When a person has a heart attack, they need to know what to do and responding quickly can help them achieve a better outcome.
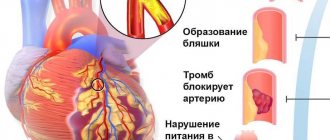
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage in blood flow to the heart, blocking the delivery of oxygen and other nutrients. This situation can damage or even kill parts of the heart tissue.
Although movies may show heart attacks to occur suddenly, many heart attacks start slowly and have many warning signs.
Signs and symptoms
A heart attack can cause pain in the shoulders and arms.
The main symptoms of a heart attack include the following:
- Chest pain or discomfort . Chest pain or discomfort may feel like pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, this may occur with or without chest pain.
- Discomfort in other parts of the body : back, arms and shoulders, neck or jaw.
- Heart rhythm disturbance
While both men and women can experience the initial signs and symptoms of a heart attack, the symptoms we've listed above are more common in men.
Women are more likely to experience additional signs and symptoms. These include:
- nausea and stomach upset
- abdominal pain
- cold sweat
- weakness
- sudden dizziness
- increased sweating
Definition:
A heart attack is a condition that poses a serious threat to human life and health. A heart attack, also called a myocardial infarction, can be a fatal event. According to statistics, heart attacks are the most common cause of death and disability among the population in developed countries. A heart attack occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow in a coronary artery (the vessel that supplies blood to the heart muscle). Interrupted blood flow to the heart can lead to damage and death of the heart muscle.
What to do
A heart attack requires emergency medical attention. If someone has a heart attack, they should immediately call 112 for emergency help before doing anything else. Act quickly - it could help save someone's life.
First aid for myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is a type of ischemic heart disease characterized by irreversible damage to the heart muscle as a result of deterioration of blood flow through the coronary arteries
Characteristic signs (symptoms) of a heart attack (myocardial infarction):
- • sudden (paroxysmal) pressing, squeezing, burning, aching pain in the chest (behind the sternum) lasting more than 5 minutes;
- • similar pains are often observed in the left shoulder (forearm), left shoulder blade, left half of the neck and lower jaw, both shoulders, both arms, the lower part of the sternum along with the upper abdomen;
- • lack of air, shortness of breath, severe weakness, cold sweat, nausea often occur together and sometimes follow or precede discomfort/pain in the chest;
- • it is not uncommon for these manifestations of the disease to develop against the background of physical or psycho-emotional stress, but more often with some interval after them.
Uncharacteristic signs that are often confused with a heart attack:
- • stabbing, cutting, pulsating, boring, constant aching pain for many hours and not changing its intensity in the heart area or in a specific clearly defined area of the chest
Algorithm of actions in case of a heart attack
If you or someone else suddenly has the above characteristic signs of a heart attack, even with weak or moderate intensity, which last more than 5 minutes, do not hesitate, immediately call an ambulance team. Do not wait more than 10 minutes - in such a situation it is life-threatening.
If you have symptoms of a heart attack and there is no way to call an ambulance, then ask someone to take you to the hospital - this is the only right decision. Never drive yourself unless you have no other choice.
In the most optimal scenario, if a heart attack occurs, you must act according to the following algorithm:
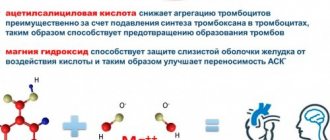
- • Immediately after an attack occurs, sit down (preferably in a chair with armrests) or lie in bed with the head of the bed raised, take 0.25 g of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) (chew the tablet, swallow) and 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin (spray one inhalation dose into the cavity mouth while holding your breath, place one tablet/capsule under the tongue, first bite the capsule, do not swallow); free your neck and provide fresh air (open the vents or windows).
- • If after 5-7 min. After taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and nitroglycerin, the pain persists, it is imperative to call an ambulance team and take nitroglycerin a second time.
- • If pain persists 10 minutes after taking the second dose of nitroglycerin, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin a third time.
- • Give the patient a sedative (motherwort or valerian). There should be silence in the room, not allowing the sick person to become nervous.
- • If after the first or subsequent doses of nitroglycerin there is severe weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, you need to lie down, raise your legs (on a bolster, etc.), drink 1 glass of water and then, as with a severe headache, do not take nitroglycerin.
- If a person with a heart attack is unconscious and there is someone nearby who knows how to provide first aid in this situation, then you need to do it immediately!
