What is the Rh factor?
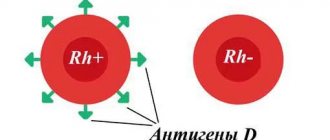
Rh factor (Rh factor) is a blood protein that is found on the surface of blood cells - red blood cells.
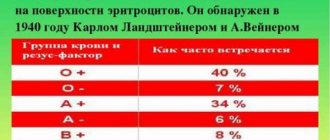
If this protein is present, then this means that the person has a positive Rh factor, but if it is not there, then it is negative. Rh factor is determined by antigen. There are five main antigens, but it is the D antigen that indicates Rh. 85% of the world's population have positive Rh factors. How to determine your Rh factor? It is enough to donate blood from a vein just once. This indicator does not change throughout life. The Rhesus status of the embryo is formed already in the first trimester of pregnancy. Determining this indicator is very important for the expectant mother, since in the case of an Rh-negative mother and an Rh-positive child, various pregnancy complications are possible. In this case, it will be especially important to follow the doctor’s instructions, avoid infectious and colds, as well as stress. Also on various websites there are so-called calculators that determine the Rh factor of the unborn child. It must be remembered that blood is donated on an empty stomach. A rapid Rh test can be taken at any independent laboratory where blood is taken (for example, Invitro). The price depends on the price list of the clinic itself. You can find out about the cost of the analysis immediately before delivery. You can also donate blood and find out your Rh factor for free if you become a donor. To do this, you need to fill out a form to register yourself as a blood donor at the appropriate institution.
The Rh factor also plays a big role in blood transfusions. A transfusion involves two people: the recipient (the one who receives the blood) and the donor (the one who donates the blood). If the blood is incompatible, the recipient may experience complications after the transfusion.
The most common myth among couples is that blood type (like the Rh factor) is inherited from a man. In fact, the inheritance of the Rh factor by a child is a rather complex and unpredictable process, and it cannot change during life. But it is worth remembering that in rare cases (about 1% of Europeans) a special type of Rh factor is determined - weakly positive. In this case, Rh is determined either positive or negative. This is where questions arise on forums: “why did my Rh minus change to plus?”, and legends also appear that this indicator may change. The sensitivity of the testing method plays an important role here.
An equally popular search on the Internet is “horoscope by blood type.” For example, in Japan, great attention is paid to deciphering blood type. Believe it or not - it's up to you.
In the world there is such a thing as a medical tattoo, photos of which can be easily found on the Internet. What do these tattoos mean and what are they for? Its designation is quite pragmatic - in case of a serious injury, when an urgent blood transfusion or surgery is required, and the victim is not able to give the doctor information about his blood type and Rh. Moreover, such tattoos (a simple application of the blood type and Rh factor) should be in places accessible to the doctor - shoulders, chest, arms.
Analyze it!
In what situations is it necessary to determine the Rh factor of blood? And in case of emergency, do you need to carry with you a reminder about what kind of blood you have?
Evgeniya, Voronezh region.
– Such an analysis must be done before planned surgery, blood transfusion and during pregnancy planning.
But it makes no sense to constantly carry with you a reminder about what kind of blood you have. According to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, which is valid in all medical institutions in our country, before each blood transfusion, each person entering the hospital must have their blood type and Rh factor rechecked, since there is no guarantee that they were determined correctly.
Rh factor and pregnancy
Compatibility of Rh factors during pregnancy is one of the tests that is carried out in the antenatal clinic. When a woman registers with a gynecologist, she will need to donate blood to determine her group and Rh factor. It can significantly affect the course of the next nine months. If the baby inherits the positive Rh of the father, and the mother has a negative Rh, then the protein in the child’s blood is unfamiliar to the mother’s body. The mother's body "considers" the baby's blood a foreign substance and begins to produce antibodies, attacking the baby's blood cells. If there is a Rhesus conflict during pregnancy, the fetus may experience anemia, jaundice, reticulocytosis, erythroblastosis, hydrops fetalis and edematous syndrome of the newborn (in the latter two cases there is a high probability of death of the child).
Possible consequences of an immune conflict
Maternal antibodies, penetrating the fetal bloodstream, destroy its red blood cells. This is how hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborns occurs, which leads to the development of anemia, intoxication, and disruption of the functioning of various organs.
