Chronic or autoimmune hepatitis.
- Non-benign neoplasms in the liver area.
- Incorrect functioning of the pancreas.
- Intoxication of the body through poisoning can also cause an increase in bilirubin.
By the way, any of the above reasons is pathological and requires immediate medical intervention and long-term treatment
Main indicators of liver tests
Let's consider the main indicators of liver tests, as well as their norms and reasons for deviations from reference values.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
ALT and AST are enzymes that are synthesized intracellularly, take part in carbohydrate and protein metabolism, support the functioning of many organs, and play a key role in the metabolism of one of the most important amino acids - alanine and aspartic acid. In the absence of pathologies, enzymes are present in the blood only in small quantities ⇓⇓⇓
| Age | ALT norms, units/l | AST standards, units/l |
| < 5 days | < 49 | < 97 |
| 5 days-6 months | < 56 | < 77 |
| 6-12 months | < 54 | < 82 |
| 1-3 years | < 33 | < 48 |
| 3-6 years | < 29 | < 36 |
| 6-12 years | < 39 | < 47 |
| 12-17 years old (girls) | < 34 | < 25 |
| 12-17 years old (boys) | < 27 | < 29 |
| over 17 years old (women) | < 31 | < 31 |
| over 17 years old (men) | < 41 | < 37 |
Despite some similarities, ALT and AST also have differences:
- ALT is produced to a greater extent in the liver, and to a lesser extent in the muscles, heart, pancreas, kidneys and other organs. In this regard, high levels of the enzyme primarily indicate liver disease.
- AST is found in the same cells as ALT, but in the myocardium its concentration is much higher. That is why the main reasons for increased AST are not only liver pathologies, but also heart diseases.
In what cases does ALT increase?
The main reasons for increased ALT include:
- death of hepatocytes (liver parenchyma cells) caused by viral hepatitis and exposure to toxic substances;
- Liver cirrhosis is a chronic pathology in which healthy organ tissue is replaced by connective tissue or stroma;
- intrahepatic cholestasis - insufficient secretion of bile due to a violation of its production by liver cells;
- fatty hepatosis is a syndrome accompanied by the accumulation of fat in the liver tissue;
- liver oncology.
Less common causes of high ALT values:
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- inflammation of the heart muscle;
- inflammation of skeletal muscles;
- severe burns;
- shock;
- alcoholism.
Also, the ALT value may be increased when taking hepatotoxic drugs, which include some antibacterial, anabolic, contraceptives, and drugs containing salicylic acid. As a rule, the increase in ALT in this case is temporary.
Symptoms indicating increased bilirubin
There are symptoms the presence of which in a person means that the percentage of bilirubin in the blood is too high:
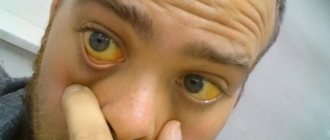
- The whites of the eyes began to turn yellow.
- The skin color becomes more jaundiced.
- Itching of the skin, which intensifies at night.
These symptoms are an important indicator that the body is undergoing internal bile poisoning; ignoring these problems can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the body.
The often manifested bitter taste in the mouth is also one of the symptoms of increased bilirubin in the blood.
treatment of direct bilirubin in the blood
A rapid increase in this substance provokes the darkening of the urinary fluid to a brown color, and solid bowel movements take on a white color. All of the above symptoms are accompanied by severe weakness, high fever and enlarged liver. If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately seek help from the nearest hospital.
Diagnostics and tests
To determine what is causing the increase in bilirubin, you need to undergo examination by a specialist. After a visual examination (checking the color of the skin, whites of the eyes, plaque on the tongue) and palpation of the abdominal cavity, the doctor prescribes laboratory diagnostics:
- BAC for the content of direct or indirect bilirubin;
- Aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase assay;
- Ultrasound examination of the liver.
Blood sampling may be prescribed for a detailed clinical analysis.
Correct therapy can be prescribed only with an accurate diagnosis. In some cases, the help of an infectious disease specialist and gastroenterologist is required.
Treatment of elevated direct bilirubin
You can influence the high concentration of bilirubin in the blood by following a diet and doing physical exercise. After undergoing a biochemical examination of the blood, based on the tests obtained, the doctor prescribes the patient a set of treatment and recommendations aimed at establishing the proper functioning of the liver and the outflow of bile. Even with the slightest discrepancy with the norms, the doctor is obliged to prescribe treatment to correct the functioning of metabolic processes; you can often undergo such a course of treatment at home, while following all the recommendations. In this case, the examination results show a disappointing picture; if necessary, surgical intervention is required, followed by hospitalization in a hospital.
Advantages of JSC "SZTsDM"
You can check the levels of all forms of bilirubin, as well as find out the cause of the violation of bilirubin metabolism in one of the laboratories of JSC SZTsDM. This is the largest center conducting all types of laboratory tests, where you can also make an appointment with specialized specialists.
