The first drug with 2000% bioavailability
As long as you wait, your chances of getting rid of hypertension are decreasing!
To learn more…
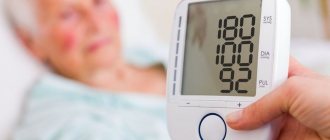
Many people who measure their blood pressure at home may notice a slight increase in their readings. As a rule, the cause is hidden in hypertension. Various forms of pathology are possible and you need to know what pressure 130 to 110 means and how to deal with it.
Norm or pathology
Pressure is an important value that indicates the state of health, in particular the heart and blood vessels. The norm is 120/80 mmHg. Art., but slight deviations are possible. A pressure of 130 to 110 indicates certain deviations, since both indicators are elevated, but the systolic value is not increased much, while the diastolic value should be 60-90 mm Hg. Art.
High diastolic pressure indicates problems with the heart or serious illness. In addition, this condition causes severe stress on the heart. At levels of 130/110 mmHg. Art. Doctors diagnose isolated diastolic hypertension.
Classification
It is important to know!
STILL STRUGGLE WITH ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION INCORRECTLY? The first bioavailable drug with proven effectiveness Read more »
Increased diastolic value in medicine is divided into 3 main degrees:
- In the first degree, patients' values will not exceed 99 mmHg. Art., fluctuate between 90-99. For older people, such pressure is considered normal as a result of natural aging and wear and tear of blood vessels, but for young people it is a reason for the development of arterial hypertension.
- At grade 2, the level will always be 100-109 mmHg. Art.
- Stage 3 pathology is characterized by a score of 110 or more.
If the diastolic value rises to 85 mmHg. Art., then doctors regard this as prehypertension. Patients need to undergo diagnostics and follow the doctor’s recommendations. The most common cause is atherosclerotic disease.
Secondary hypertension can appear as a result of diseases of internal organs and their dysfunction.
Depending on the pressure indicators, 3 stages are distinguished:
- Mild form - diastolic reading not higher than 114 mm Hg. Art. The heart and other organs are not affected.
- Severe form - the lower value rises to 124 mmHg. Art. The nervous system and eyes are most often affected, rarely the heart.
- Very severe form - lower value up to 130 mm Hg. Art., while the upper pressure can be 200 and higher. The heart and kidneys suffer.
To measure pressure correctly, you must follow some rules:
- Measurements are always taken in a sitting or lying position, in a calm state.
- The hand should lie flat and free.
- Irritating factors are excluded.
- A high-quality, working tonometer is used.
- The bottom of the cuff should be a couple of centimeters above the bend of the elbow.
- The air swings at 20 mmHg. Art. higher than the value at which the pulsation disappears.
After pumping up the air, you need to start deflating it and watch for shocks. They indicate pressure. The upper is determined during the first push, and thanks to the last, the lower is determined.
It is prohibited to take measurements after active exercise or running. In addition, the pressure may be 130 to 110 if measurements are taken immediately after consuming coffee, cigarettes or alcohol. For accuracy, you can take repeated measurements after about 5-10 minutes.
Pulse value
There is no direct and immediate connection between blood pressure and heart rate. Both levels are established according to different rules and mechanisms.
Thus, cardiac structures are characterized by automaticity: the electrical impulse is generated by the sinus node (pacemaker) and is repeated spontaneously, since cardiomyocytes are capable of spontaneous excitation.
Heart rate is slightly adjusted by external factors. Blood pressure levels are regulated by the brain (cerebral stem, hypothalamus) and endocrine organs.
However, isolated arterial hypertension is often accompanied by tachycardia (pulse 100 or higher - sinus or paroxysmal variety). Bradycardia (pulse less than 60 beats per minute) is characteristic to a lesser extent.
In such a situation there is no contradiction. Simply, both the increase in diastolic indicator and the acceleration/deceleration of heart rate are determined by the same factor. A single etiology leads to the need for complex treatment. Identical methods can be used to correct both conditions.
