Generally accepted norms of indicators
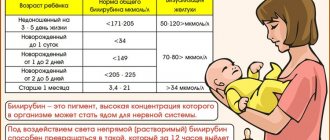
The acceptable level of bilirubin concentration for each age is different. The highest concentration of the substance in the blood is observed in newborns, in the initial stages of life, up to 200 µmol/l, this is due to the period of adaptation of the newborn’s gastrointestinal tract to the digestion of mother’s milk. The acceptable level of bilirubin concentration for each age will be different. The highest concentration of the substance in the blood is observed in newborn children, in the initial stages of life. In one-year-old children and children under 13 years of age, a satisfactory indicator of the concentration of indirect pigment is considered to be up to 20.3 µmol/l, for direct pigment up to 5.2 µmol/l.
The degree of concentration of the substance for adults should not cause concern if the survey analysis shows a level of up to 19.9 µmol/l for indirect, and 4.9 µmol/l for direct bilirubin, since such measurements are satisfactory for people of the adult age category.
Symptoms
Abnormalities in the chemical reactions of bilirubin are detected by determining its level in the blood. If the concentration is higher than normal, but does not exceed 85 µmol/l, this is a mild form of hyperbilirubinemia, up to 170 µmol/l is moderate, and from 170 µmol/l is a severe form of the disease. External signs manifest themselves differently, depending on the cause of the increase in bilirubin concentration.
- Liver problems are expressed in the following symptoms:
- Discomfort and heaviness due to liver enlargement.
- Change in urine color (it becomes like dark beer), lightening of stool.
- Heaviness after eating, drinking alcohol, frequent belching.
- Periodically occurring dizziness, general weakness, apathy.
If the cause of the pathological condition is viral hepatitis, then elevated body temperature is added to the symptoms.
- Violation of bile outflow:
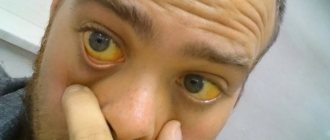
- Yellowness of the skin and sclera.
- Itchy skin.
- Intense pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Flatulence, constipation or diarrhea.
- Dark urine, light stool.
A common cause is gallstone disease. The list functions normally, neutralizes incoming bilirubin, but its removal from the body is difficult.
Prehepatic jaundice
- a condition caused by the rapid destruction of red blood cells. Expressed by the following symptoms:
- Anemia.
- Dark stools with normal urine color.
- Extensive hematomas that form without external causes.
- Skin itching, worse at rest and after warming up.
- Yellowish skin color.
Also, sometimes, regardless of the cause, symptoms such as bitterness in the mouth, changes in taste, weakness, impaired memory and intelligence may be observed.
Causes of increased bilirubin in the blood
The source of the pathological condition is caused by disruption of the liver, resulting in improper outflow of bile, which causes the occurrence of viral lesions and hepatitis.
symptoms of increased bilirubin
The cause of increased bilirubin in the blood may be:
- Chronic or autoimmune hepatitis.
- Non-benign neoplasms in the liver area.
- Incorrect functioning of the pancreas.
- Intoxication of the body through poisoning can also cause an increase in bilirubin.
By the way, any of the above reasons is pathological and requires immediate medical intervention and long-term treatment
What to do if there are signs of increased bilirubin
It will not be possible to normalize bilirubin levels without laboratory tests, because first of all you need to find out the reason for the change in the amount of pigment in the blood. This means that you need to check the level of ALT and AST enzymes, do an analysis for viral hepatitis and an ultrasound of the liver.
If the increase in bilirubin is caused, for example, by cholelithiasis, then cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) or drug therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid is indicated. If viral hepatitis occurs, antiviral therapy is necessary. If a person has a parasitic disease, the helminths must be destroyed. Those. the scheme of action depends entirely on the condition that led to the increase in bilirubin.
Symptoms indicating increased bilirubin
There are symptoms the presence of which in a person means that the percentage of bilirubin in the blood is too high:
- The whites of the eyes began to turn yellow.
- The skin color becomes more jaundiced.
- Itching of the skin, which intensifies at night.
These symptoms are an important indicator that the body is undergoing internal bile poisoning; ignoring these problems can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the body.
