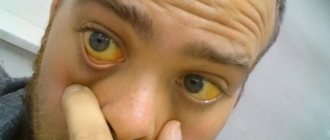
Saturation (English saturation - “saturation”) is an indicator of the level of oxygen saturation in the blood. If it is at a low level, this indicates hypoxemia - a condition requiring emergency medical attention.
It is necessary to normalize the level of oxygen in the lungs and blood, otherwise complications, including death, are possible.
Doctors use a special medical device to measure oxygen saturation - a pulse oximeter. Using this device, an analysis is made that gives an idea of the current state of the patient’s lungs and circulatory system. Thanks to the quick results, doctors decide on the need for additional oxygen support. Since it is not possible to urgently organize a computed tomography (CT) scan in all cases, reduced saturation helps specialists determine the presence of a viral infection of the respiratory system - pneumonia.
Measuring oxygen in the lungs and in the circulatory system with a pulse oximeter makes it possible to assess the patient’s condition and hospitalize him. This is especially true when affected by COVID-19. If a person who suspects he has this disease has such a device, he can analyze the condition at home. However, it is worth knowing that measurement cannot be an alternative to other methods.
Both the patient and the staff of the medical institution should not draw conclusions based on saturation - oxygen levels in the blood can vary depending on various factors:
- device sensitivity;
- the color of the patient's skin;
- type of lighting.
If we consider saturation as the main diagnostic method, the risks of incorrectly assessing the patient’s condition are quite high.
Even with a severe form of coronavirus, oxygen may be at an acceptable level in the first days, and then drop sharply. The decrease occurs at night even in those who are completely healthy.
More about saturation
Saturation is a parameter showing the oxygen level as a percentage. It enters the bloodstream from the lungs and is transported to all systems of the body. If the indicator is lowered during coronavirus, this indicates a lack of oxygen - hypoxemia is highly likely provoked by a viral infection of the respiratory system. The assumption can be confirmed or refuted by conducting other studies, such as CT, where the doctor evaluates the visual condition of the organ.
determination of oxygen norm with a pulse oximeter
When do you need to monitor blood oxygen?
When we run, lift weights, or otherwise exercise, our need for oxygen increases significantly. Thus, our breathing and heart rate increase to meet the body's increased needs.
Measuring oxygen is not just for athletes.
Fitness trackers and other devices called "pulse oximeters" can measure SpO2 levels. Here you need to divide the words into parts. The “pulse meter” measures only the pulse, while the “pulse oximeter” works with pulse and oxygen. Piece by piece the word becomes more understandable.
The latter work in the same way as heart rate monitors worn on the wrist, by passing specific wavelengths of light through the skin. usually found in the infrared spectrum . Thanks to this, a highly sensitive photo editor can “see” hemoglobin in the blood.
Best Fitness Trackers Under $100
Why are measurements taken?
The oxygen level is measured to determine the state of health and promptly identify hypoxemia, which can cause death. Through this simple analysis, the degree of the disease is determined and measures are taken to stabilize the condition.
With the advent of COVID-19, the term Silent Hypoxemia has been used, which translates as “silent hypoxemia.” Its appearance is due to the fact that about 50% of patients admitted to hospital have a low level of saturation, while the symptoms indicate the opposite. Patients do not experience shortness of breath, they are not tormented by a cough, and their body temperature is at a normal level. However, a CT scan shows significant lung damage, so the patient is placed on oxygen support.
Characteristics and properties
In adults and children, saturation is the physiological process of saturating the peripheral vessels of the human body with a certain amount of oxygen. The norm for this indicator (SPO2) varies depending on the age of the subject, his lifestyle, the presence or absence of chronic diseases of the heart, lungs, bronchial tree and blood.
Under the influence of physical activity, due to the abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products, the level of blood saturation may decrease by 1-2%. In people with respiratory failure, this indicator is critically low. Measuring blood saturation allows you to timely detect a drop in the level of oxygen saturation in the blood, as well as carry out appropriate therapy aimed at restoring stable gas exchange in the patient’s body.
