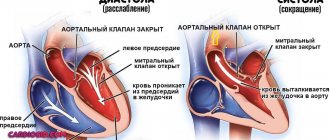
Both hyperfunction and underfunction of the thyroid gland, which are treated by an endocrinologist, are common diseases. In our country alone, hundreds of thousands of people suffer from them. Disturbances in the functioning of this small organ - the volume of the gland normally does not exceed 18-25 ml - affects the functioning of other organs and systems of the body, in particular, the functioning of the heart.
A properly functioning thyroid gland produces the amount of hormones necessary for the normal functioning of the body. If it begins to “fail,” then disruptions in its function affect the functioning of all body systems. For example, in patients with hyperthyroidism, or increased thyroid function, the endocrinologist during an appointment notes an increased heart rate - one of the characteristic symptoms of this disease. If the function of the gland is insufficient, the patient's heart may beat slower than normal - this is the so-called bradycardia.
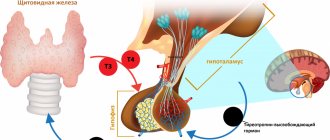
How the thyroid gland affects the heart, says an endocrinologist
A lack of thyroid hormones in the early stages of the disease provokes a decrease in blood pressure. This is manifested primarily by a feeling of constant fatigue, lethargy and drowsiness, as well as the appearance of edema in the patient. The heart of such a patient beats slower than normal, and in the intervals between beats additional contractions of the heart muscle may appear. In particularly advanced cases, this can even lead to cardiac arrest.
Cardiologists, arrhythmologists and endocrinologists note the fact that the lack of treatment for hypothyroidism leads to an increase in blood pressure over time. In turn, this may be complicated by the development of coronary heart disease or vascular atherosclerosis. Timely treatment of insufficient thyroid function by an endocrinologist is necessary
to prevent the development of these and other possible heart complications.
Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is no less dangerous for the cardiovascular system. This condition may manifest itself as follows:
- painful sensations in the chest area, the cause of which cannot be identified by an ECG;
- increased – sometimes to critical levels – blood pressure;
- interruptions in heart rhythm. Without timely seeking medical help, they can provoke a heart attack and even lead to death.
If hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is not stopped with the help of drugs selected by an endocrinologist, the patient may develop titeotoxicosis. This poisoning of the body by thyroid hormones is a serious, often life-threatening condition for the patient, which may be accompanied by:
- increased heart rate - erratic heart beats can number more than 300 per minute;
- in patients aged 45 years and older – heart failure.
“Thyroid” causes of a “restless” heart
When the heart is “out of place,” we are usually talking about experiences of a psychological nature. But, if the heart is pounding with or without reason, the cause of the condition is no longer only in emotions, but first on the list of “heart provocateurs” are thyroid hormones.
Will make you worry not only the heart
Arrhythmia is a group of heart rhythm disorders that have a paroxysmal nature and can occur both after exercise and at rest.
During such an “attack,” the heart begins to beat faster or intermittently, and the minute volume of blood passing through the heart normally decreases significantly. Blood pressure “falls”. And patients at such moments may experience shortness of breath, headaches, dizziness and even lose consciousness.
The causes of this pathology may be hidden in defects in the conduction system of the heart itself, changes in the volume and rheological properties of the blood (for example, with dehydration or anemia) or an excess of thyroid hormones.
At the same time, T4 (or thyroxine) makes not only the heart “nervous,” because the hormone is a stimulator of absolutely all metabolic, energy and recovery processes in the body. And among the common symptoms of hyperthyroidism:
- general agitation and fussiness,
- unmotivated anxiety and irritability,
- insomnia,
- exhaustion due to normal nutrition,
- increase in body temperature,
- sweating, even at normal room temperature,
- increased thirst, frequent urination,
- increased pressure,
- redness of the skin and hair loss,
- Spastic digestive disorders (abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, etc.)
- and others.
Symptoms increase unnoticed, each time demonstrating greater resistance to standard treatment regimens.
As for the heart, then:
- with mild hyperthyroidism, the heart rate during an “attack” usually does not exceed 100 beats/minute;
- with moderate severity - on average, 120-140;
- and a severe form of pathology is accompanied by tachycardia above 140 beats.
Such arrhythmia, as already noted, is resistant to the action of conventional “heart” drugs. And, in the absence of correction of thyroid (“thyroid”) hormones, it can lead to the development of fibrillation and cardiac arrest.
