Under normal conditions, the human heart beats smoothly and regularly. The heart rate per minute ranges from 60 to 90 beats. This rhythm is set by the sinus node, which is also called the pacemaker. It contains pacemaker cells, from which excitation is transmitted further to other parts of the heart, namely to the atrioventricular node, and to the His bundle directly in the tissue of the ventricles.
This anatomical and functional division is important from the point of view of the type of a particular disorder, because a block in the conduction of impulses or acceleration of impulses can occur in any of these areas.
Disturbances in heart rhythm and conduction are called arrhythmias and are conditions when the heart rate becomes less than normal (less than 60 per minute) or more than normal (more than 90 per minute). Arrhythmia is also a condition when the rhythm is irregular (irregular, or non-sinus), that is, it comes from any part of the conduction system, but not from the sinus node.
The concept of the cardiac conduction system and pacemaker migration
To better understand what the development of cardiac pacemaker migration is, it is necessary to have knowledge of the principles of functioning of the organ.
The heart consists of working muscles in the form of striated muscle, as well as atypical (special) tissue, which represents peculiar nodes and is composed of poorly differentiated muscle fibers. The sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, as well as the bundle of His, constitute the conduction system that ensures the rhythmic functioning of the organ.
Rhythmic contractions of the heart under the influence of impulses appearing directly in the organ gives it such a physiological property as automatism
Normally, the heart rate of an adult can range from 60 to 90 beats per minute, and the electrical excitation covering the heart muscle should be characterized by the consistency and uniformity of waves across the myocardium.
The self-generation of electricity, leading to regular contraction of the heart throughout a person’s life, occurs in the sinus node (pacemaker, 1st order pacemaker) - an anatomical formation not exceeding 1.5 cm in size.
The antrioventricular node and the His bundle act only as transmitters of impulses from the pacemaker to the myocardium.
Periodic change in the source of impulses (migration of the pacemaker) leads to a violation of the frequency and sequence of heart contractions. The point of origin of impulses in this case moves along the atria or to the atrioventricular node.
Impaired impulse transmission leads to the development of arrhythmia (bradycardia, tachycardia)
If the functioning of the main pacemaker is disrupted, the atrioventricular node begins to perform its functions, with a decrease in the number of impulses to 40–50 per minute, which maintains the cardiovascular system in a normal state.
When this node is blocked, the His bundle begins to function, the pulse frequency is 30–40 per minute. In case of failures in the functioning of this regenerating area, the function of the pacemaker passes to the Purkinje fibers, which set rhythmic contractions approximately 20 times per minute.
Signs on ECG
What do the waves on an ECG mean:
- the P wave characterizes the state of the atria;
- PQ – atrioventricular conduction time;
- QRS – reflects the electrical activity of the ventricular complex;
| Localization | Type of arrhythmia | ECG signs |
| Atrioventricular node – AV junction | Ventricular extrasystole |
|
| Atrioventricular node | Paroxysmal tachycardia |
|
| Sinus node, SSSU | Atrial fibrillation of the bradysystolic type |
|
| Sinus node | Supraventricular or supraventricular tachycardia |
|
Causes
It is possible that pacemaker migration may occur without specific reasons. This failure, as a rule, does not interfere with the activity of the heart, is not treated and relates to the individual characteristics of the body.
Unreasonable migration is more often observed during adolescence, as well as among young people, and after some time it goes away on its own.
Migration of the cardiac pacemaker can occur due to:
Extracardiac causes:
- infectious diseases (viral and bacterial);
- lack of microelements in the body;
- therapy with certain medications (drugs that stimulate cardiac activity);
- high activity of the vagus nerve in healthy people;
- neurocirculatory dysfunction;
- after cardiac surgery in the postoperative period.
Cardiac factors:
- myocarditis (myocardial damage, usually of an inflammatory nature);
- sinus node dysfunction syndrome, which contributes to weakening of impulses and changes in the localization of their generator;
- coronary disease, leading to oxygen starvation and disruptions in cardiac activity of various types;
- rheumatic heart disease (often a complication of angina).
In newborns, dysfunction of the conduction system occurs as a result of perinatal pathology due to prematurity, intrauterine malnutrition and infection.
