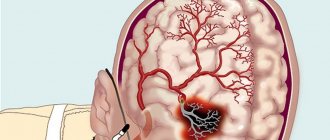
Sudden changes in blood flow to the brain are classified as hemorrhagic (bleeding) and ischemic disorders. Such a division is important for the correct choice of therapy method.
The classic abbreviated name for the pathology in acute cerebrovascular accident is “ischemic stroke.” If hemorrhage is confirmed, then it is considered hemorrhagic.
In ICD-10, ACME codes may vary, depending on the type of violation:
- G45 is an established designation for transient cerebral attacks;
- I63 - recommended for statistical registration of cerebral infarction;
- I64 - an option used for unknown differences between cerebral infarction and hemorrhage, used when the patient is admitted in an extremely serious condition, unsuccessful treatment and imminent death.
The frequency of ischemic strokes exceeds hemorrhagic strokes by 4 times and is more associated with general human diseases. The problem of prevention and treatment is considered in programs at the state level, because 1/3 of patients who have suffered the disease die in the first month and 60% remain permanently disabled requiring social assistance.
Why does a lack of blood supply to the brain occur?
Acute ischemic cerebrovascular accident is often a secondary pathology and occurs against the background of existing diseases:
- arterial hypertension;
- widespread atherosclerotic vascular lesions (up to 55% of cases develop due to pronounced atherosclerotic changes or thromboembolism from plaques located in the aortic arch, brachiocephalic trunk or intracranial arteries);
- previous myocardial infarction;
- endocarditis;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- changes in the valvular apparatus of the heart;
- vasculitis and angiopathy;
- vascular aneurysms and developmental anomalies;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes mellitus
Up to 90% of patients have changes in the heart and main arteries of the neck. The combination of these reasons sharply increases the risk of ischemia.
Possible compression of the vertebral artery by the processes of the vertebrae
Transient attacks are most often caused by:
- spasm of the arterial brain stems or short-term compression of the carotid and vertebral arteries;
- embolization of small branches.
The following risk factors can provoke the disease:
- elderly and senile age;
- excess weight;
- the effect of nicotine on blood vessels (smoking);
- experienced stress.
The basis of the influencing factors is the narrowing of the lumen of the vessels through which blood flows to the brain cells. However, the consequences of such a malnutrition may vary according to:
- stamina,
- localization,
- prevalence,
- severity of vessel stenosis,
- gravity.
The combination of factors determines the form of the disease and clinical symptoms.
An ischemic stroke can be considered recurrent if it occurs in the area of the blood supply of one vessel within 28 days after the initial manifestations of the first event. A recurrent stroke is called a stroke at a later date.
Recommendations
ONMK: what is it?
ACVA of ischemic type.
Many people ask the question of what an acute stroke is and what consequences there are after it. This article will examine the main causes of stroke and consequences.
ONMK - what is it?
Many people who have nothing to do with medicine probably do not know what stroke is. So, an acute circulatory disorder in the brain is a stroke, which causes damage and death of brain cells. The cause of this disease is the formation of a blood clot in the blood vessels of the brain or the rupture of some blood vessels, which causes the death of a huge number of nerve cells and blood cells. According to statistics, acute stroke ranks first among diseases that cause human death. Every year around the world, as the federal register of patients with acute stroke indicates, 14 percent of people die from this disease, as well as 16 from other types of diseases of the circulatory system.
Reasons why stroke may occur.
In order to prevent the occurrence of this disease, it is necessary to pay attention to your lifestyle from an early age. For example, constant exercise can significantly reduce the possibility of developing stroke. You already know what it is; some of the causes of this disease will be discussed further.
As a rule, this disease does not come suddenly; very often the diagnosis of stroke can be established as a consequence of certain diseases.
Often the cause of this condition can be:
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- high cholesterol;
- heart disease;
- alcohol and smoking;
- various types of medicines;
- high hemoglobin level;
- age;
- traumatic brain injury;
- genetic predisposition and so on.
Now it’s clear what ONMC is. These are the consequences of an incorrect lifestyle. Therefore, it is very important to monitor your health and physical condition.