How to determine oxygen deficiency
Patients with symptoms of Covid-19 can independently determine their oxygen levels. Medical assistance is required in the following cases:
- Hold your breath and compare whether you can not breathe as much as before. If it is impossible to hold your breath for a couple of seconds, it makes sense to seek help.
- You take more breaths than before and your heart rate increases.
- The skin has become pale with a slight bluish tint, which appears in the area of the mouth and fingers.
- You feel tired even without much physical activity, and feel drowsy.
- Headaches and dizziness.
- You don't remember simple information.
- Concentration is impaired.
- There are signs that are characteristic of an acute respiratory disease, for example, cough, runny nose, sore throat.
- Tingling in the chest, shortness of breath when talking or moving.
Symptoms of Covid-19
The content of the article:
- Symptoms and course of Covid 19 in adults
- ARVI and coronavirus
- Features of clinical manifestations of coronavirus in children and symptoms in pregnant women
- Saturation as an important indicator of coronavirus infection
Symptoms and course of Covid 19 in adults
Covid 19 is a disease that has caused one of the longest pandemics in the world. This term is usually understood as the name of the virus, however, this is not so. The pathogen itself is called SARS-CoV-2 and it is it that penetrates the human body, causing a dangerous disease.
Coronaviruses are a fairly well-known group of viruses that can cause an infectious process. The first serotypes were identified back in the 60s; over time they only mutated. However, one thing remained unchanged, the method of infection. The virus itself looks like a ball with teeth all over its entire area, hence its name “crown”. A viral particle invades a human cell, changes its mechanism of operation, and then reproduces many copies of itself. The immune system cannot recognize all of these mechanisms.
Of course, such a disease could not help but change, and today the following forms of coronavirus are distinguished: alpha (British), beta (South African), gamma (Brazilian) and delta (Indian). As scientists note, each new strain of the virus may be more aggressive than the previous one. Another important detail is that different strains have a greater impact on certain groups of people, for example, young people under 40 years of age are more likely to get sick with the betavirus, while pregnant women and young people are more susceptible to the gamma strain. With the latest delta strain, there is no official information yet on who is more susceptible to infection, but it is known that this type is spreading at an incredibly fast pace. According to the open Russian consortium for sequencing the genomes of SARS-CoV-2, it was the delta strain that caused the disease in more than 90% of those infected with Covid in July 2021. So far, all produced vaccines are effective against the identified strains.
What symptoms of coronavirus occur in a sick person and how to distinguish them from a regular ARVI, we will analyze in the article.
Stages of the disease:
- From 1 to 3 days. A person feels the first signs of coronavirus, experiences muscle discomfort and weakness. Body temperature can reach subfebrile levels of 37-37.5 degrees. Possible nasal congestion. The general condition is similar to the onset of a common ARVI.
- From 3 to 5 days. During this period, the virus manifests itself as a mild cough. Many sick people lose their sense of smell, they stop feeling the taste of food, or it changes. More than half of the sick experience mild abdominal pain and diarrhea during this period. Body temperature continues to rise.
- From 5 to 10 days. During this period, patients whose immune system was able to cope with the virus begin to recover. The symptoms gradually disappear. Otherwise, especially against the background of chronic diseases, the symptoms not only do not go away, but also intensify. There is a strong barking cough, chest pain, runny nose, shortness of breath, tachycardia.
- From 10 to 13 days. During this period, the disease progresses greatly. Chest pain intensifies, breathing becomes rapid, the skin becomes pale. Blood oxygen levels can drop to critical levels, which is why it is so important to constantly measure them. Lung damage is diagnosed from 20 to 60%. The patient requires hospitalization.
- From 13 to 15 days. During this period of time, two options are possible: the further course of the disease is pneumonia, which requires artificial ventilation, or recovery with properly selected treatment.
