Electrocardiography is a method that allows you to record and study the electrical fields generated during heart contractions. This type of instrumental examination is prescribed to patients of various age categories. An ECG is performed on a child for preventive purposes and if there are certain indications. Interpretation of ECG in children is more complex than in adults. This is explained by the age characteristics of young patients. To make a correct diagnosis during the procedure, the specialist must strictly adhere to the rules of the study. This will help obtain the necessary data for diagnosing a particular disease.
How is an ECG performed?
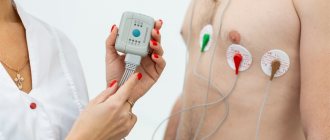
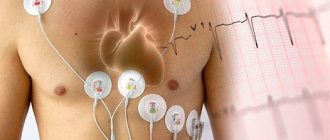
The ECG procedure is a diagnostic method during which special sensors are attached to the patient's body. With their help, electrical potentials that arise during heart activity are recorded. The pulses pass from the sensors to the electrocardiograph, which converts these signals into a graphic recording in the form of vibrations on special paper. The obtained result of the study is a cardiogram.
Children's ECG is often used to prevent birth defects in the maternity hospital and in the first year of life. At older ages, the test is prescribed to patients when symptoms are detected that indicate possible heart problems.
During the procedure, the baby is undressed down to his underwear and placed in a horizontal position. During this period, the mother is allowed to be with the child. Sensors are attached to the wrists, legs and 5 to 8 leads on the chest. The whole procedure takes from 5 to 15 minutes.
Decoding the results
ECG results are available almost immediately. When performing electrocardiography on a traditional device with recording the results on paper or when analyzing the ECG of a baby under the age of 1 year, the doctor will need some time to decipher the results. When using a computer electrocardiograph, a conclusion with calculations of all the main parameters of the cardiogram is issued almost instantly. ECG recordings in this case are stored in the form of computer files that can be viewed and printed. In the case of analyzing the cardiogram of children under 1 year of age, if deviations from the norm are found in the cardiogram, the help of a cardiologist may be required to decipher and interpret the cardiogram.
In some cases, a repeat electrocardiographic study or a special type of ECG may be required, accompanied by other types of studies (ultrasound of the heart, Doppler sonography of blood vessels).
What information does the method provide?
In addition to the characteristics of heart contractions (frequency, rhythm, regularity), electrocardiography allows you to determine the following conditions in a baby:
- decreased metabolism, lack of potassium, magnesium, calcium and other components;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- myocardial infarction, myocarditis;
- enlargement of certain areas of the heart muscle;
- decreased cardiac conductivity, rhythm disturbance;
- angina pectoris, embolism, arrhythmia;
- disturbances of metabolic processes in the myocardium under the influence of diseases, internal and external factors.
Using electrocardiography, it is possible to diagnose many heart pathologies in children and adults.
The advantages of ECG include relative cheapness and practicality. The procedure does not require special preparation. The method does not cause harm to health or negative consequences even with repeated use.
Important! Electrocardiography is a type of instrumental research that is essential for the work of pediatric and adult cardiologists.
What is special about performing an ECG in children?
Sometimes, after listening to the heartbeat of their baby, young mothers panic when they discover that the child’s heart beats much faster than that of adults. You should not be afraid of this, since the work of the heart in young patients has its own characteristics. For a child, the established norm of heart beats per minute is from 130 to 170. In adolescents, the pulse slows down to 60-80 beats. Features of ECG in children are that the indicators of a newborn, infant and adolescent may deviate from the norm. When interpreting the cardiogram, the cardiologist takes into account the patient’s characteristics. Each age group has its own permissible deviations, which must be taken into account when making a diagnosis.
It is recommended that ECGs be performed for children in medical institutions with high-quality equipment and highly qualified workers.
Special types of electrocardiography
In some cases, as prescribed by a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist, special electrocardiographic studies may be prescribed for older children.
Bicycle erogmetry (stress test): when a cardiogram is taken during dosed physical activity (rotating the pedals of an exercise bike). This study allows you to see how a child’s heart reacts to physical activity.
Holter monitoring : For an in-depth study of arrhythmias, a long-term ECG recording of 15-20 minutes may be required. To identify hidden disturbances in the blood supply to the heart and the rhythm of its work over a long period of time, ECG Holter monitoring is used. In this case, electrodes are attached to the child's skin, and a small computer-cardiograph is hung on the child's neck or belt, which constantly records the ECG.
Indications for using the method
Electrocardiography is often performed on children before discharge from the maternity hospital. The procedure is being carried out due to the increasing incidence of congenital heart defects in children. Doctors recommend doing an ECG for a child if the following signs appear:
- heart murmurs;
- dizziness, headaches;
- cases of loss of consciousness;
- fast fatiguability;
- the appearance of pain in the chest;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- development of swelling of the extremities.
These symptoms often indicate a malfunction of the heart muscle or the functioning of other internal organs. To exclude possible complications, you should undergo a medical examination using an ECG and other diagnostic methods.