Ischemic stroke.
Ischemic stroke is a stroke caused by damage to brain tissue and disruption of blood flow to one or another part of it.
Most patients with stroke of ischemic type have common diseases of the cardiovascular system. Such diseases also include arteriosclerosis, heart disease (arrhythmia, rheumatic disease), and diabetes. This type of stroke is characterized by sharp and frequent manifestations of pain, the consequence of which is a deterioration of blood circulation in the cerebral cortex. As a rule, such attacks can occur several times an hour and last for 24 hours.
Causes of ischemic stroke ACVA.
The main reason for the manifestation of ischemic stroke is a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Very often, this is why the cause of death of a person is ischemic stroke. So, we found out the features of ischemic stroke, what it is and what its symptoms are.
This is usually the result of damage to the vessels of the neck and some arteries of the brain in the form of occlusive lesions and stenosis. Let's find out the main reasons for its occurrence.
The main factors that can affect the decrease in blood flow include the following:
- Occlusions and stenoses of the main arteries of the brain and vessels of the neck.
- Thrombotic layers on the surface of an atherosclerotic plaque.
- Cardiogenic embolism, which occurs when there are artificial valves in a person’s heart.
- Dissection of the main arteries of the cervical spine.
- Hyalinosis of small arteries, as a result of which microangiopathy develops, which leads to the formation of lacunar infarction of the human brain.
- Hemorheological changes in blood composition, which occurs with vasculitis, as well as coagulopathies.
Very rarely, the cause of this disease can be external injuries to the carotid arteries and various inflammatory processes, which can significantly impair the flow of blood through the vessels. Also, very often, the main cause of stroke in the brain can be osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, during which blood vessels are significantly pinched, which can lead to a decrease in blood flow. Patients with osteochondrosis are constantly recommended to massage the cervical spine and smear it with various warming preparations, which can significantly dilate blood vessels and improve blood circulation.
Symptoms of stroke.
Signs of this disease can often appear abruptly or increase gradually. As a rule, the main symptoms of this disease include speech and vision disorders in the patient, disturbances in various reflexes, movement coordination, headaches, disorientation, sleep disturbances, noise in the head, memory impairment, paralysis of the face, tongue, lack of sensation in some limbs, etc. Further.
In acute cerebrovascular accident, the following consequences occur: cerebral stroke, circulatory disturbance in the cerebral cortex due to the formation of blood clots in the vessels and main blood arteries of the head, etc.
When symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident last more than a day, a stroke is diagnosed. In the first stage of this disease, severe headache, dizziness, nausea, gag reflexes, and so on may also occur. If you do not immediately pay attention to these manifestations, this can cause a person’s death.
According to the register of patients with stroke, according to statistics, the main cause of these manifestations may be high blood pressure, which can be observed during severe physical exertion. A sharp increase in blood pressure can cause rupture of cerebral vessels, followed by hemorrhage and intracerebral hematoma.
In most cases, the above symptoms are observed before ischemia. Typically, they can last several hours or several minutes. As a rule, with the manifestation of ischemic stroke, the symptoms constantly become more active. According to experts, when these symptoms appear, most people experience disorientation, as a result of which the person loses vigilance, coordination of movements worsens, so many patients simply fall asleep. According to statistics, 75 percent of ischemic heart attacks occur during sleep.
Diagnosis of acute cerebrovascular accident of ischemic type.
To identify the problem, it is necessary to conduct diagnostics and various studies using the ICD system. Doctors will be able to diagnose stroke after the following procedures:
- Blood test for electrolytes, glucose, hemostasis, lipid spectrum, antiphospholipid antibodies.
- Electrocardiography of changes in blood pressure.
- Computed tomography of the cerebral cortex, as a result of which it will be possible to detect the affected parts of the brain and the resulting hematomas without any problems.
- Cerebral angiography and so on.
Treatment of acute cerebrovascular accident in ischemic type.