- From 15 to 30 days. During the recovery process, even with significant improvement in the condition, shortness of breath continues to persist. Smell and taste may not return for a long time. The norm is taken to be from one month to six months.
Currently, various clinical variants of the course and manifestations of coronavirus in humans have been recorded, including the following:
- pneumonia with acute respiratory failure;
- pneumonia without respiratory failure;
- damage to the upper respiratory tract;
- septic shock;
- thrombosis, blood clotting disorder.
Symptoms of coronavirus can vary depending on the severity of the disease: mild, moderate, severe.
The mild form implies the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels;
- dry cough with almost no discharge;
- weakness in the body.
Less common, but also possible, are the following:
- loss of taste and smell;
- nasal congestion;
- sore throat;
- headache, migraine;
- conjunctivitis;
- diarrhea;
- skin rash.
The symptoms are similar to the onset of a standard respiratory illness, except for the loss of smell and taste.
Severe disease involves symptoms such as:
- dyspnea;
- severe cough with discharge, possibly blood;
- loss of appetite;
- severe chest pain;
- high temperature, 38 degrees or more;
- feverish state, loss of consciousness;
- a sharp drop in blood oxygen levels according to pulse oximetry.
Less common, but also possible:
- irritability, anxiety;
- convulsions;
- tachycardia;
- severe vitamin D deficiency.
In older people, the disease may have an atypical course, including various neurological disorders.
It should also be remembered that after infection with coronavirus, chronic diseases of the heart, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract often become more active, which means consequences such as stroke, ischemia, etc. are possible.
Attention! Symptoms may not fully manifest themselves; for example, cases of coronavirus without fever are not uncommon. Even more often, there are no symptoms at all, and the person experiences Covid in a very mild form, believing that he has a runny nose for 2-3 days.
ARVI and coronavirus
The coronavirus spread so quickly partly because it was impossible to diagnose it correctly right away. Covid, unlike ARVI, can lead to more serious complications, so you need to learn to distinguish between the symptoms of a common cold and coronavirus. For example, the sense of smell can disappear even with a cold.
Similar symptoms:
- cough;
- runny nose;
- a sore throat;
- elevated body temperature.
The difference between coronavirus and ARVI:
- long incubation period. ARVI develops rapidly, while Covid-19 enters the acute phase only after 2 weeks.
- low-grade fever that lasts up to a week. While with ARVI, the temperature rises to febrile levels already on the 2-3rd day.
- Cough with coronavirus is prolonged, often dry, barking, accompanied by pain in the sternum. With ARVI, the cough becomes productive with sputum discharge.
- During Covid, diarrhea and vomiting are often observed, while with ARVI such signs are absent, unless the respiratory disease is accompanied by poisoning.
What is the difference between coronavirus and flu
Common features of influenza and coronavirus:
- chills, body aches, general state of weakness;
- diarrhea;
- Influenza is also transmitted by contact and airborne droplets.
Main differences:
- unlike coronavirus, the flu develops rapidly, body temperature rises to 39-40 degrees;
- the patient feels a headache, pain in the eyes, and may experience light and sound sensitivity.
Interesting on the topic: Loss of smell due to a cold
Features of clinical manifestations of coronavirus in children and symptoms in pregnant women
The total percentage of children infected with coronavirus in the world is about 10%; in Russia this figure is 6-7% of the total number of cases.
For the most part, children tolerate coronavirus much easier, often without even realizing they are infected, since there are no obvious symptoms. But there are often severe and moderate cases when babies need hospitalization.
More often, children become infected with Covid from sick adults.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease in children:
- fever;
- dry cough without discharge;
- nausea and vomiting;
- scratchy sore throat;
- diarrhea.
Children, just like adults, may lose their sense of smell and taste, but most often they do not attach any importance to this and do not experience severe discomfort.
A characteristic visual sign of coronavirus for children is blue-white fingers that appear to be frozen.
In children, as in adults, a practically asymptomatic course of coronavirus is possible, which means that any changes can only be observed on a computed tomogram (characteristic lung lesions are visible).
