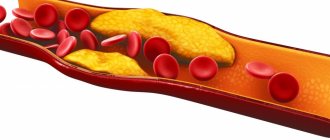
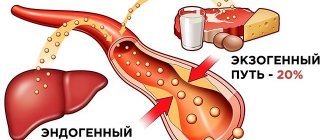
This organic fat-like substance performs many important functions. Without it, the synthesis of hormones, the absorption of most vitamins, the formation of bile acids, and hematopoiesis are impossible. Most of the cholesterol is produced inside the body, about 20% comes from the outside, with food. An increase in the level of this compound is fraught with the development of atherosclerosis and other diseases. Excess cholesterol fills the lumen of blood vessels and settles in the gallbladder in the form of stones.
What is good and bad cholesterol
In tissues and blood, cholesterol forms special complexes with groups of lipoprotein proteins. They ensure its stable suspended state. Some of them have high density, others low. These properties of lipoproteins determine the types of cholesterol:
- “good”: HDL, protects cells from damage, ensures normal blood flow and vascular elasticity;
- “bad”: LDL, prone to precipitation, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
It is low-density cholesterol that is meant when they talk about its harm to health. This is true, since its excess is directly related to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, poor circulation and the risk of strokes. LDL promotes the accumulation of triglycerides - simple fatty acids, overloads the liver, and contributes to the development of gallstones. High-density cholesterol inhibits these pathological processes and partially neutralizes the effect of the “bad”.
How to reduce high TG levels
A prerequisite for normalizing triglycerol levels is a special diet:
- Fast carbohydrates are replaced with complex ones: when consuming polysaccharides and limiting glucose, the risk of such a problem is minimal.
- The amount of saturated fat is minimized, giving preference to seafood that contains polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- It is better to replace industrial mayonnaise and other products containing trans fats (spread, margarine) with olive oil.
- Metabolic processes can be activated with adequate energy loss. Instead of alcohol and nicotine, physical activity will give you energy and good mood.
- It is important to promptly treat all inflammations and infectious diseases.
At the initial stage, such measures will be sufficient; if the problem has gone beyond prevention, the doctor will prescribe a lipid profile, analyze the functioning of the heart and recommend appropriate drug treatment.
Measuring cholesterol levels: general norms
To determine the level of cholesterol in the blood, a special unit is used: millimoles (mmol). Calculate the number of mmol per 1 liter of biological fluid. The total cholesterol content is important, as is the concentration of HDL and LDL separately. The level of triglycerides in the blood is also important, which is used to judge the risk of atherosclerotic changes in the body, disorders of fat metabolism and liver function.
- Normal total cholesterol: 3–7.8 mmol/l. During life it fluctuates depending on age and hormonal status. This is the average rate throughout life, the same for men and women.
- Low-density cholesterol—“bad” LDL—ideally should range between 1.8–2.8 mmol/L. The upper limit for women is up to 4.5 mmol/l. For men - up to 4.8 mmol/l. Its limit level: 5.7 mmol/l.
- The level of high-density “good” HDL is normally half that of “bad”: 0.8–2.4 mmol/l for women and 0.7–1.7 mmol/l for men.
The higher the low-density cholesterol level, the more critical the health condition. Especially if the level of a good high-density connection does not reach the norm:
- A regular increase in LDL levels to 4 or more mmol/l is dangerous;
- a constant decrease in LPV to 0.7 mmol/l also signals problems in the body.
Triglycerides are measured in the same way as other cholesterol levels. Their normal level in the blood throughout life is up to 2.2 mmol/l. It is the same for the male and female halves of humanity.
Signs of violations:
- elevated triglyceride levels: 2.3–5.6 mmol/l;
- dangerously high, signaling a disease: 5.7 mmol/l or more.
The risk of developing atherosclerosis is real at any age, but young people are more protected from it due to their high metabolic rate. Their cholesterol is quickly consumed by hormones and other physiological processes. Estrogen protects women from deposits of fatty plaques in blood vessels. However, with a sedentary lifestyle, a love of unhealthy foods, or the presence of systemic diseases, cholesterol also increases in young people. Over the years, its level grows even faster.