When there is too much thyroxine
Hyperthyroidism, or excess thyroid hormones, can result from:
- excessive independent activity of the gland (diffuse toxic or nodular goiter, overdose of iodine-containing drugs)
- or an excess of the pituitary hormone TTT, which controls the activity of the gland.
In the first case, the cause of excess production of hormones may be either in the thyrocytes themselves (thyroid cells) or in stimulating antibodies. But the second - in most cases, in the pathology of the pituitary gland.
The exact cause of the disease can only be identified with the help of blood tests, ultrasound of the gland (with a biopsy in some cases), as well as CT or MRI, if necessary.
When is it time to see an endocrinologist?
The presence of arrhythmia along with several of the listed symptoms is a good reason to check the “health” of the thyroid gland. And in this case you will need:
- blood test for TSH,
- and free
- as well as antibodies to TSH receptors.
A decrease in TSH, even against the background of still normal or slightly elevated T4 and T3, indicates latent (subclinical hyperthyroidism); and if they significantly exceed the normative limits - about the clinical form (requiring immediate treatment) of the disease.
An increase in T4 and T3 simultaneously with TSH is a sign of pituitary pathology.
Detection of antibodies in the presence of symptoms is evidence in favor of Graves' disease.
How to keep your thyroid gland and heart healthy?
The only possible way to prevent the development of thyroid pathologies and protect your heart from possible complications is regular examination by an endocrinologist . This is especially important for patients with unfavorable heredity in terms of gland health, women during pregnancy and menopause, as well as those who are over 45 years old.
Thyroid dysfunction and other endocrine diseases detected in the early stages are successfully treated by specialists. Endocrinologists at our medical center in St. Petersburg select an effective treatment regimen for each patient. Compliance with all recommendations of the attending physician and timely examination to monitor the treatment will not only normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland, but also maintain the health of the cardiovascular and other body systems.
Hypothyroidism and the heart
Cardiologist of the Cardiology Department No. 2 Subotka T.A.
Heart damage in hypothyroidism is caused by a decrease in the content of thyroid hormones in the body, which can occur as a primary process or result from surgical treatment of thyroid diseases (total or subtotal resection) or treatment with radioactive iodine. In these cases, the activity of metabolic processes in the heart muscle is significantly suppressed, and the work of the heart decreases.
Heart damage is most severe in primary hypothyroidism. The intensity of oxidative phosphorylation decreases, protein synthesis slows down, and oxygen absorption in the myocardium decreases. Developing disorders lead to a decrease in myocardial contractility associated with dysfunction of contractile proteins. With hypothyroidism, anemia often develops, aggravating the course of MCD.
Clinical picture and diagnosis . Patients complain of shortness of breath associated with minimal physical activity, swelling of the face and legs. Pain in the heart area occurs in less than 50% of cases. The presence of general manifestations of hypothyroidism is characteristic: muscle weakness, physical inactivity, mental retardation, drowsiness. The boundaries of the heart are significantly displaced due to myocardial edema and the presence of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The heart sounds are muffled, the activity is rhythmic, bradycardia and a small slow pulse are characteristic.
Due to the disturbance of lipid metabolism that occurs with hypothyroidism, it is quite difficult to carry out a differential diagnosis with ischemic heart disease, especially against the background of the presence of angina-type pain syndrome. When carrying out differential diagnosis of these conditions, the following signs must be taken into account:
Manifestations of hypothyroidism are characterized by:
- pain in the heart area like cardialgia
- negative results of stress tests
- the presence of sinus bradycardia;
- absence of acrocyanosis;
- localization of swelling on the face and legs
- absence of pits when pressing in the area of edema
- absence of liver enlargement, congestion in the lungs, cardiac asthma (in the initial stages of the disease)
- low absorption of iodine-131;
- decreased levels of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- Hormone replacement therapy gives positive results.
Treatment . It is carried out against the background of hormone replacement therapy with thyroid hormones with careful selection and control of the dose. Inadequate doses can provoke attacks of angina pectoris and aggravate the symptoms of circulatory failure.
The slightest malfunction of the thyroid gland, and the disturbed balance affects the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and brain. This also causes problems of a sexual nature.
An inconspicuous tubercle on the neck looks like a butterfly (two lobes are connected to each other by an isthmus). By squeezing the larynx like a noose, it can cause difficulty swallowing.
Having very small sizes (weight 10-25 g, volume 20-25 ml),
The thyroid gland is responsible for energy supply to all internal organs.
