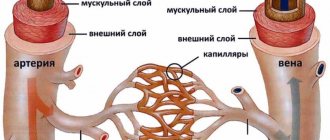
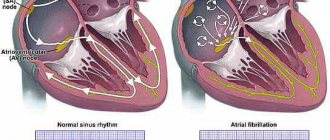
Palpitations - a feeling that the heart is beating too quickly or is beating too hard - is a reason to consult a doctor.
Heartbeat
is a patient complaint about the subjective sensation of a rapid, arrhythmic or heavy heartbeat. Normally, we do not notice our heartbeat. But any deviation from the norm becomes immediately noticeable. Patients typically describe palpitations as the following: the heart pounding too hard (or “loudly”) in the chest, the heart “jumping” out of the chest, pounding, “jerking,” “spinning,” or “fluttering.” Increased heartbeat may be accompanied by a feeling of pulsation in the neck, temples, pit of the stomach or fingertips. Palpitations may also be accompanied by tinnitus, pain in the heart area, a feeling of tightness in the chest or difficulty breathing. Such symptoms may indicate heart pathology, but in most cases, complaints of increased heartbeat with accompanying symptoms, instrumental studies do not reveal signs of heart damage.
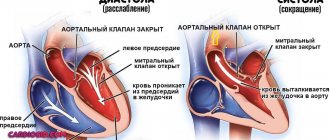
Palpitations should be distinguished from tachycardia. Tachycardia
– this is an objective increase in heart rate. The normal heart rate for an adult at rest is 60-80 beats per minute. If more than 90 beats per minute are recorded, then tachycardia is diagnosed. However, the patient may not feel that his heartbeat is rapid.
Palpitations and tachycardia: what is the difference?
Palpitations are a condition in which you feel your own heart beating—too fast, too slow, or irregular. You may feel like your heart is pounding or fluttering. They can be alarming, but do not always reflect serious heart disease.
A rapid heartbeat may have an obvious cause:
- physical activity
- emotional stress
- stopping medication
- caffeine
- nicotine
This type of heartbeat is usually not a cause for concern. However, it is important to distinguish palpitations caused by objective reasons from palpitations that may indicate an underlying heart disease. In everyday life, it is impossible to distinguish between these symptoms; if you feel your heart, it is better to consult a cardiologist. But here a difficulty arises, because symptoms may not appear at the appointment.
I recommend that patients combine an electrocardiogram (ECG) for symptoms of irregular heart rhythm with Holter monitoring. This is a portable device that the patient carries with him for 24 hours. It is connected to your chest with wires and seamlessly records your heart rate. A day later, the patient returns the monitor, and I decipher it. In 99% of cases, combining two studies is enough to determine the cause of rapid heartbeats.
Cardiologist at the Stimul Clinic Grachev Sergey Aleksandrovich
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia: first aid
Vagal tests can be used as an emergency aid. Their meaning is to irritate the receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system, as a result of which the vagus nerve is activated. Performing these techniques will help either interrupt the paroxysm or lower the heart rate and reduce symptoms.
- Valsalva maneuver. While sitting or standing, take a deep breath, then pinch your nose, close your mouth and try to exhale, while straining the anterior abdominal wall.
- The cough reflex is simple to perform: the patient needs to cough.
- The gag reflex is to press on the root of the tongue.
- Squatting with straining.
- Diving dog reflex: hold your breath, pinch your nose and lower your face into a container of cold water.
- Carotid sinus massage. Prohibited for patients with atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries and/or a history of stroke. It is carried out as follows: the pulsation point on the neck is determined and several pressures are applied on it for 3-5 seconds.
- Danini-Aschner test - pressure on the eyeballs; currently not recommended for use.
In addition to vagal tests, medications are used for emergency care. Verapamil is widely used, but its use is possible only when it is reliably known that there are no additional pathways in the myocardium. If atrial fibrillation has developed, then Propafenone, the “pill in your pocket” technique, can help. This drug is taken only if it has been previously successfully used in a hospital under the control of an electrocardiogram.
In my practice, during transesophageal pacing, patients often developed an attack of reciprocal AV nodal tachycardia. The use of vagal maneuvers (Valsalva and carotid sinus massage) made it possible to stop paroxysm. The entire process is demonstrated on the screen of the ECG installation: against the background of a smooth sinus rhythm, an attack of tachycardia with narrow QRS complexes suddenly occurs. This is accompanied by typical patient complaints (dizziness, nausea, darkening of the eyes, etc.), a massage of the carotid sinus is performed, and the attack suddenly ends.
If wide complex tachycardia develops during TEE, you can try to stop it using several electrical stimuli. The cessation of paroxysm in this way indicates the supraventricular nature of the arrhythmia. If the source is located in the ventricles of the heart, then stimulation will not affect the course of the attack in any way.