Reasons for deviation from the norm TG
The prerequisite for secondary triglyceridemia may be one of the concomitant diseases:
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels – atherosclerosis, hypertension, coronary artery disease;
- Liver failure, problems of the bile ducts, causing dyskinesia (obstruction) and infectious hepatitis;
- Kidney diseases – both acute and chronic;
- Diabetes;
- Inflammation of the pancreas;
- Increased levels of uric acid in the blood serum (hyperuricemia);
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland (myxedema);
- Overweight;
- Long-term use of certain medications (diuretics, beta-blockers, corticosteroids);
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
Analysis for triglycerides is usually carried out in combination with other lipoproteins - HDL, LDL, total cholesterol.
During the day, the concentration of triglycerol constantly changes. After eating (after 15-20 minutes), their level increases noticeably; it will take 10-12 hours for the levels to return to normal. For this reason, testing for TG is carried out on an empty stomach (16 hours without food).
For an objective picture, several days before the examination you should avoid overeating, excessive physical activity and stressful situations. An increased concentration of TG may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, so patients at risk are recommended to be examined annually. If the lipid profile shows deviations from the norm, repeat tests are prescribed.
The main reason for high triglycerol levels is considered to be an unbalanced diet with a large number of high-calorie foods. As a result of biochemical reactions, excess calories are deposited in adipose tissue in the form of triglycerides, which break down into glycerol and fatty acids . In this way, the body stores energy for extreme situations.
But the cause of our diseases is not triglycerides: a person creates an imbalance of TG, “good” and “bad” cholesterol himself. At blood transfusion stations, donors are constantly warned that before such an important act for someone’s life they must follow a low-calorie diet, since fatty blood with an increased level of TG (medically called “chyle” blood) is unsuitable for transfusion.
Doctors encounter low levels of triglycerides less often and such deviations do not play a special role in diagnosis.
Like other lipoproteins, TG can decrease with:
- Overactive thyroid gland;
- Kidney pathologies;
- Heart attack;
- Prolonged fasting, disruption of intestinal function;
- Hypolipoproteinemia;
- Malabsorption syndrome, when due to improper absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract, the body loses them.
A vegetarian diet, constant intake of vitamin C, inadequate exercise, injuries and severe burns also help reduce TG levels.
Changes in cholesterol standards by age in women
Differences in metabolism and the functioning of body systems at each stage of life also affect cholesterol levels. Over the years, due to a slowdown in metabolism, it inevitably increases. Changing total cholesterol averages for women:
- up to 5 years: from 2.90 to 5.18 mmol/l;
- 5-10 years: from 2.26 to 5.30 mmol/l;
- 10-15 years: from 3.21 to 5.20 mmol/l;
- 15-25 years: from 3.10-5.5 mmol/l;
- 25-35 years: from 3.37 to 5.96 mmol/l;
- 35-40 years: from 3.63 to 6.27 mmol/l;
- 40-50 years: from 3.81 to 6.53 mmol/l;
- 50-60 years: from 4.45 to 7.77 mmol/l;
- 60-70 years: from 4.45 to 7.69 mmol/l;
- 70 years or more: from 4.48 to 7.25 mmol/l.
A significant increase in the upper limit of indicators in women over 60 years of age is explained by the decline of ovarian function. During this period, the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and osteoporosis increases.
Testing triglyceride levels
A test for triglycerides is taken in the morning on an empty stomach and only from venous blood.
On the eve of the blood sampling procedure, it is recommended to avoid eating the following products that may affect the result of the biochemical analysis:
- Fatty foods;
- Fried food;
- Smoked and salted products;
- Mayonnaise and industrial sauces.
Dinner should be light food with the maximum amount of vegetables and no later than 19:00. 30 minutes - 1 hour before the blood sampling procedure, do not smoke, because the TG index in the blood may show in the analysis significantly higher than normal.
Typically, a TG test is taken as part of a lipid spectrum, which shows the index of all lipoprotein fractions in the lipid profile:
- Total cholesterol index;
- Low molecular density lipoprotein indicator;
- High molecular density lipoproteins.
On the eve of the blood sampling procedure, it is recommended to avoid fatty foods.
Changes in cholesterol levels over the years in men
Men are naturally protected from atherosclerosis less than women. They do not have a high level of estrogen in the body, but they have a higher craving for bad habits that increase the risk of dangerous diseases.
