Coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is a radiopaque research method that evaluates the condition of the arteries of the heart. Coronary angiography is the most accurate and reliable way to diagnose coronary heart disease, which allows you to decide on the patient’s treatment tactics in each specific situation, for example, the possibility of continuing treatment with medications, the need for such treatment procedures as angioplasty and stenting or coronary artery bypass grafting. This procedure is invasive, which involves the introduction of a special catheter in an operating room and can be performed both for diagnostic purposes and to monitor the condition of blood vessels after operations already performed.
Price
Today, coronary angiography can be done at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia in Moscow, a modern center that has everything necessary to conduct high-quality and informative diagnostics at the most affordable price.
Coronary angiography with ventriculography
38 500 ₽
It is important to understand that timely examination with the help of innovative equipment will allow us to timely determine the presence of disorders of the cardiovascular system and prevent the occurrence of life-threatening complications.
Why is coronary angiography performed only in a hospital setting?
The main reason that made it mandatory for the patient to be in the hospital when performing this study was the need for puncture (puncture) of the peripheral artery (femoral) and associated complications. The femoral artery is a large vessel located at a depth of 2-4 cm from the skin surface in the groin area. To prevent bleeding, which can be dangerous, after the study the patient is prescribed a limited motor regimen under the supervision of medical personnel. But recently another access has appeared - through the small radial artery, which we palpate on the wrist. An approach called radial, which does not result in serious bleeding. The patient can get up immediately after the examination; bed rest is not necessary. Observation is limited to a few hours. In the CELT clinic, radial (radial) arterial access is used as the main approach. Experience with this technique indicates a lower incidence of local complications, which is 0-0.7%. The possibility of early rehabilitation of the patient after CAG with radial access and the almost complete absence of side effects make it possible to perform CAG on an outpatient basis.
Indications for use
Coronography of the heart is used:
- For chest pain and shortness of breath, often indicating a narrowing of the blood vessels of the heart;
- In cases where treatment with medications does not bring results, and the symptoms of the disease intensify;
- Before undergoing heart valve replacement surgery (to identify narrowing of the heart vessels);
- After bypass surgery to evaluate the results of surgery;
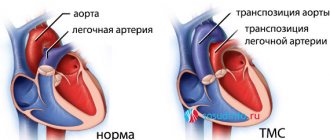
- If there is a suspicion of congenital defects of the heart vessels;
- For diseases of the heart vessels;
- In case open heart surgery is planned;
- For heart failure;
- For serious chest injuries;
- On the eve of surgery, which is associated with a risk of heart problems.
How is outpatient coronary angiography performed?
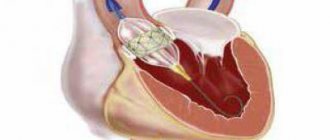
The algorithm for performing coronary angiography on an outpatient basis includes three stages. At the first stage, patients are selected for a diagnostic procedure, and the necessary additional examinations are carried out. Indications for coronary angiography : - identified or suspected ischemic heart disease; - pain in the chest, suspicious for angina pectoris; - myocardial infarction; - planned surgery for heart defects; - heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias. Indications for coronary angiography are determined by the attending physician in accordance with accepted criteria. In preparing the patient for coronary angiography , the necessary tests and studies are performed. In addition to these, additional studies may be prescribed. The second stage of outpatient CAG angiography procedure itself . The patient is admitted to the day hospital ward. After assessing the stability of his condition, premedication is administered and he is transported to the cath lab, where the coronary angiography . After anesthetizing the access area, research begins - a special catheter is passed through the artery of the forearm into the lumen of the coronary arteries . Using a catheter, a radiopaque substance is injected into the blood, thanks to which the lumen of the vessels becomes visible on a special device - an angiograph. During coronary angiography, the degree and size of damage to the coronary vessels is determined, which determines further treatment tactics. This procedure is low-traumatic, which allows it to be performed under local anesthesia without the use of general anesthesia. The duration of the procedure, as a rule, does not exceed 20 minutes. From the operating room, the patient, accompanied by medical personnel, is taken to the day hospital ward. The third stage of outpatient coronary angiography is observation of the patient in a day hospital ward for 4-5 hours after the examination. In the ward, the patient can drink water or juices without restrictions and have lunch. If there are no complications, the patient is sent home. On the day of the outpatient coronary angiography, the patient receives a conclusion with recommendations on further treatment tactics and a disk with the results of coronary angiography . If complications arise during coronary angiography or during the control period, patients are hospitalized in the intensive observation unit of the hospital.
