With such problems, patients often turn to cardiology centers, not realizing that their unpleasant sensations are not associated with any particular disease, but are secondary clinical signs of spinal pathology. After performing a set of special studies, it is discovered that in such patients the heart does not have any abnormalities; the cause of tachycardia should be looked for elsewhere. Why does tachycardia and heart pain occur with osteochondrosis?
Tachycardia with osteochondrosis
Consequences of spinal osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is an insidious and intractable disease that can progress for years. Treatment requires great effort from both medical staff and patients.
What is the danger of osteochondrosis (consequences and complications)
Important. When patients present with complaints of tachycardia or heart pain, doctors first check the patient for the presence of myocardial infarction and angina. Only after such serious diseases have been ruled out are further examinations performed to determine the actual causes of the discomfort.
In-depth comprehensive examinations allow you to have a complete picture of the patient’s health status. Quite often, heart problems arise due to osteochondrosis of the spine or subluxation of the first cervical vertebra. Such diseases should be accompanied by neurologists and orthopedic traumatologists.
Physiology of tachycardia
Symptoms of a herniated cervical spine
A cervical hernia develops gradually and does not manifest itself at first. The sudden appearance of severe pain or other manifestations of a hernia is most often associated with some triggering factor - a sudden turn of the head, injury, stress or illness.
First signs of illness
At first, the signs of a cervical hernia are vague:
- periodic neck pain that goes away on its own;
- a feeling of numbness and crawling on one side of the neck when tilting or turning the head for a long time; numbness of fingers on one side;
- crunch in the neck when turning;
- changes in blood pressure;
- frequent headaches, which are not always associated with the condition of the spine;
- periodic attacks of dizziness;
- double vision, tinnitus;
- drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night.
If such signs appear, it is better to immediately consult a doctor and undergo a course of treatment - at this stage, a developing hernia is best treated.
Obvious symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of a cervical hernia usually develop after several years. In the cervical spine, symptoms have a clear connection with the level of disc damage. Symptoms are very varied:
Radicular syndrome
Radicular syndrome develops when the roots of the spinal nerves are pinched and manifests itself in the form of pain, motor and sensory disturbances, and metabolic disorders. When different discs of the cervical spine are affected, the following symptoms develop:
- C2 – C3.
Tormenting headaches - migraines. Pain and sensory disturbances in the neck are often unilateral. Visual, auditory, olfactory disorders. Lesions of the facial nerve - paresis and paralysis, impaired tongue movements. Frequent inflammatory processes of the ENT organs. Hernias in this disc develop extremely rarely. - C3-C4.
Sensory disturbances extend to the entire half of the neck. The pain radiates to the teeth, face, ear. Visual and hearing impairments. Mental disorders are typical - depression, panic attacks. A rare type of hernia. - C4 – C5.
Numbness and pain spread throughout the neck, inner and front surface of the shoulder. Muscle weakness. It is difficult to turn your head and bend your arm at the elbow. A common type of hernia. - C5 – C6.
Pain and sensory disturbances along the back of the shoulder. The pain may spread along the outer edge of the arm to the thumb. The neck muscles are tense. Paresis and paralysis. Cough, shortness of breath, bronchospasms, hoarseness. The most common location of cervical hernia. - C6 – C7.
The pain spreads along the outer and back surface of the arm, radiating to the shoulder blade, elbow, 2nd to 5th fingers. The function of the thyroid gland is impaired. Happens frequently.
When different cervical vertebrae are affected, different symptoms appear.
Autonomic disorders
Often the main symptoms of cervical disc herniation are autonomic disorders. They develop when the autonomic fibers of the spinal nerve roots, which innervate internal organs and the walls of blood vessels, are pinched.
At the same time, pain in the heart of a very different nature, changes in blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, sweating, changes in body temperature, and hand tremors appear.
Dizziness
The cause of dizziness due to cervical disc herniation is vertebral artery syndrome. This group of symptoms develops when the vertebral artery that supplies the brain is compressed by a hernial protrusion. The two vertebral arteries enter the lateral foramen of the vertebrae at the level of C6. And once they enter the cranial cavity, they merge into a single basilar artery, which supplies the base of the brain, the medulla oblongata, which contains the vital vasomotor and respiratory centers.