How to distinguish angina from myocardial infarction?
| Typical angina pectoris | Typical myocardial infarction |
| Pain in the center of the chest, in the middle third of the sternum, can spread to the left arm, shoulder blade, lower jaw, and upper abdomen. | The pain is similar to that of angina pectoris, but more often it is felt as more intense, unbearable, tearing and affects the entire left half of the chest. |
| Discomfort is mild or moderate. | Severe discomfort, increased sweating, dizziness, nausea, increasing feeling of lack of air, fear of death. |
| An attack of angina is more often associated with previous physical activity or emotional arousal. | Myocardial infarction can occur at any time, including at rest. |
| The pain attack takes about 3 – 15 minutes. | A painful attack with discomfort and suffocation lasts for at least 15 – 30 minutes or more, and there is a tendency for symptoms to increase. |
| With rest, the pain usually goes away. | In a state of physical rest, the pain does not go away completely and intensifies when talking and deep breathing. |
| The use of nitroglycerin under the tongue or in the form of an aerosol from 1 to 3 doses interrupts an attack of angina. | Symptoms do not completely resolve after 3 doses of nitroglycerin. |
Causes and risk factors
A person needs to be aware of the risk factors so that they can take steps to prevent a heart attack.
There are some heart attack risk factors that people can control and others that they cannot.
Risk factors include:
- Age: men and women over 60 years old.
- Gender : Men are more likely than women to have and die from a heart attack.
- Family history: People with a family history of cardiovascular disease are more likely to suffer a heart attack.
- Race and ethnicity : Some ethnic groups, including African Americans, some Asians, and Mexican Americans, are more likely to have a heart attack than others.
Although people cannot influence the risk factors listed above, there are many risk factors they can change or treat to prevent a heart attack.
Modifiable risk factors for heart disease and heart attack include:
- obesity
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- diabetes
- unhealthy diet high in saturated fat and sodium
- tobacco use
- excessive alcohol consumption
- not enough exercise
Surgical methods
In addition to drug therapy, the following procedures are offered for effective treatment of myocardial infarction:
- Coronary angioplasty and stenting;
An emergency angioplasty procedure aims to open a blocked artery, allowing blood to flow freely to the myocardium. The doctor will insert a special long, thin tube (catheter) into the blocked coronary artery through an artery in the leg in the groin area or in the arm in the wrist area. Through this catheter, a special guide and balloon are brought to the affected area of the artery.
The balloon is guided through a guidewire to the affected area of the artery and inflated, facilitating the opening of the vessel. After this, a metal stent is implanted into this section of the artery - it will maintain the artery in a straightened state for a long time. It is better to implant a stent with a drug coating, which prevents restenosis - repeated narrowing of the vessel in this area. Read more about the benefits of balloon angioplasty here.
- Coronary bypass surgery;
In difficult cases, cardiac surgeons perform emergency coronary bypass surgery during a myocardial infarction. Coronary bypass surgery involves suturing a vein or artery to a coronary artery in a place after blockage or narrowing of the latter, thus restoring blood flow through the vessel.
Preventing the risk of heart disease and heart attack
The best way to prevent a heart attack is to reduce any risk factors.
You can reduce your chances of having a heart attack:
- weight loss if you are obese or overweight
- treating high blood pressure and high cholesterol by consulting your doctor
- Controlling diabetes through diet, medications, and blood sugar control
- Eat a diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits, low in saturated fats and processed foods
- quit smoking
- limit your alcohol consumption!
- at least 2-3 hours of moderate physical activity per week
Also, get regular checkups with your doctor. Regular screenings can help identify new risk factors for heart disease that a person may develop and monitor any existing ones.
Heart attacks are a medical emergency. Knowing the signs and symptoms of a heart attack can help a person get the help they need as early as possible. Reducing risk factors for heart disease can help a person prevent a heart attack.
Medications
- Aspirin. You will receive aspirin from emergency personnel or upon arrival at a medical facility. Aspirin reduces blood clotting and helps maintain blood flow through a narrowed vessel.
- Other antiplatelet drugs. The emergency room doctor may give you other drugs that work similar to aspirin and prevent blood clots. These are clopidogrel (Plavix), ticagrelor (Brilinta) and other drugs - platelet aggregation inhibitors.
- Thrombolytics. These drugs, also called “clot killers,” are widely used in the treatment of cardiac ischemia. They help dissolve blood clots that block blood flow in the coronary arteries. The earlier treatment with thrombolytics is started during myocardial infarction, the greater the chance of survival and the smaller the area of damaged myocardium.
- Other drugs that thin the blood. These include heparin, which makes the blood less “viscous” and less capable of dangerous blood clots. Heparin is given intravenously or subcutaneously in the first few days after myocardial infarction.
- Medicines that relieve pain. If you experience severe chest pain, you will be prescribed painkillers such as morphine. This will reduce the unpleasant symptoms of vascular diseases.
- Beta blockers. These drugs help relax the heart muscle, slow the heart rate, and lower blood pressure, making it easier for the heart to pump. Beta blockers limit damage to the heart and prevent future heart attacks.
- Nitroglycerine. The drug is used to treat angina pectoris. It temporarily widens the arteries, improving blood flow to and from the heart.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs. These are statins, niacin, fibrates and bile acid sequestrants. They help lower levels of unwanted blood cholesterol and are useful soon after a heart attack to improve survival.