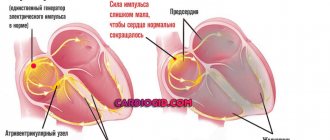
Heart failure is associated with decreased heart function. The heart muscle cannot produce the energy needed to pump the required amount of blood throughout the body.
In Russia alone, about 7 million people suffer from heart failure. In people over 70, one in four people are affected, with men typically affected at a much younger age than women. The risk for men is approximately one and a half times higher than for women. In Russia, diseases of the circulatory system are the most common cause of death.
- What is heart failure?
- What causes heart failure?
- What are the types of heart failure and what are their symptoms? Left-sided heart failure
- Right-sided heart failure
- Global heart failure
- Systolic heart failure
- Diastolic heart failure
- Chronic heart failure
- Acute heart failure
Forms of the disease
Physiological
One of the normal options. The disease can develop due to excessive physical activity or when moving to a high mountain region (low blood pressure is observed during the adaptation period).
Pathological
- Primary. It can be reversible or over time take a chronic form, that is, turn into a hypotensive disease, accompanied by dizziness, headaches, etc. It occurs against the background of puberty, stress, overwork, thinness, heredity, etc. Source: K.M. Dzilikhova, M.G. Dzgoeva, Z.D. Kaloeva, S.Ch. Khestanova, A.K. Shavlokhova Primary arterial hypertension in children // Pediatrics, 2010, v. 89, no. 3, pp. 116-122
- Secondary. It manifests itself due to cardiovascular disorders, pathologies of the endocrine system, diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, pneumonia, diabetes mellitus, etc. The second reason is certain drugs, after discontinuation of which arterial hypotension goes away. Source: N.N. Arkhipova Arterial hypotension in children and adolescents // Practical Medicine, 2008, No. 4(28), pp. 63-65
What is hypotension?
The term arterial hypotension (hypotension) defines a decrease in blood pressure. This is not a separate disease, but a syndrome that develops as a result of exposure to various provoking factors or against the background of diseases. A decrease in the indicator leads to a decrease in the volume and speed of blood flow in peripheral tissues. First of all, the cells of the nervous system, which are very sensitive to energy and oxygen starvation, are affected.
Low blood pressure - causes
Arterial hypotension develops due to exposure to a large number of pathological or physiological causes. The most common ones include:
- Poisoning of the body
– ingestion of various toxins from the outside with food, inhaled air, or intoxication due to the development of an infectious process.
- Violation of the regulatory influence of nervous system structures
on arterial vessels, leading to a sharp decrease in the tone of their walls - cerebral stroke, organic changes, infectious processes in the structures of the central nervous system, previous traumatic brain injuries, functional disorders of various origins.
- Dilatation of arteries against the background of decreased tone of the whole body
, which occurs against the background of physical and mental fatigue, lack of sleep, poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis (hypovitaminosis is an insufficient supply of one or more vitamins to the body).
- Decrease in circulating blood volume due to blood loss
(internal or external hemorrhage) or dehydration (loss of fluid due to uncontrollable diarrhea, vomiting, insufficient water intake).
- Severe allergic reactions
, accompanied by a pronounced decrease in arterial tone - anaphylactic shock.
- Changes in hormone levels in the blood
, which have a regulating effect on arterial tone, heart rate, blood pressure and other hemodynamic indicators - adrenaline, hormones of the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland influence the course of a large number of physiological processes in the body.
- Redistribution of fluid in the body
with a transition from the vascular bed to the intercellular substance of tissues, which leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood with arterial hypotension.
- Weakening of the contractile function of the heart
, provoked by pathological processes in the myocardium - infarction, myocardiopathy, myocarditis.
- Violation of the rhythm and frequency of heart contractions
, caused by various pathological factors and leading to a decrease in blood pressure.
A decrease in the level of systemic blood pressure is a consequence of pathological processes in other organs, in particular with diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, and anemia. Physiological arterial hypotension develops during the period of adaptation of the human body to a reduced concentration of oxygen in the inhaled air (stay in high mountain areas). Causes of low blood pressure in women include the effects of hormonal changes during menstruation, early pregnancy, and menopause (age-related decline in reproductive function).