Compression of the artery leads to disruption of the blood supply to the brain, causing severe dizziness, weakness, fainting, sudden loss of coordination, visual and hearing disorders. Headaches in the form of migraines (half of the head hurts) are also typical.
Numbness
Numbness of individual parts of the body develops when the sensory fibers of the spinal roots are pinched. This is one of the manifestations of radicular syndrome. Sometimes, instead of numbness, the patient has a feeling of goosebumps crawling throughout the body.
Symptoms of cervical hernia in men
Cervical hernia occurs more often in men than in women. They are more likely to experience pain along the pinched roots and impaired movement. More common are segmented types of hernia with segments entering the spinal cord, developing paresis and paralysis.
Symptoms of cervical hernia in women
Women are characterized by a wide variety of manifestations of cervical hernia. Especially often they develop vegetative symptoms with heart pain and changes in blood pressure. Panic attacks and very often migraines occur.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
Dangerous symptoms
The most dangerous symptoms of a cervical hernia include:
- partial or complete movement disorders - paresis and paralysis - they signal that the spinal cord has been damaged;
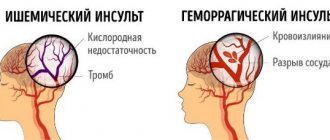
- a sharp sudden onset of dizziness, headache with nausea, vomiting and loss of consciousness - indicates a sudden disturbance of cerebral circulation, which can be complicated by the development of ischemic stroke.
If such symptoms appear, the patient must be hospitalized, so it is necessary to call an ambulance.
The mechanism of tachycardia
Over time, the process of damage to the spine and intervertebral discs necessarily affects the nerve pathways, of which there are a lot in the column. They emerge from the spine and connect the internal organs with the central nervous system. Mechanical irritation and compression cause swelling of the nerve bundles, as a result they generate pain, concentrated in the chest area. Most often, such secondary clinical symptoms appear during osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Symptoms of arrhythmia in osteochondrosis
The pain radiates to the left arm, back, and the fingers may go numb. Heart diseases also have the same clinical picture; this greatly worries patients and forces them to turn to cardiologists. But there is a difference between pain caused by heart disease and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Table. Types of cardiac pathologies depending on the cause.
| Type of heart pathologies | Causes and clinical description |
| Caused by heart disease | Most often, unpleasant sensations appear after excessive physical activity, untimely intake of medications, critical psycho-emotional stress, abuse or smoking. If pain or tachycardia has a clear cause in the patient’s inappropriate behavior, then they are associated with cardiac problems, you should urgently contact a cardiologist. And, of course, be more attentive to your health and follow all doctors’ recommendations. |
| Caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine | These unpleasant symptoms have nothing to do with the problems of the heart itself; they appear as secondary clinical signs of osteochondrosis. The reason is that there are many nerve bundles in the spine that begin with a connection with the heart. Such pains are reflex, they innervate the muscle. The organ itself is completely healthy, and all discomfort is a consequence of the underlying disease. The problems are long-term and increase as the load on the cervical spine increases. This could be ordinary walking or running, sudden tilting of the head, or pressing on the vertebrae. |
Pain due to hernia of the cervical spine
Acute pain from a herniated cervical spine is of two types: associated with compression of the spinal nerve roots - radiculopathy and headaches associated with cerebrovascular accidents and autonomic disorders.
In addition, patients may be bothered by constant aching pain that intensifies with various movements or after a long stay in the same position.
Symptoms of a cervical hernia include constant aching pain.
Cervical lumbago (cervical radiculopathy, cervicago)
The pain begins suddenly after a sharp turn or tilt of the head and is associated with pinching of the spinal nerve roots. The pain is very severe, patients compare it to an electric shock. This pain is most often localized on the back of the neck and spreads along the upper limb to the hand and fingers.
At the same time, a sharp spasm of the neck muscles occurs - the patient is unable to move his head. Severe pain does not allow movement, sometimes it is difficult for the patient to even talk, cough or sneeze. After some time, the pain may become less acute, but continues to be excruciating. Without medical help, it can last several hours or even days, and then over time become chronic with exacerbations and remissions.
Cervical migraine
These are attacks of painful unilateral headaches that develop against the background of vertebral artery syndrome. The cause of the sudden development of migraine may be tissue swelling or prolonged positioning of the head in the same position, followed by a sudden change in position.
