general characteristics
Arterial pulse is a rhythmic contraction of the arterial wall caused by the release of blood during contraction of the heart muscle. Pulse waves are formed at the mouth of the aortic valve during the period of blood ejection from the left ventricle. The stroke volume of blood occurs at the moment of increase in systolic pressure, when the diameter of the vessels expands, and during diastole, the dimensions of the vascular walls are restored to their original parameters. Consequently, during the period of cyclic contractions of the myocardium, a rhythmic oscillation of the aortic walls occurs, which causes a mechanical pulse wave that spreads to large and then to smaller arteries, reaching the capillaries.
The mechanism of pulse wave formation in blood vessels
The further the vessels and arteries are located from the heart, the lower the blood and pulse pressure becomes. In the capillaries, pulse fluctuations are reduced to zero, which makes it impossible to feel the pulse at the level of the arterioles. In vessels of this diameter, blood flows smoothly and evenly.
Charging at the workplace
Everyone knows that a sedentary lifestyle has a negative impact on health. It is not without reason that most office workers, who sit for up to 10 hours a day, have musculoskeletal diseases.
To prevent the development of illnesses, experts recommend doing a short warm-up at the workplace every two hours. It looks like this:
Read also: Why do you need a washer for a bolt?
- First, pay attention to your neck. Slowly rotate your head back and forth, up and down. Repeat this at least 10 times.
- Then stretch your arms. Lift them up, clasp your palms together and stretch as high as possible. Next, make circular movements with your shoulders, 10 times.
- Pay attention to your wrists. Make 15 circular movements with your brushes.
- Stand on the floor and try to reach your palms to your feet without bending your knees. If it doesn't work, stretch as far as you can. Hold the position for 15 seconds.
- Sit on the edge of a chair with your legs extended in front of you without bending your knees. Keeping your back straight, pull your feet towards you and then back.
This complex must be carried out every 2-3 hours at work.
Rhythmic beat detection parameters
Recording heartbeats is of great importance for determining the state of the cardiovascular system. By determining the pulse, you can find out the strength, frequency and rhythm of myocardial contractions.
The following properties of the pulse are distinguished:
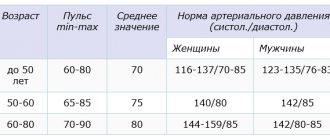
- Frequency. The number of contractions the heart makes in 60 seconds. In an adult at rest, the norm is 60-80 heartbeats per minute.
- Rhythm. Regular repetition of pulse fluctuations and frequency of contractions of the heart muscle. In a state of health, pulse beats follow one after another at regular intervals.
- Filling. The characteristic depends on the pressure values, the amount of circulating blood and the elasticity of the arterial walls. Depending on the presented parameters, good, normal, satisfactory and insufficient pulse are distinguished.
- Voltage. It can be determined by the force that must be applied to stop the propagation of the pulse wave through the artery at the point of compression. When blood pressure is high, the pulse becomes tense and hard. At low blood pressure, the pulse can be assessed as soft.
- Speed. It is determined at the peak of pressure rise, when the artery wall reaches maximum pulse fluctuations. The speed depends on the increase in pressure during systole in the arterial system.
How to measure pulse using a tonometer?
You can use special instruments for measurements. There are several options to check your pulse and at the same time find out some other important indicators. One of them is a tonometer. Such a device records pulse and blood pressure, and modern models are capable of:
- Save results in memory;
- Compare indicators with the norm, identify deviations;
- Calculate average values for a certain period;
- Transfer information through applications to mobile devices or to a computer, where you can conduct a full analysis, including using graphs and diagrams.
To get accurate results, you need to take measurements correctly. Measurements are taken in a sitting position, the cuff on the arm should be at the level of the heart. It is important to calm down and comply with all the requirements listed in the instructions for the device.
Automatic blood pressure monitors inflate the cuff themselves and take measurements. The user can only estimate his pulse and pressure using the numbers on the display.