Low blood pressure - symptoms?
Arterial hypotension is accompanied by a violation of the functional state of various organs and systems, which develops against the background of energy and oxygen starvation. Symptoms of low blood pressure include the following:
- General weakness
– a constant symptom of hypotension, the severity of which depends on the degree of decrease in blood pressure.
- Dizziness
– the result of oxygen starvation of neurocytes.
- Memory impairment, decreased mental performance
– low blood pressure affects a person’s higher nervous activity; signs usually appear with prolonged moderate hypotension, as well as against the background of the development of anemia.
- Paleness of the skin and visible mucous membranes
– the sign appears in cases where arterial hypotension develops sharply and is accompanied by a decrease in circulating blood volume (after bleeding).
- Headache
, which is predominantly localized in the temples, crown and can have varying severity.
With severe hypotension, a person loses consciousness, which is associated with oxygen starvation of the cerebral cortex. If systolic pressure is below 70 mm Hg. Art. acute renal failure develops, decompensation of the functions of all organs, which becomes the cause of death.
To understand why a particular patient has low blood pressure, a doctor (general practitioner, family doctor, cardiologist) must prescribe an additional objective examination. It includes various techniques, namely clinical blood tests, urine tests, ECG, X-rays, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging. Based on a thorough and reliable diagnosis, the correct treatment is prescribed.
Diagnosis of pathology
The following methods are used to detect arterial hypotension:
- ECG;
- ECHO-KG;
- EEG;
- clinical and biochemical blood tests (indicators of cholesterol, glucose, etc. are important).
The pressure is measured by a specialist three times and a cuff is selected according to age. Therefore, it is highly not recommended to independently diagnose a child and begin self-medication based on the readings of a home blood pressure monitor. Reduced numbers when measured should only be a reason for rechecking with a pediatrician.
During diagnosis, the child may be prescribed 24-hour blood pressure monitoring. This is a very informative study that can identify pathology at an early stage.
Causes of the disease
This disease can develop even in newborns.
If we talk about older children, then number of factors cause arterial hypotension :
- heredity (usually from the mother);
- adolescence (puberty);
- strong psycho-emotional stress, which is typical for schoolchildren;
- stress;
- poor living conditions;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic infections;
- excessive workload at school;
- decreased function of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, pituitary gland.
Symptoms of arterial hypotension
For newborns, diagnosis is difficult. Even parents often cannot see problems in behavior, as a result of which they do not draw the attention of the pediatrician observing the child. At this age, the child almost always sleeps, but during periods of wakefulness, a healthy baby will be active and cry. If the child is always calm and rarely cries, then this should alert you. Excessive calm is not typical for a newborn. Source: T.M. Tvorogova, N.A. Korovin Arterial hypotension in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal, 2007, No. 21, pp. 1519-1524
At a very early age, children can be susceptible to physical inactivity, which results in decreased muscle tone. The external manifestation is the child’s ability to straighten an arm or leg more than 180 degrees in the joint area. Children with low blood pressure, among other things, lag behind in the development of motor skills and have difficulty sucking and swallowing.
Since the baby cannot complain about feeling unwell, parents must be very attentive!
Older children may present complaints, and they are also characterized by noticeable symptoms :
- if the child abruptly assumes a vertical position, he or she may faint or complain of severe dizziness;
- poor tolerance of stuffy rooms;
- frequent mood swings, short temper, timidity;
- nosebleeds;
- sudden attacks of poor health, accompanied by weakness, nausea, increased heart rate, cold sweat, pallor (this condition is called “vegetative crisis”)
- pain in muscles and joints, in which the child can hardly determine where exactly it hurts;
- decreased performance, fatigue even under light loads, lack of improvement after rest and even sleep;
- pain in the heart area;
- headaches in the area of the crown, back of the head, forehead, most often manifested in the morning;
- feeling of suffocation;
- weather sensitivity.
“SM-Clinic” recommends that if you detect any of the listed symptoms, you and your child should visit a pediatrician as soon as possible. This disease is especially dangerous for newborns, because it can cause abnormal development and lag behind peers. Be sure to consult a doctor and do not self-medicate!