Despite the fact that the causes of failure in children and adults may be identical, the structure of the heart and its functioning are significantly different
The child is born with a cone-shaped, oval or spherical heart with insufficiently developed heart muscles, ventricles and large atria. The imperfection of the conductive system lies in its massiveness and unclear contouring of the fibers. As the baby grows, the cardiovascular system continuously develops and improves. This is especially pronounced at the age of 2–6 years and during puberty. At the age of 14, the organ becomes the same shape as in adults.
Active growth of the heart and the process of improvement of the conduction system leads to rhythm disturbances in childhood. Negative symptoms, as a rule, disappear without the use of therapeutic therapy as soon as the restructuring of the organ is completed.
Changes in the localization of the cardiac impulse generator often occur in children who are easily excited, but are completely healthy. Thus, electrocardiography, which evokes fear and negative emotions, records the migration of the rhythm source. As soon as the child realizes the safety and painlessness of the procedure, normal, stable sinus rhythm is restored.
Children's hearts are different:
- great endurance of the myocardium and its good blood supply;
- uneven growth of the organ, leading to functional disorders;
- physiological tachycardia caused by restructuring of the cardiovascular system.
Under no circumstances should a child’s abnormal heart rhythm be ignored, which can be caused not only by physiological changes in the body, but also by disease.
Period after implantation
Typically, the recovery period after surgery is quite short. You may have some pain around the pacemaker implantation site, in which case your doctor will prescribe a pain reliever. You may need some time to get used to your pacemaker. However, the feeling of discomfort will pass very soon. You should have your first examination with your doctor soon after surgery. He will check the electrical activity of your heart and the functioning of your pacemaker. If necessary, the doctor will adjust the parameters of the program according to which the pacemaker operates to suit your individual needs. On average, you should have regular checkups every six months. In general, you will be able to live a full life soon after implantation. You can continue to do your normal activities - work in the garden or around the house, drive a car. You can shower, bathe or swim. After consulting with your doctor, you can resume sports, favorite activities, and resume sexual activity.
Symptoms
A healthy person does not experience any undesirable effects when the cardiac pacemaker migrates.
If malfunctions in the conduction system are caused by pathological changes in the body, the symptoms will depend on the concomitant disease.
General symptoms are characterized by:
- malaise;
- disorders of consciousness;
- weakness, fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- a feeling of impaired heart rhythm;
- pain syndrome in the heart;
- dizziness;
- fainting states;
- increased blood pressure.
Symptoms may not appear for a long time or may occur periodically.
Young patients who experience rhythm generator migration caused by diseases are susceptible to psychovegetative disorders, delayed puberty, neurological syndrome and decreased motor activity
In case of malfunction of the conduction system in children:
- breathing is impaired in the form of shortness of breath;
- some areas on the body, lips and fingertips turn blue;
- appetite decreases or is completely absent;
- sleep is disturbed;
- pulsation of blood vessels in the neck is observed;
- there is a feeling of discomfort in the heart area;
- blood pressure decreases;
- There is a quick feeling of heaviness and fatigue when playing sports or any physical activity.
In severe cases, the child begins to systematically lose consciousness. The occurrence of complications increases the likelihood of sudden death.
At puberty, the disease acquires pronounced symptoms, characterized by cardialgia, hyperexcitability, insomnia, and weather sensitivity.
In the presence of what complaints can pathology be suspected?
There are no complaints that reliably belong to this condition. Most often, pacemaker migration is diagnosed randomly during an electrocardiographic examination. It should be noted that in practice, there are supraventricular (supraventricular) and ventricular forms (very rare) pathologies.
Patients may feel:
- fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart;
- attacks of rapid heartbeat.
Quite rarely, symptoms of cardialgia, shortness of breath with difficulty breathing, dizziness, and episodes of syncope (short-term loss of consciousness) occur.
Disease detection
Often, malfunctions in the conduction system are detected randomly during preventive electrocardiography. This is due to the absence of clear symptoms of pathology or a negligent attitude towards one’s health.
It is very important to monitor your child’s condition and, at the first clinical manifestations, consult a doctor for further diagnostic measures and, if necessary, timely treatment.
Pathology is detected using:
- examination by a specialist of the patient’s health complaints;
- identifying a person’s relatives with heart disease;
- analysis of the patient’s chronic diseases, traumatic injuries and surgical interventions;
- physical examination;
- blood and urine tests;
- a chest x-ray, which can help diagnose some heart conditions;
- echocardiography (ultrasound), aimed at identifying morphological and functional changes in the heart and its valve apparatus;
- phonography for recording heart sounds and noises.
