Cardiac tachycardia - what is it?
Tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia in which the heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute.
A rapid heartbeat is a variant of the norm if heavy physical work is performed, a person experiences a strong emotional shock, after drinking alcoholic beverages or sports training. Pathological tachycardia of the heart manifests itself:
- pronounced pulsation of neck vessels;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- feeling of anxiety.
Explaining what tachycardia is and why it is dangerous, cardiologists focus on the fact that the basis of the disease is the increased automaticity of heart contractions, which normally sets the rhythm and pace of heart contractions. The pathology can lead to cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and the development of acute heart failure.
Classification of tachycardia
Based on the name of the area of the heart in which the impulse causing tachycardia is generated, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
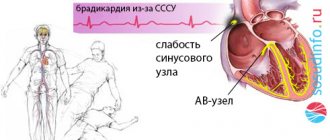
- Sinus tachycardia. The source is in the sinus node.
- Supraventricular tachycardia (also known as atrial tachycardia). The source is in the atria.
- Ventricular tachycardia. The source is in the ventricles.
According to the time criterion, it happens:
- Paroxysmal tachycardia. An attack of rapid heartbeat suddenly begins and ends abruptly (heart rate ranges from 120 to 250 beats per minute).
- Constant (chronic) tachycardia.
Causes.
Reasons for accelerated work
problems with the heart muscle can range from trivial to serious.
Most often this is poor nutrition, and as a result obesity, hypertension, diabetes, constant stress or a long period of dehydration. Sometimes an episode of tachycardia
occurs after drinking large amounts of alcohol, coffee, or smoking cigarettes.
It should be remembered that any reason, even prosaic, but often repeated, can lead to serious illness
.
However, tachycardia often accompanies or is associated
I have other cardiac diseases (hypertension, coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, recent heart attack), endocrine disease (hyperthyroidism) or diabetes (hypoglycemia).
Episodes of tachycardia can also occur after heatstroke or flu.
Causes of tachycardia
As an independent disease, an increase in heart rate develops extremely rarely. It usually accompanies other diseases and is their symptom, so the causes of cardiac tachycardia are usually attributed to:
- Adrenal insufficiency. Tachycardia is combined with weakness, fatigue, and a poorly palpable pulse. Stomach colic, impaired bowel movements, vomiting, nausea, disturbances of taste and smell, and increased libido may also occur.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflammatory life-threatening lung disease. In addition to cardiac tachycardia, it is characterized by: shortness of breath, cyanosis of the skin, anxiety, rapid breathing, and wheezing. During the diagnostic examination, abnormalities are found on the chest x-ray
. - Anaphylactic shock. A type of allergic reaction manifested by rapid heartbeat, swelling of the airways, anxiety, and shortness of breath.
- Anxiety, fear, unsatisfactory emotional state, severe stress. Symptoms of tachycardia go away on their own as soon as the person calms down.
- Alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Occurs in people who abuse alcohol. In addition to an increase in heart rate after quitting alcohol, they complain of insomnia, increased sweating, rapid breathing, weakness, and irritability.
- Anemia. Heart disease is often a sign of anemia. In parallel with the rapid heartbeat, the following are noted: a tendency to bleeding, fatigue, weakness, pallor, difficulty breathing (a feeling of “lack of air”).
- Aortic stenosis. Tachycardia is provoked by heart disease.
- Aortic insufficiency. Heart disease, which causes tachycardia, angina pectoris, and circulatory disorders.
- Heart contusion (concussion). Develops due to chest trauma. Accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, tachycardia.
- Arrhythmia. Often, a rapid heartbeat “echoes” its irregularity. The patient complains of low blood pressure, dizziness, weakness, and a feeling of strong and rapid heartbeat. The skin becomes pale and cold.
- Cardiogenic shock. Left ventricular failure, in which myocardial contractility sharply decreases.
- Cardiac tamponade. The cause of tachycardia, in which fluid accumulates in the pericardial cavity. In addition to rapid heartbeat, there are: swelling of the neck veins, shortness of breath, wetness and cyanosis of the skin, anxiety.
- Cholera. An infection characterized by vomiting and diarrhea. Due to severe loss of fluid, tachycardia develops, skin turgor decreases, convulsions occur, and blood pressure drops sharply.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. Tachycardia is their basic symptom along with cough, cyanosis, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Untimely/illiterate treatment of them is fraught with the development of a “barrel-shaped” chest.
- Fever (high body temperature).
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (carbohydrate metabolism disorder). Its symptoms include: tachycardia, nausea, fruity breath, vomiting, stomach pain.
- Left-sided heart failure.
- Hypertensive crisis. High blood pressure is always accompanied by an increased heart rate.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Tachycardia, tremors, migraine, double vision, and increased sweating are observed.
- Hyperosmolar non-ketoacidotic syndrome. It is characterized by: tachycardia, decreased skin turgor, rapid breathing, decreased blood pressure.
- Hypoxia. When there is a lack of oxygen, the heart begins to beat faster and the skin becomes bluish.
- Hyponatremia (lack of sodium in the blood). Rarely accompanied by tachycardia.
- Myocardial infarction. There may be both tachycardia and bradycardia.