The edematous variant of hemolytic disease can be diagnosed during pregnancy by performing an ultrasound of the fetus. Ultrasound examination reveals:
- swelling of the placenta;
- polyhydramnios;
- accumulation of exudate in the abdominal and pleural cavity;
- hypertrophy of the liver, spleen, myocardium, thickening of the intestinal walls;
- “Buddha pose” - the fetal abdomen is enlarged in size, and the legs are placed in different directions
With the icteric variant of hemolytic disease, clinical symptoms appear after the birth of the child:
- a blood test reveals a high level of indirect bilirubin;
- the baby's skin becomes jaundiced;
- a newborn may experience an enlargement of the spleen, liver, heart, and lymph nodes.
Blood type and Rh factor: compatibility
The cause of incompatibility may be not only Rh blood type, but also blood type.
What are the different blood types? They are distinguished by the presence of specific proteins.
Four groups:
- the first (occurs most often) - O - there are no specific proteins in it;
- the second - A - contains protein A;
- the third - B - contains protein B;
- the fourth (the rarest of all) - AB - contains both type A and type B proteins.
First
(Rh negative) can provoke a conflict in the mother:
- for protein of the second group (A);
- for protein of the third group (B);
- for Rh protein (positive).
Second
(Rh negative) can provoke a conflict in the mother:
- for protein of the third group (B);
- for protein of the fourth group (B);
- for Rh protein (positive).
Third
(Rh factor is negative) the mother can provoke a conflict:
- for protein of the second group (A);
- for protein of the fourth group (A);
- for Rh protein (positive).
Fourth
does not conflict with any other group. The only case when an immune reaction is possible is if the mother has group IV and is Rh negative, and the father is positive.
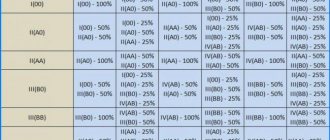
Table 1. Statistics
| Blood groups parents | Possible blood type of the child (probability, %) | |||
| I+I | I (100%) | — | — | — |
| I+II | I (50%) | II (50%) | — | — |
| I+III | I (50%) | — | III (50%) | — |
| I+IV | — | II (50%) | III (50%) | — |
| II+II | I (25%) | II (75%) | — | — |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | — | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III+III | I (25%) | — | III (75%) | — |
| III + IV | — | II (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) |
| IV + IV | — | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
Why might it change?
The group is determined by the adhesion of red blood cells. To do this, serum containing antibodies (agglutinins) α, β, α and β are dripped onto a special plate. Then a drop of blood is added to each, and there should be about ten times more serum. After this, the agglutination reaction (sticking together) of red blood cells is observed under a microscope for five minutes. Based on the results of this reaction, the blood type is determined:
- if gluing did not occur in any serum, then it is I;
- if the reaction is positive with sera containing α and α+β antibodies, then this is II;
- if agglutination occurred in serum with antibodies β and α+β, then this is III;
- if all sera give positive results, this means that the blood contains both antibodies and belongs to type IV.
Blood group determination
Why might the group change? To do this, it is necessary that red blood cell antigens cease to be produced or their production is greatly weakened. There is an opinion that this can happen with infectious diseases, pregnancy, tumors, and some diseases associated with increased production of red cells. In this regard, in laboratory tests, antibodies cannot detect such a small amount of antigens or the reaction is so weak that it is not visible. Thus, under certain conditions, a temporary change in test results is possible, but not a change in group membership.
Rh positive during pregnancy
If you are Rh positive, then your husband’s Rh negative will not affect the course of your pregnancy. In the case when a child inherits a negative Rh factor, there is no protein in his blood that is “unfamiliar” to the mother’s immune system, and a conflict will not arise.
- Rh-positive mother + Rh-positive father = Rh-positive fetus
The child has inherited the positive Rh factor of the parents, and the pregnancy will pass without complications. - Rh-positive mother + Rh-positive father = Rh-negative fetus
Even if the parents' Rh factor is positive, the baby can be negative. In this case, we can still talk about the compatibility of Rh factors during pregnancy: the mother’s body is “familiar” with all the proteins in the child’s blood. - Rh-positive mother + Rh-negative father = Rh-positive fetus
Both the mother and the fetus are positive, and there is no conflict during pregnancy. - Rh-positive mother + Rh-negative father = Rh-negative fetus
Although mother and fetus have different Rh blood factors (mother and child have positive and negative, respectively), there is no conflict.
As already mentioned, Rh blood is a protein. And since the mother’s body already has this protein, the fetal blood does not contain components unfamiliar to the mother’s immune system.
Don't need stock?
I will soon have major heart surgery. But I have Rh negative blood. They say that in such cases you need to go to a blood transfusion station and donate it “in reserve” - in case of bleeding. Is it worth doing?
