What do the indicators mean?
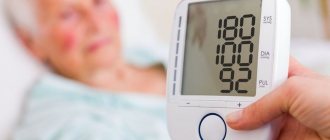
Normal blood pressure readings are 120 to 80 mmHg. Art. Deviations in one direction or another may indicate the onset of a disease or characterize individual physiological characteristics.
For pregnant
During pregnancy, it is recommended to monitor blood pressure daily. If it decreases, this may indicate problems with bearing the fetus or the appearance of diseases in the expectant mother.
In the first trimester, blood pressure levels can be affected by changes in hormonal levels.
The blood supply to blood vessels in a pregnant woman may decrease due to hypoxia. Lack of oxygen negatively affects the development of the fetus, since with constant oxygen starvation the child may be born with pathologies.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to track low blood pressure. It often falls during sleep. Therefore, doctors recommend eliminating all possible factors that could affect it.
For adults and seniors
As you get older, many body functions deteriorate. Therefore, in old age, the functioning of the vascular system, heart, joints, liver, brain, kidneys, etc. is often disrupted.
If you had low blood pressure in your youth, then in old age it returns to normal, but this is subject to a healthy lifestyle.
The pressure may decrease with sudden movements, for example, when changing body position. At this time, a person experiences stars in his eyes, tinnitus, and sometimes faints. Falling can cause serious injury as you age.
Despite the fact that hypertension carries more dangers, hypotension should also not be left to chance. Indeed, in its presence, the blood supply to vital organs suffers, especially in the brain. Cell death occurs, which leads to the development of such dangerous diseases as:
- ischemic stroke;
- dementia - senile dementia, etc.
To prevent hypotension from developing in older people, they need to move more often and not stay in bed for a long time. But sometimes this cannot be avoided, for example, in case of illness, injury or after surgery. In this case, you need to get out of bed slowly to avoid dizziness.
And also read on our website: What does blood pressure 190 over 120 mean - causes, symptoms, what to do and how to bring down high readings?
In some cases, blood pressure drops sharply when you overdose on hypertension medications. Therefore, you should not take these medications without a doctor's prescription.
For children and teenagers
In children, everything depends on the physiological characteristics of the growing organism. According to the standard, the children's norm is considered to be 90–92% of adult blood pressure.
Thus, children under 10 years old can have an average pressure of 100 over 60, and after 10 years – 110 over 70 mmHg.
The indicator can also be affected by the child’s gender, place of residence, lifestyle, heredity, etc.
Therefore, a reduced blood pressure of 80 to 40 may be one of the physiological hallmarks. This is due to the structural features of the nervous system and does not affect well-being.
If a child suffers from hypotension due to chronic diseases, then insufficient vascular blood supply is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Weakness, loss of appetite.
- Decreased activity, dizziness.
- Headaches.
- Tendency to collapse and fainting.
- Disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Possible complications of low blood pressure during pregnancy
In pregnant women with hypotension, as with other vascular disorders, gestosis often (in 25% of cases) develops (the appearance of edema, protein in the urine, increased blood pressure). In this condition, in patients with hypotension, blood pressure may not exceed normal values (120/80 mmHg), but it will be 30% higher than the initial one, and this is considered to be a pathology. As already mentioned, such patients are more likely than healthy women to develop early toxicosis of pregnancy with arterial hypotension.
The main complications of pregnancy with arterial hypotension include its spontaneous termination. With this disease, it is observed at various stages of pregnancy 3-5 times more often than in healthy women. The opposite effect is also noted: in women who remain in bed for a long time due to the threat of miscarriage, blood pressure steadily decreases, apparently due to muscle inactivity.
Arterial hypotension contributes to intrauterine growth retardation due to reduced uteroplacental blood flow.
In patients with arterial hypotension, complications of labor are often observed; they are mainly associated with impaired contractility of the uterus. This creates difficulties in the management of childbirth and promotes the expanded use of surgical methods of delivery (caesarean section) in order to provide assistance to the suffering fetus. Childbirth is often accompanied by bleeding.
Symptoms and signs
The main danger of hypotension is organ hypoxia, when they do not receive the required amount of oxygen. Nerve cells are primarily affected. With chronic low blood pressure, cerebral circulation suffers.