Symptoms of Covid in pregnant women
Pregnant women are at greater risk of contracting coronavirus because their immune system is less active while pregnant.
Their signs of infection are the same as for other people:
- headache, muscle pain;
- fatigue;
- loss of smell and taste;
- slight increase in temperature.
However, symptoms that are characteristic only of pregnant women and threaten the life and health of the mother and child may also occur:
- high blood pressure;
- severe swelling;
- abdominal pain;
- bleeding;
- a sharp drop in saturation.
Any of the above symptoms requires urgent hospitalization of the woman. When saturation drops and blood pressure rises, the woman needs to be connected to a ventilator, since both she and the child suffer from oxygen starvation. It is not uncommon to have an emergency caesarean section if the fetus has a slow heartbeat.
Pregnancy is a condition during which chronic diseases can worsen. Covid can worsen the negative consequences of the following diseases:
- diabetes;
- asthma or other lung diseases;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- kidney or liver diseases.
Saturation as an important indicator of coronavirus infection
Saturation is a term that has become firmly established in the everyday life of doctors and patients around the world, since this term refers to the level of oxygen in the blood, and as we know, during Covid this indicator decreases significantly.
In a normal state, a person’s lungs work in such a way that constant gas exchange occurs, as a result of which the blood and tissues are saturated with oxygen. With Covid, the alveoli become inflamed and dangerous conditions such as hypoxia and hypoxemia occur. In the first case, the tissues do not receive oxygen, in the second, blood.
Symptoms of low saturation:
- a feeling of lack of air, a person literally begins to suffocate during a conversation or intense movements;
- severe weakness and fatigue;
- dizziness;
- ringing or any other noise in the ears;
- cyanosis - blue discoloration of the lips, areas around the mouth, and fingers.
A severe form of hypoxia is also possible, in which a person experiences hallucinations, cannot navigate in space, and may faint.
The oxygenation rate is 98-99%. For smokers or people with lung diseases, this figure is lower - about 92-95%.
If the saturation rate is in the range of 80-90%, then this is a reason to use an oxygen mask. When the critical value is less than 80%, connection to artificial ventilation is required.
Uncharacteristic symptoms of Covid
According to the latest data, scientists believe that one of the characteristic signs of Covid may be a skin rash. There have been many cases where coronavirus infection causes damage to the walls of small blood vessels in the skin, resulting in erythema, exanthema and lichen, measles-like rash, and blisters of unknown etiology.
The symptoms of coronavirus are now quite well studied, so at the first signs of the disease you need to seek medical help. Treatment of coronavirus requires a systematic approach and, most often, constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
How to measure saturation with a pulse oximeter
Every person will be able to buy a device for measuring saturation on a finger - a pulse oximeter, for the purpose of monitoring it at home. It is visually similar to a clothespin.
As mentioned above, it is fixed on the finger. Within 60 seconds, the sensor built into the device reads and analyzes the data. The pulse oximeter is equipped with a display that displays two numbers. One shows the percentage of oxygen, the second shows the pulse.
PRbpm (pulse rate beats per minute) on a pulse oximeter shows the strength of the pulse, measured in the number of beats per minute.
In medical institutions, invasive equipment is used to obtain the gas composition of biological material.
How to determine
The SPO2 norm in adults is determined using 2 main methods. This is a measurement of saturation using a pulse oximeter or laboratory blood test.
Pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive way to diagnose the level of oxygen saturation in the blood. This type of instrumental research is based on the spectrographic method for determining saturation.
The conduct of this survey is as follows:
- The patient is in a sitting or lying position on the couch.
- The healthcare worker places the pulse oximeter on the index finger of the subject's dominant hand.
- After this, the doctor or nurse presses the start button on the pulse oximeter control panel.
- Within 3-5 s, 2 digital values will appear on the monitor.
- The top number shows the percentage of oxygen in the blood, and the bottom number indicates the heart rate.