Make an ECG for a child at the Paracelsus clinic, Aleksandrov
ATTENTION:
Online consultations with doctors (more than 18 specialties) are available.
Electrocardiography
of a child in pediatrics is a screening method that is used to analyze the functioning of the cardiovascular system. ECG for children is a highly informative type of research in pediatric cardiology, as the first stage of examination. The functioning of the cardiovascular system in children of different ages has many features. Therefore, it is important that the ECG results are interpreted by a competent pediatrician or cardiologist.
Is preparation necessary?
No special preparation is required before the procedure. Shortly before the examination, it is worth taking care of the normal moral state of the baby. To do this, you need to eliminate stress and excessive emotional experiences of your child.
Before conducting an ECG on a child, you should explain to the child what the essence of the procedure is.
To prevent your child from being scared at the doctor’s office, you should simulate the upcoming procedure at home, play doctor, and explain to your child how the examination will take place. You can show the electrocardiography process on video. It is possible to record an ECG in children under one year of age during sleep, but this can be done extremely rarely.
Important! The reliability of the data obtained during an ECG will directly depend on the moral state of the child during the procedure. The calmer the baby is, the more accurate the information obtained during the study will be.
Preparing a child for an ECG
Preparing your child for an electrocardiogram does not require restrictions on food and drink: your child can eat and drink as usual. It is recommended to feed the baby a few minutes before the test to calm him down. For an older child, you can take his favorite toy with you for research.
Your baby's skin should be clean: You should not apply any cream, lotion, powder or baby oil to your baby's skin on the day of the test.
The child's clothing should allow electrodes to be attached to the child's chest, wrists and ankles. Infants will need to be swaddled as directed by the nurse to ensure they remain still during the examination.
Basic ECG indicators
The cardiogram is deciphered exclusively by a specialist. Basic information for making a diagnosis is obtained taking into account such ECG components as waves, segments and intervals. At the same time, their presence or absence, height, location, duration, sequence and direction are assessed.
The basic concepts of ECG include:
- sinus rhythm of the organ. This is the name given to the rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle, which occurs under the influence of the sinus node. These data make it possible to assess the coherence of contraction of the ventricles and atria, the sequence of this process;
- heart rate (HR);
- source of excitation. In a healthy person, nerve impulses diverge from the sinus node throughout the nervous system. In some diseases, migration of the pacemaker to other parts of the organ is observed, for example, to the ventricular, atrial or atrioventricular node. These deviations can be diagnosed by examining the P wave;
- cardiac conduction. Under normal conditions, electrical impulses propagate from one pacemaker to the next without changing the order;
- electric axis. The data is calculated based on the analysis of the Q, R and S waves in the first, third leads. The information allows you to assess the functioning of the His bundle.
To assess the condition of various parts of the heart, special symbols in the form of Latin letters are used
To make a diagnosis and identify certain abnormalities in the functioning of the heart, the teeth are used. In the diagram they are displayed in capital letters:
- T – indicates the process of relaxation of the ventricles of the heart;
- P - speaks of contraction and relaxation of the atria;
- Q, S – indicates excitation of the septum between the ventricles of the organ;
- R – excitation of the ventricles themselves.
The PQ interval determines the time it takes for an electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
The segments on the cardiogram are as follows:
- TR – relaxation of the heart in the interval between contractions;
- ST – peak of ventricular excitation;
- QRST – ventricular contraction time.
Above are only the main indicators used by a specialist when making a diagnosis.
Physical foundations of electrocardiographic research.
An electrocardiograph is a galvanometer device for recording the difference in electrical potentials between two areas of the heart’s projection onto the surface of the child’s body. During operation, the electrical activity of the heart constantly and rhythmically changes. For each stage of contraction or relaxation of the heart muscle of each section, there is its own unique “electrical” pattern, which is recorded by an electrocardiograph and issued in the form of a characteristic graph - a cardiogram on a strip of paper or a computer screen. The shape and parameters of the characteristic elements of the cardiogram (main intervals, amplitudes, shapes and sizes of teeth) carry information for the doctor about the normal or pathological physiology of the heart. The number of waves per minute on the graph shows the heart rate, the distances between identical elements of the cardiogram - heart rate. ECG waveforms show how the heart's electrical impulses are formed and how well the individual parts of the heart work together. Characteristic changes in the shape of the size and position of the waves on the cardiogram carry information about any damage to the heart.
Electrical activity from the surface of the body is recorded through small metal plates (electrodes) that are placed in specific places on the child's chest, arms and legs. The electrodes are connected to the cardiograph by wires through which information is recorded. The electrocardiograph records the electrical activity of the heart, all parameters that are measured, analyzed and printed for the doctor.
Normal indicators in children
After electrocardiography, the absence of heart disease is indicated by the following indicators:
- heart rate – children under 3 years old from 100 to 110 beats/min, children 3-5 years old – 100 beats/min, 6-8 years old – from 90 to 100 beats/min, 9-12 years old – 70 – 85 beats/min min;
- QRS segment – from 0.06 to 0.1 s;
- wave P – not higher than 0.1 s;
- PQ – within 0.2 s;
- QT – no more than 0.4 s.