Unlike classic migraine, in which the headache is associated with a sharp dilation of blood vessels and stagnation of blood, with cervical migraine there is compression of the vessels supplying the brain and the nerve plexuses surrounding them. The pain is one-sided, severe, and can begin either suddenly or relatively gradually. May have a pressing, tearing character. It often begins in the back of the head, then spreads to the eye socket, ear, teeth, and forehead. Accompanied by nausea, vomiting, visual and hearing impairment. The attack can last for several hours.
How to relieve pain
With a cervical lumbago, the patient should:
- lie down on a hard surface with a small pillow under your knees; or take a different position in which the pain is felt less;
- ask others to call an ambulance;
- take any painkiller orally: Analgin, Pentalgin, Ibuprofen, etc. You can apply pain-relieving ointments externally to painful areas: Voltaren, Fastum-gel, etc.
Voltaren, Fastum-gel, Analgin, Pentalgin, Ibuprofen will help get rid of cervical lumbago.
Emergency doctor:
- will give a painkiller injection; For this purpose, drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs are usually used; the most effective is Diclofencac;
- muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) are administered to relieve muscle tension;
- if this does not help, a paravertebral blockade is performed - an anesthetic (Novocaine, Lidocaine) is injected into the soft tissue near the exit site of the spinal roots.
If this does not help, the patient is hospitalized and an epidural block is performed - an anesthetic is injected into the space between the hard shell of the spinal cord and the bone of the spinal column.
For cervical migraine, the patient should:
- take the most comfortable position to help reduce pain during a spinal hernia; for most patients this is a supine position;
- ask loved ones to open a window or window - the patient needs fresh air;
- close the curtains on the window, reduce the number of sets, remove any sounds;
- take a painkiller - Analgin, Nise, Paracetamol.
If the pain does not go away for a long time, you can call an ambulance. The doctor will enter:
- intramuscularly any drug from the NSAID group - Diclofenac, Nise;
- glucocorticoid hormones (Dexamethasone) – will relieve tissue swelling and reduce constriction of the vessel;
- nootropic drugs – reduce tissue oxygen demand (Nootropil);
- drugs that improve blood flow - Pentoxifylline.
What is tachycardia
During this disease, the number of heartbeats at rest exceeds 90 bps. If such a fast rhythm is observed during a period of physical activity, then the phenomenon is considered not pathological, but normal physiological.
Increased heart rate with tachycardia
Important. Tachycardia is not a disease, but a symptom of many other pathologies. Most often it occurs due to problems of the autonomic or endocrine system and various forms of arrhythmia. Osteochondrosis can pinch nerve fibers and bundles located on the surface of the vertebrae. As a result, problems arise in the activity of the autonomic nervous system, and tachycardia appears. Depending on the cause, tachycardia can be sinus, paroxysmal and fibrillation. During osteochondrosis, sinus tachycardia occurs; its clinical signs will be discussed in this article.
Features of sinus tachycardia in osteochondrosis
The cause of disturbances in the physiological rhythm of the heart is distorted nerve impulses from the sinus node. Disturbances in its functioning appear as a result of irritating effects on nerve endings. Some patients may not notice a change in heart rate, while others may experience a feeling of fear and shortness of breath. Severe attacks contribute to increased sweating.
How is tachycardia related to osteochondrosis?
Patients should remember that regardless of the cause of tachycardia, it has the same negative impact on the body. With long-term pathology, the heart muscle may degenerate, the general blood supply to internal organs may deteriorate, etc. If there are problems with disturbances in the rhythm of contraction of the heart muscle, then physical and motor activity should be limited.
Possible complications
With osteochondrosis, the development of ventricular types of heart rhythm disturbances, which include tachycardia, is usually observed. Its atrial paroxysmal form is rarely diagnosed. The pathogenesis is based on organic damage to the heart muscle in combination with osteochondrosis. If left untreated, vertebral artery syndrome develops, which causes cerebral circulation disorders in the vertebrobasilar region. And this leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the cardiovascular system.
Symptoms of pathology
Tachycardia, as mentioned above, in most cases is not an independent disease, but a clinical sign of other complex disorders in the functioning of the body. During attacks, the patient complains of such problems.
- Unsharp and wave-like pain. They do not cause much inconvenience, but last for a long period of time. Symptoms may increase or decrease, depending on physical activity and head movements.
- There is a feeling of warmth in the chest, its character causes anxiety. Heat is not related to the parameters of the indoor microclimate or the weather outside; it occurs suddenly and for no apparent reason.
- The left arm weakens, it is impossible to lift the usual weights. In difficult cases, the little finger becomes numb, tactile perception disappears, and mobility is sharply limited.
How does tachycardia manifest?
Important. With such symptoms, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and take heart medications. This is a waste of time; it is necessary to eliminate the causes of unpleasant sensations - to treat osteochondrosis.
Modern diagnostics
Only experienced doctors can make an accurate diagnosis of the disease. Several methods are used for this.
- Novocaine blockade. Patients are given an injection of novocaine into the cervical spine. This manipulation blocks the passage of impulses from the nerve endings on the vertebrae to the heart muscle. If the tachycardia disappears, then this is an important confirmation of its cause. It is in severe stages of osteochondrosis that pathological changes in bone tissue and intervertebral discs cause compression of nerves and, as a result, tachycardia.
Novocaine blockade - Injections with distilled water . This medical procedure checks the connection between the nerve bundles of the cervical spine and the chest. If after the injection you feel warmth in your chest for some time, this also confirms the connection between tachycardia and osteochondrosis.
Water for injections
Another diagnostic method is palpation of the vertebrae. When the places near the exit of the nerve endings are compressed, the tachycardia intensifies, and all negative sensations increase. Based on a preliminary diagnosis, the patient should be sent for a thorough examination.
General recommendations for the treatment of osteochondrosis and the prevention of tachycardia
In order to speed up the process of treating osteochondrosis and cardiac arrhythmia, you must use the following recommendations:
- To refuse from bad habits;
- Diversify your daily diet with fresh vegetables and fruits, eat more products containing gelatin;
- Allow more time for rest and sleep;
- Systematically monitor your heart rate;
- Avoid stressful situations.
In addition, you should not:
Expose the body to high temperatures (visit baths and saunas, make hot compresses, take a hot shower). An increase in temperature can increase inflammation, speed up the heartbeat, increase blood pressure, cause swelling and increase compression of capillaries and nerve roots. Carry out massages yourself
Mechanical impact on the affected spine without the participation of a specialist can aggravate the situation. Take medications that affect the condition of tissues and the cardiovascular system without consulting a doctor. In addition, it is important to monitor your posture and avoid spending long periods in front of the computer. It is also recommended not to use a pillow and choose a firmer mattress.
Visit baths and saunas Perform massages Take medications Monitor your posture
Additional examinations for a final diagnosis
Depending on the patient’s condition and preliminary diagnosis, examinations using modern medical devices may be prescribed.
Computer diagnostics
Allows doctors to see the condition of the bone tissue of the vertebrae in a 3-D image. A CT scanner takes a large number of images at intervals of three millimeters, which are then processed by a computer program and collected into one image. The device provides high accuracy and allows medical workers to become familiar with the real condition of the cervical spine down to the smallest detail. The disadvantage of CT is the inability to diagnose the condition of soft tissues.
CT scan of the cervical spine
Magnetic resonance imaging
The most modern and safest examination method for the patient’s body. The image is obtained by capturing magnetic vibrations of soft tissue. The waves are recorded by special high-precision equipment and recorded on image media. Due to the fact that the nerve endings that cause tachycardia do not have bone formations, their condition can only be determined by MRI.
The use of traditional X-ray machines does not apply to modern methods of diagnosing problems with the cervical spine and is currently used only in poorly equipped clinics.
MRI of the cervical spine
Based on a complete diagnosis, doctors determine the cause of tachycardia. If pathological phenomena are provoked by osteochondrosis, then the innervation of the heart muscle is explained by the following factors.
- Nerve fibers associated with the autonomic nervous system are pinched. This distorts the nerve impulses entering the heart muscle; the strength and frequency of its contractions are not related to the actual needs and loads. If tachycardia is provoked by physiological impulses reflecting increased physical activity or a psychological state, then such a reaction is considered normal and is not considered a pathological condition.
- Associated problems with the left arm appear due to impaired blood flow. When osteochondrosis becomes complicated, not only nerve endings are pinched, but also blood vessels. Their lumen narrows, the nutrition of the arm muscles worsens. Medical science at this stage does not have proven information about the connection between hand numbness and other pathologies.
Stages of osteochondrosis
As practice shows, by carefully monitoring their condition, patients can help doctors correctly identify the cause of tachycardia. At the appointment, you need to tell us in as much detail as possible about your feelings: how the pain is changing, are there any associated problems. What might be of interest to the attending physician?
Types of cervical hernias
All manifestations of the disease depend on the direction in which the nucleus pulposus is displaced. Based on this feature, the following types of cervical hernias are distinguished:
- Dorsal
– the nucleus falls back into the canal where the spinal cord passes. They occur frequently and are divided into:- median
- the nucleus wedges into the spinal cord in the middle and compresses the spinal cord; the largest in size, accompanied by paresis and paralysis; - paramedian
- with deviation from the middle; causes pinching of two roots - at this and the following levels; accompanied by severe pain along the nerves - radiculopathy. - Foramial
- the nucleus pulposus wedges into the hole from which the spinal nerve root emerges and pinches it. Severe radiculitis pain along the pinched nerve. - Lateral
- causes pinching of the root at a given level, but less severe than foramial. The cervical vertebrae are small and there is practically no distinction between foramial and lateral species. - Ventral
- the nucleus moves forward without touching the spinal cord, so it does not manifest itself for a long time. Pain and decreased mobility gradually appear due to ossification of the ligaments. A rare type of cervical hernia. - Schmorl's hernia (vertical)
- the nucleus is wedged into the bone of a vertebra located above or below the hernia. It occurs mainly in children or with severe osteoporosis - loss of bone tissue due to loss of calcium. It is asymptomatic, but can sometimes cause vertebral destruction.
Also distinguished:
- diffuse (widespread) cervical hernia
- a large protrusion occupying half the circumference of the disc; - sequestered cervical hernia
- the separated segment enters the spinal canal; the most dangerous type of hernia.
What types of hernias develop in individual cervical discs
Lateral and foramial intervertebral hernias most often develop in the C6-C7 discs. They make up 60% of all hernias in a given disc. Median and paramedian hernias with movement disorders are much less common.
When the C5–C6 disc is affected, lateral and foraminal hernias with radicular pain are much less common, in approximately a quarter of cases. Here you can often find median hernias with significant motor impairments.
All types of posterior and lateral hernias occur on discs C4 – C5. On the upper discs, hernias are very rare and can have different directions.
Read about other types of spinal hernias here.
Each type of intervertebral hernia has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easy it is to get rid of a hernia in 10 sessions
Treatment methods
The goal of treating tachycardia in osteochondrosis is to eliminate the cause of the pathology. The course is prescribed by a doctor, the treatment is long and requires a lot of patience. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to achieve complete restoration of health through medication; in the most difficult cases, operative surgical methods have to be used.
Treatment of tachycardia in osteochondrosis
Drug therapy
Currently, medical science has developed quite effective drugs that make it possible not only to stop the development of pathology, but also to achieve noticeable restoration of damaged tissues.
Important. Angina pectoris with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine does not go away after taking painkillers. They do not block the nerve endings that cause heart rhythm disturbances; such drugs are prescribed only to relieve severe pain.
Differences between angina and heart pain due to osteochondrosis
Orthopedic products
There are special medical corsets that can reduce the load on degraded vertebrae and intervertebral discs. In addition, neck braces significantly limit the mobility of the vertebrae. Both effects have a positive impact on the patient’s well-being; this effect is achieved by reducing the degree of compression of nerve endings. But you should always remember that wearing support corsets for a very long time has negative side effects. The muscles do not take part in maintaining body weight and atrophy over time, which further aggravates the situation.
Neck corset for osteochondrosis
Important. It is recommended to use corsets only during periods of exacerbation of the disease; when the health status has stabilized, other methods of treating osteochondrosis should be used.
Ultrasound therapy
A traditional and quite effective method. Ultrasonic waves heat strictly defined areas of the spine located inside the body. An increase in temperature stimulates blood circulation - nutrition of damaged tissues improves, restoration processes in tissues are accelerated and activated. Modern ultrasound machines can specifically deliver drugs to limited areas of the vertebrae. This is very important when using aggressive medications that have critical side effects. Medicinal substances are supplied only to those areas that require drug treatment, all nearby tissues and internal organs are almost not affected.