A prerequisite for determining saturation using pulse oximetry is that at the time of measurement manipulations, the dominant hand should not be in a suspended state. The upper limb should be placed on the bed or surface of the manipulation table.
This type of diagnosis can be carried out independently, at home. To do this, it is enough to purchase a pulse oximeter, the average cost of which is from 1200 to 1650 rubles. depending on the manufacturer.
Laboratory research
To carry out laboratory diagnostics of saturation levels, the patient’s venous or arterial blood is used. In this case, 5 to 10 ml of biological material is sufficient. Blood sampling takes place under sterile conditions using disposable consumables.
The results of laboratory testing are known 1-2 days after the collection of biological material. In emergency cases, faster diagnosis is possible. For example, if the patient is in serious condition. Laboratory testing for blood saturation levels is carried out free of charge as part of providing emergency medical care to the patient.
Pulse oximeter errors
The device may provide inaccurate data in the following cases:
- low quality device;
- the battery is not charged or the batteries are exhausted;
- measurements are performed immediately after physical activity;
- nails are decorated with a decorative coating;
- fingers are cold;
- There is a mask on the face, the material of which does not allow air to pass through.
To obtain correct results, it is important that the device is of high quality - it is better to buy a pulse oximeter from time-tested manufacturers. Measurements should be taken at rest. If a person walked or did homework before the test, the body should be given time to rest.
Oxygen saturation rate
The norm for the normal functioning of the lungs and other organs is a saturation rate of 100% .
However, this parameter depends on the organism. So, with anemia, chronic pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, it may be lower. Age and the presence of bad habits, such as smoking, also matter.
At night, the indicator decreases, and the difference with the norm can be impressive. Thus, in patients with chronic lung diseases, the body has managed to adapt to the lack of air, and saturation during night rest can drop by 10%.
According to statistics compiled from the observations of medical specialists who work with patients with coronavirus, the peak of the decrease occurs between three nights and seven in the morning. This is the most dangerous time for people who become ill – during this period the highest number of deaths is recorded.
Select equipment
With such therapy, the disease progresses more easily, the body recovers at a rapid pace, and the rehabilitation period is shortened.
What is the norm of saturation in adults table
It should be borne in mind that the oxygen norm is a relative concept. It happens that people who have signs of coronavirus measure it, and the results obtained, for example 95%, cause panic - the person calls an ambulance.
Normal saturation in adults (table)
The normal oxygen level is arbitrary. Often, patients who exhibit symptoms of the disease panic and call emergency help when the saturation rate is 95%. According to medical data, the conditional norm depends on various parameters:
- In healthy people, the norm is from 95 to 98%.
- For smokers - from 92 to 95%, while the parameter decreases when consuming alcoholic beverages, coffee, and energy drinks.
- For chronic pathologies of the respiratory system - from 92 to 96%.
- In children in the first months of life – 93-97%.
With coronavirus, oxygen support is needed in the following cases:
- If the rate is less than 93%, the person feels short of breath, has a cough and a runny nose.
- Computed tomography shows lung damage - 50%.
- An elderly patient has symptoms of the disease.
- Low saturation – less than 90%.
- During pregnancy.
- Hospitalization is required for patients with immunodeficiency.
- Patients who are overweight and have diabetes also need medical attention.
If a hospitalized patient has a low reading that cannot be normalized with oxygen, he or she is transferred to the intensive care unit for tracheal intubation.
What is apnea
For ordinary people, monitoring SpO2 can be a useful indicator of sleep apnea. This is a condition in which a person wakes up periodically during the night due to difficulty breathing. This can happen due to physical blockages that make it difficult to breathe, or due to blockages in the signals the brain sends during the breathing process.
People with this condition often wake up feeling already tired. Frustration throughout the day, lack of concentration, indifference - all these are symptoms of apnea. Just don't confuse this with lack of sleep. If you constantly sleep for 5 hours or less, or if you have long, but irregular sleep without reference to a specific time, then your fatigue is not due to apnea.