This is manifested by the following signs:
- dizziness appears, mental abilities and memory decrease;
- pulse increases to 80 beats per minute and above;
- frequent fainting and interruptions in cardiac activity;
- headaches and visual disturbances;
- overall performance decreases;
- rapid fatigue even with minor physical and mental stress;
- It gets dark before your eyes, and you get a feeling of flies flickering.
There is also a violation of the filtering ability of the kidneys, which leads to disturbances in the outflow of urine. This causes the accumulation of waste and toxins in the body. This condition manifests itself as bags under the eyes and a puffy face.
Hypotension: symptoms of the disease
Arterial hypotension as an independent disease (it is also called neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type) is a typical vascular neurosis. The onset of the disease can often be associated with neuropsychic trauma, emotional stress, and fatigue.
In cases where arterial hypotension is manifested only by a decrease in blood pressure, and there are no complaints or discomfort, it is classified as stable
(
compensated
) stage of the disease.
Unstable
(
subcompensated
) stage of the disease, in addition to a decrease in blood pressure, is manifested by other symptoms. Patients usually complain of headache, dizziness, general weakness, palpitations, discomfort in the heart area, sweating, memory loss, decreased ability to work, chilliness of the hands and feet, and meteosensitivity (deterioration when the weather changes). Some women experience so-called orthostatic phenomena: when getting out of bed, they experience dizziness, darkening of the eyes, even fainting. Fainting of a non-orthostatic nature can develop during an exacerbation of the disease or occur against the background of good health. Patients often develop irritability, emotional instability, and a tendency toward low mood.
Decompensated
arterial hypotension is characterized by hypotensive crises, easily occurring fainting, sleep disturbances, the appearance of acrocyanosis (bluish coloration of the fingertips, nose, lips, earlobes), loss of ability to work.
Hypotonic crises can last several minutes. During a crisis, blood pressure drops to 80/50 mmHg and below, headache and dizziness intensify, and vomiting may occur; patients feel severe weakness, a feeling of stuffy ears; A short-term loss of consciousness may occur, the skin and mucous membranes turn pale, and cold sweat appears. Fainting often develops in a stuffy room, in transport, after excitement, or during prolonged standing. Fainting is a fairly common occurrence in pregnant women.
In patients with arterial hypotension, blood pressure does not always remain persistently low: periodically it can reach normal and even elevated numbers - for example, when excited, upon admission to the hospital. However, it is rapidly declining.
Women with hypotension more often have an asthenic build (tall, thin) with pale skin. Almost half of them have varicose veins in their legs. The arms and legs feel cold to the touch, the pulse is somewhat lower than usual (about 60 beats per minute). No changes were detected during cardiac examination, including electrocardiography.
Causes
Most often, blood pressure decreases due to cardiovascular diseases. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, metabolic disorders, infections, and poisoning of the body with drugs or alcohol can also affect this indicator.
And also read on our website: What does blood pressure 190 over 100 mean, the reasons, what to do with it and how to reduce it at home?
In pregnant women
During pregnancy, a number of the following factors can affect the decrease in blood pressure:
- Toxicosis in the first trimester, accompanied by vomiting and loss of fluid.
- In the second half of pregnancy, inferior vena cava syndrome may appear. It occurs due to the growing uterus, which, when lying on the back, compresses the vena cava and prevents blood flow to the heart. A woman may even lose consciousness. However, when changing position, the pressure is restored.
- The presence of extagenital diseases that affect blood pressure.
The danger of this condition during pregnancy is spontaneous abortion in the early stages or premature birth. Knowing about a woman’s pathology, the doctor must constantly keep in touch with her.
In adults and older people
Sometimes at a pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. Art. a person has to be hospitalized, especially if such a condition appears in a hypertensive patient, since a stroke or heart attack can occur with a sharp rise in blood pressure.
The cause of pressure 80 to 40 in an elderly person can be the following circumstances:
- Having suffered a serious illness.
- Operations performed.
- Long rehabilitation, forcing a person to spend a long time in bed.
- Taking certain medications.
To identify the exact cause of the appearance of pressure 80 to 40, it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination.
In children and adolescents
The most common causes of low blood pressure in children and adolescents are:
- Hereditary factors.
- Anatomical congenital or acquired features - for example, thickening of the skull bones, birth trauma, improper overgrowth of the fontanel, etc.
- Hormonal changes and puberty in adolescents.
- Psycho-emotional pressure on the child.
- Chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract, such as sinusitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis, etc.