The Northwestern Center for Evidence-Based Medicine is chosen because it has a network of its own laboratories with the latest equipment, as well as:
- qualified medical and friendly employees work;
- high accuracy and quick availability of results are guaranteed;
- collection of materials can be carried out at home and in the terminal, where comfortable conditions for anonymity have been created;
- You can collect the results in several ways.
Another distinctive advantage is the convenient location of laboratories within transport accessibility.
You can get detailed information by calling: 8 (800) 234-42-00.
Complexes with this research
Biochemistry of blood.
8 indicators Minimum biochemical blood test 990 ₽ Composition Female infertility Analysis of women's reproductive health 9,310 ₽ Composition
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure 14,350 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 5,360 RUR
- Preventive check-up RUB 3,440
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators RUB 3,620
- For those at risk of COVID-19 RUB 2,430
- Biochemistry of blood. 13 indicators 2,100 ₽
References
- Clinical guidelines “Drug-induced liver damage”, 2019. - 35 p.
- Pakhomova, R.A., Kochetova, L.V. Clinical manifestations of obstructive jaundice and liver failure, depending on the severity of obstructive jaundice of benign origin.” — Modern problems of science and education, 2021. — No. 6. — P.47.
- Sullivan, J., Rockey., D. Diagnosis and evaluation of hyperbilirubinemia. — Current opinion in gastroenterology, 2021. — Vol. 33(3). — P. 164-170.
Jaundice
Hepatitis
22312 November 26
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Jaundice: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Jaundice is a condition in which the skin and mucous membranes turn various shades of yellow. Moreover, not in all cases this indicates pathological processes in the body.
Types of jaundice
There are false and true jaundice. False jaundice occurs when carotenes accumulate in the skin due to excessive consumption of carrots, beets, oranges, pumpkin, or when certain drugs are ingested (acriquine, picric acid, etc.).
True jaundice is a consequence of an increase in the concentration of total bilirubin in the blood plasma.
Jaundice discoloration of the skin and icterus (yellow pigmentation) of the sclera occur when the concentration of total bilirubin in the blood plasma is more than 35-45 µmol/l. The milk of nursing women, pleural and pericardial effusion, ascitic fluid, and semen may have a yellow tint.
The clinical picture and duration of true jaundice depend on the underlying disease, against the background of which an increase in blood bilirubin developed.
There are:
1. Hemolytic (prehepatic) jaundice:
- jaundice due to genetic diseases (hereditary microspherocytosis, hereditary stomacytosis, etc.);
- autoimmune (acquired) hemolytic anemia.
2. Parenchymal (hepatic) jaundice:
- caused by infectious diseases (viral hepatitis A, B, C, D, E; herpetic hepatitis, cytomegalovirus hepatitis, yellow fever, infectious mononucleosis, relapsing fever, intestinal yersiniosis, psittacosis, leptospirosis, salmonellosis, pseudotuberculosis, etc.);
- caused by non-infectious diseases (acute alcoholic hepatitis, drug-induced hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, poisoning with oxidizing agents based on nitric acid, hydrazine and its derivatives, chloroethane, ethylene glycol).
3. Constitutional jaundice
(Gilbert syndrome, Crigler–Najjar syndrome, Dabin–Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome).
4. Mechanical (subhepatic) jaundice
occur against the background of cholelithiasis, cholangitis, cicatricial strictures of the extrahepatic bile ducts, cancer of the head of the pancreas, major duodenal papilla, and gall bladder.
Hemolytic jaundice is characterized by moderate manifestations, lemon staining of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes, a slight enlargement of the liver and often a noticeably enlarged spleen. Anemia is observed.
In acute viral hepatitis, dull aching pain in the right hypochondrium and in the joints is disturbed, the temperature rises, appetite decreases, and the patient experiences weakness. Yellowness of the skin, dark urine and insufficiently colored feces appear. There may be bruises on the skin as a result of hemorrhages. Skin itching is not typical for acute viral hepatitis, since sufficient evacuation of bile through the bile ducts is ensured. When interviewing a patient, it is possible to identify a risk factor for developing the disease (contact with patients with hepatitis, recent surgical operations, blood transfusions, injections and manipulations associated with damage to the skin and mucous membranes).
With obstructive jaundice, the clinical picture may begin acutely or develop gradually.
With the acute onset of the disease (cholelithiasis), colicky pain suddenly appears in the right hypochondrium radiating to the right and to the back, chills, and fever. Then jaundice and skin itching occur. With the gradual development of the disease (cancer of the head of the pancreas), the patient may be bothered by moderate dull or pressing pain under the right costal arch, nausea, belching, and weight loss. Palpation of the abdomen reveals pain in the right hypochondrium. The yellowness of the skin gradually increases, the urine becomes dark in color, the feces become lighter, as less bilirubin is released into the intestines.
Constitutional jaundice is characterized by moderately severe intermittent (periodic) jaundice. Selective staining of the skin of the face, nasolabial triangle, palms, soles and axillary fossae is noted. Jaundice occurs or worsens after physical or mental stress, exacerbation of a concomitant disease, or alcohol intake. The liver and spleen do not increase in size.