The often manifested bitter taste in the mouth is also one of the symptoms of increased bilirubin in the blood.
treatment of direct bilirubin in the blood
A rapid increase in this substance provokes the darkening of the urinary fluid to a brown color, and solid bowel movements take on a white color. All of the above symptoms are accompanied by severe weakness, high fever and enlarged liver. If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately seek help from the nearest hospital.
Hereditary disorders
Gilbert's syndrome
. A harmless form with a favorable course. The reason is a violation of the uptake and transport of bilirubin by liver cells. Unconjugated (unbound) bilirubin increases in the blood.
Rotor syndrome
. It is expressed in a violation of the uptake of bilirubin and, as a result, its removal from the body. It appears at an early age and does not lead to serious consequences.
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
. A rare form of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The transport system is disrupted, which causes difficulties in removing bound bilirubin. The syndrome does not lead to dangerous conditions, the prognosis is favorable.
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
. Severe form of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The reason is the lack or complete absence of glucuronyl transferase, a substance necessary for the conjugation of bilirubin in the liver. Causes damage to the nervous system and can lead to premature death.
Timely diagnosis, pathogenetic therapy, proper nutrition, work and rest schedules can qualitatively improve the lives of most patients with hereditary hyperbilirubinemia.
Treatment of elevated direct bilirubin
You can influence the high concentration of bilirubin in the blood by following a diet and doing physical exercise. After undergoing a biochemical examination of the blood, based on the tests obtained, the doctor prescribes the patient a set of treatment and recommendations aimed at establishing the proper functioning of the liver and the outflow of bile. Even with the slightest discrepancy with the norms, the doctor is obliged to prescribe treatment to correct the functioning of metabolic processes; you can often undergo such a course of treatment at home, while following all the recommendations. In this case, the examination results show a disappointing picture; if necessary, surgical intervention is required, followed by hospitalization in a hospital.
If bilirubin is elevated during pregnancy
The appearance of jaundice can occur during all stages of pregnancy. If the analysis reveals an excess of bilirubin, this may be associated with the following diseases:
- viral hepatitis in acute form;
- intrahepatic cholestasis;
- acute fatty liver degeneration.
It is viral hepatitis that is the main cause of jaundice in pregnant women - it accounts for up to 50% of identified cases. Symptoms of the disease are varied. The pathology begins to manifest itself with weakness, fever, joint pain, skin rashes, and changes in the color of urine and feces. In these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor, take a blood test and other tests.
The second most common cause of abnormal bilirubin levels in pregnant women is intrahepatic cholestasis (another name is hepatosis). It accounts for up to 25% of identified cases. The main symptoms are;
- frequent itching of the skin;
- moderate jaundice;
- darkening of urine;
- stool lightening;
- rarely – prolonged, repeated vomiting.
As a rule, the described signs progress during the 3rd trimester, less often they appear at earlier stages. When taking an analysis, it turns out that bilirubin exceeds the norm by 4-5 times.
Finally, jaundice may also be associated with acute fatty degeneration. This pathology is much less common - 1 in 13,000 births. It manifests itself as a complication, more often in primiparous women in the last stage of pregnancy. The exact cause of the pathology has not yet been established.
Removing bilirubin with a detox diet
A diet for elevated bilirubin is not an independent method of therapy, but it promotes rapid recovery and enhances the effect of medications. It is easier to lower the required indicators with its help. The basic rule of nutrition is to strictly avoid the following foods:
- salt - dishes are prepared without adding it;
- salt-containing spices;
- some greens - sorrel, spinach, green onions;
- flour, especially fresh baked goods;
- canned food, pickles;
- smoked meats, sausages;
- sugar, sweets;
- alcohol.
The rest of the products can be eaten. It is difficult for overweight people to reduce bilirubin, so when choosing a diet for them, the doctor can set the permissible amount of calories. Fiber-containing foods can be especially good at reducing pigment levels.
Diagnosis of Gilbert's syndrome
Making a diagnosis includes an analysis of existing complaints and clinical manifestations of the disease, clarification of the presence of episodes of jaundice and pathology of the hepato-biliary system in close relatives, and the use of laboratory and instrumental research methods.
Differential diagnosis of Gilbert's syndrome is carried out with viral and chronic hepatitis, mechanical and hemolytic jaundice, Crigler-Nayyar syndrome, Dabin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome, primary shunt hyperbilirubinemia, congenital cirrhosis of the liver, bile duct atresia. The main distinguishing feature of this disorder is an increase in the fraction of unconjugated bilirubin in the blood serum, not associated with hemolysis of erythrocytes, and a hereditary burden.