If you want to get quick, accessible and short information about frequent heartbeats, watch the video on our channel dedicated to this topic. Ask questions to experts in the comments.
Causes of rapid heartbeat
Sinus tachycardia - rapid heartbeat without interruptions - is a normal variant. The reasons that trigger it are physiological and emotional stress.
But sometimes it can be associated with a systemic pathological process, for example:
- drop in blood sugar;
- increased body temperature;
- decreased blood pressure;
- adrenal tumor;
- anemia.
Also, sinus tachycardia can be provoked by the use of:
- coffee;
- energy workers;
- strong tea;
- some medications.
Other types of tachycardia are pathological. The main reasons in this case are:
- IHD;
- high blood pressure;
- atherosclerosis of myocardial vessels;
- myocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects;
- chronic diseases of the bronchi and lungs;
- excess weight;
- sarcaidosis and amyloidosis;
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
In children
Heart rate norms in children are higher than in adults. In newborns it can reach 160 beats/min, in one-year-old babies - 130-140, by the age of seven - 80-100. Changes occur quickly in a child’s body, and the heart adapts to new conditions, so it is not always possible to accurately determine the causes of tachycardia.
A fast heartbeat in a child can be dangerous and lead to heart disease in the future. It is important that the child leads a healthy lifestyle.
The causes of pathological tachycardia in children are the same as in adults. They are diagnosed with sinus, paroxysmal and chronic tachycardia. Paroxysmal is dangerous, in which the heart rate increases two to three times. The child develops shortness of breath, bluish skin, veins begin to pulsate, and he may become very frightened. During an attack, you need air flow and rest. It is usually relieved by intravenous injections of glycosides.
Increased heart rate with blood pressure
High blood pressure
Quite often, tachycardia occurs when blood pressure rises. There is a direct relationship here - the more often the heart contracts, the higher the pressure in the arteries. High blood pressure and rapid heartbeat may have the same causes. Therefore, therapy aimed at stabilizing arterial division also normalizes the heartbeat.
Low pressure
A sharp decrease in pressure can be observed in various shock conditions - traumatic, anaphylactic, infectious-toxic, psychogenic, etc. In this case, the body accelerates the contraction of the heart to increase the pressure. Also, a similar compensatory mechanism is observed with significant blood losses.
Normal pressure
Tachycardia can be observed without pressure fluctuations. With normal indicators, a rapid heartbeat can be associated with anemia, thyroid pathologies, vegetative-vascular dystonia and other diseases. It is impossible to independently determine the cause of increased heart rate, much less self-medicate. If you experience heart palpitations, you should consult a doctor.
When is palpitations a reason to see a doctor?
A rapid heartbeat is a reason to see a doctor if it:
- too intense;
- is protracted (does not go away for a long time);
- occurs with less and less exposure to the above factors;
- occurs independently of the above factors;
- is uneven in nature (arrhythmia can be assumed - a violation of the heart rhythm).
In these cases, rapid heartbeat may be a manifestation of serious disorders and diseases, such as:
- avitaminosis;
- anemia (low hemoglobin and iron in the blood);
- tetany (a condition caused by a lack of calcium);
- endocrine diseases;
- heart pathologies.
However, as a rule, in the case of myocarditis, other heart diseases, and hyperthyroidism, palpitations are not the main complaint. With such diseases, first of all, they complain of pain in the heart and shortness of breath.
It is necessary to react promptly if, against the background of increased heartbeat, dizziness, shortness of breath, pale skin, and sweating are observed. In this case, you should call an ambulance.
Tachycardia after coronavirus
If observations are made that the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 may also cause a rapid heartbeat called postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). This is a debilitating condition in which your heart speeds up at least 30 beats per minute after you move from a sitting or lying position to a standing position. Moreover, symptoms may not appear immediately, but 10-15 minutes after you get up. In addition to palpitations, you may experience dizziness or even faint.
This syndrome is little known and difficult to diagnose, since it also includes general signs of malaise after an illness:
- fatigue
- exercise intolerance
- gastrointestinal disorders
- headache
- sleep disturbance
At the Stimul clinic, we not only identify this syndrome, but also prescribe competent, effective treatment after examining the body. The therapy has an extremely positive result and leads to complete recovery in a short time.
How to choose a cardiologist
If you want to go to a medical institution for consultation because of rapid heartbeat, then first of all it is important to choose a clinic that has proven itself well. Advantages of the EXPERT Clinic:
- multidisciplinary medical center, which allows you to get advice from various specialists if necessary
- experienced and attentive cardiologists
- modern examination equipment, as well as practicing specialists in ultrasound and functional diagnostics
- the ability to quickly take all tests and provide examination results
- the most attentive attitude towards patients, only an individual approach, a detailed study of the problem
- convenience and comfort in the clinic, responsive medical staff.