Ultrasound for osteochondrosis
Reflexology
Also a traditional method for eliminating tachycardia in spinal osteochondrosis. The human body reacts differently to external stimuli and mechanical influences. In combination with properly selected medications, a significant improvement in the patient’s condition is observed. Reflexology includes mud baths, acupuncture and other neurostimulation methods.
Acupuncture
Therapeutic exercise and massage
As for therapeutic exercise and special massage, they should be treated with extreme caution; all manipulations should be performed only under the supervision of the attending physician. There are additionally several very strict requirements for massage.
- Massage should only be performed by a specially trained certified specialist with a medical education. The fact is that a large number of vital blood vessels and nerve endings are concentrated in the area of the cervical spine. Inept actions cause not only their mechanical irritation with the appearance of sharp pain syndromes, which in itself is very bad. There are frequent cases of vascular ruptures and pathological changes in nerve fibers. The consequences of such unprofessional interventions are very serious. Eliminating them requires a lot of time and money. But there are situations when it is impossible to restore tissue damaged during unprofessional massage, and a person becomes disabled for the rest of his life.
- At the slightest deterioration in health, the massage should be stopped immediately. Repeated manipulations are possible after an unscheduled examination of the patient and consultation with a doctor.
Neck massage
Massage can cause both very positive changes in the patient’s health and very negative ones.
Surgical treatment
The decision to undergo surgical intervention is made only in exceptional cases when the ineffectiveness of medication methods has been proven in practice or in case of a sharp deterioration in health. Patients must understand that such actions can have serious consequences, which are extremely difficult to eliminate in the future. If tachycardia significantly worsens the patient’s well-being, makes him unable to work, or is accompanied by severe pain, then only removal of the damaged areas of the spine gives hope for alleviating the condition. Tachycardia in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine rarely becomes a symptom for making a decision about surgical intervention.
Exercise therapy for herniated cervical spine
Why is therapeutic exercise so important for cervical hernias? The fact is that a feature of the intervertebral discs of an adult is the lack of blood supply. Nutrition to their tissues comes osmotically from the environment. But in order for the nutrient fluid necessary for metabolism in cartilage tissue to appear in the environment, muscles must work.
Only muscle work can maintain the discs in normal condition. With a sedentary lifestyle, and if you are still overweight, the discs are quickly destroyed. Exercise therapy also helps strengthen the muscles that support the spine, improves blood circulation and blood flow to the muscles, brain and spinal cord.
Therefore, complexes of therapeutic exercises are included in the treatment program immediately after pain relief. A set of exercises is selected by a physical therapy doctor and performed under the supervision of an instructor
Exercises for morning exercises
Together with an instructor, you can select a number of exercises for daily morning exercises, perform them under his supervision, and then continue exercising at home. Here are some exercises:
- lie on your back, relax and begin to clench and unclench your fists with force; do 20 times, relax, count to 20 and repeat;
- sit on a chair, hang your arms down and rotate your shoulders first in one direction, then in the other; perform 5 – 10 times; if difficult, 2 – 3 times;
- sit on a chair, back straight, arms hanging down; raise your arms first to the sides, then, without stopping, up, and then lower them in the reverse order; repeat 3 times.
By doing morning exercises, you can gradually increase the number of exercises performed and the number of approaches.
If pain occurs during the exercise, exercise should be stopped immediately. The next day it can be performed only if there is no pain and the load has been reduced.
Methods for preventing tachycardia in osteochondrosis
When sleeping, use special orthopedic mattresses and pillows. They enable the body to occupy a physiological position, due to this the risks of compression of nerve endings are reduced, and the degree of tachycardia is reduced. If the underlying disease is not in the acute stages, then tachycardia can completely stop during sleep.
Orthopedic mattress
The rule is always relevant: it is much easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. Tachycardia in osteochondrosis does not appear if the underlying disease is absent. And the risks of pathological changes in the bone tissue of the spine can be reduced through an active and correct lifestyle, physical education (but not high-performance professional sports), optimal nutrition and timely visits to the clinic for examination. In the early stages of the development of the disease, the appearance of tachycardia can be completely excluded; it makes itself felt in cases of serious pathologies of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
Rules for a healthy lifestyle