What surprised us with the new Xiaomi Mi Band 6 besides the frameless screen
Devices that measure oxygen levels and track movement during sleep could potentially alert an owner to problems. Some of today's wearable SpO2 devices only allow spot checks during the day, while others work at night as well . Monitoring SpO2 overnight may significantly reduce the battery life of a wearable device, but the extra charge is nothing compared to the benefit you can get.
Sometimes oxygen meters look like something from outer space.
Saturation with coronavirus
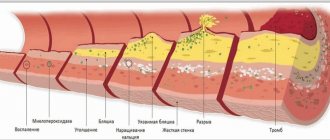
Coronavirus disease is characterized by powerful and comprehensive damage to the main respiratory organ – the lungs. The alveoli are primarily affected - single cells that perform gas exchange between the air entering the lungs and the blood that carries oxygen to the cells of the body.
The alveoli and their septa are blocked by the virus and become inflamed, as a result of which their useful work is reduced to zero in a short period of time. Inflammation spreads to neighboring alveoli, and the affected area increases. As a result, the volume of oxygen entering the body per unit of time continuously decreases.
The condition gradually or quite sharply (over 3-5 days) worsens, the state of health is subjectively assessed with the epithets “tired” or “exhausted”, and cold symptoms appear.
The important thing is that the victim does not know about the fact of infection until a state is discovered in which the body is already exhausted, and the volume of lesions in the lungs can lead to disaster.
Oxygen saturation during coronavirus is a criterion for the degree of damage to the body. If the value is too low, immediate medical attention is required, including connection to a ventilator.
TECHNICAL SUPPORT FOR MONITORING VENOUS SATURATION
ScvO2 and SvO2 can be measured discretely by analyzing the gas composition of venous blood samples taken from a central venous catheter or the distal lumen of a Swan-Ganz catheter, respectively. However, for a number of reasons outlined above, continuous measurement of ScvO2/SvO2 may have a number of advantages, particularly in the face of rapid and difficult to predict changes in tissue blood flow and other determinants of oxygen delivery. Currently, there are several systems for continuous measurement of ScvO2/SvO2, operating on the principle of venous photometry (oximetry). The continuous measurement method is based on the use of a small-diameter catheter into which fiber-optic conductors are integrated, one of which emits light of a certain wavelength into the venous blood flow, and the second transmits the reflected signal to the optical sensor of the monitor (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Principle of continuous reflectance venous oximetry
1. CeVOX and PiCCO2 monitoring systems (Pulsion Medical Systems, Germany). The sensor for venous oximetry is installed through one of the lumens of the central venous catheter. Continuous ScvO2 measurements require CeVOX (PC3000) or PiCCO2 central units equipped with an optical module (PC3100) and a disposable fiber optic sensor (PV2022-XX, 2F (0.67 mm), 30–38 cm). Initial calibration of the monitor in vivo requires insertion of the sensor into the superior vena cava. After confirming a high-quality signal, a sample of venous blood is taken to determine its oxygen saturation and hemoglobin concentration. Entering these values into the monitor menu completes the calibration procedure. The convenience of the system is that repositioning, removing or replacing the oximetry sensor does not require repositioning or removing the central venous catheter. According to a recent study by Baulig W. et al.6 (2008), ScvO2 measured using the CeVOX system has acceptable sensitivity and specificity for predicting significant changes in the indicator. The PiCCO2 system allows continuous monitoring of DO2 and VO2 values.
2. The PreSepTM system (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, USA) includes a triple-lumen central venous catheter with a pre-integrated fiberoptic guidewire for continuous monitoring of ScvO2. The catheter can be connected to a number of Edwards Lifesciences systems, in particular Vigilance-I, Vigilance-II and VigileoTM. At 20 cm in length, the catheter diameter is 8.5F (2.8 mm). In vitro and in vivo calibration is required before installation. The quality of the ScvO2 signal can be impaired by pulsation in the area of the catheter tip, periodic contact with the vessel wall (catheter jamming), kinking and formation of a blood clot, and hemodilution. Updating the hemoglobin and hematocrit values in the monitor menu is necessary when these values change by 6% or more. Models with the “H” marker have the traditional antibacterial and heparin coating of AMC Thromboshield. Currently, PreSepTM catheters are protected from bacterial contamination by a patented OligonTM complex (a complex coating including silver, platinum and carbon atoms), the action of which is based on the release of active silver ions.