Causes of pressure 130 to 110
Reasons for diastolic pressure of 110 mm Hg. Art. different and among them the following are distinguished:
- The appearance of hypertension in the initial (primary) form.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
- Diabetes.
- Previously suffered a heart attack.
- Heart diseases.
Most often, a pressure of 130 to 110 appears as a result of impaired cardiac function.
The causes of heart problems, both in the male and female half of the population, are hidden in lifestyle, which is not considered correct:
- Eating before bed.
- Overeating, resulting in excess weight.
- Frequent consumption of fats, carbohydrates and salt.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Bad habits.
- Regular stress.
- Strong physical and emotional stress.
Almost always, people who smoke develop hypertension, because tobacco smoke is poison for the body, especially for the heart and blood vessels. In some cases, the cause of pressure surges may be medications that are used to treat a particular disease. This manifestation refers to the side effects of the drug and after stopping their use the condition returns to normal.
Causes
Doctors do not know the true reasons why such a reaction occurs. An increase in diastolic blood pressure against the background of a normal systolic indicator is a compensatory reaction of the body to an increase in cardiac output.
Important! An isolated increase in diastolic blood pressure is rarely diagnosed. In most cases, this is a symptom of some health problem.
Potential causes of pathology may be the following:
- Cardiac ischemia. It develops gradually and quickly becomes chronic. Causes disruption of myocardial nutrition.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system. In particular, those arising against the background of encephalopathy, stroke, vertebrobasilar syndrome and osteochondrosis.
- Hypercorticism. Increased production of the hormone cortisol by the adrenal glands. The primary form of pathology develops against the background of tumor processes. The leading cause of the disease is corticotropinoma.
- Hyperthyroidism. Can occur at any age. Provoking factors are disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland. Sometimes – poor nutrition.
- Liver diseases. An increase in diastolic indicator provokes a violation of general hemodynamics.
- Pathologies of the excretory system - pyelonephritis, renal failure, etc.
Provoking factors can also be those under a person’s control.
- Smoking. Nicotine causes vasospasm and increased blood pressure - a natural result of a bad habit.
- Alcoholism. Alcohol has a similar effect. Only the negative effect is stronger and occurs much faster. Sometimes it is enough for a person to drink 50 g of strong alcohol to provoke hemodynamic disorders.
- Poor nutrition.
- Stressful situations.
- Chronic lack of sleep.
The listed factors can be corrected as part of the prevention and treatment of an existing disease.
Symptoms
With high lower pressure, symptoms will not always be present; more precisely, it is difficult to determine, since they do not manifest themselves clearly. In addition, the signs may differ depending on the reasons for the increase in indicators.
Most often, attacks can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Dyspnea.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Increased pulsation.
- Increased sweating
- Deterioration of vision, loss of sharpness, appearance of “goosebumps” in the eyes.
With a constant pressure of 130 to 110, as well as shortness of breath, this often indicates the development of hypertension. At the very beginning of the development of the pathology, shortness of breath will occur only after exertion, but later it appears even in a calm state. With headaches, localization occurs in the occipital region, at this time there may be tinnitus, nausea, and after vomiting it becomes easier.
Patients have disturbed sleep and have difficulty falling asleep. If the problem is caused by heart pathologies, the patient experiences pain in the chest area, often similar to angina pectoris. In advanced forms, swelling appears and the limbs go numb.
Could there be headaches?
Headaches with blood pressure 130/100 are quite common. The cause is insufficient nutrition of the brain vessels. It is the disruption of cerebral blood supply that causes headaches. In this case, most often the headache is in the morning.
The condition may be accompanied by increased fatigue, general weakness, and black spots flashing before the eyes. Diastolic hypertension can be asymptomatic. The pathology in this case is diagnosed accidentally, for example, during a medical examination or measuring blood pressure at home.