The standard list of tests when examining for Gilbert's syndrome includes:
- General clinical blood test. In some cases, there is an increase in hemoglobin levels or a decrease in the number of platelets.
- Blood chemistry. The main symptom of the disease is an increase in the concentration of total bilirubin to 34.2–85.5 µmol/l due to its indirect fraction. The values of other liver blood enzymes, such as AST, ALAT, GGTP, alkaline phosphatase, are usually within normal limits. Dysproteinemia and increased total protein concentrations may be present.
- Analysis of urine. Creatinine determination is carried out.
- Determination of markers for viral hepatitis in blood serum. In Gilbert's syndrome, the presence of Ig G to HBcAg, hepatitis A and C is uncharacteristic.
- Coprogram. A stool test for stercobilin for the pathology in question has a negative result. In difficult cases, functional laboratory tests are indicated. A decrease in bilirubin level while taking phenobarbital and its increase by 1.5-2 times after fasting, a low-calorie diet or intravenous administration of nicotinic acid confirms the diagnosis.
If indicated, DNA defects are also determined using the polymerase chain reaction method.
Research in Gilbert's syndrome reveals genetic polymorphism in the DNA fragment encoding the UDPGT enzyme. Of the instrumental methods, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is most often performed to exclude other liver pathologies and cholelithiasis. In children, you can use a method for determining the hepatosplenic index using ultrasound data.
Additionally, duodenal intubation and thin layer chromatography are possible. Percutaneous puncture of the liver with subsequent morphological assessment of the obtained biomaterial is performed if the patient is suspected of having chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
Forms
Thus, two forms are distinguished:
- Straight. It does not pose a danger to the body, since it is water-soluble and is easily excreted from the body through the liver and intestines with feces, turning them brown.
- Indirect. It is a toxic substance. It is fat soluble, which explains its local accumulation in adipose tissue. It is excreted from the human body exclusively by converting it into its direct form.
Treatment of Gilbert's syndrome
The mere presence of Gilbert's syndrome in children and adults is not an indication for drug treatment.
To prevent exacerbation of the disease and the development of complications, general measures are important: limiting participation in strenuous sports, prolonged exposure to the sun, consumption of alcoholic beverages and hepatotoxic drugs. Such patients need to eat right, avoid prolonged fasting, as well as foods containing indigestible fats - fatty meats, fried and spicy foods, canned foods. During an exacerbation of the clinical manifestations of the disease, plenty of fluids and a gentle diet corresponding to table No. 5 are prescribed. Conservative therapy during this period is aimed at reducing the formation and accelerating the removal from the body of excess amounts of unconjugated hemoglobin and includes:
- taking microsomal enzyme inducers (phenobarbital, zixorine);
- taking activated carbon;
- phototherapy.
For the prevention of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis in Gilbert's syndrome, the use of choleretic herbs, hepatoprotectors (ursosan, ursofalk), essential phospholipids, choleretics (cholagol, allochol, holosas) and B vitamins is recommended.
Increased indirect bilirubin
The reason is the rapid breakdown of red blood cells. It can occur as a complication of sepsis, acute intestinal infection, congenital, toxic, acquired autoimmune anemia.
An increase in the indirect form of bilirubin also occurs with Gilbert's syndrome. This is a benign, chronic disease caused by disruption of the intracellular transport of bilirubin. Among the causes of hyperbilirubinemia, Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a disruption of the process of combining bilirubin with glucuronic acid, formed during the oxidation of D-glucose.
The Lucy-Driscol symptom is unusual. It occurs exclusively in infants due to breastfeeding. Breast milk contains an enzyme that disrupts the conjugation of bilirubin. With the transition to artificial feeding, the disease goes away. However, indirect bilirubin is very dangerous, so the occurrence of jaundice after 3-5 days of life requires urgent medical examination.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis of the disease at any age is favorable.
Hyperbilirubinemia in Gilbert's syndrome persists for life, but is benign in nature, is not accompanied by progressive changes in the liver and does not affect life expectancy. Source of statistical data: Visual pediatric gastroenterology and hepatology: textbook. allowance — Kildiyarova R. R., Lobanov Yu. F. 2013. — 124 p. : ill. (Chapter 6. Liver diseases (vmede.org).
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist