Are you experiencing back pain and numbness in your limbs? These are the first signs of osteochondrosis. Insufficient mobility in lifestyle, sedentary work, stress on the neck and spine lead to cartilage wearing out, losing moisture, resulting in micro-tears.
With cervical osteochondrosis, degenerative changes occur in the intervertebral discs. Not only the discs are damaged, but also the vertebrae and joints in the cervical region. If the disease is not treated for a long time, the patient’s general well-being worsens: constant headaches, the appearance of a vertebral hernia, deterioration of cerebral circulation, as a result of which cognitive functions decrease.
Reasons for the development of osteochondrosis
An incorrect sitting position, in which the neck is pulled forward, leads to the development of cervical disease. In this case, excessive pressure occurs on the intervertebral discs, which leads to changes in the nuclei pulposus and compression of blood vessels. This is the position a person takes at a workplace in front of a computer. Therefore, office workers are most often exposed to the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
In addition, the reasons for the development of pathology may be:
- improper load distribution when carrying bags;
- excessively soft sleeping place (the spine bends in an unnatural shape);
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet;
- endocrine system disorders;
- curvature of the spine and poor posture during active growth of the body;
- cervical vertebrae injuries;
- presence of bad habits.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of osteochondrosis consists of maintaining a proper diet and ensuring the proper level of physical activity. If the patient is overweight, measures should be aimed at reducing weight through diet and sports training, taking into account pressure restrictions. Optimal types:
- swimming;
- walk;
- stretching;
- physiotherapy;
- yoga.
During an exacerbation, it is recommended to wear a collar with a rigid base to unload the cervical vertebrae and relieve muscle spasms. Self-massage in the form of rubbing and stroking will help improve blood circulation and speed up metabolism. To prevent the disease, doctors recommend periodically checking blood pressure and consulting a doctor at the first signs of osteochondrosis.
Checks should be carried out at least once a year, and in the case of problems with intervertebral discs - at least once every six months.
Stages of the disease
Determining whether your pain symptoms are signs of the development of cervical osteochondrosis and what stage of development of the disease can only be determined by an experienced doctor after examination and palpation. In total, cervical osteochondrosis goes through four stages of development:
- The nucleus pulposus, the central part of the intervertebral disc, undergoes moderate dehydration during the first stage. As a result, the supporting and shock-absorbing functions of the intervertebral discs are gradually lost. During the first stage, you will experience pain with sudden movements, hypothermia, and staying in one position for a long time.
- The second stage of development is characterized by the appearance of congestion and spasms, which compress capillaries and blood vessels, preventing normal blood circulation. As a result, the frame of the intervertebral disc becomes thinner, forming a protrusion (bulging forward or backward). Under the influence of excessive load, osteophytes are formed on the cervical vertebrae - bone growths. Pain sensations are localized in one place; with sudden turns and tilts of the head, dislocations of the cervical vertebrae can occur.
- Extrusions are formed as a result of thinning of the intervertebral discs. The edge of the nucleus pulposus breaks the fibrous ring and extends beyond the edges of the vertebral body. Muscles and nerve endings are compressed. Pain is felt in the neck, back and limbs.
- At the fourth stage of the disease, the intervertebral discs are displaced and central and lateral hernias form. In addition, scars form on the discs, which leads to immobility of the affected joint. The patient experiences persistent back pain that radiates to other parts of the body, a constant feeling of fatigue, and asymmetry of parts of the body occurs.
Contraindications
Despite the relative safety of the gymnastics complex, there are a number of situations when Shishonin’s exercises should be postponed or even abandoned.
Such restrictions include:
- hypertensive crisis (Fig. 1);
- periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- acute infectious processes;
- exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis;
- exacerbation of joint diseases, rheumatological diseases;
- recovery period after a stroke or heart attack;
- recent meningitis;
- oncological neoplasms;
- bleeding;
- general exhaustion of the body [7].
It is also important to remember that a set of exercises cannot be considered as an isolated treatment method. Shishonin gymnastics is an effective addition to the main methods of treating hypertension, and exercises from this complex can reduce the number of antihypertensive drugs.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine manifest themselves differently depending on the stage of development of the pathology. In the early stages it can occur with virtually no symptoms. Pain in the neck and back can only appear if you stay in one position for a long time, sharply bend or turn.
At later stages of development, a crunching sound is heard in the spine, back pain radiates to other limbs, and numbness occurs in parts of the body. When osteophytes and extrusions form, the following occurs:
- headaches in the back of the head and parietal part;
- speech disorders and numbness of the tongue;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin of the neck;
- breathing disorders;
- changes in blood pressure;
- heartbeat disturbances;
- noise and congestion in the ears;
- fainting.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women are much more pronounced than in men. This is due to the fact that women have a predisposition to vascular diseases and a more fragile structure of the bone segments of the spine. Signs of the disease begin to appear when intervertebral discs change. This leads to disruption of normal blood circulation and causes severe headaches, dizziness, and neuroses. An exacerbation of the disease in women often occurs during menopause, when the body is subject to hormonal changes.
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men are similar to those in women; erectile dysfunction can be observed separately.
Headache with cervical osteochondrosis is caused by poor circulation in the brain and spinal cord. When the vertebrae become misaligned, they compress the arteries and the oxygen content in the blood decreases. Unfortunately, such pain may not go away even after taking strong painkillers. Therefore, it is important to approach solving the problem comprehensively. Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis may be accompanied by darkening of the eyes and the appearance of tinnitus. This happens because spasming muscles cause a reduction in oxygen supply to the brain.
A lump in the throat with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as burning, difficulty breathing and muscle spasms are a common occurrence. The disease provokes compression of the nerve fibers of the cervical spine to the head and neck. Disturbances in nerve impulses cause sore throat.
Due to spasms of blood vessels and irritation of nerve endings, jumps in blood pressure occur. Increased lower pressure in osteochondrosis indicates that the blood supply to certain areas of the brain is impaired, since the vertebral artery is compressed by the intervertebral discs. As a result, oxygen starvation occurs and blood pressure rises.
Possible complications
High blood pressure in combination with osteochondrosis can lead to serious complications for the body. The consequences in the absence of funds and timely treatment are disastrous:
- Inability to lead a normal lifestyle due to concomitant symptoms of pathological changes and pain;
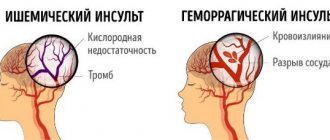
- increased risk of heart attack or bleeding;
- decreased mental performance, memory;
- deterioration and abnormal vision.
With a complex course of the disease, the patient can not only become disabled, but also significantly increase the risk of death.
How is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine diagnosed?
Diagnosis of pathology begins with consultation with a specialist. At the first manifestations of osteochondrosis, consult a rheumatologist, neurologist, surgeon or orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor will ask about the symptoms and the frequency of their occurrence; you need to provide the specialist with a complete medical history and the results of earlier studies (if any). The specialist will conduct a visual examination and palpation, and refer you for tests. During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to neck mobility, muscle tone, skin sensitivity and identifies the most painful areas.
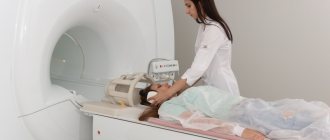
To identify the condition of muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, and to detect inflammatory processes or tumors, an informative and safe diagnostic method is prescribed - MRI of the cervical spine. During an MRI of osteochondrosis, the patient lies on a special sliding table with his back. Rollers are placed on the patient's head to relieve muscle tension, and the limbs are secured with belts. Any slight movement during the procedure can affect the quality of the result. Next, the table moves into the tomograph area. The procedure does not cause pain. The tomograph makes a lot of noise during scanning, so you can use headphones to avoid discomfort.
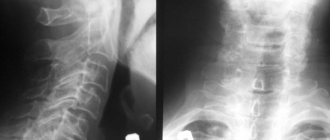
If MRI is contraindicated, there are other diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and radiography. X-ray is suitable only for primary diagnosis and does not provide a layer-by-layer image of the affected tissue. However, this study is the simplest and most economical, allowing you to examine the patient’s body in several projections. Due to the strong radiation exposure to the body, radiography cannot be performed frequently.
During a computed tomography scan, a scan is performed using one or more beams of ionizing rays. They pass through the human body and are recorded by detectors. The detectors move along the patient's body in opposite directions and record up to 6 million signals. The image displays tissues of different densities with precise definition of the boundaries of organs and the affected areas in the form of a section. The procedure allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image.
Lack of air
If you notice symptoms, check your blood pressure. But do it right.
- It is better to measure pressure with a mechanical tonometer
- Rest before measuring your blood pressure
- It is advisable not to eat or exercise half an hour before measuring blood pressure
- Pay attention to the position during measurement: straight back, legs uncrossed, standing straight, feet on the floor.
- Empty your bladder before the procedure.
- Clothes should be loose.
- Blood pressure is measured at least twice on the same arm.
- The following indicators are considered normal: 120 to 80.
First aid
If your health suddenly deteriorates due to low or high blood pressure, you must call an ambulance. Then you need to remove constrictive clothing or unfasten buttons, take a reclining position, and cover your legs with a warm blanket. As a rule, in such a state a person becomes restless, anxiety, fear appear, and panic attacks are possible. You should take 10-15 drops of motherwort or valerian tincture. Nifedipine, Captopril or Moxonidine can be used to lower blood pressure. Strong, sweet tea, tinctures of Eleutherococcus, and ginseng will help increase blood pressure.