Arterial hypotension may be accompanied by symptoms such as increased gas formation, cramping abdominal pain, impaired bowel function, constipation, and frequent belching.
Causes of pressure, nausea, headache
Acute headaches, nausea, weakness and deterioration in health, as well as various heart rhythm disturbances are symptoms that may indicate both high and low blood pressure. Normally, this figure is 120/80 mm. rt. Art., but in some people it remains at a higher or lower level. When measuring it, various factors are taken into account, but chronic hypertension or hypotension cannot be considered normal.
High blood pressure
Hypertension is an increase in blood pressure. It often occurs in a chronic form and can be diagnosed at any age. Blood pressure indicators with constant hypertension remain within the range of 140∕90 mm or more. rt. Art. Doctors recommend exercising with caution if you have this disease, avoiding stress, and regularly measuring your blood pressure at home.
Causes of hypertension
The main cause of hypertension is weakness of blood vessels and decreased elasticity of their walls. With a sharp increase in blood pressure, they cannot adapt to the load. This can happen in the warm season, during physical activity, under stress and nervous tension. In addition, chronic hypertension can be diagnosed, which manifests itself in both adults and children. Its causes may be:
- congenital or acquired diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- excess weight, which increases the load on the heart muscle;
- abnormal physical activity;
- age-related changes - in older people, blood vessels become less strong and elastic, and adapt less well to pressure changes;
- unhealthy diet, as well as frequent alcohol consumption;
- atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disease in which plaques and blood clots (often cholesterol) form on the inner wall of the arteries.
Attacks of hypertension can be associated with stressful situations, in which blood pressure increases and the heartbeat accelerates. Thus, severe fear causes a sharp increase in blood pressure, accompanied by pain in the heart area. Symptoms also often occur during intense physical activity, especially at high temperatures and insufficient ventilation.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
More than 20% of people in the world suffer from chronic hypertension. The danger of this disease is that at the first stage it can be asymptomatic. The clinical picture is noticeable during the next attack, but during periods of remission the disease does not manifest itself in any way. When blood pressure increases, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- acute headache, dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting, regardless of food intake;
- acceleration of heart rate, manifestation of various types of arrhythmia;
- redness of the skin in certain areas, often on the face;
- the appearance of small subcutaneous hemorrhages - they are associated with rupture of capillaries from increased blood pressure and can also be found on the mucous membranes;
- deterioration of hearing and vision, the appearance of black dots or circles in the field of vision;
- fainting is possible.
The first symptoms of hypertension may remain unnoticed, but the load on the heart increases significantly. If you do not take this feature into account and continue to undergo intense physical activity, this can lead to dangerous consequences. A sharp increase in pressure is the main cause of vascular rupture and the development of hemorrhagic stroke with hemorrhage in the brain. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend regularly measuring blood pressure at home, even if there are no prerequisites for this. This simple procedure will allow you to recognize hypertension in the early stages and prevent dangerous consequences.
Lower blood pressure
Hypotension (low blood pressure) is an equally dangerous disorder. With this disease, blood does not move through the vessels intensively enough and does not reach areas distant from the heart. Thus, the blood supply to the lower arms and legs, internal organs and brain may be disrupted. It is important to monitor your health and take prescribed medications, since low blood pressure can cause ischemic stroke.
Causes of hypotension
Hypotension is diagnosed if, as a result of several measurements, blood pressure readings are 90∕60 mm. rt. Art. and less. It can be a chronic disease of the cardiovascular system and can also occur in healthy individuals under certain conditions. So, the causes of hypotension can be:
- deterioration of vascular tone, their constant expansion - the result of poisoning, allergic reactions and other disorders;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia is a disease in which the regulation of vascular tone occurs, so their walls lose tone and elasticity;
- dehydration of the body due to insufficient fluid intake, especially in the heat, in case of poisoning or during sports – leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood;
- congenital and acquired diseases and heart defects, valve failure;
- systemic use of certain medications, including drugs against hypertension, which lead to a persistent decrease in blood pressure.