The most common cause of death is stroke. Treatment should therefore take place under the supervision of experienced doctors. For this disease, the following therapy is carried out:
- Maintaining vital functions of the human body. The patient should take antihypertensive drugs when the blood pressure in the body is 200 to 120 mm. Hg Art. The use of anticoagulants (used for concomitant pathologies and used for a long time after normalization of the condition), vasoactive drugs, antiplatelet agents, decongestants, neuroprotectors, and so on is also prescribed.
- Various sets of exercises are performed - speech therapy classes and breathing exercises.
- The issue of thrombolysis is being considered when a patient is admitted to a medical facility within 3-6 hours from the onset of the disease.
- Secondary prevention of disease.
- Various rehabilitation measures are carried out and so on.
As a rule, the main points of treatment will be prescribed only by a doctor, who will become more familiar with the victim’s illness.
If there is a suspicion of acute cerebrovascular accident, it is necessary to contact highly qualified specialists in this field of activity. As a rule, first of all it will be necessary to undergo magnetic resonance imaging, which can accurately determine all pathologies of the cerebral cortex. In this way, it will be possible to prevent the possibility of complications of the disease and begin treatment even before it fully manifests itself. A specialized department of acute stroke, as a rule, must have special equipment that will significantly improve treatment.
First aid for stroke.
The very first thing to do when you notice symptoms of this disease is to call an ambulance. During the manifestation of symptoms of this disease, a patient should in no case be disturbed without reason, therefore, immediately after the first signs it is necessary to isolate him.
At the next stage, all patients with stroke should lie in such a way that the upper body and head are raised, it is also necessary to rub the collar area of the body in order to make breathing easier for the patient. It is also necessary to provide fresh air access to the room where the patient is located (open the window, doors, and so on).
If the patient experiences vomiting, it is necessary to turn his head to the left side and clean the mouth with gauze or just a clean napkin. This is done to prevent the possibility of vomit entering the lungs when breathing, which can lead to additional problems.
One of the most common symptoms of stroke is an epileptic seizure - a person completely loses consciousness, after a few seconds a wave of convulsions sweeps through the body, which can last for several minutes. It is also worth noting that such attacks can be repeated several times.
How to prevent the occurrence of stroke diseases.
Based on the above statistics, it is clear that this disease manifests itself even in children. It is easy to guess that every year there are more and more people who suffer from this disease. All this is associated with poor diet, inactive lifestyle and high mental stress.
If a person does not lead an active lifestyle and constantly spends time at the computer, he has a high chance of contracting this disease. Obesity, as stated, is the main cause of this disease, which is why the issue of maintaining physical fitness is very relevant today for the younger generation.
Sudden loads also very often become a source of problems, since with an increase in blood pressure there is a risk of rupture of blood arteries and veins, which will also lead to stroke. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly exercise, lead an active lifestyle, and eat right - and the risk of stroke will significantly decrease.
The most deadly and terrible disease in our time is stroke. You already know what it is and what causes this disease, so you need to adhere to the above recommendations in order to prevent the disease in the future.-
Pathogenesis of various forms of acute cerebral ischemia
Transient ischemic attack was previously called transient cerebrovascular accident. It is identified as a separate form because it is characterized by reversible disorders; the heart attack does not have time to form. Usually the diagnosis is made retrospectively (after the disappearance of the main symptoms), within a day. Before this, the patient is treated as if he had a stroke.
The main role in the development of hypertensive cerebral crises belongs to the increased level of venous and intracranial pressure with damage to the walls of blood vessels and the release of fluid and protein into the intercellular space.
Swelling of brain tissue in this case is called vasogenic
The feeding artery is necessarily involved in the development of ischemic stroke. The cessation of blood flow leads to oxygen deficiency in the lesion formed in accordance with the boundaries of the basin of the affected vessel.
Local ischemia causes necrosis of an area of brain tissue.
