A stroke requires a lot of courage from the patient and a lot of patience and love from his loved ones. Because a stroke, or acute cerebrovascular accident, is the most dangerous disease of the cerebral vessels. It is characterized by the occurrence of motor, behavioral, mental, emotional and other disorders that disrupt the patient’s normal functioning.
A stroke is not a one-time event, but a process that develops in time and space - from minor functional changes to irreversible structural damage to the brain - necrosis.
What is insidious about a stroke? The fact that in the first stages of its development a person may not experience any pain. The arm and cheek become numb, speech changes slightly, and sometimes dizziness or blurred vision appears. Neither the patient himself nor his relatives suspect that a brain catastrophe is occurring. Precious time is missed: those six hours from the onset of the disease when adequate therapy can reduce the size of brain damage.
How does a stroke occur? A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, that is, a rupture, spasm or blockage of one of the brain vessels. Stroke is divided into hemorrhagic (cerebral hemorrhage) and ischemic (cerebral infarction).
Hemorrhagic stroke
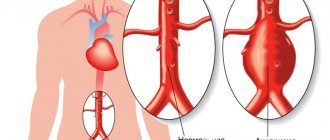
The most severe variant of the disease is hemorrhagic stroke.
It is a complication of hypertension. The blood vessel, unable to withstand the increased pressure on the wall, ruptures, and blood enters the brain matter. The resulting hemorrhage compresses the brain, causes swelling, and the area of the brain dies. This type of stroke occurs more often after a difficult, stressful day. By evening my head is splitting with pain. Objects begin to appear red, nausea and vomiting appear, and the headache gets worse - these are the harbingers of a stroke. Then movements, speech, and sensitivity are disrupted, and conditions ranging from mild stupor to loss of consciousness and coma arise—this is the stroke itself.
Rehabilitation after stroke
After being hospitalized for a stroke, many patients are left with problems with physical, speech, and mental function. However, in many cases the brain has great potential for recovery.
The rehabilitation process plays a critical role in helping patients regain lost skills so that the patient can regain independence and maintain quality of life. With active, timely, painstaking daily work, these prospects for improving the condition can become even better. Rehabilitation can continue for years after a stroke, but for many patients it occurs most quickly in the first year after the stroke.
This is why it is important for medical specialists - neurologists, physiotherapists, speech therapists and others - to begin working with the victim as soon as possible after a stroke.
A multifunctional medical center is able to offer not only the help of highly qualified specialists, but also has a modern diagnostic base for monitoring the patient’s condition during rehabilitation after a stroke in Moscow, as well as assessing the risks of developing a recurrent stroke, since the proportion of recurrent strokes is high and leads to increased disability or death outcome.
Consequences of a stroke
People come to the clinic for rehabilitation of the consequences of both ischemic and hemorrhagic types of stroke. Depending on which area of the brain is damaged, a stroke can cause the following types of dysfunction:
- Paralysis, paresis
- Pain or loss of sensation
- Problems with speech recognition and articulation
- Cognitive disorders (thinking, memory)
- Emotional disorders
- exacerbation of diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory, excretory systems, etc.
- Bedsores and their complications in the absence of proper care for a bedridden patient
- swallowing disorders (dysphagia), etc.
Recovery stages
Conventionally, the rehabilitation period after a stroke is divided into several stages:
During the acute period
the main task is to maintain the basic functions of the body and preserve the life of the patient in the hospital.
Early recovery period
in the first six months after a stroke, it is especially important to restore the patient’s motor skills and cognitive abilities - passive gymnastics, massage, breathing exercises and speech restoration classes.
Late recovery period
from six months to a year is characterized by daily supportive sessions with specialists.
Remote period
after 1 year allows one to judge the results achieved in previous periods and the degree of restoration of the functions of dead brain cells.
At each stage, continuity and regularity in the organization of rehabilitation measures are important.