Purpose of coronagraphy
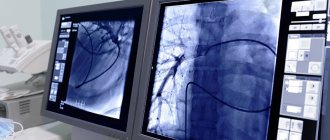
Coronography allows the doctor to see on a monitor screen what is happening in the patient’s blood vessels, through which blood is delivered to the heart. This method allows you to track the dynamics of blood circulation, diagnose blockage of blood vessels, or their narrowing. In this case, the doctor can clearly see the place of narrowing of the artery.
The procedure also helps identify congenital heart vascular defects. If it is necessary to replace a coronary vessel (bypass surgery), coronography reveals the area for future surgical intervention.
FAQ:
Question: I am 56 years old and have coronary heart disease . The cardiologist recommends a coronary angiography . I don't quite understand what this is? Answer: Coronary angiography is a study of the vessels of the heart, which, like a crown, surround the heart, supplying it with oxygen-rich blood. These are called coronary arteries. Narrowing of the coronary arteries leads to a decrease in blood supply to the heart, which leads to oxygen starvation, i.e. to cardiac ischemia. It is very important to know the condition of the arteries of the heart, because... the obstruction to blood flow can be eliminated, radically relieving the person of the symptoms of coronary heart disease . Question: How is coronary angiography performed? Answer: Coronary angiography is an x-ray examination in which a special contrast agent is injected into the vessels of the heart using a flexible thin probe. As the contrast agent passes through the vessels, short-term x-rays are taken with significant magnification using high-resolution equipment. The slightest changes in the coronary bed are visible “at a glance.” The results are recorded in digital format and are available for viewing on any personal computer. Question: Is coronary angiography performed under anesthesia? Answer: No general anesthesia is required. The pulse is determined in the groin area or on the wrist, and a probe or catheter is inserted into the lumen of the artery under local anesthesia. The subject does not feel how the catheter moves through the vessels, because There are no sensory nerve endings inside the arteries. There is no pain, the patient is fully conscious and, together with the operator, monitors the progress of the study on the monitor. The duration of the procedure is no more than 15-20 minutes. Further monitoring of the patient for several hours is necessary. At the CELT clinic, coronary angiography is performed exclusively through the radial artery (at the wrist). Immediately after the examination, the patient can get up and walk, the bandage on his arm does not limit him in any way (see ambulatory coronary angiography ). After 4 hours the patient is discharged home. If the examination is carried out through the groin, then bed rest is necessary and the period of stay in the clinic is extended to a day. Question: If coronary angiography does not reveal narrowing in the vessels of the heart, then there is no coronary heart disease? Answer: Yes, the absence of changes in the coronary arteries practically excludes the diagnosis of coronary heart disease . In rare cases, ischemia of the heart muscle can occur in the presence of “normal” coronary arteries, but the absence of damage to the arteries of the heart is the most reliable predictor of a good prognosis. This is very important information for choosing the right patient management tactics. Question: At what age is coronary angiography , what are the contraindications to coronary angiography? Answer: Coronary angiography is performed at any age, in all cases when there is a need for it, namely if the patient has angina pectoris after myocardial infarction. Coronary angiography, in the first hours of myocardial infarction , makes it possible to determine where the blockage of the vessel is causing the heart attack and immediately eliminate it. Coronary angiography is necessary for all adults with heart defects before surgery, before “major” vascular operations. Some patients at high risk for coronary heart disease , such as diabetes , may not have symptoms of the disease. In this case, coronary angiography is, in fact, the only reliable way to exclude or confirm coronary disease . Question: I need a coronary angiography . I contacted the Federal Center. They gave me a list of tests and put me on the waiting list. They said I needed hospitalization for 2-3 days. Answer: We coronary angiography on the day of admission! All tests and additional studies are carried out within 4-5 hours, including coronary angiography. Question: How can I get a coronary angiography at your center? Answer: You can come any day, appear at the clinic, at the cardiovascular surgery department in the morning at 08:30 on an empty stomach, PRIORLY AGREEING YOUR ADMISSION WITH US BY PHONE 305-34-04 or 788-33-88. Before admission, before performing coronary angiography , you should have on hand the results of the following tests and studies: - General blood test; — General urine analysis; - Biochemical analysis - protein, urea, creatinine, bilirubin and its fractions, lipid profile, potassium and sodium, glucose; — Coagulogram; — Blood type and Rh factor, Rh antibodies; — Blood test for HIV, RV, antibodies to hepatitis B and C; — Ultrasound of the heart, ECG. If you do not need tests and studies, then they can be performed with us on the day of admission. Question: coronary angiography cost you and what are the prices for coronary angiography in Moscow in other clinics? Answer: Coronary angiography including the stay costs 30,000 rubles. Today, if you analyze the prices for coronary angiography in Moscow, this is the minimum cost.