Separately, physiological hypotension is distinguished - a decrease in blood pressure, which is within normal limits. Thus, indicators may be underestimated as a compensatory response to environmental conditions. Residents of high mountain regions experience a mild degree of chronic hypotension, which is not harmful to health. It also develops in athletes who regularly engage in intense physical activity. An increase in the mass and volume of the heart and an increase in the volume of circulating blood lead to the fact that for proper blood circulation in normal mode, a low blood pressure is sufficient. In some healthy people, blood pressure is constantly slightly reduced, and this is considered normal. In other cases, hypotension is a pathology and requires timely treatment.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
Hypotension can be asymptomatic only with a slight decrease in pressure. If the indicators are 90∕60 mm. rt. Art. and less, the clinical picture is clearly expressed. The disease manifests itself in attacks that sharply worsen health and can lead to fainting. The onset of an attack can be determined by the characteristic symptoms:
- aching headache that can spread over the entire surface of the head or pulsate in the temples;
- constant weakness, drowsiness, slow reaction to stimuli;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, with a sharp decrease in pressure to critical levels, their cyanosis may be observed;
- decrease in skin temperature on the distal parts of the extremities (hands and feet) due to their insufficient blood supply;
- nausea and vomiting;
- tendency to faint when the ambient temperature rises, during physical exertion, while dieting, and in other cases.
If you often have a headache and feel sick, and your blood pressure is constantly below the normal limit, you should consult a doctor for a more complete diagnosis. Hypotension is dangerous to health, since the rate of blood circulation in this disease is significantly reduced. The main risk is insufficient oxygen and nutrients to the brain cells, which causes fainting. Ischemic areas form in the brain tissue, which cannot function fully. Persistent hypotension can lead to the development of ischemic stroke - an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. This condition poses a threat to the patient’s life, so it is important to take care to prevent its occurrence.
Other reasons
Nausea, weakness, high or low blood pressure, and headache are symptoms of a number of diseases caused by circulatory failure. They pose varying degrees of danger to the patient, but equally require full diagnosis and proper treatment. It is difficult to recognize the disease and make a correct diagnosis at home. In addition, many dangerous pathologies in the initial stages are disguised as ordinary malaise and fatigue.
- Poisoning is a condition in which toxic substances enter the body or are formed as a result of metabolism. Food intoxication is the most common; poisoning with gases, alcohol and medications, and heavy metals is also identified. They are manifested by nausea and vomiting, decreased blood pressure due to dehydration, as well as acute headaches.
- Heart defects can be congenital or acquired. They represent insufficiency of the heart valve apparatus. This leads to a deterioration in the movement of blood through the vessels, insufficient blood supply to internal organs, and an increased risk of myocardial infarction.
- Atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disorder in which the walls of blood vessels become dense and inelastic. Plaques and blood clots form on their inner wall, preventing normal blood flow. Often the cause of atherosclerosis is a violation of cholesterol metabolism, and this element is deposited on the walls of blood vessels and in the internal organs.
Blood pressure, nausea, headache - these symptoms may indicate severe fatigue, nervous tension, and stress. They can also appear in a healthy person, especially during sudden changes in weather conditions. Also, this picture may be a sign of poor nutrition, a lack of certain vitamins and minerals in the diet.
Treatment methods
Therapy may be prescribed with or without medications. For long-term and persistent forms of the disease, a combination of two methods is often used.
Non-drug therapy involves lifestyle adjustments:
- good sleep;
- strict daily routine;
- walks in the air every day for about two hours;
- easy charging after waking up;
- eating small portions 4 to 6 times a day (unlike hypertension, with arterial hypotension there is no need to limit salt intake).
Physiotherapy, water procedures, psychotherapy, medicinal baths can be used.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes a massage course for the child. It can be general or one of the areas: calves, hands, neck-collar area.
If non-drug therapy does not demonstrate effectiveness, drugs are added to the treatment plan. In some cases, according to a specialist, drug treatment begins immediately. It includes a set of medications, their type and dosage are selected strictly individually.