Norms of total cholesterol in men:
- up to 5 years: from 2.95-5.25 mmol/l;
- 5-10 years: from 3.13 to 5.25 mmol/l;
- 10-15 years: from 3.08 to 5.23 mmol/l;
- 15-25 years: from 2.93 to 5.59 mmol/l;
- 25-35 years: from 3.44-6.58 mmol/l;
- 35-40 years: from 3.78-6.99 mmol/l;
- 40-50 years: from 3.91 to 7.15 mmol/l;
- 50-60 years: from 4.09 to 7.17 mmol/l;
- 60-70 years: from 4.12 to 7.15 mmol/l
- 70 years or more: from 3.73 to 7.86 mmol/l.
The closer the cholesterol level is to the lower limit of normal, the safer it is for blood vessels and the heart. Regular levels exceeding 5–6 mmol/l signal the need to prevent atherosclerosis. It is especially important to monitor indicators for men over 50 years of age. From this age their growth accelerates.
Dietary supplements and fat burners
The beneficial properties of triglycerides form the basis of a diet for weakened patients who are unable to absorb fat naturally. Medium-chain triglycerols, unsaturated fatty acids (β-3 and β-6), together with vitamins and microelements, are included in the recipes of various nutritional mixtures that are used in tube feeding of oncological and mentally ill patients.
Medium-chain triglycerides, better known by their acronym MCT, are a hot topic for those looking to quickly lose body fat, increase muscle growth, or gain the energy needed to win sports. Sports supplements do not have a scientifically proven basis, so many experts question their effectiveness.
But supplements based on unsaturated fatty acids ?-3 and ?-6 are respected not only by athletes who pay special attention to their diet. Such healthy fats are not produced in the body, but the body really needs them, since it uses these acids to neutralize “bad” lipids that provoke atherosclerosis and its consequences.
Unsaturated fatty acids are contained in sufficient quantities in seafood (fish oil in particular) and vegetable oil (olive, soybean, corn, flaxseed).
It is worth recalling that the doctor analyzes triglycerol levels in combination with other indicators of lipid metabolism that determine the diagnosis, so there is no point in increasing or decreasing individual TG data.
Ways to Maintain Normal Cholesterol Levels
High levels are recorded in a biochemical blood test. If the numbers regularly exceed the norm, it is important to undergo a medical examination of the thyroid, pancreas, liver, and take a hormonal profile test. To normalize fat metabolism, courses of antilipid drugs are prescribed.
A therapeutic diet low in meat and dairy products also helps lower total cholesterol. It is useful to include sea fish containing Omega-3 complex, olive, flaxseed, sunflower oils, fresh vegetables, and herbs in your food.
Triglyceride molecules
The triglyceride molecule is a complex lipid compound that is the main supplier of nutrition and energy to every cell of the female body. Triglycerides are derivatives of glycerol compounds that enter a woman’s body with food.
The main suppliers of these molecules to the body are the following foods:
- Fatty meats;
- Lard;
- Meat by-products;
- All varieties of nuts;
- Vegetable oils.
After entering the female body with food, triglyceride molecules enter the lipid process through liver and intestinal cells.
With the help of the mucous membrane of the walls of the small intestine, the molecules enter the blood and disperse through the bloodstream to the cells of the body.
Unused triglycenin calories are stored in fat on the abdomen and thighs.
Triglycerides
Treatment of triglycerides above normal
There are 2 methods for reducing TG molecules:
- Non-drug therapy - lifestyle and nutrition adjustments;
- Drug therapy.
The basis of non-drug therapy for TG levels above normal is diet. With the help of a balanced diet, you can reduce triglycerides by up to 25.0%.
It is necessary to include in the diet of women the following products:
- Sea fish and seafood;
- Garlic and fresh vegetables;
- Lean meats;
- Fresh fruits and herbs;
- Eliminate carbonated drinks from the menu;
- Do not eat white bread and pastries;
- Boiled and smoked sausage;
- Pickles and marinades;
- Alcohol;
- Lard and fatty meat.
Fats in the diet should not exceed 30.0% and the main share should be vegetable oils.
Lean meats
Drug therapy
To reduce triglycerides in the blood of women to normal levels, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Group of fibrates - the decrease occurs due to a decrease in the synthesis of lipoproteins, which transport triglyceride molecules through the bloodstream;
- Preparations with nicotinic acid have the properties of an acid, like fibrate medications, but only they also increase HDL molecules in the blood of women;
- A group of statin drugs - reduce triglycerides with low-density lipoprotein molecules;
- Omega-3 drugs - reduces TG.