Vsevolod, Moscow
Article on the topic
Where to donate blood faster and cheaper?
– Rh negative blood is always in short supply. But, if we are talking about a planned operation, like yours, the medical institution, as a rule, orders blood for it in advance. Especially if the risk of bleeding is expected.
A difficult situation with Rh-negative donor blood can arise in the event of an emergency operation, when a person is admitted to the hospital after a traffic accident or other accident. You can't think about it anymore. We need to act. How? Contact blood transfusion stations located in large (preferably federal) medical centers. Or look for the blood you need in the city’s medical network. If it was not possible to resolve this issue in this way, you need to call out friends and acquaintances or go to the nearest military or fire station and look for voluntary donors with the blood Rh blood you need.
By the way, when getting ready for surgery, remember if you have ever had a massive blood transfusion (blood transfusion). In this case, you need to select donor blood especially carefully. Otherwise, with your next blood transfusion, you may experience serious or even life-threatening problems, regardless of your Rh factor.
Rh factor negative during pregnancy
Rh negative during pregnancy is not always a death sentence for the baby. The main thing is that it is the same for both the baby and the mother.
- Rh-negative mother + Rh-negative father = Rh-negative fetus
The baby inherited the Rh factor of his parents. And since both the mother and the fetus have no protein (Rhesus) in their blood and their blood is similar, then a conflict does not arise. - Rh-negative mother + Rh-positive father = Rh-negative fetus
This is one of the cases when the Rh factor is very important: the compatibility of the blood of the mother and the fetus affects the next nine months of intrauterine life. Although a woman is Rh negative during pregnancy, it is good that the fetus is also Rh negative. There is no Rh in either the mother's blood or the fetus's blood.
Let's sum it up
When conceiving a child, the compatibility of the parents according to the Rh factor does not matter, but this is one of the important criteria that affects the successful course of pregnancy. Therefore, it is so important to thoroughly prepare the female body for bearing a child.
Pregnoton, which contains folic acid, iodine, vitamins E, C, B6, and zinc, will help with this. It eliminates the lack of micronutrients important for conception and early pregnancy, and also normalizes the functioning of the reproductive system, reduces prolactin levels in hyperprolactinemia, increases the thickness of the endometrium in women with thin endometrium and increases the likelihood of pregnancy (more information about the product can be found here).
THIS IS NOT AN ADVERTISING. THE MATERIAL WAS PREPARED WITH THE PARTICIPATION OF EXPERTS.
When does Rh-conflict pregnancy occur?
Rh negative mother + Rh positive father = Rh positive fetus
Please note: no matter what group the mother has, negative Rh during pregnancy becomes a cause of conflict. In this case, the embryo inherits it from the father and brings the “new protein” into the body of the Rh-negative mother. Her blood “does not recognize” this substance: there is no such protein in the body. Accordingly, the body begins to defend itself and produce antibodies. They penetrate the placenta into the baby's blood and attack his red blood cells. The fetus tries to defend itself: the spleen and liver begin to work hard, and they increase significantly in size. If a child has few red blood cells left, he develops anemia, or anemia.
Treatment of the consequences of Rh sensitization
The most effective way to treat severe Rh incompatibility is intrauterine blood transfusion, which is performed if the fetus has severe anemia. During the procedure, red blood cells are injected into the fetal umbilical cord vein under ultrasound guidance.
The procedure allows you to:
- improve the condition of the fetus by maintaining the volume of red blood cells above critical;
- smooth out the immune reaction of the female body.
However, even intravenous blood transfusion is not a panacea for hemolytic disease of the fetus. In the future, this procedure must either be repeated, or the question of early delivery must be raised.
After the birth of the child, a neonatologist treats him. If necessary, the baby is placed under a special photo lamp. Ultraviolet rays penetrate the skin and promote the formation of a water-soluble form of bilirubin, which is quickly eliminated from the body.
If a baby has hemolytic disease, breastfeeding is prohibited for several weeks. If there is no hemolytic disease, then the mother is allowed to breastfeed after an immunoglobulin injection. The drug is administered once, which helps prevent the development of Rh conflict in the next pregnancy.
Rh negative during pregnancy
There is a vaccine - anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin, which prevents Rh-conflict during pregnancy. It binds the antibodies that the mother’s body produces and brings them out. Vaccination can be carried out during pregnancy. If you are Rh negative and your husband is positive, this is not a reason to give up motherhood. Over the course of 40 weeks, you will have to donate blood from a vein several times:
- up to 32 weeks - once a month;
- from the 32nd to the 35th week - 2 times a month;
- from the 35th to the 40th week - once a week.