Important! Electrocardiogram readings may differ depending on certain features. This can be affected by the time of day, the moral state of the patient, incorrect application of electrodes, and more.
Dangerous diseases
Based on the cardiogram indicators, the doctor can determine this or that disease in the child.
Heart rhythm disturbances
In medical practice, this condition is called extrasystole. In this case, the patient periodically feels an increase in heart rate with its subsequent freezing. Extraordinary contraction is caused by impaired conduction of cardiac impulses.
Many children have heart disease diagnosed immediately after birth using electrocardiography.
In rare cases of arrhythmia attacks, there is no danger to health. Attention should be paid to regularly recurring disturbances in heart rhythm, accompanied by shortness of breath, pain and other negative symptoms.
Arrhythmia
With this pathology, changes in the periodicity of sinus rhythm occur, while the arrival of cardiac impulses occurs at different frequencies. Arrhythmia is sometimes asymptomatic and does not require special treatment. Only in 30% of cases does this condition cause serious health consequences. On the ECG, arrhythmia is manifested by the following deviations:
- the distance between RR intervals is more than 0.16 sec;
- adjacent RR intervals are marked;
- between cardio intervals from 0.3 to 0.6 sec;
- the difference between successive RR intervals is more than 62%;
- the difference between the maximum and minimum RR interval is 780 ms over a recording time of 5 minutes.
Bradycardia
The disease is a type of arrhythmia, with the patient experiencing a decrease in heart rate to 60 beats/min or lower. Sometimes bradycardia is explained by recording an ECG during sleep. Patients with a heart rate less than 40 beats/min experience dizziness, lethargy, fainting, difficulty breathing and other unpleasant symptoms.
Bradycardia is characterized by certain abnormalities on the ECG
Tachycardia
Unlike bradycardia, this disease is accompanied by an acceleration of the heart rate. Temporary tachycardia can be caused by severe physical exertion, psycho-emotional overload, infectious and viral diseases, accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Depending on the age of the child, the following indicators indicate tachycardia:
- newborns – above 170 beats/min;
- children under one year old – above 160 beats/min;
- children under 2 years old – above 155 beats/min;
- 4-6 years – above 125 beats/min;
- 6-8 years – above 118 beats/min;
- 8-10 years – above 110 beats/min;
- 10-12 years – 100 beats/min;
- 12-15 years – above 95 beats/min.
When an ECG indicating the presence of tachycardia is obtained, a repeat study is often performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Cardiac conduction disorder
Normally, the main part of the heart through which electrical impulses pass that excite the atria and ventricles is the sinus node. If this process is disrupted, the patient feels weak, the child experiences a decrease in motor activity, dizziness, lethargy, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
Important! The above and other heart diseases require immediate medical treatment, as they cause serious complications, sometimes incompatible with life.
ECG monitoring in children
To obtain detailed information about the functioning of the heart muscle, ECG monitoring has recently become increasingly common. Diagnosis is performed using special devices that continuously record ECG readings. The method is used among adults and children.
ECG monitoring is a common method for diagnosing heart disease in adults and children.
The purposes of ECG monitoring include:
- detection of heart rhythm disturbances in patients at risk (with heart defects, cardiomyopathies, pulmonary hypertension and other conditions);
- making a diagnosis if a child experiences heart pain, weakness, low motor activity, or loss of consciousness;
- assessment of the frequency of recurrences of previously identified cardiac dysfunctions;
- assessing the effectiveness of therapy for diseases.
Electrocardiography in a child can detect many heart diseases. With the correct use of the method and competent interpretation of the data obtained, it is possible to make a diagnosis and select the necessary treatment for a particular patient.
Electrocardiographic monitoring of the heart condition in a child
As your baby develops from fetus to newborn, infant to child, teenager to adult, the body's growth and development causes major permanent changes in the size and position of your baby's heart. The most dramatic of these changes occur at birth and during the first year of life. Unfortunately, not all children undergo such significant changes in the body without complications. Therefore, doctors recommend regular preventive electrocardiographic monitoring of your child’s heart function. Early detection of pathology or a predisposition to it will allow you to choose and carry out the required treatment with maximum effectiveness, or make sure that your child is healthy and his body is developing without deviations from the norm.
Remember that if any abnormalities are detected on the ECG, further examination of the child’s cardiovascular system is recommended. Also, all children with detected changes on the ECG are subject to dynamic monitoring by a pediatric cardiologist.
Electrocardiography is an informative, fast and safe method of studying the condition of a child’s heart, which allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis and carry out the required treatment with maximum efficiency, or get rid of worries and doubts about the state of your baby’s health.
To obtain additional information about electrocardiography for a child, you can sign up for diagnostics at a medical center by calling +7 (812) 331-24-22.