Intestinal flu - causes, symptoms and treatment
Rotavirus infection is an infectious disease caused by rotaviruses. Rotavirus, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in moderately severe symptoms of enteritis or gastroenteritis, is often combined with respiratory and intestinal syndromes during the initial manifestation of the disease. People of any age are susceptible to rotavirus infection, however, the incidence is most often observed among children from six months to two years. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Rotavirus infection is also defined as RI, rotavirus gastroenteritis, rotavirosis, stomach or intestinal flu. The virus is transmitted primarily through food, that is, through unwashed food, dirty hands, etc. Thus, infection is possible in a variety of ways and, again, through products with rotavirus (in particular, dairy products should be highlighted here, which are especially susceptible to infection due to the specifics of their production). It is noteworthy that rotaviruses can live even in the refrigerator for a long period of time; chlorination of water does not affect them. Contrary to the generally accepted opinion regarding the effect of holy water on viruses due to its altered structure, it should be emphasized that it does not in any way affect the activity of rotaviruses.
Considering that rotavirus also provokes inflammation in the respiratory tract, its spread occurs in a similar way to the traditional influenza virus, that is, by droplets (coughing, sneezing). The virus penetrates the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), with the small intestine being predominantly affected. When the gastrointestinal tract is affected, rotavirus infection causes a disease such as enteritis, which manifests itself in inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, respectively, after which symptoms characteristic of rotavirus infection occur. They are expressed, in particular, in disturbances in the digestion of food, which provokes the development of diarrhea with simultaneous dehydration.
ROTAVIRUS INFECTION: SYMPTOMS IN CHILDREN
The course of the disease in children is more severe than in adults. The patient becomes a spreader of the virus from its first manifestations, remaining infectious until their complete completion along with the disease itself. Recovery, as a rule, comes in five to seven days, and the body develops a fairly strong immunity to the virus, which allows us to assert that subsequent infection with rotavirus is practically impossible. The incubation period ranges from 1 to 5 days, with the acute period beginning in children from 3-7 days. The severe course of the acute period of the disease can provoke a subsequent intensification and duration of this period, in this case it can be over 7 days. It takes about 4-5 days to recover from an illness.
Rotavirus infection is characterized by an acute onset. Its main manifestations are vomiting and a sharp increase in temperature, and diarrhea is possible. Stool with rotavirus infection is quite characteristic. So, on the first day it is yellow, liquid, on the second and third - clay-like, gray-yellow in color. As a rule, among the sick there is a runny nose and redness of the throat, as well as pain that occurs when swallowing. The acute period is characterized by a lack of appetite, as well as a state of loss of strength. Most often, rotavirus infection in children is characterized by the following scenario. So, the child gets up in the morning with lethargy and moodiness, and in the morning nausea appears. Vomiting is possible (often with mucus), and it is relevant even if the stomach is empty. Appetite is significantly reduced, after eating, vomiting occurs with the release of pieces of undigested food, and it also occurs after drinking liquid in a volume of over 50 ml.
The temperature then rises, and by the evening it can exceed 39°C. It is noteworthy that the disease is characterized by a stable and high temperature, that is, it is very difficult to bring it down. The duration of the condition with a high temperature can be about 5 days. Additionally, symptoms of rotavirus infection manifest themselves in the form of loose stools with an unpleasant odor, as well as abdominal pain. In very young children who are not yet able to explain their painful sensations, crying with a characteristic rumbling in the tummy is a sign of the presence of pain. Babies become irritable and whiny, in addition, they also rapidly lose weight. The second day of illness (as well as subsequent days) is characterized by drowsiness. Correct treatment allows you to eliminate all manifestations of the infection in question within up to 7 days, after which complete recovery occurs. The only thing that may subsequently cause discomfort for some time is loose stools. As for the intensity of manifestations, as well as the severity and duration of symptoms that rotavirus infection brings with it, in general they are different. It is noteworthy that the symptoms characteristic of infection are similar to the symptoms of other diseases of a more severe nature. These include, for example, salmonellosis or cholera. It is for this reason that if a child’s temperature rises, as well as nausea and/or loose stools, a doctor should be immediately called to the home. If you experience severe abdominal pain as an additional symptom, you should call an ambulance. Self-medication should be excluded until specific doctor's instructions.