What to do after a stroke - types of rehabilitation
Medication correction
is selected by the attending physician in the hospital and can then be adjusted by the supervising neurologist. Drugs are used to help relieve symptoms - analgesics, muscle relaxants, sedatives, as well as drugs that help restore and maintain current processes in the patient's body - improve cerebral blood supply, activate metabolic processes, restore brain cells, etc.
Physiotherapy
promotes positive dynamics in restoring processes in the brain and preventing the worsening of negative consequences.
In complex therapy, the best results are shown by electrophoresis with drugs; circulatory insufficiency of the affected brain is well eliminated with the help of regular courses of electrical myostimulation; both darsonvalization and magnetic therapy are used for the affected limbs.
Acupuncture
Safely and effectively helps launch self-healing and self-regulation processes. The advantage is that the procedures can be performed even on bedridden patients.
Neuropsychologist and psychologist
with the help of certain techniques they can relieve symptoms of anxiety and apathy in the patient, and adjust the psychological mood.
Massage
after a stroke, it is indicated in the absence of complications for patients with ischemic stroke, starting from the early recovery period.
Physiotherapy
(exercise therapy) promotes the recovery process, the development of new conditioned reflex connections, including compensatory mechanisms for functional restoration.
Hirudotherapy
prescribed only for ischemic stroke. Substances contained in the saliva of leeches contribute to the rapid restoration of brain vessels, strengthening the walls of blood vessels, which prevents recurrent strokes.
Factors influencing the success of rehabilitation
Several factors play a role in successful rehabilitation after stroke:
- The degree of damage to brain tissue. The smaller the damage, the more dynamic the recovery.
- Patient's emotional state. A person's positive attitude after a stroke can help them cope with difficulties and focus on getting better.
- Support from relatives. Maximum support for the family is to provide not only proper care, but also reassure the patient of his need and importance for the family.
- Time before the start of rehabilitation. Rehabilitation should begin as soon as possible after a stroke. Even simple tasks such as exercising paralyzed muscles and turning a person over in bed should begin very soon after a stroke. Stroke rehabilitation is most successful when it is a team effort. The stroke patient and family must work with their physician and other rehabilitation specialists.
Stroke does not go away without leaving its mark, and rehabilitation is the key to achieving small victories along the road to recovery.
Advantages of visiting the Miracle Doctor clinic
24-hour hospital
Preventive, therapeutic and rehabilitation procedures can be carried out in comfortable rooms.
Comprehensive examination
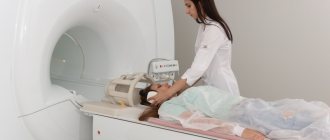
A full range of tests, vascular ultrasound, CT and CT angiography, MRI, ECHO-CG, Holter ECG monitoring and other studies are performed immediately after the appointment.
Interdisciplinary approach
Highly qualified clinic specialists (cardiologists, neurologists, therapists, endocrinologists) can interact on site, which allows achieving results comparable to the effect of a patient being in a rehabilitation center after a stroke.
Individual approach
Each stroke case is unique, so all types of rehabilitation are selected individually.
Woman after 45 years: disaster or new life? Part 1
For a modern woman after 45 years of age, life is just beginning. By this age, as a rule, a career has already been built, children have grown up, sufficient life experience has been accumulated, and the time comes to live freely and enjoy the fruits of your many years of work. In other words, a woman at this age experiences a “rebirth.” And more than ever at this time, she wants to be healthy, active, beautiful, full of strength. But it is precisely during this period that female physiology comes into its own, and the age of 45+ can become not a “second birth”, but real torture. "What is happening to me? Why have I changed so much? Why do I explode for no reason? The slightest trouble makes me angry. I don't sleep well, I constantly yell at my husband and children. And every day it becomes more and more scary to look in the mirror. Is it really coming... menopause?
