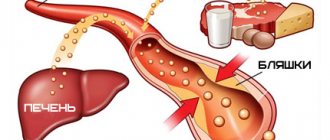
Poor nutrition leads to high blood cholesterol levels. Many will say that there is nothing wrong with this, but in reality this is not so, since a large amount of this substance contributes to atherosclerosis and damage to the vascular system.
First, the vessel wall is damaged. This is where cholesterol and fats go. As a result, a plaque forms that blocks the vascular lumen, which leads to poor circulation. If a plaque forms in the brain, a stroke occurs, and if it forms in the heart, a heart attack occurs. To avoid serious health problems, special drugs that belong to the group of statins are prescribed.
What are statins?
Statins are medications that lower cholesterol levels.
In most cases, doctors prescribe these drugs to prevent cardiovascular complications of atherosclerosis:
- coronary, coronary heart disease;
- heart attack;
- stroke.
Statins, unlike other drugs, are taken according to a dosage regimen. When should you take statins, morning or evening, before or after meals?
Relevance
The results of meta-analyses and systematic reviews indicate a decrease in cholesterol levels during statin therapy, which is important in the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Typically, statins are prescribed in the evening because cholesterol biosynthesis peaks at night and most statins have a short half-life. However, the optimal timing of administration and adherence to therapy depending on the timing of administration are not known.
The effect of statins on the body
- Statins are also called HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. The second name reflects their operating principle. The drugs have the ability to block one of the enzymes, without which the chemical compound of cholesterol is impossible.
- Sterol gets a bad rap, but the human body needs it. It is an essential component of cell membranes, the main material for the synthesis of vitamin D and steroid hormones.
- To prevent a deficiency of this substance, the body finds reserve sources of cholesterol. For example, statins increase the confluence of lipoproteins with a high density of HDL, which helps improve the walls of blood vessels and prevents the formation of blood clots.
Action
When is the best time to take statins?
There are many opinions on when it is best to take statins. But each medication comes with instructions that tell you how and when to take them.
Cholesterol synthesis occurs in large quantities at night. During this period, the concentration of statin in the blood should be high. The drug blocks the largest number of cholesterol formation reactions and most effectively reduces its concentration.
Each drug has a different half-life:
- Lovastatin - 3 hours;
- Simvastatin - 2 hours;
- Fluvastatin - 7 hours;
- Pitavastatin - 9 hours;
- Atorvastatin - 14 hours;
- Rosuvastatin - 19 hours.
Statins with the shortest elimination period should be taken in the evening, otherwise a small amount of the drug will remain by the time cholesterol is active. Statins with a long elimination period, such as atorvastatin or rosuvastatin, are eliminated from the body slowly, so they can be taken at any time.
Have an effect on cholesterol
- According to studies conducted on the effect of drugs on the level of triglycerides, total cholesterol and HDL, no significant differences were found between morning and evening doses.
- The analysis of statins with the shortest elimination period did not show significant differences between taking the drug in the morning and in the evening. But based on changes in total cholesterol and LDL, it was found that evening dosing was more effective.
- Studies of statins with long-term release of the drug also showed no significant difference in cholesterol and LDL cholesterol readings. But evening doses were more effective in terms of HDL levels.
- There are exceptions, such as pitavastatin. The drug occupies an intermediate position. But the instructions for use indicate that you should take this pill before bed.
Use of atorvastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and acute coronary syndrome
The randomized GREACE trial in patients with documented coronary artery disease demonstrated the ability of escalating doses of atorvastatin (from 10 to 80 mg, mean dose 24 mg) to reduce overall and cardiovascular mortality by 43% (p = 0.002) and 47% (p = 0.00). 0017) respectively. Taking atorvastatin was accompanied by a reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular events (MI, unstable angina, repeated myocardial revascularization) by 54% (p<0.0001) and cerebral strokes by 47% (p=0.034) [5].