Main danger
If no treatment is provided at a constant pressure of 130/110 mmHg. Art., then serious consequences and complications are possible. Against the background of this problem, hypertension develops and becomes more severe, when pressure levels increase significantly and hypertensive crises occur.
Complications also include:
- Heart attack.
- Stroke.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Aneurysms.
Most often, crises appear, but at a pressure of 130/110 mm Hg. Art. it's almost impossible. A crisis will occur if the systolic and diastolic values become extremely high, when organs cannot work normally and constant malfunctions occur in their work. There is no specific meaning for a crisis, each person has their own, so exclude the occurrence at 130/110 mm Hg. Art. no need.
Diagnostics
If your blood pressure is constantly high, regardless of the lower or upper value, you must undergo a medical examination.
The essence of this procedure is frequent measurement of pressure, questioning of the patient, percussion, as well as laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound.
- ECG.
- Blood and urine tests.
- Other.
In the case of normal heart function, secondary hypertension is possible. Additional examinations of various organs will be required. During the initial visit to the doctor, the doctor takes measurements on both hands 2 times, with an interval of up to 2 minutes. If the data differs, the average value is displayed.
Drug treatment
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
STILL STRUGGLE WITH ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION INCORRECTLY? Reduces stress hormone levels and prevents oxygen starvation Read more »
To normalize lower pressure, as well as upper levels, doctors often use the following medications:
- AFP inhibitors – Captopril, Ecalapril.
- Beta blockers – Atenolol, Bisoprolol.
- Diuretics – Indapamide, Hypothiazide.
- Calcium antagonists – Verapamil, Nifedipine.
- Angiotensin-2 antagonists – Losartan.
If a patient is diagnosed with hypertension, then medications must be taken on an ongoing basis, every day, and pressure measurements must be taken additionally. If you stop taking medications quickly, there may be unpleasant consequences. In addition, statins and sedative medications can be added to the course of therapy.
In case of high diastolic pressure due to renal pathologies, doctors add antibiotics and steroids, anti-edema tablets to the course. In certain cases, the patient is hospitalized for stronger and more effective treatment.
Once diagnosed with persistent primary hypertension, people will need to take medications for life, since the disease cannot be completely cured. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis will be favorable.
What can you take at home?
You can do little on your own. Since blood pressure is unstable, the upper reading is normal, the lower reading is elevated, selective action on the root cause of the condition and symptomatic manifestations is required.
An approximate algorithm is as follows:
- Measure objective indicators: heart rate and blood pressure. If the gap grows over a short period of time, you should urgently consult a doctor; you should not rely on self-medication. In other cases, you can resort to the next point.
- Take 1/4 Captopril tablet.
- Take calcium antagonists (1 tablet of Diltiazem or Verapamil). Exceeding dosages and taking unspecified medications is strictly prohibited. It’s impossible to say in advance what this will lead to. But this does not bode well.
- Sedatives based on motherwort or valerian will help. Just not in the form of an alcohol tincture. Ethanol excites the nervous system, increasing blood pressure and heart rate.
- Take phenobarbital. Pharmaceutical forms - Corvalol, Valocordin. They calm the body and have a positive effect on the heart. The mild action explains the possibility of independent use.
- Open a window or vent to ensure a flow of fresh air into the room or space. This will improve your well-being.
Now you need to lie down and observe the symptoms. If everything is done correctly, the condition will most likely return to normal. Monitoring is carried out using an automatic tonometer.
If there is no effect, you should not continue amateur activities. Especially if the condition worsens. It is necessary to call an ambulance. Before the brigade arrives, you should rest and not make sudden movements.
What you should never do:
- Showers, hot and cold baths are contraindicated.
- You can’t do physical exercise, no mechanical activity.
- You should not consume drugs in the second round. Capoten does not reduce blood pressure selectively, so a drop in the upper reading will lead to hypotension. If the level is reduced sharply, a stroke or heart attack is possible.
It is also not recommended to neglect the presented combination of medications. It allows you to keep systolic numbers at the same level.