- Neurogenic shock. Loss of sympathetic innervation, causing tachycardia.
- Hypovolemic shock. A consequence of large blood loss, which develops: decreased elasticity of the skin, decreased temperature, thirst, dry tongue, tachycardia.
- Orthostatic hypotension (dysregulation of blood vessel tone).
- Septic shock. Tissue perfusion is reduced, and the delivery of oxygen and other necessary substances to the tissues is disrupted. Accompanied by tachycardia.
- Pheochromocytoma. A hormonal active tumor, the symptoms of which include: rapid heartbeat, surges in blood pressure, tremors, panic attacks, insomnia, sweating.
- Pneumothorax. Air entering the pleural cavity, causing shortness of breath, tachycardia, cyanosis, chest pain, wheezing.
- Thyrotoxicosis. The level of thyroid hormones increases, which causes a feeling of palpitations, enlargement of the thyroid gland, weight loss, and protrusion of the eyeballs.
- Pulmonary embolism. First, chest pain and shortness of breath develop, later - tachycardia.
In addition to the listed diseases, the causes of tachycardia are:
- taking certain medications;
- carrying out diagnostic procedures;
- postoperative period.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms of tachycardia
The symptoms of cardiac tachycardia, as well as the treatment of the disease, depend on its form. Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a regular rhythm and increased heart rate to more than 90 beats per minute. Patients report increased fatigue. The development of the disease is provoked by extracardiac pathologies. Therefore, it is impossible to get rid of it without eliminating the negative effect of causative factors on the body.
Atrial (supraventricular) paroxysmal tachycardia is characterized by:
- Severe palpitations that the patient feels without even feeling the pulse. Heart rate – from 140 to 250 beats.
- Feeling of unreasonable fear.
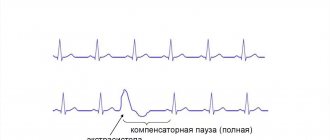
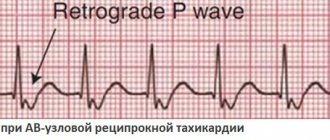
If atrial tachycardia is rhythmic, cardiologists speak of atrial flutter. If the pulse is uneven, we are talking about atrial fibrillation.
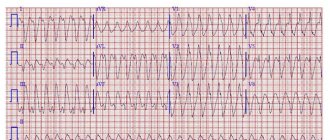
Ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia is an attack in which it is difficult to calculate the pulse (heart rate - more than 140 beats per minute). The patient feels weakness, rapid heartbeat, discomfort in the heart area/behind the sternum. The pathology usually develops against the background of severe heart damage.
It is possible to distinguish atrial tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia (forms in which the heart rate exceeds 140 beats) only after an electrocardiogram
.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Symptoms.
As already mentioned, a typical symptom
- This is a rapid but steady and regular heartbeat.
Often such palpitations can be accompanied by a feeling of shortness of breath, chest pain, weakness, dizziness, coughing and even difficulty breathing
.
However, it happens that the heart begins to beat faster for other reasons not related to illness, such as physical stress, strong emotions, dehydration
, or the use of alcohol or other substances that increase the heart rate.
In such cases, once the cause has disappeared, the heartbeat returns to its normal rate and there is no cause for concern. On the other hand, a warning sign is tachycardia
, occurring at rest for no reason and often recurring.
Immediate response is required when symptoms are accompanied by chest pain or shortness of breath.
Diagnostics
To determine how to treat tachycardia, a cardiologist
conducts the following research:
In parallel, the following are appointed:
- general blood analysis;
- electroencephalography
; - coronary angiography.
All these types of diagnostics can be provided in any modern cardiology clinic
.
How to treat tachycardia
The main principles of treatment of tachycardia include:
- Treatment of a disease that provokes cardiac pathology (accelerated heartbeat).
- Correction/elimination of conditions causing the disease.
- Normalization of work and rest schedules.
- Refusal of alcoholic beverages, smoking, drinking large quantities of coffee and strong tea.
- The use of sedative therapy aimed at improving the emotional state.
- Prescription of magnesium and potassium supplements that normalize heart function.
- The use of antiarrhythmic therapy - tablets for tachycardia, which affect heart rhythm and tempo.
Most often, in the treatment of tachycardia, complex therapy is used, which involves the synthesis of antiarrhythmic drugs and measures aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and eliminating causative factors. Patients are given intravenous injection of lidocaine (1 mg per 1 kg of body weight). The procedure takes a few minutes. If the expected effect does not occur, the administration of lidocaine is repeated after 15 minutes.
For recurrent tachycardia, an intravenous drip infusion of the drug is performed at a rate of 1 to 2 mg per minute. The duration of the treatment session is from 1 to 2 days. Drugs for the treatment of cardiac tachycardia, such as Ajmaline, Novocainamine and b-blockers, are used by doctors when lidocaine does not block the rapid heartbeat.
If tachycardia is accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, the latter is increased with the help of norepinephrine or other pressor amines, thereby normalizing sinus rhythm. If there is no effect, additional electropulse therapy is performed.