Such thoughts occur to many women who have reached adulthood. Of course, modern women are much more educated in matters of their physiology than the fair sex who lived 70 or 100 years ago. Modern women are familiar with such concepts as ovulation, fertility, menopause, menopause. But in reality, for most of them, this knowledge turns out to be absolutely superficial, built on myths, rumors and stories from friends and colleagues. Therefore, for a large number of women, the onset of menopause marks the beginning of the end, a kind of tragic point, after which a woman loses her purpose and, in essence, ceases to be a woman.
Menopause is shrouded in so many myths that women are often truly afraid of its onset. Today in our article we will talk about what menopause is and whether it is really that terrible. The gynecologist-endocrinologist at the Smitra Clinic, Vita Vitalievna Andolenko, will help us understand this difficult issue and also tell us about the secrets of women’s health and longevity.
In a woman’s life, there are two main critical biological periods: the period of formation of the reproductive function, when the girl’s body is just preparing for childbirth, and the period of extinction of this function, that is, the very menopause.
You need to understand that menopause does not occur in one day. This is a long, multi-stage process that takes place over many years, and each woman experiences it individually.
Traditionally, there are three stages in the menopausal period:
1.
Premenopause
– the beginning of the menopause.
The main manifestation of this period is disruption of the menstrual cycle, too heavy or scanty menstruation. 2. Menopause
is the last period in a woman’s life.
Diagnosed after the fact, provided there is no menstruation for 12 months. 3. Postmenopause
– a woman’s life after menopause
What happens at this time in a woman’s body?
With the onset of the premenopausal period, the number of follicles in the ovaries gradually decreases, and as a result, the level of the female hormone estradiol decreases.
Estradiol is the main female sex hormone from the estrogen group.
Estradiol is considered a female hormone, as it is the “creator” of female beauty and health. Thanks to this hormone, a woman’s waist becomes thin, her voice becomes high, her skin becomes smooth and soft, her mammary glands become enlarged, and her hips become rounded. Estradiol is also responsible for libido (sexual desire) and turgor (firm and elastic state) of the skin and mucous membranes. As the doctor notes, there is no need to worry about a decrease in estradiol levels during menopause, because its function is partially taken over by hormones that continue to be produced by the adrenal glands. In addition, an excessive amount of estradiol during this period can even be dangerous for the female body and is extremely undesirable: excessive production of estradiol at this time can lead to uterine bleeding and endometrial hyperplastic processes.
During the physiological course of the premenopausal period, the woman’s physical well-being does not suffer. Of course, a decrease in estradiol can cause some unpleasant symptoms, but they can be easily managed. Here are some tips from the doctor:
- if the skin has lost its elasticity
, has become flabby and uneven - this is a symptom of a decrease in its turgor, which can be compensated for by special care products - creams, serums, gels, and various cosmetic procedures. - discomfort in the intimate area
, such as dryness, difficulty during sexual intercourse associated with a lack of female lubrication, can be eliminated with the help of water-based lubricants, as well as ointments and suppositories containing estriol (used strictly as prescribed by a doctor).
Unfortunately, a woman's menopause does not always go smoothly. Vita Vitalievna told us in what cases a woman definitely needs to see a doctor.
1) Onset of early menopause (up to 44 years of age)
. Menstrual function usually subsides around the age of 50. If this process occurs much earlier, a doctor’s consultation is necessary! In this case, bone tissue density sharply decreases, that is, osteopenia and osteoporosis develop, which leads to fractures (femoral neck, vertebrae) and, as a consequence, to disability. The doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate medications.
2) Deterioration in quality of life.
Let us repeat once again that physiologically occurring menopause does not cause significant changes in a woman’s physical condition. The occurrence of hot flashes (sudden attacks of heat), chills, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating) and tachycardia is a symptom of severe estrogen deficiency and requires mandatory drug correction.
3) Pain in tubular bones
(phalanxes of fingers, wrists, feet) and projections of large joints (knee, hip, ankle joints) are a serious indication for X-ray densitometry - diagnosing bone density and the likelihood of fractures. This diagnostic method will confirm or exclude the presence of osteoporosis in a woman and, accordingly, prescribe timely treatment.
