Home / Articles / Tachycardia with hypotension: treatment
Tachycardia is a phenomenon characterized by an acceleration of the heart rate. It can be physiological in nature and occur, for example, after physical activity or emotional stress. Usually after some time the patient's condition returns to normal.
If tachycardia is combined with severe hypotension - a decrease in blood pressure, then you should not hope for independent healing; you need to consult a specialist and undergo treatment. The combination of these symptoms indicates disturbances in the functioning of the heart and may also indicate severe intoxication, blood loss and other lesions. Low blood pressure provokes a number of negative changes in the functioning of the body.
Causes of tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia occurs in different age groups, more often in healthy people, as well as among patients with heart and other diseases.
The occurrence of sinus tachycardia is promoted by intracardial (cardiac) or extracardial (extracardiac) etiological factors.
Sinus tachycardia in patients with cardiovascular disease is most often an early symptom of heart failure or left ventricular dysfunction. Intracardial causes of sinus tachycardia include: acute and congestive chronic heart failure, myocardial infarction, severe angina, myocarditis of rheumatic, toxic-infectious and other origins, cardiomyopathies, cardiosclerosis, heart defects, bacterial endocarditis, exudative and adhesive pericarditis.
Physiological extracardiac causes of sinus tachycardia may include physical activity, emotional stress, and congenital characteristics.
Neurogenic tachycardias make up the majority of extracardiac arrhythmias and are associated with primary dysfunction of the cerebral cortex and subcortical nodes, as well as disorders of the autonomic nervous system: neuroses, affective psychoses (emotional tachycardia), neurocirculatory dystonia. Neurogenic tachycardias most often affect young people with a labile nervous system.
Among other factors of extracardiac tachycardia, there are endocrine disorders (thyrotoxicosis, increased production of adrenaline in pheochromocytoma), anemia, acute vascular failure (shock, collapse, acute blood loss, fainting), hypoxemia, acute pain attacks (for example, with renal colic).
The appearance of tachycardia can be caused by fever that develops with various infectious and inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, tonsillitis, tuberculosis, sepsis, focal infection). An increase in body temperature by 1°C leads to an increase in heart rate, compared to normal, in a child by 10-15 beats per minute, and in an adult by 8-9 beats per minute.
Pharmacological (drug-induced) and toxic sinus tachycardia occurs when the function of the sinus node is influenced by drugs and chemicals: sympathomimetics (adrenaline and norepinephrine), vagolytics (atropine), aminophylline, corticosteroids, thyroid-stimulating hormones, diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, caffeine (coffee, tea) , alcohol, nicotine, poisons (nitrates), etc. Some substances do not have a direct effect on the function of the sinus node and cause so-called reflex tachycardia by increasing the tone of the sympathetic nervous system.
Sinus tachycardia can be adequate or inadequate. Inappropriate sinus tachycardia can persist at rest, unaffected by exercise or medication, and be accompanied by sensations of palpitations and shortness of breath. This is a fairly rare and little-studied disease of unknown origin. Presumably, it is associated with a primary lesion of the sinus node.
First aid
With a high pulse and hypotension, you need to be able to provide timely assistance. The heartbeat must be slowed down and blood pressure increased.
If the attack is not stopped in time, the situation may worsen even further.
You definitely need to lie down, raise your legs just above head level, unfasten the buttons on your clothes, loosen the belt on your trousers or the belt on your dress, and unfasten your shoes. You should do everything to be able to breathe calmly and deeply. To do this, you need to open the windows and doors, ensure a flow of fresh air, and turn on the fan to heat it up.
Sweet tea helps a lot. You can even drink two cups at once. If this is not possible, you should slowly suck on a couple of pieces of refined sugar or simply put a spoonful of loose sugar (sand) in your mouth. A piece of dark chocolate will also help increase blood pressure, but this is only if there is no vomiting.
If you feel hungry during an attack, you are allowed to eat a sandwich with cheese, but without butter, so as not to provoke nausea. You need to chew your food slowly and bite a little at a time.
To slow down your pulse, you need to take deep breaths, holding your breath for a few seconds. Tension of the abdominal muscles and pressure with your thumbs on the upper eyelids directly under the eyebrows also help.
Important!
In case of a severe attack, you should not take medications. The maximum you are allowed to drink before the ambulance arrives is Citramon.
Symptoms
The presence of clinical symptoms of sinus tachycardia depends on the degree of its severity, duration, and the nature of the underlying disease.
With sinus tachycardia, subjective symptoms may be absent or minor: palpitations, discomfort, a feeling of heaviness or pain in the heart area.
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia can be manifested by persistent palpitations, a feeling of shortness of breath, shortness of breath, weakness, and frequent dizziness. Fatigue, insomnia, decreased appetite, decreased performance, and worsened mood may occur.
The degree of subjective symptoms is dictated by the underlying disease and the sensitivity threshold of the nervous system. In case of heart disease (for example, coronary atherosclerosis), an increase in the number of heart contractions can cause attacks of angina pectoris, worsening the symptoms of heart failure.