If the accelerated heartbeat is due to intoxication with cardiac glycosides, they are canceled and an additional intravenous drip of lidocaine and sodium chloride or a slow jet injection of Obzidan is prescribed.
Minimally invasive surgery for the treatment of tachycardia
Minimally invasive surgery may be used to treat palpitations. Commonly used methods include:
- Installation of a pacemaker. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. A skin incision is made parallel to the collarbone. By puncturing the subclavian vein, a pacemaker electrode is inserted. To control its movement, the radiographic method is used. Once the electrodes are connected to the heart muscle, their loose fragments are connected to a pacemaker. Then, equipment is installed in a specially formed cavity (performed in the projection of the pectoralis major muscle).
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation. To determine the source of arrhythmia, catheter electrodes are inserted through large veins. Before this, hemostatic introducers (in the form of tubes) are installed in large vessels to protect the vessels. The electrodes are delivered directly to the heart under fluoroscopic guidance. Then, using an “ablation” electrode, the foci of tachycardia are “cauterized.” On average, the operation takes 45 minutes - the time depends on the depth and size of the lesion. Already on the second day the patient is discharged.
In many modern medical surgery centers
successfully carry out such operations.
Treatment of tachycardia in pregnant women
Sinus tachycardia during pregnancy is a normal variant if it does not have a negative effect on the woman’s condition. Manifestations of the disease are explained by the increased load on the heart during pregnancy, weight gain, and the need to maintain constant blood flow to the uterus.
The following help improve the condition of a pregnant woman with sinus tachycardia:
- dietary nutrition;
- complete rest;
- drinking at least 2 liters of fluid per day;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
If tachycardia is severe and the heart rate increases to more than 90-100 beats per minute, consultation with a cardiologist is required. When treating the disease in pregnant women, it is permissible to use:
- beta blockers (allow you to control the effect of adrenaline on the sinus node);
- antiarrhythmic drugs and calcium channel blockers (responsible for regulating the generation of electrical impulses by the sinus node).
Self-selection of medications for a pregnant woman without medical advice is unacceptable, since many antiarrhythmic drugs can cause serious disturbances in the development of the fetus.
Treatment.
Modern medicine for tachycardia, of course, provides drug treatment (beta-blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, digoxins)
. Natural methods of prevention and treatment of this dangerous disease
The first step—as with almost all ailments—is to focus on causes and prevention. Almost all cardiovascular diseases
caused by poor diet.
Therefore, it is necessary to exclude (or reduce as much as possible) animal fats (meat, butter), meat products, bad carbohydrates (white bread, white pasta, sugar and confectionery) and sweet drinks from the diet. The kitchen should be dominated by vegetables, fruits, cereals
, whole grain rice and clean, healthy water.
This will allow us to maintain normal body weight, reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, heart disease (including tachycardia), diabetes and other serious diseases. However, if we have already suffered from any of these ailments
, a healthy diet combined with physical activity will restore health. Also, do not abuse alcohol.
In the treatment of tachycardia, electrical cardioversion is also used, which consists in regulating the work of the heart with short-term electrical discharges. Some patients also have an implanted cardioverter-defibrillator
, especially for patients with the ventricular form of the disease. This device responds in the event of an attack of tachycardia by reducing the heart rate to the appropriate level.
Therefore, in addition to the increased heart rate caused by a physiological reaction (physical activity, stress),
it is necessary to promptly respond to symptoms of tachycardia.
Of course, it is best to live a healthy lifestyle and avoid serious heart disease.
Diet for tachycardia
In case of tachycardia, it is recommended to avoid:
- caffeinated drinks and products;
- alcohol;
- spicy, salty, smoked and fatty foods;
- sauces;
- heavy cream and sour cream;
- products containing soda;
- boiled and fried eggs.
The daily menu should include:
- natural juices;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- milk;
- dairy products;
- dietary meat.
Meals should be regular, in small portions. You should avoid eating before bed. Limit sweets. Give preference to low-calorie foods rich in potassium and magnesium. Once a week it is advisable to carry out fasting days (the best option is vegetable ones).
Prevention
In order not to face the question of how to treat tachycardia in the future, doctors recommend:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- control blood pressure;
- include more vegetables and fruits in the diet and limit the consumption of animal fats;
- control blood cholesterol levels;
- be examined annually by a cardiologist
.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Tachycardia with endocrine disorders
Some disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system directly affect the functioning of the heart. Sinus tachycardia occurs under the influence of excess amounts of thyroid hormones during thyrotoxicosis. In addition to palpitations, this disease is characterized by
- feeling of heat,
- elevated body temperature,
- excitability and frequent mood swings,
- insomnia,
- weight loss with increased appetite,
- menstrual irregularities in women,
- change in facial expression (it takes on an angry look).
Much less common are tumors of the adrenal glands, which intensively synthesize adrenaline. Rapid heartbeat is observed with pheochromacytoma. In addition to tachycardia, this disease manifests itself with a sharp increase in blood pressure, feelings of fear, anxiety, chills, headaches, pain in the heart, nausea, sweating and a feeling of thirst. Often these symptoms occur simultaneously, so the condition can be described as an attack. If these signs occur along with tachycardia, you should contact an endocrinologist.