COMPLICATIONS OF ROTAVIRUS INFECTION IN CHILDREN Proper treatment of rotavirus infection does not cause complications. However, if you exclude frequent drinking during diarrhea and vomiting, especially for children under one year of age, dehydration can even lead to death (up to 3% of all cases). Failure to take the required measures can also lead to the addition of an intestinal bacterial infection to the virus, which will further complicate the course of the disease and the child’s condition. It is imperative to monitor the child’s temperature, because if it rises for a long time within 39°C, the load on the cardiovascular system increases significantly, and convulsions are possible. In general, the disease does not carry with it any long-term consequences, so one can indicate favorable prognoses for the future.
SYMPTOMS OF ROTAVIRUS INFECTION IN ADULTS
As we have already noted, the course of the disease in adults is milder than in children.
As for recurrent incidence, here, in contrast, with a low level of antibodies, immunity is not developed properly against rotavirus infection, and therefore its symptoms may recur again. The specificity of the disease is the same. So, it is also a viral gastroenteritis, the course of which affects the gastrointestinal tract, and is also expressed in dehydration and general intoxication. The most common method of infection is contact with contaminated food, but household, water and other contact cannot be ruled out. In adults, intoxication is moderate, with lethargy, muscle weakness, headache and weakness, low-grade fever (up to 37.7°C). The pharynx becomes swollen, a white coating appears on the tongue, and the heart sounds are muffled (as determined by examination by a doctor). The onset of the disease is also characterized by its own severity, which manifests itself during the first day from the moment of infection. Pain in the abdomen (epigastric region) also occurs. The stool is watery (within 3-9 times per day), nausea and vomiting are also present among the symptoms. With this infection, diarrhea is profuse, characterized by a sharp odor and pale color, in some cases there may be an admixture of mucus, lasting up to a week. Given the severity of fluid loss, dehydration also develops quickly, which, in turn, can lead to circulatory failure and the body stopping the production of urine (anuria). It should be noted that rotavirus infection is often a current phenomenon that occurs as a complication of diseases affecting the respiratory tract (rhinitis, pharyngitis). Meanwhile, in many cases, the disease is characterized by a mild course with the absence of its characteristic symptoms in the form of nausea and vomiting, while stools are loose and infrequent. In any of the variants of the course of the disease, the patient is a carrier of the infection, and accordingly, in this he is dangerous for the people around him. ROTAVIRUS INFECTION: TREATMENT IN CHILDREN
There are no drugs as such to eliminate rotavirus. For this reason, treatment of infection is symptomatic, and, therefore, is aimed at normalizing the condition by restoring the water-salt balance, which is disrupted due to vomiting and diarrhea. Also, the goal of treatment is to combat the results obtained from infectious exposure in the form of dehydration, toxicosis and disturbances in the functioning of the urinary and cardiovascular systems. The manifestation of symptoms indicating gastrointestinal disorders in a child should in no case allow the consumption of milk and dairy products in any form, because they currently represent an excellent aid for the growth of bacteria. The child may also have a decreased appetite or it may be completely absent - in any case, there is no need to force him to eat. A good alternative to food in this state would be a small amount of jelly (water, jam and starch, that is, homemade), you can also give chicken broth. If the child does not refuse food, you can give him liquid rice porridge without oil (slightly sweetened). The main thing in nutrition is the insignificance of portion sizes, which will prevent the gag reflex with gradual saturation.