4) Weight gain.
The appearance of extra pounds after the cessation of menstrual function is a common problem. If a woman watches her diet, and the scale shows a higher number every day, this is a reason to consult a doctor. The examination in this case will be aimed at excluding insulin resistance - a harbinger of diabetes mellitus and its timely correction.
5) Bladder problems
. Frequent urination, urinary incontinence when laughing, coughing, or physical activity are common companions for women over 45 years of age. Such manifestations are not directly related to a deficiency of female hormones, but often appear in adulthood and require consultation with a doctor and appropriate treatment.
But even if a woman goes through menopause without any problems, she still needs to see a doctor, especially if menstrual function begins to fade early (before 44 years of age). Continue reading in the next article.
The material was prepared with the participation of Vita Vitalievna Andolenko, gynecologist-endocrinologist of the SMITRA Clinic.
© 2010-2020 SMITRA. All rights reserved. No material on this site may be copied or used without written permission except for private, non-commercial viewing.
Differential diagnosis of neck pain
As a rule, most back pain is associated directly with changes in the discs (protrusion, disc herniation), however, for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to use medical imaging methods.
Differential diagnoses include:
- Cervical spondylosis.
- Traumatic prolapse of an intervertebral disc.
- Neck pain: acute neck strain, postural neck pain, or pain associated with whiplash injury
- Headache.
- Referred pain - for example, from the shoulder.
- Malignancies: primary tumors, metastases or myeloma.
- Infections: discitis, osteomyelitis or tuberculosis.
- Fibromyalgia.
- Vascular insufficiency.
- Psychogenic neck pain.
- Inflammatory diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Metabolic diseases: Paget's disease, osteoporosis.
Diagnosis of disc protrusion
Neck pain from radiculopathy and the absence of red flag symptoms usually do not require imaging or other special tests. However, for verification purposes, the doctor may prescribe the following research methods:
Blood tests
may be prescribed to exclude infectious or inflammatory diseases (a decrease in hemoglobin may be a sign of anemia; an increase in ROE may be a sign of both infection and inflammation; the level of rheumatoid factor and HLA-B27 determination may indicate systemic connective tissue diseases).
Medical imaging tests are very important, but they must be interpreted in light of the clinical picture, since positive results are quite common in people without any complaints:
• Radiography
. Plain x-rays of the cervical spine can be used to evaluate chronic degenerative changes, metastatic tumors, infection, spinal deformity, and motion segment stability. Interpretation of study results is often difficult because degenerative signs are almost universal in people over 35 years of age.
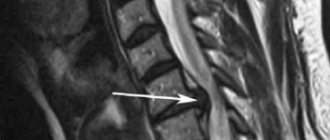
• MRI.
This imaging method may be prescribed if radiography does not allow the genesis of symptoms to be determined. MRI should be performed to diagnose disc protrusion (herniation) and the presence of compression of nerve structures.
• CT myelography
can be used if there are any contraindications to MRI.
•EMG (ENMG
) - these methods can be informative in the presence of radiculopathy or the need to determine the level of damage and differentiate cervical radiculopathy from nervous compression syndromes.
Causes
- Degeneration or wear that leads to disc failure.
- Repetitive flexion (extension) and twisting movements, especially in combination. These movements have the greatest impact on the outer annulus fibrosus of the disc.
- Discs are most susceptible to injury in a sitting or bending position because pressure on the disc is shifted anteriorly and the vector of force forces the contents of the disc posterolaterally toward the thinner, weaker portion of the annulus fibrosus.
- Fall or injury such as a car accident.
- Repetitive stress injuries from overhead work or weightlifting.
- Genetic factors may, to a certain extent, contribute to the early development of degenerative changes in the discs (osteochondrosis).
- Smokers are more likely to develop early disc degeneration
- Infection (discitis)