As a result of long-term toxic effects of high concentrations of bilirubin on the body, damage to the central nervous system develops, foci of necrosis form in parenchymal organs, the cellular immune response is suppressed, and anemia occurs. Children may experience serious complications: kernicterus, mental retardation, cerebral palsy.
Possible causes of jaundice
True jaundice is the result of an imbalance between the formation and excretion of bilirubin. The cause of this disorder may be increased formation of bilirubin (hemolytic jaundice), a failure in its transportation to liver cells and excretion by these cells, as well as deterioration in the binding processes of free bilirubin (parenchymal jaundice). Obstructive jaundice occurs as a result of deterioration in the secretion of bilirubin through the extrahepatic ducts.
The basis of the mechanism of development of hemolytic jaundice
lies hemolysis (increased destruction of red blood cells), when the life span of red blood cells is significantly shortened, sometimes to several hours. Hemolysis can be intravascular and extravascular. Intravascular hemolysis occurs as a result of mechanical destruction of red blood cells in small blood vessels (marching hemoglobinuria), turbulent blood flow due to dysfunction of prosthetic heart valves, as a result of incompatibility of red blood cells in the AB(0), Rhesus or any other system, due to direct toxic effects ( snake venom), etc.
Extravascular hemolysis occurs in the spleen and liver as a result of the capture and destruction of altered red blood cells. The spleen is capable of capturing and destroying slightly altered red blood cells, the liver – red blood cells with major disturbances.
Hepatic (parenchymal) jaundice
are caused mainly by damage to hepatocytes (liver cells). In some cases, this syndrome is associated with damage to liver cells and stagnation of bile, for example, in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. In others, the release of bilirubin is impaired (with cholestatic jaundice, cholestatic hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis).
Obstructive (mechanical) jaundice occurs when there is a disturbance in the outflow of bile through the extrahepatic bile ducts.
.
, enzymopathic or constitutional jaundice occurs
. The most common is Gilbert's syndrome, which develops against the background of impaired uptake of free bilirubin and its binding to glucuronic acid due to deficiency of the enzyme glucuronyltransferase.
In 60-80% of newborns, yellowness of the skin is observed, which appears on the 2-3rd day of life.
Jaundice in newborns can be caused by a high release of red blood cells during childbirth, a high content of fetal hemoglobin, rapid destruction of bilirubin after birth, and a deficiency of conjugating enzymes in the liver. In this case, the rise in bilirubin levels does not reach critical values, and the child’s condition remains satisfactory.
Breast milk jaundice (jaundice from mother's milk) is not considered a pathology and is associated with the baby's body's reaction to the fats contained in breast milk. This condition develops on the 3rd-7th day after birth, when the baby already receives a sufficient amount of mother’s milk. Stopping breastfeeding for 24-48 hours leads to a sharp decrease in bilirubin and a decrease in the severity of jaundice. If the baby continues to receive breast milk, jaundice persists for 4-6 weeks, then gradually decreases - the condition of the skin and mucous membranes returns to normal by the 12-16th week of life.
Hemolytic disease of newborns is caused by incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus for various antigens, when the body of a pregnant woman produces antibodies that penetrate the placental barrier into the blood of the fetus and cause destruction (hemolysis) of its red blood cells. The intensity of jaundice depends on the level of bilirubin - when critical numbers are reached, this enzyme can affect neurons in the brain, resulting in the development of bilirubin encephalopathy (kernicterus).
Which doctors should I contact?
If jaundice appears, to clarify the diagnosis and determine further treatment tactics, the patient should consult a general practitioner, or if the patient is a child. In the future, a consultation with a hematologist, an infectious disease specialist, may be indicated.
Diagnosis of jaundice
To determine the cause of jaundice, a set of laboratory and instrumental examination methods is performed (according to indications):
- clinical blood test with determination of hemoglobin concentration, number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets, hematocrit and erythrocyte indices (MCV, RDW, MCH, MCHC), leukoformula and ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes);
Nutrition to normalize bilirubin
To normalize bilirubin levels, men are advised to exclude salt from their diet and reduce the amount of meat and bread. Doctors also do not recommend eating the following foods:
- mushrooms;
- mayonnaise, mustard;
- lemon, onion;
- smoked products, sausages;
- seafood;
- canned foods;
- alcohol;
- products containing dyes or sweeteners.
You should eat small meals; you should not eat fast foods. Doctors recommend drinking more fluid - up to 2.5 liters per day. This includes not only water, but also green tea and unsweetened compotes.
List of allowed foods and dishes to normalize bilirubin levels:
- cottage cheese, milk;
- non-acidic fruits;
- chicken and quail meat, rabbit meat;
- soups with vegetable broth or milk;
- herbal infusions.
Traditional medicine recommends drinking beet juice, decoctions of various herbs, and motherwort.