Depending on the pathogenesis of ischemic changes, types of ischemic strokes are distinguished:
- atherothrombotic - develops when the integrity of the atherosclerotic plaque is disrupted, which causes complete closure of the internal or external feeding arteries of the brain or their sharp narrowing;
- cardioembolic - the source of thrombosis is pathological growths on the endocardium or heart valves, fragments of a blood clot, they are delivered to the brain with the general blood flow (especially when the foramen ovale is not closed) after attacks of atrial fibrillation, tachyarrhythmia, atrial fibrillation in patients in the post-infarction period;
- lacunar - more often occurs when small intracerebral vessels are damaged in arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, is characterized by the small size of the lesion (up to 15 mm) and relatively minor neurological disorders;
- hemodynamic - cerebral ischemia with a general decrease in blood circulation speed and a drop in pressure against the background of chronic heart disease, cardiogenic shock.
In case of hemodynamic disturbances, blood flow in the vessels of the brain may decrease to a critical level and below
It is worth explaining the development of strokes of unknown etiology. This often happens when there are two or more reasons. For example, in a patient with carotid artery stenosis and fibrillation after an acute infarction. It should be taken into account that elderly patients already have stenosis of the carotid arteries on the side of the alleged disorder, caused by atherosclerosis, in the amount of up to half the lumen of the vessel.
Blockages and spasms of blood vessels without heart attack
In clinical practice, there are often cases where disruption of blood flow does not cause necrotic changes. According to ICD 10, such conditions are included in two large groups:
- I 65 – includes damage to the carotid, vertebral and basilar arteries emerging from it;
- I 66 – this code indicates spasm or embolism of the cerebral and cerebellar arteries.
Nerve cells are very sensitive and quickly die due to oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. But the brain is structured in a unique way; it contains the so-called “Circle of Willis” - these are “spare” connections between arteries, thanks to which blood can flow through bypass vessels. That is why sometimes obstruction does not lead to cerebral infarction.
Let us note the main reasons that can create an obstruction in the artery:
- Spasm is a narrowing of a vessel due to contraction of its muscles, resulting in a decrease in its capacity. Usually the cause is neurogenic;
- Narrowing - differs from the previous version by violating the anatomical integrity of the vascular wall in a certain area. Such changes are irreversible;
- Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot on the artery wall, which gradually increases in size and creates an obstruction;
- Embolus - circulates along with the blood, enters a vessel of a smaller caliber and causes its blockage. Usually this is a detached blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque.
The listed reasons often lead to cerebral infarctions or the development of severe conditions after stroke, having a certain code according to ICD 10.
Stages of cerebral infarction
The stages of pathological changes are distinguished conditionally; they are not necessarily present in every case:
- Stage I - hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) disrupts the process of permeability of the endothelium of small vessels in the lesion (capillaries and venules). This leads to the transfer of fluid and protein from the blood plasma into the brain tissue and the development of edema.
- Stage II - at the level of capillaries, pressure continues to decrease, which disrupts the functions of the cell membrane, the nerve receptors located on it, and electrolyte channels. It is important that all changes are reversible for now.
- Stage III - cell metabolism is disrupted, lactic acid accumulates, and a transition to energy synthesis occurs without the participation of oxygen molecules (anaerobic). This species does not allow maintaining the necessary level of life of neuronal cells and astrocytes. Therefore, they swell and cause structural damage. Clinically expressed in the manifestation of focal neurological signs.
What is the reversibility of the pathology?
For timely diagnosis, it is important to establish a period of symptom reversibility. Morphologically, this means preserved neuronal functions. Brain cells are in a phase of functional paralysis (parabiosis), but retain their integrity and usefulness.
The ischemic zone is much larger than the necrosis area; the neurons in it are still alive
In the irreversible stage, it is possible to identify a zone of necrosis in which cells are dead and cannot be restored. Around it there is an ischemic zone. Treatment is aimed at supporting adequate nutrition of neurons in this area and at least partially restoring function.
Modern research has shown extensive connections between brain cells. A person does not use all reserves and opportunities in his life. Some cells are able to replace dead ones and provide their functions. This process is slow, so doctors believe that rehabilitation of a patient after an ischemic stroke should continue for at least three years.
Preventing recurrence of attacks
25% of patients who have had an ischemic stroke are at risk of experiencing a recurrence. The greatest likelihood exists within the next year. In this regard, it is important, after taking emergency measures to save the patient, to engage in secondary prevention. Let us note that AI is not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This determines the set of preventive measures:
- Drug therapy aimed at eliminating cardiovascular diseases and rapid regression of neurological disorders.