Age-related changes in heart rate
Typically, heart rate changes with age due to degenerative disorders in the circulatory system. In older people, the pulse becomes less frequent, which indicates stretching of the walls of blood vessels and a decrease in their blood supply.
At the beginning of life, the heart rate is unstable and very often irregular, but by the age of seven the pulse parameters become stable. This feature is associated with the functional imperfection of the neurohumoral activity of the myocardium. In emotional and physical rest in children 7-12 years old, heart contractions do not tend to slow down. In addition, during puberty, the heart rate increases. And only from the age of 13-14, processes are activated that help slow down heart contractions.
In childhood, the heart rate is higher than in adults, which is associated with rapid metabolism and high tone of the parasympathetic nervous system. An accelerated pulse plays a major role in ensuring minute blood volume, which guarantees the necessary blood flow to tissues and organs.
What can cause a high heart rate?
Tachycardia is the medical term for a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute. [6]. With a high pulse, the heart cannot cope with pumping blood to all systems and organs of the body. This leads to oxygen starvation and the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath;
- discomfort, chest pain;
- fainting.
Tachycardia can be determined in some people only by measuring the pulse and an electrocardiogram. Sometimes it's normal to have a racing heart. Heart rate may increase due to non-cardiac factors such as:
- heat;
- low red blood cell count (anemia);
- excessive use of stimulants, including caffeine;
- stress;
- poor physical fitness.
Sometimes tachycardia is asymptomatic or without complications. But if left untreated, the body's normal functioning can be disrupted, leading to serious complications, including heart failure.
Determination methods
The study of the arterial pulse is carried out on the main (carotid) and peripheral (wrist) arteries. The main point for determining heart contractions is the wrist, where the radial artery is located. For an accurate examination, it is necessary to palpate both hands, since situations are possible when the lumen of one of the vessels may be compressed by a thrombus. After a comparative analysis of both hands, the one on which the pulse is better palpated is selected. When examining pulse impulses, it is important to place your fingers so that 4 fingers are on the artery at the same time, with the exception of the thumb.
Determination of pulse fluctuations on the radial artery
Other ways to determine your pulse:
- Thigh area. The study of pulse impulses on the femoral artery is carried out in a horizontal position. To do this, you need to place your index and middle fingers in the pubic area, where the inguinal folds are located.
- Cervical region. The carotid artery is examined using two or three fingers. They should be placed on the left or right side of the neck, 2-3 cm away from the lower jaw. It is recommended to carry out palpation from the inside of the neck in the area of the thyroid cartilage.
Determining the pulse on the radial artery can be difficult in case of weak cardiac activity, therefore it is recommended to measure the heart rate on the main artery.
Where and how can you explore?
There are a limited number of places on the human body where pulse contractions can be examined. And there are many fewer options for studying it at home. It is possible to examine the pulse without using instruments only by palpation. You can find and measure the quality and strength of your heartbeats at:
- wrist (near the radius);
- elbow;
- brachial or axillary arteries;
- temples;
- feet;
- neck (where the carotid artery is located);
- jaws.
In addition, pulsation can be easily felt in the groin or popliteal fossa.
Normal limits
The normal pulse rate for a healthy person is 60-80 beats per minute. Deviation of these norms to a lesser extent is called bradycardia, and to a greater extent - tachycardia. These deviations indicate the development of pathological changes in the body and act as signs of various diseases. However, there are cases when situations arise that cause physiological acceleration of pulse impulses.
The pulse rate in women is slightly higher than in men, which is associated with instability of the nervous system
Conditions that cause physiological changes in heart rate:
- Sleep (in this state, all metabolic processes slow down, the heart does not experience additional stress, so the frequency of its contractions becomes less frequent).
- Daytime fluctuations (at night, the heart rate slows down, and in the afternoon it accelerates).
- Physical activity (hard physical labor provokes an increase in the frequency of the heart, mainly strengthening the work of the left ventricle).
- Emotional and mental stress (anxious states and periods of joy cause increased pulse fluctuations, which go away on their own after the restoration of normal emotional background).