The main treatment, in addition to dietary restrictions, is the use of rehydration therapy; sorbents (activated carbon, attapulgite, dioctahedral smectite) are also applicable. Days on which severe vomiting or diarrhea occurs require replenishment of salts and fluid volumes lost through vomit and loose stools. This provides for the possibility of using rehydron (a sachet per liter of water) 50 ml at intervals of every half hour or hour until the liquid runs out. If you miss taking this solution because of sleep, you should not wake up the child, just as you should not give him a solution in a volume exceeding 50 ml for this reason, because he may simply vomit it. As for temperature, an important point is the fact that the virus dies at 38°C, therefore, there is no need to lower the temperature below this limit. This applies not only to rotavirus infection, but also to, say, a common cold - the well-known fact is that lowering the temperature before reaching this point is highly not recommended (figuratively speaking, the body and its immune system in particular need to be allowed to “fight”). To bring down a higher temperature, the doctor will prescribe suppositories for children under 3 years of age (ceficon); for older children, paracetamol is prescribed (in accordance with the dosage for a specific age). To bring down the temperature, you can also use rubdowns using a weak vodka solution (the whole body is wiped without allowing temperature changes in the areas between its individual sections). Rubbing is performed half an hour after taking medication for fever if there is no result. Gastrointestinal disorders with fever are eliminated by taking Enterofuril as prescribed by the doctor in the dosage indicated by him. The drug is intended for the treatment and prevention of infection, as well as to prevent prolonged diarrhea in a patient. Abdominal pain is eliminated with no-shpa, again, as prescribed by the doctor and in the dosage specified by him (usually in the form of a solution).
ROTAVIRUS INFECTION: TREATMENT IN ADULTS
Considering the greater adaptability of the adult organism to this type of shock (and the adaptability of the gastrointestinal tract to them in particular), as well as their stronger immunity, the disease occurs in a mild form of exposure. Considering this, special treatment is not required in this case. If the symptoms are severe, then treatment is aimed at eliminating specific symptoms. So, this may include preventing dehydration by frequently drinking saline solutions (based on rehydron), as well as water and tea.
Additionally, sorbents are taken to accelerate the removal of toxins and improve well-being, as well as astringent medications. An important point is also the dietary restriction (in particular, the restriction applies to the consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates in the form of fruits, sugar, vegetables), again, dairy products are excluded. Due to the fact that the disease is contagious, the patient must be isolated during treatment, thereby limiting the spread of rotavirus infection. Hospitalization is possible based on epidemiological and clinical indications. If you suspect a rotavirus infection, you should contact your primary care physician (pediatrician) or infectious disease specialist, who will determine the necessary treatment based on the tests required. Additionally, he can refer the patient to a gastroenterologist.
Interested?For detailed information, contact us in a way convenient for you: This block can be edited or deleted . | Place an order Ask a question |
Disease prevention
Nutrition plays one of the most important roles in the prevention of arterial hypotension. It should be frequent (4-6 times a day) and in small portions. You should not eat before bed, with the exception of fresh vegetables. The diet should contain a lot of protein foods (cheese, peas, cottage cheese, lentils and other legumes), little sweets, with the exception of marshmallows, dark chocolate, marshmallows, fruits, dried fruits. If a teenager has arterial hypotension, do not limit him to coffee or black tea. Protect your child from stress and family quarrels, create conditions for him to engage in hobbies, and offer to enroll in a sports section.
Signs and consequences of low blood pressure
According to specialists from Carnelian MC, the manifestation of low blood pressure is typical for young women under the age group of 40 years.
Symptoms of disturbances include:
- insufficient blood circulation, leading to throbbing pain in the temporal region of the head;
- sudden change of mood;
- constant apathy, lethargy, feeling tired. The body is not able to recover after a good rest and sleep.
Low blood pressure can manifest itself for various reasons: as a result of previous infections, underweight, anemia, unfavorable work factors, changes in climatic conditions or seasonality. Also, pressure can change as a result of a lack of vitamins, indicating anemia, pre-infarction condition, weight deficiency, cardiosclerosis, VSD, renal failure, low hemoglobin, circulatory disorders, etc.
With a slight change in blood pressure, people live full lives. To avoid health problems, experts recommend exercise, adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition, often walk in the fresh air, give up alcohol and take vitamins and fruits. A person should also avoid stress and take care of his health, constantly monitor his blood pressure and keep it normal. Measurements should be taken several times a week; you should not drink alcoholic drinks or coffee, play sports, smoke, or swim in hot water beforehand.
Advantages of contacting SM-Clinic
In our clinic you can visit a pediatrician and pediatric cardiologist without queues and at an affordable cost. Some of the best specialists in St. Petersburg work at SM-Clinic; they have modern equipment and diagnostic equipment. The doctor will quickly determine the presence and extent of the disease and prescribe treatment that will return your child to the joy of a healthy and fulfilling life.