- Lifestyle modification: getting rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), correcting body weight (bringing it to normal), performing special physical exercises, following the principles of proper nutrition, including reducing the amount of animal fat consumed.
Signs of transient cerebral circulatory disorders
Clinicians include the following in the group of transient cerebrovascular accidents:
- transient ischemic attacks (TIA);
- hypertensive cerebral crises.
Features of transient attacks:
- the duration ranges from several minutes to a day;
- every tenth patient after a TIA develops an ischemic stroke within a month;
- neurological manifestations are not grossly severe;
- mild manifestations of bulbar palsy (focus in the brain stem) with oculomotor disorders are possible;
- blurred vision in one eye combined with paresis (loss of sensation and weakness) in the limbs of the opposite side (often accompanied by incomplete narrowing of the internal carotid artery).
Features of hypertensive cerebral crises:
- the main manifestations are cerebral symptoms;
- focal signs occur rarely and are mild.
The patient complains of:
- sharp headache, often in the back of the head, temples or crown of the head;
- state of stupefaction, noise in the head, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting.
People around note:
- temporary confusion;
- excited state;
- sometimes - a short-term attack with loss of consciousness, convulsions.
Transient disorders are not accompanied by any abnormalities in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, since they do not have organic changes.
Signs of a cerebral stroke
Ischemic stroke means the occurrence of irreversible changes in brain cells. At the clinic, neurologists distinguish periods of the disease:
- acute - continues from the onset of symptoms for 2–5 days;
- acute - lasts up to 21 days;
- early recovery - up to six months after the elimination of acute symptoms;
- late recovery - takes from six months to two years;
- consequences and residual effects - over two years.
Some doctors continue to distinguish small forms of stroke or focal ones. They develop suddenly, the symptoms do not differ from cerebral crises, but last up to three weeks, then completely disappear. The diagnosis is also retrospective. During the examination, no organic abnormalities were found.
Cerebral ischemia, in addition to general symptoms (headaches, nausea, vomiting, dizziness), manifests itself locally. Their nature depends on the artery that is “turned off” from the blood supply, the state of the collaterals, and the dominant hemisphere of the patient’s brain.
Let's consider the zonal signs of blockage of the cerebral and extracranial arteries.
If the internal carotid artery is damaged:
- vision is impaired on the side of the blocked vessel;
- the sensitivity of the skin on the limbs and face on the opposite side of the body changes;
- paralysis or muscle paresis is observed in the same area;
- possible loss of speech function;
- inability to realize one’s illness (if the focus is in the parietal and occipital lobes of the cortex);
- loss of orientation in parts of one’s own body;
- loss of visual fields.
Narrowing of the vertebral artery at the level of the neck causes:
- hearing loss;
- nystagmus of the pupils (twitching when deviating to the side);
- double vision.
If the narrowing occurs at the confluence with the basilar artery, then the clinical symptoms are more severe, since cerebellar damage predominates:
- inability to move;
- impaired gesticulation;
- chanted speech;
- violation of joint movements of the trunk and limbs.
The possibility of developing compensatory collateral circulation is much higher when the patency of extracranial vessels is impaired, since there are connecting arteries for blood flow from the other side of the body.
If there is insufficient blood flow in the basilar artery, manifestations of visual and brain stem disorders (impaired breathing and blood pressure) occur.
If the anterior cerebral artery is damaged:
- hemiparesis of the opposite side of the body (unilateral loss of sensation and movement), often in the leg;
- slowness of movements;
- increased tone of flexor muscles;
- loss of speech;
- inability to stand and walk.
Blockage of the middle cerebral artery is characterized by symptoms depending on the damage to the deep branches (feeding the subcortical nodes) or long ones (approaching the cerebral cortex)
Obstruction of the middle cerebral artery:
- when the main trunk is completely blocked, a deep coma occurs;
- lack of sensitivity and movement in half of the body;
- inability to fix the gaze on an object;
- loss of visual fields;
- loss of speech;
- inability to distinguish the left side from the right.