Possible complications
You should know that, like many other procedures performed on the heart and blood vessels, coronography in some cases can have negative consequences for the patient. However, serious problems are rare.
Complications after coronography can manifest as:
- Heart attack;
- Rupture of the heart or artery;
- Separation of blood clots from the walls of blood vessels, leading to a heart attack or stroke;
- Artery injuries;
- Changes in heart rhythm (arrhythmias);
- Allergic manifestations to drugs used during the procedure;
- Infections;
- Kidney damage;
- Excessive exposure to x-rays;
- Heavy bleeding.
Contraindications for the procedure
Coronary angiography has only relative contraindications. There is a list of diseases that increase the risk of complications. But even against the background of such diseases, fluoroscopy of blood vessels can be performed if the patient’s life depends on it. Coronary angiography is performed with extreme caution when:
- impaired blood clotting;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- allergies to contrast agent;
- arterial hypertension;
- severe renal failure - the contrast agent has a bad effect on diseased kidneys;
- internal bleeding - postponed until this problem is resolved.
All possible contraindications must be taken into account when prescribing coronary angiography. Absolute contraindications include only a severe allergic reaction to contrast. In most cases, the study is simply postponed.
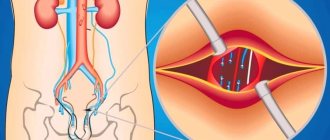
Vascular angiography: what it is and how it is done, indications, consequences
You can quite simply describe what angiography means - it is obtaining images of blood vessels. This diagnostic procedure allows you to conduct a full examination of the vessels, determine where they are blocked, identify areas of blood clots, places of narrowing and thinning of the vascular walls. For angiography
a special contrast agent is introduced, which is highlighted during scanning and helps to identify potential or existing pathologies.
Is this examination dangerous?
Everyone who is about to undergo this procedure is interested in what the consequences and complications may be. This type of diagnosis is considered a safe manipulation; the process is controlled using an X-ray or computed tomograph. Nevertheless, the risk of complications is still present; the most dangerous consequence is damage to blood vessels by the catheter.
The likelihood of such a complication is very low; it can occur from sudden movements or carelessness of the doctor. If the patient has not undergone proper preparation, an allergic reaction or bleeding may occur (with poor clotting). All these risks can be reduced if you carefully prepare and relax before the procedure.
If you are overcome by fear and anxiety in the X-ray operating room, you can warn the doctor about this and he will prescribe sedatives.
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound and MRI of the heart
Today, high-quality cardiac MRI requires very expensive equipment - a tomograph with a magnetic field power of at least 3 Tesla. Research using such an ultra-high-field device will be expensive, so the main disadvantage of cardiac MRI is its high price. In addition, MRI of the coronary vessels and heart cannot measure the speed of blood flow and its actual volume. Cardiac ultrasound can better cope with this task.
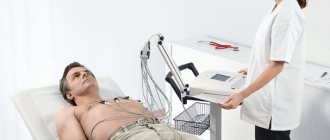
Previous NextMethod of performing electrocardiography
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
For the procedure, the patient is placed comfortably in a horizontal position on his back. Special electrodes are attached to the chest area, legs and arms. The device starts and the heart function is recorded. The duration of the procedure can vary from 1 to 10 minutes. The results obtained are sent to the doctor for interpretation and diagnosis.
Decoding the results
There is a certain technique for deciphering angiography results. Markers are identified for each vascular pathology. For example, if the vessels have intermittent outlines in the images, we can talk about the presence of pathologies such as thrombosis or atherosclerosis. The detection of protrusions in the walls of blood vessels in the images indicates that there are either congenital changes, an aneurysm, or the same thrombosis. We can also talk about congenital pathologies in cases where the contrast agent does not enter the capillaries, but passes directly into the vein.
If, upon administration of contrast, there is a lack of its spread, this indicates the presence of thrombophlebitis, thrombosis or thromboembolism.