- Insufficient nutrition, limited intake of fortified foods.
Reducing blood pressure in pregnant women
A slight decrease in blood pressure during early pregnancy is normal. However, if the levels decrease significantly, it can be dangerous for both mother and child.
Low blood pressure can be a symptom of the development of serious diseases, from stomach ulcers to adrenal insufficiency. Hypotension is especially dangerous due to impaired blood circulation in the placenta. This impedes the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, hypoxia, non-developing pregnancy and the risk of premature termination of pregnancy.
Blood pressure during pregnancy may decrease due to:
- Constant stress;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Infectious diseases;
- Hormonal changes;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Serious blood loss;
- Malfunctions of blood vessels and heart.
In this case, the woman feels weak and drowsy, gets tired quickly, dizziness, darkening of the eyes and fainting are possible. Self-medication in such cases is unacceptable; you must definitely visit a doctor.
Is this condition dangerous?
For prolonged hypotension, a doctor's consultation is necessary. Otherwise, the process may become chronic.
The danger of pressure 80 to 40 and even 85 to 55 is that a person may not feel it for a long time. While the pathological processes in his body continue to progress.
The most dangerous consequence of hypotension is myocardial infarction.
Other unpleasant consequences of low blood pressure include:
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Opening of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Decreased functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
And also read on our website: What does blood pressure 170 over 80 mean: causes, symptoms, what to do and how to reduce it at home?
How to deal with the problem?
If hypotension develops in a healthy person due to excessive stress and stressful situations, these negative factors should be eliminated, and within a few hours or days everything will return to normal.
Often blood pressure decreases due to anemia, pathologies of the nervous system and thyroid gland. In this case, the disease that caused the hypotension is treated directly.
A healthy lifestyle plays a big role in normalizing blood pressure. The following rules must be adhered to:
- Take frequent walks in fresh air.
- Stick to moderate physical activity.
- Take a daily contrast shower.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Night sleep should last at least 8 hours.
If, despite a decrease in blood pressure to 80/40, a person feels unwell, it is necessary to urgently call a doctor . While waiting, you can offer the patient a glass of sweet tea or coffee, or a few drops of tincture of radiola rosea, lemongrass or eleutherococcus.
Raising blood pressure and keeping it at the required level is often much more difficult than lowering it.
How to normalize blood pressure
Blood pressure should always be within age norms. If frequent jumps down or up are observed, specialists prescribe special treatment and adjust the child’s lifestyle.
Table “Methods of normalizing pressure”
| How to lower blood pressure | Follow the daily routine. Getting up in the morning and going to bed at night should be at the same time every day |
| Limit the consumption of pickled and canned foods. Reduce the daily dose of salt (food should be lightly salted) | |
| Improve your sleep. The need for a child’s body to sleep at night is at least 8–9 hours a day. Preschool children should be put to sleep during the day (1.5–3 hours) | |
| Treatment with antihypertensive drugs (diuretics, antispasmodics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors). Medicines are selected by the doctor individually, based on the underlying disease | |
| Avoid overwork. Physical activity should be moderate, and training should be dosed | |
| Maximum limitation of stress factors, emotional stress | |
| Spend more time outdoors | |
| In adolescence, avoid the abuse of weak alcoholic drinks and smoking | |
| How to increase blood pressure | Balance the diet so that the young body receives all the necessary substances. The child should eat more fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, dairy products, legumes and cereals. Meals must be divided into fractions (5–6 times a day) |
| To live an active lifestyle. Running, swimming, cycling, gymnastics, and dancing help increase low blood pressure. The main thing is to take into account the interests of the child | |
| Strengthen the body's defenses. Long walks in the fresh air (at least 40 minutes) and good nutrition will help with this. | |
| Use adaptogens (after consultation with your doctor). Tincture of lemongrass, ginseng or eleutherococcus increases the tone and elasticity of blood vessels | |
| Use physical therapy. A contrast shower and underwater massage help a lot. Normalization of pressure using similar methods occurs after 7–10 sessions | |
| Massotherapy. Conducted by a specialist. Restores normal functioning of the heart, blood vessels and nervous system, stabilizes blood pressure |
Preventive measures and specific therapy help restore normal functioning of the heart and blood vessels, strengthen the defenses of the young body and improve the general condition of the child. The main thing is to first examine and identify the causes of deviations, and then begin treatment.