Obstruction of the posterior cerebral artery causes:
- blindness in one or both eyes;
- double vision;
- gaze paresis;
- seizures;
- large tremor;
- impaired swallowing;
- paralysis on one or both sides;
- respiratory and blood pressure disturbances;
- brain coma
When the optic geniculate artery is blocked, the following appears:
- loss of sensation in the opposite side of the body, face;
- severe pain when touching the skin;
- inability to localize the stimulus;
- perverted perceptions of light, knocking;
- “thalamic hand” syndrome - the shoulder and forearm are bent, the fingers are extended at the terminal phalanges and bent at the base.
Impaired blood circulation in the area of the visual thalamus is caused by:
- sweeping movements;
- large tremor;
- loss of coordination;
- impaired sensitivity in half of the body;
- sweating;
- early bedsores.
The combination of damage to several branches causes complex syndromes of loss of sensitivity and false sensations in the limbs. The ability to diagnose ischemic changes depends primarily on the neurologist’s knowledge of the clinical manifestations of vascular disorders.
In what cases can acute stroke be suspected?
The above clinical forms and manifestations require careful examination, sometimes not by one, but by a group of doctors of different specialties.
Cerebrovascular accident is very likely if the patient exhibits the following changes:
- sudden loss of sensation, weakness in the limbs, face, especially one-sided;
- acute loss of vision, the occurrence of blindness (in one eye or both);
- difficulty in pronunciation, understanding words and phrases, composing sentences;
- dizziness, loss of balance, impaired coordination of movements;
- confusion;
- lack of movement in the limbs;
- intense headache.
Additional examination allows us to establish the exact cause of the pathology, the level and location of the vessel lesion.
Remaining classification
We have listed the main gradation of cerebrovascular disorders, which are often encountered in clinical practice. Let us note the remaining pathologies, concomitant diseases and conditions after stroke, which correspond to their code according to ICD 10:
- I 64 – set when it is not possible to distinguish hemorrhage from ischemia;
- I 67 – cerebrovascular pathologies not related to strokes and heart attacks;
- I 68 – cerebrovascular accident in other diseases;
- I 69 – complications of stroke.
Purpose of diagnosis
Diagnosis is important for choosing a treatment method. To do this you need:
- confirm the diagnosis of stroke and its form;
- identify structural changes in brain tissue, focal area, affected vessel;
- clearly distinguish between ischemic and hemorrhagic forms of stroke;
- based on pathogenesis, establish the type of ischemia for starting specific therapy in the first 3–6 in order to get into the “therapeutic window”;
- assess indications and contraindications for drug thrombolysis.
It is practically important to use diagnostic methods on an emergency basis. But not all hospitals have enough medical equipment to operate around the clock. The use of echoencephaloscopy and cerebrospinal fluid studies yields up to 20% errors and cannot be used to resolve the issue of thrombolysis. The most reliable methods should be used in diagnosis.
Foci of softening on MRI allow differential diagnosis of hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes
Computed and magnetic resonance imaging allows you to:
- distinguish a stroke from space-occupying processes in the brain (tumors, aneurysms);
- accurately determine the size and location of the pathological focus;
- determine the degree of edema, disturbances in the structure of the ventricles of the brain;
- identify extracranial locations of stenosis;
- diagnose vascular diseases that contribute to stenosis (arteritis, aneurysm, dysplasia, vein thrombosis).
Computed tomography is more accessible and has advantages in studying bone structures. And magnetic resonance imaging better diagnoses changes in the parenchyma of brain tissue and the size of edema.
Echoencephaloscopy can only reveal signs of displacement of the median structures with a massive tumor or hemorrhage.
During ischemia, cerebrospinal fluid rarely shows slight lymphocytosis with increased protein. Most often no change. If the patient has a hemorrhage, blood may appear. And with meningitis - inflammatory elements.
Ultrasound examination of blood vessels - Dopplerography of the arteries of the neck indicates:
- development of early atherosclerosis;
- stenosis of extracranial vessels;
- sufficiency of collateral connections;
- the presence and movement of an embolus.