With sinus tachycardia, there is a gradual onset and end. In the case of severe tachycardia, symptoms may reflect disturbances in the blood supply to various organs and tissues due to a decrease in cardiac output. Dizziness and sometimes fainting appear; with damage to cerebral vessels - focal neurological disorders, convulsions. With prolonged tachycardia, there is a decrease in blood pressure (arterial hypotension), a decrease in diuresis, and coldness of the extremities is observed.
What does high pulse and low blood pressure mean?
Normally, blood pressure should be 120 over 80, and the heart rate should be 60-70 per minute. Indicators may differ slightly. Some people feel great with low blood pressure and a slow pulse, while some, on the contrary, feel great with high blood pressure. But this is an exception to the rule.
If, with low blood pressure, the heart rate exceeds 90-100 per minute, this indicates that serious poisoning, hemorrhage has occurred in the body, or there is some kind of cardiac pathology.
In parallel, headaches, dizziness, nausea and even loss of consciousness are noted. This may be caused by the following factors:
- varicose veins of internal organs;
- bleeding ulcers;
- hemophilia;
- cirrhosis;
- shock;
- dehydration;
- diarrhea or vomiting;
- decreased protein levels in the blood;
- emphysema;
- burns;
- physical and mental stress;
- sun or heatstroke;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland or kidneys;
- hidden diseases and infections;
- taking medications (antidepressants, pills for hypertension, diabetes).
But the reasons are not always so frightening. Often this condition can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle, overeating or eating new foods that are difficult to digest, bad habits, etc.
Note!
A high heart rate with low blood pressure can be caused by changes in weather, lack of sleep or extreme fatigue.
Diagnosis of tachycardia
The leading role in the differential diagnosis of the type of tachycardia, determination of rhythm and heart rate belongs to electrocardiography (ECG). When arrhythmia paroxysms occur, daily Holter ECG monitoring is highly informative. This method allows you to identify and analyze any disturbance of heart rhythm during the day, as well as determine ischemic ECG changes during the patient’s normal physical activity.
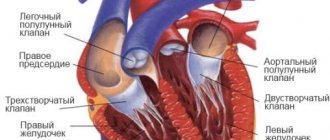
A routine research method to exclude heart pathology in case of any rhythm disturbances is echocardiography, which provides information on the size of the heart chambers, the thickness of the myocardial walls, disturbances of local contractility and pathology of the valve apparatus. In rare cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the heart is performed to identify congenital pathology.
Invasive methods for examining patients with tachycardia include electrophysiological studies. The method is used in the presence of appropriate indications before surgical treatment of arrhythmia only to a limited number of patients. Using an electrophysiological study, the doctor obtains information about the nature of the propagation of the electrical impulse throughout the myocardium and determines the mechanisms of tachycardia or conduction disorders.
To identify the cause of tachycardia, additional research methods are sometimes prescribed: a general blood test, a blood test for thyroid hormones, electroencephalography, etc.
What can you do
The principles of treatment of sinus tachycardia are determined, first of all, by the causes of its occurrence. Treatment should be carried out by a cardiologist together with other specialists.
It is necessary to eliminate factors that contribute to an increase in heart rate: eliminate caffeine-containing drinks (tea, coffee), nicotine, alcohol, spicy foods, chocolate; protect yourself from psycho-emotional and physical overload. Physiological sinus tachycardia does not require treatment.
Treatment of pathological tachycardia should be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. In case of extracardiac sinus tachycardia of a neurogenic nature, the patient needs to consult a neurologist. Treatment uses psychotherapy and sedatives (luminal, tranquilizers and antipsychotics: tranquilan, relanium, seduxen).
In the case of reflex tachycardia (with hypovolemia) and compensatory tachycardia (with anemia, hyperthyroidism), it is necessary to eliminate the causes that caused them. Otherwise, therapy aimed at reducing heart rate can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure and aggravate hemodynamic disorders.
For sinus tachycardia caused by thyrotoxicosis, β-blockers are used in addition to thyreostatic drugs prescribed by the endocrinologist. Preference is given to β-blockers of the oxyprenolol, practolol and prindolol group. If there are contraindications to β-blockers, alternative medications are used - non-hydropyridine calcium antagonists (verapamil, diltiazem).
For sinus tachycardia caused by heart failure, cardiac glycosides (digoxin) are prescribed in combination with beta-blockers.
Treatment
Treatment of tachycardia with hypotension depends on the reasons that provoked the pathological changes. Typically, drugs that slow your heart rate also lower your blood pressure. Therefore, the therapy of the pathology is complex and consists of a whole range of means. Taking any medications on your own is strictly prohibited.
The patient must not only take the prescribed medications, but also follow the doctor’s recommendations. You need to follow a daily routine and a special diet, and avoid stress. You should stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Experienced specialists at the medical center in Lyublino treat tachycardia due to hypotension. Doctors have extensive experience and successfully cope with pathology. To make an appointment and for more information, please call.
All articles
5% discount Print coupon from our website
Ask your question on the website Get professional advice!