The double-blind, randomized TNT (Treating to New Target) study in patients with documented coronary artery disease (n=10,001) assessed the effectiveness of different doses of atorvastatin (10 and 80 mg). Thus, on therapy with atorvastatin 80 mg, the primary endpoint (cardiovascular death, non-fatal MI, cardiac arrest with resuscitation, stroke) was identified in 8.7% of patients, and on therapy with atorvastatin 10 mg - in 10.9%. In summary, patients receiving atorvastatin 80 mg had a 22% lower risk of major events than patients receiving atorvastatin 10 mg (odds ratio (OR) 0.78, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.69–0 .89, p<0.001) [6, 13].
The ability of high doses of atorvastatin 80 mg to reduce the incidence of ischemic events compared with endovascular treatment was demonstrated in the AVERT (Atorvastatin Versus Revasculatization Treatment) study in 341 patients with stable CAD. Patients treated with atorvastatin 80 mg for 18 months had a 36% lower incidence of ischemic events than patients on standard therapy who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (p=0.048). Thus, aggressive statin therapy may be as effective as endovascular treatment in reducing the incidence of ischemic events in patients with CAD [8].
The effectiveness of the original atorvastatin at a dose of 80 mg as secondary prevention of CVD was also assessed in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Thus, in the randomized, double-blind MIRACL (Myocardial Ischemia Reduction with Aggressive Cholesterol Lowering) study of 3086 patients with ACS (unstable angina or acute non-ST segment elevation MI), the primary endpoint (death, non-fatal MI, cardiac arrest with resuscitation, or resumption of episodes of myocardial ischemia requiring readmission) was achieved in 228 patients (14.8%) in the atorvastatin group and 269 patients (17.4%) in the placebo group (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.70–1.00 , p=0.048). There was also a lower incidence of symptomatic myocardial ischemia requiring emergency readmission in the atorvastatin group compared with placebo (6.2% vs. 8.4%, p=0.02) [7]. In 171 patients with ACS in the ARMYDA-ACS (Atorvastatin Pretreatment Improves Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes Undergoing Early Percutaneous Coronary Intervention) study, atorvastatin reduced the risk of 30-day cardiovascular events after endovascular treatment by 88% compared with the group placebo (in the case of atorvastatin therapy 12 hours before endovascular intervention with 40 mg perioperatively) (OR 0.12, 95% CI 0.05–0.50, p = 0.004) [14].
Another study, PROVE IT-TIMI 22 (Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 22 Investigators), assessed the effectiveness of atorvastatin 80 mg and pravastatin 40 mg in 4162 patients undergoing PCI due to the development of ACS. Compared with pravastatin 40 mg, atorvastatin 80 mg was associated with a reduction in the composite endpoint of death, MI, stroke, unstable angina leading to hospitalization, and revascularization within 30 days of endovascular treatment (21.5% vs. 26.5%, OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.67–0.91, p=0.002), as well as rates of infarction-related revascularization (11.4% vs. 15.4%, p=0.001) and non-infarction -connected arteries (8.0% vs. 10.5%, p=0.017) [15]. Based on this study, it was concluded that atorvastatin therapy reduces the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with ACS undergoing PCI.
How to take statins: before or after meals?
- Food does not have any significant effect on the absorption of satins. Diet plays a big role. The effectiveness of statins can be easily negated by food. To do this, it is enough to add foods high in cholesterol, trans fats, saturated fats, and sugar to the menu.
- The products do not affect the absorption of dietary sterol. A large amount of cholesterol in the body compensates for the lack of synthesis through food. And as a result, the sterol level does not decrease.
- A prerequisite is the exclusion from the diet of alcoholic beverages , which cause a strong blow to the liver. Added to this is the medication burden. Smoking also has a negative effect on lowering cholesterol because nicotine damages the vascular system.
- While taking statins of the 1st-3rd generation, drinking grapefruit juice . It contains substances that block the transport enzyme needed to remove the drug from the body. The amount of medication in the blood increases, which causes side effects.
- An exception is the drug lovastatin. It is taken during dinner.