3. The CCOmbo system (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, USA) is a Swan–Ganz catheter with an integrated fiberoptic element. When connected to monitoring systems, Vigilance provides continuous measurement of SvO2, CO, as well as right ventricular end-diastolic volume and ejection fraction. The cost of the catheter is relatively high.
What to do if saturation is low
If the saturation has dropped, this is not a reason to panic. The indicator can be quickly returned to normal, and even an indicator in the region of 70-80% is not a threat to life. At the same time, those who suffer from chronic lung diseases also have a chance to recover, since the body is adapted to the lack of oxygen.
If coronavirus is diagnosed and the parameter has decreased by 5, 6, 10, 15%, and the measurements were performed correctly (it is important to make sure that the device is charged), you should call an ambulance.
Measures taken by the doctor
Why you need to monitor your blood oxygen levels
Of course, there are two categories of people who primarily need to monitor their oxygen levels. The first category includes athletes whose training requires them to carefully monitor SpO2 (for example, divers and climbers training at high altitudes or depths). The second category includes people with lung diseases or those affecting their ability to breathe. Probably, this also includes those who call themselves biohackers and are trying to find a way to better use the capabilities of their body.
You need to monitor not only oxygen, but also other indicators of the body.
How to normalize saturation yourself
Before the ambulance arrives, a person can raise their oxygen level through simple gymnastics:
- Having previously relaxed, you should raise your hand and touch an object, for example, a door handle. In this case, the second hand rests on the chest. The person takes deep breaths, raising the chest.
- Sit down, raise your hand, and extend the other one forward. Taking a deep breath, turn in the direction opposite to your raised arm.
You should also ensure a flow of fresh air by ventilating the room. In general, doctors who have worked with patients with severe forms of the disease note that oxygen support is less effective than breathing exercises. It is advisable that the patient do them under the supervision of medical personnel.
Indications for the study
The SPO2 norm in adults can change under the influence of external and internal factors.
Diagnostics to determine the level of blood saturation is indicated for people who have the following diseases and pathological conditions of the body:
- obstructive pulmonary disease;
- postoperative rehabilitation period;
- viral or bacterial pneumonia;
- severe forms of anemia and other hematological diseases, during which the process of transporting oxygen to the tissues of the body is disrupted;
- benign and malignant neoplasms in the structure of bronchopulmonary tissue;
- restoration of normal body functions after prolonged anesthesia;
- pulmonary artery thrombosis, as well as accompanying complications associated with the presence of this pathology;
- acute respiratory failure;
- obstructive apnea syndrome;
- severe injuries to the lungs and bronchial tree;
- acute allergic reaction accompanied by a prolonged asthma attack;
- emphysema.
Determining the level of blood saturation is indicated for patients who are undergoing complex therapy using oxygen and a ventilator.
An analysis of blood saturation levels can be prescribed by a pulmonologist, cardiologist, therapist or pediatrician. For patients with signs of viral or bacterial pneumonia, a referral for this type of diagnosis is prescribed by an infectious disease specialist.
Saturation after pneumonia and coronavirus
It is not uncommon for the coronavirus to recede, but saturation remains low. Within the framework of pneumonia, this is considered normal, since the lungs need to be restored. Patients are advised to take a leisurely walk in the fresh air every day, as well as perform breathing exercises.
To prevent the formation of adhesions in the lung tissue, recovered patients whose CT scan showed serious fibrotic changes are prescribed antioxidant treatment, which involves following a diet, consuming acetylcysteine, vitamin E. Monitoring through computed tomography is also necessary.