Sources:
- N.N. Arkhipova. Arterial hypotension in children and adolescents // Practical Medicine, 2008, No. 4(28), pp. 63-65.
- T.M. Tvorogova, N.A. Korovina. Arterial hypotension in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal, 2007, No. 21, pp. 1519-1524.
- K.M. Dzilikhova, M.G. Dzgoeva, Z.D. Kaloeva, S.Ch. Khestanova, A.K. Shavlokhova. Primary arterial hypertension in children // Pediatrics, 2010, v. 89, no. 3, pp. 116-122.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a cardiologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Electrocardiography (ECG) | 1400 rub. |
| Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) | 3500 rub. |
Causes of the pathogenic condition
Symptoms that are not due to disease.
If you suddenly feel dizzy and nauseous, do not be afraid. Usually the reasons for this condition are:
- a person spun on a carousel, swung on a swing, or was at a height for a long time;
- a person eats poorly, goes hungry and is on the wrong diet;
- thoughts are confused;
- stress and nervous environment;
- long stay in an unventilated and stuffy office;
- magnetic storms;
- taking medications and vitamins without consulting a doctor;
- got sick in the car;
- seasickness.
Causes of the pathogenic condition in girls.
Women have an unstable emotional and hormonal state, unlike men. They often go on diets, fast, and do fasting days to lose weight and maintain body shape.
As a result of such activities, their glucose levels decrease, frequent dizziness begins, digestive ailments worsen, and hair falls out, which leads to stress and depression.
Dizziness in women is possible only if they are pregnant, have recently been under stress, premenstrual syndrome is about to begin, or it is time for menopause.
Causes of nausea and dizziness associated with illness.
Severe dizziness and nausea lead to loss of coordination and balance. These anomalies indicate diseases:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- injuries to the head, hearing organs and spine;
- migraine;
- inflammation of the middle ear (labyrinthitis);
- episyndrome;
- Meniere's syndrome;
- disruption of the circulatory system of the brain;
- brain tumors;
- alcohol intoxication;
- spinal cord diseases;
- infections and meningitis;
- perilymphatic fistula;
- stroke.
An ambulance should be called if the patient, in addition to nausea and dizziness, experiences:
- fainting;
- vomit;
- elevated temperature;
- cardiopalmus;
- tingling hands;
- darkening of the eyes;
- ears began to hear poorly;
- dizzy after lying down for more than an hour;
- grainy image;
- pallor.
Pathogenic condition due to vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Staggering while walking, objects that “float”, nausea, anxiety, confusion of thoughts, a feeling of extreme hunger and lack of oxygen in the brain (the head is pressed from all sides) and dizziness are indicators of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
When you suddenly and abruptly change your body position, you begin to feel dizzy for a short period of time, and your health worsens due to the fact that the vessels do not have time to deliver a sufficient volume of blood to the brain.
Causes of pathogenic conditions that occur in the dark
. Systems such as the visual, vestibular, proprioceptive, and cerebral systems collectively regulate our balance. But if at least one of them has a disruption in the functioning of the organ, then dizziness will begin at night.
Causes of the pathogenic condition in a patient with diabetes mellitus.
During attacks, a patient with diabetes experiences chills, dizziness and nausea. This can lead to fainting or even coma. To avoid such symptoms, you need to get tested in advance, take the right amount of insulin or take medications, follow your diet and measure your sugar more often.
What to do if you feel dizzy and feel nauseous
Independent actions in case of dizziness and nausea:
- do not make quick movements, restore breathing;
- look at one specific object;
- drink cold water with a small piece of sugar;
- in case of strong emotional stress, drink a sedative or tea with oregano or chamomile;
- when your blood pressure drops, drink strong brewed black tea with chocolate (important: green tea, on the contrary, lowers blood pressure);
- if you have hypoglycemia (diabetics), eat candy with a lemon or mint flavor, or a piece of sugar, wash it down with warm tea;
- go outside or ventilate the room;
- if you start to feel very sick and everything around you is spinning, then you need to bend over and let your head go between your knees.
If the advice does not help, immediately call 003.