If Rh antibodies appear in your blood, your doctor can detect the onset of a Rh conflict in time. In case of conflict pregnancy, immediately after birth, the newborn is given a blood transfusion: the group and Rh factor must be the same as that of the mother. This is especially important in the first 36 hours of the baby’s life - the mother’s antibodies that enter the child’s body are neutralized when they “meet” familiar blood.
Can BG change with transfusion?
Transfusion does not affect the BG in any way, however, there are certain exceptions to this rule:
- When identifying blood to a certain group, the health worker made a mistake.
- The patient suffers from a disease of the hematopoietic system (aplastic anemia), after treatment of which, his red blood cells acquire new antigenic properties that were previously suppressed by the disease.
- If the patient has been transfused with a large volume of donor blood: until the “new” red blood cells die, the patient may be diagnosed with another GC for several days.
- The patient underwent a donor bone marrow transplant, before which all his blood progenitor cells were destroyed using chemicals. As a result, the “new” bone marrow can produce cells with a different structure and change the BG. This probability is minimal, but it exists.
- How to find out the Rh factor of the fetus
When can immunoglobulin prophylaxis be carried out?
To prevent conflict in subsequent pregnancies, women with a negative Rh factor should undergo prophylaxis. This is done after:
- childbirth (within three days);
- abortion;
- analysis of amniotic fluid;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- placental abruption;
- transfusion.
Remember: if you and your baby’s group and Rh are different, this is not an indication that there will definitely be problems. Group and Rh are just the presence or absence of specific proteins in the blood. The reaction of the body and the development of pathologies in our time can be successfully controlled with the help of medications. Your attentiveness to your body, as well as an experienced doctor, will help you bear a healthy baby.
Problem filter
I heard that the problem of Rh sensitization can be solved with the help of plasmapheresis. But can pregnant women do this?
Margarita, Yaroslavl
– Not only is it possible, but it is also necessary! By removing antibodies that are harmful to the fetus from the bloodstream or reducing their concentration, plasmapheresis (blood purification method) is a very effective prevention of Rh conflict. True, if a woman has so-called complete antibodies in her blood, which are slowly synthesized and more difficult to pass the placental barrier. It is much more difficult to “pull out” a pregnancy with incomplete antibodies: they are synthesized in 10–14 hours, and it is impossible to “cleanse the blood” every day. Minimum – in 1–1.5 days. In order to maintain a normal antibody titer, some women have to undergo this procedure throughout their pregnancy.
Plasmapheresis has become a real lifesaver in the treatment of toxicosis in the first and second half of pregnancy, as well as in placental insufficiency, which is the main cause of intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and fetal growth retardation.
How do your chances of conceiving depend on your blood type?
Quite a lot is already known about the influence of blood groups, for example, on the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's disease, cancer, blood clots, etc. However, virtually nothing was known about the effect on fertility. And finally, thanks to the efforts of Turkish doctors, research has appeared in this area.
A study published last week found that men with type O are four times less likely to develop impotence compared to guys with other blood types. Experts from Ordu University in Turkey noted that blood type is as important a risk factor as smoking, excess weight, and high blood pressure. The reason is not clear, but scientists have said that in people with type A blood, the penis has a large number of veins, the lining of which can become damaged, leading to erectile dysfunction.
Blood type also affects female fertility. Girls with the second group are more likely to bear a healthy child for a long time than with the first. Studies have shown that women in the first group quickly deplete their egg reserves early in life. But at the same time, women with type 0 have a lower risk of developing preeclampsia - high blood pressure during pregnancy, which can be dangerous for mother and baby.
Naturally, representatives of the rest of humanity (which, by the way, are a little more than half, because people of the 1st group account for a little more than 40%) should not panic either - a higher probability does not mean a 100% chance. Likewise, representatives of the “happy” group should not relax ahead of time - reduced risk does not mean zero.
Rh factor, blood group, blood protein, antibody production, anemia, immune reaction, Rh compatibility, anemia, hydrops, fetal edema, immunoglobulin
The likelihood of an immune reaction in a pregnant woman with Rh-
If a woman is pregnant for the first time, then the risk of her developing antibodies tends to zero: the likelihood of contact between the blood of the fetus and the mother is too small. As a rule, contact occurs during the birth of the baby, after which the immune reaction starts. With each subsequent pregnancy, the immune reaction increases and the risk of developing Rh sensitization increases.