She instantly reacts to any disruptions in their work caused by stress, severe pain or hormonal imbalances.
At such moments, you may feel pressure on the front of your neck, bloating, or a lump in your throat that you want to swallow.
How the thyroid gland affects the well-being of the entire body
The hormones that the thyroid gland secretes into the blood control the correct course of processes such as:
- blood oxygen saturation,
- the formation of free radicals (substances that control the process of contraction of vessel walls and stimulate programmed cell death),
- production of female and male sex hormones.
It is easy to come to the conclusion that problems with the thyroid gland provoke problems with sexual desire in men and women.
In addition, if the thyroid gland malfunctions, premature aging of cells will accelerate. The immune system will slow down its activity, weakening the body's defenses against germs and viruses.
Accelerating metabolism will disrupt the balance of all systems, including the nervous system, leading to irritability, sudden mood swings, decreased memory and learning ability.
How the thyroid gland affects the heart
Thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) have the following effects on the heart.
1. Increase cardiac output and blood flow in tissues.
Excess thyroid hormones cause an increase in cardiac output by 60% of the original, and blood flow by 50%.
The reason is an increase in metabolism and tissue needs for oxygen and nutrients. So a harmless compensatory reaction can “drive” the heart like a racing horse.
As blood flow increases, the blood vessels dilate and the skin becomes moist and hot to the touch.
2. Increases heart rate and pulse. The more blood the heart has to pump out, the faster the pulse will be.
3. Strengthen heart contractions. To cope with the increased load, heart muscle cells spend more strength and energy, forgetting about rest and sleep. A couple of years, or even months, of such hard work, and the tired heart wears out.
4. Increase blood pressure. An excess of thyroid hormones increases the upper (systolic) pressure, and, on the contrary, lowers the lower (diastolic) due to a rapid pulse.
A large difference between the upper and lower numbers leads to headaches.
How can a thriving man not turn into a helpless disabled person?
The effect of excess thyroid hormones on the heart muscle increases the cells' need for oxygen, increases heart rate, and provokes rhythm disturbances, primarily tachycardia and extrasystole.
When we speed up our pace or under conditions of generally habitual stress, we suddenly discover that our heart rate grows faster and more often, and maintains its pace even at night during sleep.
Not being able to fully rest increases the stress on the heart and lungs.
See also: Biathlon legend Bjoerndalen vs atrial fibrillation: who will win?
There is a lack of air, a feeling of rapid heartbeat, interruptions in the functioning of the heart and swelling of the legs. In such conditions, heart failure develops very quickly.
If you ignore the first warning signs and warning signs, you may miss a serious illness. In a couple of months, a thriving man can turn into a helpless invalid. Harmless tachycardia can turn into atrial fibrillation, and the worn-out heart will have to be replaced with a new one.
Therefore, consult a doctor in time!
How to find out if everything is okay with the thyroid gland
You can check your thyroid gland by touch if you really want to. Tilt your head back and place your fingers on the neck area in the Adam's apple area. When swallowing, an elastic tubercle can be felt under the fingers.
However, self-palpation of the thyroid gland is not a substitute for a professional examination.
Symptoms of a lump in the throat, especially when swallowing, and a feeling of fullness in the neck are a reason to see a doctor for a detailed examination.
After asking about your complaints, the doctor will send you for an ultrasound, where the structure and size of the thyroid gland will be determined. In complex cases, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will be needed to clarify the diagnosis.
How to check your heart if you have a thyroid disorder
You can also go to a regular clinic. I first advise you to measure your pulse and blood pressure at home for a week (keep a self-monitoring diary).
A frequent pulse in the morning after sleep and 10 minutes after rest in the evening with a simultaneous increase in the upper pressure figure is already a reason to think about problems with the cardiovascular system.
See also: Halter to choose from: implants or breast shaving?
Taking an ECG in a calm state or Holter monitoring will help to find rhythm disturbances and circadian rhythms of the pulse. Signs of a worn-out heart (thickening of the walls, dilation of the heart chambers, decreased cardiac output) can be detected by ultrasound.
The “butterfly” squeezes not only the throat, but also the heart
See also: Common signs of heart disease. Activate your senses!
Medical practice shows: there are no unimportant organs and systems in our body. The coordinated functioning of the heart is impossible without the normal functioning of the thyroid gland and vice versa. Today we raised the topic of how excess thyroid hormones rob the heart of its strength. However, hormone deficiency also harms the heart. More on this in future publications.
Main photo of the article from the site alternativemedicinemiami.com