Statins for cardiovascular diseases
WOSCOP (West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study). The West of Scotland study was the first randomized placebo-controlled trial of primary prevention of coronary artery disease in middle-aged men at high risk of coronary atherosclerosis and with hypercholesterolemia (LDL cholesterol ≥5 mmol/l). Pravastatin 40 mg/day was compared with placebo. The study lasted 5 years and included 6595 people. During the study, in the group taking pravastatin, LDL cholesterol levels were reduced by 26%, the incidence of deaths and non-fatal MI decreased by 31%, the need for coronary artery bypass grafting decreased by 37%, and mortality from all causes decreased by 22%. Long-term follow-up of study participants showed that the effect of treatment persisted after 5 and 10 years, despite the fact that after the end of the study, the treatment of participants in the main and control groups did not differ [].
According to the Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (AFCAPS/TexCAPS), lovastatin was shown to reduce the likelihood of a first coronary attack (unstable angina, fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death) in patients of both sexes with low risk, without clinical signs of cardiovascular disease and close to average LDL levels of 3.9 (3.4 - 4.9) mmol/l. For every 1000 patients treated with lovastatin for 5 years, 12 myocardial infarctions and 17 coronary revascularization procedures were prevented. The drug had no effect on overall mortality.
Similar results were obtained in the ASCOT-LLA study, which examined the effects of simvastatin (10 mg) in a group of men and women with relatively normal serum cholesterol levels who had hypertension and at least three additional CVD risk factors.
The JUPITER study examined the use of rosuvastatin at a dose of 20 mg per day in healthy young patients of both sexes with elevated C-reactive protein levels and LDL levels below 3.4 mmol/l and showed a significant reduction in the primary endpoints: cardiovascular complications (acute myocardial infarction, unstable angina , sudden cardiac death) and death from all causes (hazard ratios 0.56 and 0.80, respectively).
How to take statins: recommendations
When using cholesterol-lowering medications, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Take the tablet only with clean water. It is prohibited to do this with drinks such as tea, coffee, juice, milk, etc.
- Statins are not chewed; the tablet is taken whole. This increases its effect. Tablets with a notch for division can be broken if necessary, since their composition allows for fractional administration of the drug.
- It is necessary to take HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors without daily binding regularly at the same time. Compliance with the schedule contributes to a stable concentration of the drug in the blood, which reduces the amount of cholesterol. There will be no positive result if the dosage schedule fluctuates.
- If you missed a statin dose and there are more than 12 hours left until the next one, take the medicine as soon as possible. If more time has passed, wait until you take the medicine as usual. There is no need to increase the dosage.
It is permissible to split the tablet
. Thus, statins are drugs that reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. This medicine is a prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Taken in the morning or evening at the same time. According to research, these drugs can be taken regardless of meals.
We will also tell you:
- How to drink vodka during a feast
- How to drink gin correctly
- L-carnitine: what is it for, how to drink it
- Gelatin for joints - how to drink
- How to drink water correctly
Statins and why you shouldn’t be afraid of them
Why should you take statins and should you not be afraid of them?
Statins are the main class of drugs used to treat patients with hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis.
Over the past 15 years, dozens of randomized clinical trials have been conducted with statins. Their results showed a significant reduction in cardiovascular and overall mortality, regardless of gender, age, and initial cholesterol levels.
Currently, 6 drugs of this class are registered in the Russian Federation: atorvastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin and fluvastatin.
Mechanism of action and pharmacological effects.
Statins have both lipid and non-lipid (pleiotropic) effects, which include anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative and antioxidant effects. The reduction in Low Density L-C levels depends on the statin dose. Each doubling of the dose leads to an additional reduction in Low Density L-C levels by 6% (rule of six). The effectiveness of different statins in reducing Low-Density L-C levels is not the same. Each patient's response to statin therapy may vary.