In addition, the likelihood of sensitization increases:
- induced and spontaneous abortions;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- premature placental abruption;
- amniocentesis (examination of amniotic fluid);
- chorionic villus biopsy (examination of the tissue of the outer membrane of the embryo);
- cordocentesis (examination of fetal cord blood);
- some obstetric manipulations. For example, external obstetric rotation (turning over the fetus, which is in a position unfavorable for childbirth);
- increased permeability of the blood-placental barrier;
- abdominal organ injuries.
Sensations in the world of medicine
I would like to mention one, the only (!) scientifically recorded case. After a liver transplant, a fifteen-year-old Australian woman completely changed all her immune system parameters, and her Rh changed from “minus” to “plus.” However, the blood type remained the same, first.
In my opinion, it is also worth mentioning one scientific study that promises to be sensational. Brazilian scientists, in the course of a series of experiments, discovered that during liver and spleen transplantation (with the coincidence of many additional conditions, of course), the protein found in red blood cells can change. This means that a change in rhesus during life is possible. Moreover, the blood type always remains the same.
Thus, this theory is slowly acquiring scientific background. But there is still no conclusive evidence to support it.
That's all. What blood secrets do you know? Share your life situations. We are always happy to communicate.
See you again!
Sources
- Ceniceros LC., Capitanio JP., Kinnally EL. Prenatal Relocation Stress Enhances Resilience Under Challenge in Infant Rhesus Macaques. // Front Behav Neurosci - 2021 - Vol15 - NNULL - p.641795; PMID:33854420
- Raguz MJ., Prce Z., Bjelanovic V., Bjelanovic I., Dzida S., Mabic M. 20 Years of Follow-up Alloimmunization and Hemolytic Disease in Newborn: Has Anything Changed in the Field Over the Years? // Klin Padiatr - 2021 - Vol232 - N6 - p.314-320; PMID:33063311
- Shirtcliff EA., Lubach GR., Mooney R., Beck RT., Fanning LK., Coe CL. Transgenerational propensities for infant birth weight reflect fetal growth history of the mother in rhesus monkeys. // Trends Dev Biol - 2021 - Vol12 - NNULL - p.55-65; PMID:32616989
- Deere JD., Chang WLW., Villalobos A., Schmidt KA., Deshpande A., Castillo LD., Fike J., Walter MR., Barry PA., Hartigan-O'Connor DJ. Neutralization of rhesus cytomegalovirus IL-10 reduces horizontal transmission and alters long-term immunity. // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA - 2021 - Vol116 - N26 - p.13036-13041; PMID:31189602
- Lee DS., Ruiz-Lambides AV., Higham JP. Higher offspring mortality with short interbirth intervals in free-ranging rhesus macaques. // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA - 2021 - Vol116 - N13 - p.6057-6062; PMID:30877247
- Aljuhaysh RM., El-Fetoh NMA., Alanazi MI., Albaqawi AS., Alanazi WM., Alanazi NS., Alanazi RM., Alanazi AM., Alnemer EM., Alenezi RA., Alabdullatif TK., Alanazi RA., Alanazi SS., Alsultan KS., Alanazi IM., Alsunayni DS. Maternal-fetal Rhesus (Rh) factor incompatibility in Arar, northern Saudi Arabia. // Electron Physician - 2021 - Vol9 - N12 - p.5908-5913; PMID:29560141
- Bishop CV., Stouffer RL., Takahashi DL., Mishler EC., Wilcox MC., Slayden OD., True CA. Chronic hyperandrogenemia and western-style diet beginning at puberty reduces fertility and increases metabolic dysfunction during pregnancy in young adult, female macaques. // Hum Reprod - 2021 - Vol33 - N4 - p.694-705; PMID:29401269
- Krendl C., Shaposhnikov D., Rishko V., Ori C., Ziegenhain C., Sass S., Simon L., Müller NS., Straub T., Brooks KE., Chavez SL., Enard W., Theis FJ ., Drukker M. GATA2/3-TFAP2A/C transcription factor network couples human pluripotent stem cell differentiation to trophectoderm with repression of pluripotency. // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA - 2021 - Vol114 - N45 - p.E9579-E9588; PMID:29078328
- Dettmer AM, Woodward RA, Suomi SJ. Reproductive consequences of a matrilineal overthrow in rhesus monkeys. // Am J Primatol - 2015 - Vol77 - N3 - p.346-52; PMID:25382028
- Dizik GM., Pavliuk RP. . // Klin Khir - 2011 - Vol - N9 - p.69-72; PMID:22168031