Duplex sonography can determine the condition of the atherosclerotic plaque and artery walls.
Cerebral angiography is performed if technically possible for emergency indications. Typically, the method is considered more sensitive in identifying aneurysms and foci of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Allows you to clarify the diagnosis of pathology identified on tomography.
Cardiac ultrasound is performed to detect cardioembolic ischemia in heart disease.
It is mandatory to study blood clotting: hematocrit, viscosity, prothrombin time, level of platelet and erythrocyte aggregation, fibrinogen.
Examination algorithm
The examination algorithm for suspected acute stroke proceeds according to the following plan:
- examination by a specialist in the first 30-60 minutes after the patient’s admission to the hospital, examination of the neurological status, clarification of the medical history;
- taking blood and studying its coagulability, glucose, electrolytes, enzymes for myocardial infarction, and the level of hypoxia;
- if it is not possible to conduct MRI and CT, do an ultrasound of the brain;
- spinal puncture to exclude hemorrhage.
Treatment
The most important importance in the treatment of cerebral ischemia belongs to the urgency and intensity in the first hours of admission. 6 hours from the onset of clinical manifestations is called the “therapeutic window”. This is the time for the most effective use of the thrombolysis technique to dissolve a blood clot in a vessel and restore impaired functions.
Regardless of the type and form of stroke, the following are carried out in the hospital:
- increased oxygenation (filling with oxygen) of the lungs and normalization of respiratory function (if necessary, through transfer and mechanical ventilation);
- correction of impaired blood circulation (heart rhythm, blood pressure);
- normalization of electrolyte composition, acid-base balance;
- reducing cerebral edema by administering diuretics and magnesium;
- relief of agitation and seizures with special antipsychotic drugs.
A semi-liquid diet is prescribed for the patient's nutrition; if swallowing is impossible, parenteral therapy is prescribed. The patient is provided with constant care, prevention of bedsores, massage and passive exercises.
Rehabilitation begins from the first days
This allows you to get rid of negative consequences in the form of:
- muscle contractures;
- congestive pneumonia;
- DIC syndrome;
- pulmonary embolism;
- damage to the stomach and intestines.
Thrombolysis is a specific therapy for stroke of ischemic type. The method allows you to preserve the viability of neurons around the necrosis zone, returning all weakened cells to life.
You can read more about the indications and methods of thrombolysis in this article.
The administration of anticoagulants begins with Heparin derivatives (in the first 3–4 days). Drugs of this group are contraindicated for:
- high blood pressure;
- peptic ulcer;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- bleeding;
- impossibility of organizing regular monitoring of blood clotting.
After 10 days they switch to indirect anticoagulants.
Drugs that improve metabolism in neurons include Glycine, Cortexin, Cerebrolysin, Mexidol. Although they are not listed as effective in the evidence-based medicine database, their use leads to improvement in the condition.
Decompression craniotomy is performed in case of increasing edema in the brain stem area
Patients may need symptomatic treatment depending on the specific manifestations: anticonvulsants, sedatives, painkillers.
Antibacterial agents are prescribed to prevent kidney infection and pneumonia.
Recovery process
Stroke is the No. 1 cause of chronic disability in the world. 40% of people unwittingly develop physical and psychological dependence on loved ones, doctors, nurses. However, neurological disorders tend to regress naturally. The main task of specialists is to speed up this process.
The body's ability to recover is based on the mechanism of neuroplasticity:
- Departments of the central nervous system may be reorganized.
- Neurons have the ability to undergo structural and functional changes.
The recovery process has three stages:
- Spicy. Spontaneous recovery.
Immediately after AI (within a week), many body functions resume:
- cerebral edema decreases;
- blood circulation improves in areas bordering the lesion.
- Subacute. Full recovery.
During treatment the following changes occur:
- Brain tissues are functionally reorganized.
- The tissue around the lesion increases its activity.
- Synaptogenesis is activated.
- Chronic. The compensation is improved coordination and increased muscle mass.