Do not delay visiting a cardiologist, because timely identification of the main problem of “rapid heartbeat” can sometimes save your life.
Diagnosis of heart palpitations
To find out the causes and make a diagnosis, the doctor conducts the following studies:
- interviewing the patient - what provokes tachycardia, how long an attack usually lasts, how often it occurs, what lifestyle the person leads, etc.;
- examination - listening with a stethoscope;
- ECG;
- daily monitoring - special devices are attached to the patient’s body, which during the day record the heart rhythm and changes in its work in familiar living conditions;
- blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the heart.
Folk remedies to combat rapid heart rate
- Pour 1 teaspoon of celandine and 10 grams of dried hawthorn into a glass of boiling water, leave well.
- Mix 1 share of chokeberry juice, 3 shares of cranberry juice, 2 shares of carrot juice and 2 shares of alcohol. Squeeze 1 lemon into the mixture.
- A mixture of lemon and honey is incredibly effective. You need to take 1 kg of lemons, 1 kg of honey, 40 apricot kernels. Grate the lemons, peel the seeds and crush them. Mix everything with honey.
A rapid heart rate can be the cause of many diseases. Timely detection of the disease is the key to its successful treatment!
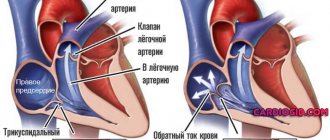
Why is tachycardia dangerous?
Long-term disruption of the heart leads to a disorder of myocardial contractility and right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Insufficient nutrition of the heart muscle can cause coronary heart disease and acute myocardial infarction.
The most dangerous tachycardia is considered to be increased heart rate in the following pathologies:
- ischemia;
- accumulation of fluid in the lungs;
- cardiogenic shock;
- ventricular fibrillation;
- chronic heart failure.
Why should tachycardia be eliminated?
Rapid heartbeat is a rather dangerous symptom that must be eliminated as soon as possible. Due to frequent contractions, the heart does not get enough rest and quickly becomes exhausted. The result is heart failure - a discrepancy between the body's oxygen needs and the work of the heart.
Therefore, if tachycardia occurs, you should consult a doctor. Even in the absence of specific symptoms that would accompany a rapid heartbeat, it is enough to first visit a therapist. After conducting the necessary examinations, he will refer you to the appropriate specialist.
Treatment for palpitations
Treatment for palpitations depends on the underlying cause. If it is physiological, for example, an increase in temperature, you just need to eliminate this factor.
In mild cases, preparations based on mint, valerian, and motherwort help. Sometimes your doctor may prescribe medications to slow your pulse.
If tachycardia is provoked by chronic pathologies, the doctor prescribes medications individually. In this case, treatment may take a long time.
Without concomitant pathologies, tachycardia does not lead to a deterioration in a person’s condition, but can still cause many dangerous complications. If attacks occur against the background of heart pathologies, there is a real risk of their progression. A person who experiences recurring attacks should definitely contact a cardiologist to identify possible disorders.
After drinking alcohol
Heart palpitations after drinking alcohol are common. In this case, the heart always starts beating faster, and this is a normal reaction of the body. Such tachycardia is considered physiological if alcohol is taken occasionally. In chronic alcoholism, pathological tachycardia develops. An experienced alcoholic has impaired heart function, and most often it is no longer possible to restore it even after giving up the addiction.
After drinking alcohol, physiological tachycardia develops, but with alcohol abuse it becomes pathological.
Microelements for the heart with tachycardia
Vitamins and minerals have a strong impact on the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Micronutrient deficiency very often causes tachycardia and arrhythmia. Therefore, to prevent the development of such a situation, drugs for tachycardia are used in the form of vitamin and mineral complexes. Minerals are responsible for the functioning of the heart and blood vessels:
- magnesium, which prevent blood clots by normalizing metabolic processes and controlling blood viscosity;
- calcium, which normalizes myocardial contractile function;
- phosphorus – a conductor of nerve impulses;
- selenium, which increases local immunity, providing protection to heart cells and blood vessels;
- potassium that accompanies the generated electrical impulse through the myocardial conduction system.
As a preventive measure
In order to prevent attacks of tachycardia, it is recommended:
- Avoid stress and high physical activity.
- Avoid drinking black tea and coffee or limit their consumption and give preference to green tea.
- Instead of tea, you can drink an infusion of hawthorn and rose hips, which helps normalize heart rate. To prepare it, mix the fruits of these plants in equal proportions, add boiling water and infuse.
- If tachycardia develops against the background of hypertension, green oat juice (drink 50 g three times a day) or infusion of blue cornflower flowers (take ½ glass three times a day) helps well. If you are prone to heart attacks with high blood pressure, it is recommended to take a tablespoon a day of Adonis infusion and drink green tea with mint or lemon balm leaves.