- Fever (with each degree of increase in temperature, heart contractions accelerate by 10 beats per minute).
- Drinks (alcohol and caffeine speed up the heart rate).
- Medicines (taking libido enhancers and antidepressants can cause frequent pulse beats).
- Hormonal imbalance (women during menopause experience tachycardia caused by changes in hormonal levels).
- Athletes (the cardiovascular system of this category is trained, therefore it is not susceptible to sudden changes; they are characterized by a rare pulse).
How does a pulse oximeter work?
Another modern pulse device is a pulse oximeter. Its functions are to determine saturation and count the heart rate (pulse rate). This is a medical device, before using it you need to understand the features of its use.
So, pulse oximeter – what is it and how does it work? The device is equipped with two light sources with different wavelengths and a photosensor that detects the reflection/absorption of light waves by various tissues. The light is partially reflected/absorbed when passing through soft tissues and blood, this makes it possible to determine saturation - the saturation of arterial blood with oxygen as a percentage. The normal rate varies from 95% to 100%; lower values indicate malfunctions in the functioning of the body systems.
To measure your pulse with this device, you need to attach the sensor to your fingertip, press the button and wait a few seconds. The display will show two indicators simultaneously: pulse and saturation. If the values are outside the normal range, a beep will sound.
Diagnostic methods
The study of heart rate allows you to assess the state of the cardiovascular system and identify possible deviations from the norm. Using the generally accepted characteristics of the pulse, you can learn about the condition of the myocardium, heart valves and the elasticity of the vascular walls. Pulse impulses are recorded using graphic research methods, as well as by palpation of vessels located on the surface of the body.
The main method of studying the pulse is palpation, which allows you to evaluate its properties.
There are two main methods for determining pulse fluctuations:
- Sphygmography. A method that allows you to graphically display the arterial pulse. Using special sensors, the pulse wave is recorded.
- Palpation. During the examination, the pulse in the radial artery is determined. Using your fingers, the frequency of the pulse impulses is determined.
Determination of arterial pulse plays an important diagnostic role in assessing the patient's health status. Knowledge about the properties of pulse fluctuations makes it possible to identify possible hemodynamic disorders and pathological changes in the functioning of the heart.
Decide:
- if the victim reacts, leave him in the same position, try to find out the reasons for what is happening and call for help, regularly assess the victim’s condition;
- if the victim does not respond, call loudly for help, call the resuscitation team, turn on his back and open the airways by throwing back the head and pulling up the chin - you need to press on the forehead with your hand, and pull up the chin with the other hand. An alternative method is to tilt the head back by placing one hand under the patient’s neck and the other on the victim’s forehead.
- Keeping your airways open requires you to see, hear and feel the breath by observing the movements of the chest, listening to the sound of breathing and feeling the movement of air on your cheek. Continue the study for no more than 10 seconds.
Pros of using devices
Such devices are very popular due to their many advantages:
- A person can always evaluate his physical activity and, if necessary, adjust it;
- Calorie counter helps you stay fit;
- Heart rate measurement is carried out in real time with high accuracy;
- The cost of the devices is quite affordable;
- The bracelets look stylish and elegant;
- The device combines many useful functions.
In addition, fitness bracelets are easy to use. With their help, it is convenient to monitor your pulse during training without being distracted by taking measurements. Just place your finger and wait a few seconds for the measurement result.
What can fitness bracelets do?
One way to check your pulse and get a lot of other useful information is to use fitness bracelets.
The compact device is fixed on the wrist according to the same principle as a watch. It doesn’t interfere with work, walking, training, and it’s even comfortable to sleep with. All this time the device measures:
- Number of steps taken and distance in km;
- Duration of sports training;
- Achievement of set goals in %;
- Volume of calories burned;
- Duration and quality of sleep.
The range of options depends on the model. For example, some devices synchronize with a smartphone, inform about incoming calls and messages, and transfer the results of all measurements to a mobile device for subsequent analysis. All fitness bracelets function as watches and alarms.