The effect of statins on the levels of TG and high-density cholesterol depends on their initial values. This is due to the fact that, along with a decrease in LDL-C levels, statins intensify the process of catabolism of VLDL and DILI, which contain TG. Statins reduce TG levels by an average of 15-20%.
Pharmacokinetics of statins.
The main site of pharmacological action of all statins is the liver. Minimal renal excretion of statins is observed with atorvastatin and fluvastatin. This circumstance must be taken into account when prescribing statins to patients with chronic kidney disease. The maximum plasma half-life of rosuvastatin (19 hours) and atorvastatin (14 hours), which explains their more pronounced lipid-lowering effect compared to other statins.
Effect of statin therapy on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
The results of randomized clinical trials with statins demonstrated a significant reduction in cardiovascular mortality in both primary and secondary prevention studies. These studies, which lasted at least 5 years, involved over 100,000 patients. A decrease in LDL-C levels with statin monotherapy was accompanied by a significant decrease in the incidence of complications of atherosclerosis, including cardiovascular death, nonfatal and fatal myocardial infarction, myocardial infarction, and peripheral atherosclerosis.
Statins and the liver.
In patients with chronic liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or fatty liver disease with normal liver enzyme levels, statin therapy is not contraindicated.
Dietary recommendations for reducing total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol
| Dietary recommendations for reducing total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol Preferably consumed | Consume in moderation | Use rarely in limited quantities | ||||
| Bread, cereals | From whole grains - 6 or more servings per day - the amount depends on BMI. 1 serving = 1 piece of bread, or 1 cup (200 ml, 200 g) of porridge, or 100 g of pasta or rice. | Bread and pasta made from refined flour, white rice, biscuits, corn flakes. | Baked goods (buns, croissants) | |||
| Vegetables and fruits | Fresh and processed vegetables, fresh and frozen fruits - at least 5 servings per day. 1 serving: 1 cup (200 g) fresh or cooked vegetables, 1 apple, 1 banana, 1 orange, 1 pear, 2 kiwi, 2 plums, 1 slice melon or pineapple, 1 glass juice | Dried fruits, jellies, jams, canned vegetables, fruits, fruit chips | Vegetables cooked with butter or sauces | |||
| Legumes | All (including soy and soy protein) – 3 – 4 servings per week. 1 serving: ½ cup (100 g) | |||||
| Meat and fish | Lean and fatty fish, skinless poultry – 100 g per day (it is advisable to consume fish at least 2 times a week, giving preference to fish from the northern seas) | Lean beef, lamb, pork and veal, seafood, shellfish | Sausage, frankfurters, bacon, internal organs | |||
| Dairy and eggs | Skim (skim) milk and fermented milk products – 1 cup (200 ml), 30 g of cottage cheese or cheese (low fat) per day. | Milk, other dairy products, low fat cheese, | Cheese, cream, egg yolks, whole milk and dairy products | |||
| Eggs | Protein | Yolk 2-3 per week | ||||
| Fats used for cooking, salad dressings | Vinegar, ketchup, mustard, fat-free dressings | Vegetable oils: sunflower, corn - 2-3 teaspoons, olive - no more than 1 teaspoon, soft margarine (no more than 5 g) mayonnaise | Butter, hard margarine, trans fats, palm and coconut oils, pork and lamb fat, dressings with egg yolks. | |||
| Nuts, seeds | All | Coconut | ||||
| Sweets | Low calorie | Sugar, honey, fructose, glucose, chocolate, candy | Cake, ice cream | |||
| Cooking food | Grilling, cooking, steaming | Frying, stewing | Deep frying | |||
Conclusion:
Lipid metabolism disorders are one of the important risk factors for the development and progression of CVD. Timely and correct diagnosis of hypercholesterolemia is a necessary component of rational prevention and therapy of atherosclerosis.
Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC)
National Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis (NOA)
Russian Society of Cardiosomatic Rehabilitation and Secondary Prevention (RosOKR)
Diagnosis and correction of lipid metabolism disorders for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis
Russian recommendations
V revision.
Moscow. year 2012