The main method for diagnosing cardiac rhythm migration is electrocardiography, which reveals the specificity of the pathology:
- different shape and polarity of the P wave with each heartbeat;
- periodic change in the duration of the P–Q and RR intervals.
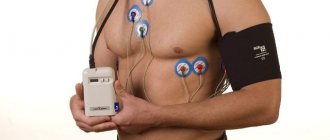
It is also advisable to prescribe Holter ECG monitoring - continuous recording of an electrocardiogram for a day or a longer time using a cardiac recorder. At the end of the examination, the specialist analyzes the records, identifying disturbances in the conduction system of the heart and the reasons that provoked it.
Carrying out an electrocardiographic study in a child requires a special approach
Implantation
Thanks to modern technology, the operation of implanting a cardiac pacemaker has become much easier. This procedure usually takes less than an hour. Typically, your doctor will apply local anesthesia to the area under your right collarbone. The electrode is then carefully inserted through a vein into the heart. Typically, the correct placement of the lead in the right atrium or ventricle is monitored by X-ray imaging. Only after a thorough check of the correct operation of the pacemaker is the electrode secured in the pacemaker. The pacemaker itself is implanted under the skin, in a small pocket below the right collarbone, and then the doctor places several stitches in the incision.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen is prescribed individually and directly depends on the disease that provoked failures in the conduction system.
However, in each case it is required:
- Strictly adhere to the doctor's instructions.
- Have a full rest. Normalize night sleep and rest during the day. This is especially true for children who are overloaded not only with the curriculum, but also with additional classes.
- Eliminate intense psycho-emotional stress, avoid stressful and conflict situations.
- Engage in moderate physical activity as permitted by your doctor. Spend more time outdoors with your child.
- Give up heart-damaging habits (alcohol, smoking).
- Normalize the diet, from which fatty, spicy and salty foods should be removed.
Migration of the heart pacemaker, not caused by pathological changes in the organ, does not require treatment
In some cases, it is advisable to prescribe medications that have a positive effect on cardiac activity: Hypoxen, Riboxin, Mildronate and others.
Sick sinus syndrome requires a pacemaker.
Stimulator operating life
The exact length of time your pacemaker battery lasts depends on the type of pacemaker, your health, lifestyle, and other factors. Typically, the duration of work is from 5 to 10 years. You can get more information about the type of pacemaker you have from your doctor. How is a pacemaker replaced?
It is generally a safe and simple procedure to replace your old pacemaker with a new one. During the process of replacing a pacemaker, the doctor monitors the electrodes. If they function flawlessly, the doctor only connects them to a new pacemaker.
Preventive actions
As such, there are no preventive measures to prevent pacemaker migration. It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and teach your children to:
- include heart-healthy foods in your diet (vegetables, fruits, herbs, fish), do not overeat;
- do not drink alcohol, do not smoke, conduct educational conversations with children about the dangers of these habits;
- control weight;
- do at least half an hour of physical exercise;
- walk with your child as often as possible;
- completely recover from viral and bacterial diseases.
Both adults and children should undergo systematic routine examinations. With timely diagnosis using modern methods of therapy, you can get rid of many diseases and prevent serious complications.
Features in children
The most common cause of rhythm source migration in children is vegetative-vascular dystonia. The pathology is characterized by a change in the tone of the vascular wall. The sensitivity of the structures and tissues of the arterial endothelium contributes to functional disorders of areas of the conduction system of the heart, causing migration of the pacemaker to the atrioventricular node.
In addition, changes in the source of the rhythm can be observed with endocarditis or in the presence of a pathological athlete's heart. In adolescence, the picture of the disease becomes more pronounced. There are constant complaints of headaches and chest pains, slow development, and sleep disturbances.
Prevention measures
To prevent the occurrence of this pathological condition, doctors advise adhering to the following rules:
- eat well (do not overeat, reduce the consumption of animal fats, add fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs to the diet);
- stop drinking alcohol;
- quit smoking;
- engage in moderate exercise;
- control weight (prevent obesity);
- avoid conflict and stressful situations.
In addition, it is important to follow recommendations for the prevention of angina, a complication of which is damage to the muscle fiber of the heart.
Also, measures to prevent illness include undergoing routine medical examinations and timely treatment of various diseases.