Clinical course of the disease
Dementia is a disease that manifests itself as impairment of cognitive functions (attention, memory, thinking) and personality disorder. Psychiatrists distinguish three stages of the disease:
- The first stage is called early or mild dementia. At this stage of the disease, symptoms are not expressed. Patients may experience decreased concentration, they quickly get tired, and become lethargic. Their memory suffers, their interest in their surroundings decreases. People become emotionally unstable;
- The second stage of the disease is manifested by moderate dementia. Clinical signs of the disease are more pronounced. Patients' memory is severely impaired and their character deteriorates. They lose the ability to navigate in space, become apathetic or aggressive, irritable. Patients cannot perform simple tasks: take care of the house, eat, take care of themselves. At this time, they need the attention and care of loved ones;
- The third stage of the disease is manifested by severe dementia. Patients at this stage are completely dependent on the people around them. They are unable to perform even simple actions without outside help and lose control of urination and bowel movements. Patients often lie in bed and find it difficult to swallow food.
Consequences
Senile dementia is a severe irreversible condition. The prognosis depends on how early the symptoms and signs of dementia in the elderly are identified and on compliance with the prescribed treatment program.
It is impossible to cure a person in this condition, but you can:
- slow down the development of negative changes;
- smooth out unpleasant symptoms;
- prolong life by improving its quality.
The patient's condition depends on:
- the presence of concomitant diseases;
- quality of care;
- psycho-emotional atmosphere.
How to communicate with a patient
Regardless of the cause of dementia, irreversible changes occur in the cerebral cortex that radically change a person’s life. He loses the ability to remember and understand new information, recognize his children and other loved ones, and think logically. Over time, life skills are impaired, and the sick person cannot be left alone. He loses his personality traits.
Psychologists at the Yusupov Hospital advise people caring for people with dementia to acquire new communication skills:
- Avoid raising your voice;
- Speak slowly, smoothly;
- To make sure that you managed to attract attention to the information, you should look into the patient’s eyes during a conversation and touch him carefully;
- Be the first to take the initiative to talk, since as dementia progresses, it is more difficult for the patient to start a conversation;
- Formulate questions so that the respondent can give an unambiguous answer: I don’t know, no, yes;
- If the patient does not understand what he is being asked about, the thought needs to be formulated differently;
- It should be noted that patients with dementia remember the past better than the future;
- Try to talk more often with the patient about the past, as this calms him down;
- If the patient stops responding to the phrases you say, you do not need to talk about him in his presence in the third person, as this may be perceived as humiliation.
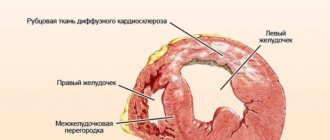
Etiology
Vascular dementia typically occurs in situations where multiple brain infarcts (or sometimes hemorrhages) result in the death of enough neurons or axons to impair brain function.
- Vascular dementia includes the following:
- Extensive lacunar infarction
: Damage to small blood vessels. Multiple lacunar infarcts occur deep within the white and gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres. - Multi-infarct dementia
: Damage to medium-sized vessels. - Single infarctions in strategic areas
: Single infarction in a functionally significant area of the brain (for example, angular gyrus, thalamus). - Binswanger's disease (subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy)
: It is a rare form of dementia that occurs due to damage to the small vessels of the brain and is associated with severe, poorly controlled arterial hypertension and systemic damage to the vascular system. This causes diffuse and irregular loss of axons and myelin with widespread gliosis, tissue death due to infarction, or loss of blood supply to the white matter of the brain.
Living with someone with dementia
People with dementia behave like little children. At the same time, they gradually lose skills without acquiring new ones. Relatives should take this fact for granted and not blame themselves for anything. If you detect the first signs of memory impairment, you should convince your loved one to contact a neurologist. Typically, at the onset of dementia, patients agree to this proposal. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital advise people who live next to a person with dementia to adhere to the following rules:
1. Don't be left alone with your problems. Caring for a loved one should not destroy connections with the outside world. You should ask relatives to call and come more often. You need to find people who were in a similar situation and communicate with them; 2. Do not refuse the help of your family and friends. You need to make others feel that their participation is extremely important to you; 3. Do not wait for negative emotions to spill out in the presence of the patient. Take your anger out somewhere else; 4. If you are tired or experiencing emotional exhaustion, contact a psychologist at the Yusupov Hospital. It will help prevent depression; 5. Pay proper attention to yourself, visit beauty salons, dress well.
If a loved one has memory impairment, you should not leave him alone with the problem. By contacting the specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, the patient’s relatives will receive recommendations that will allow them to live more comfortably. Our experts will tell you how to care for it, organize your life, and ensure safety.
Organization of patients' everyday life
If doctors have diagnosed a patient with dementia, his relatives should specially arrange rooms for the patient to live. You need to put locks in them, leave a minimum number of things and furniture, and remove sharp and cutting objects. Most people with dementia exhibit aggression and a tendency to vandalism. They can harm themselves and others. To prevent the patient from throwing away or destroying money and documents, they should be removed from the room and hidden.
A patient suffering from dementia will never be able to appreciate the actions of a caregiver or show gratitude. There is no need to be offended by him about this, just as we are not offended by small children. Dementia does not necessarily progress to the third stage of the disease. In many cases, severe memory impairment can be prevented with adequate therapy.
Some memory disorders are reversible. Sometimes, through the joint efforts of doctors and people caring for a patient, it is possible to partially restore impaired functions and improve the quality of life. Neurologists, psychotherapists and rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital together create an individual treatment program for each patient. This guarantees the maximum effect of the therapy. Doctors at the neurology clinic constantly monitor patients and, if indicated, change medications, their doses, and the regimen of use.
To provide your loved one with adequate medical care and professional care if dementia develops, call the contact center at any time of the day, regardless of the day of the week. Our specialists will select a convenient time for consultation with a neurologist who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of memory disorders.
Nutrition for dementia
Dementia is a pathology that develops against the background of organic brain damage and is manifested by impaired intellectual activity and personality disorder. According to statistics, older people are more susceptible to the disease, although the onset of dementia at an early age cannot be ruled out. The pathology is characterized by progression and a gradual increase in severity; the patient does not immediately lose acquired skills, knowledge and abilities. At the Yusupov Hospital, a personal nutritionist will develop an individual menu according to the recommendations of the attending physician.
Proper and healthy nutrition for dementia
A balanced and nutritious diet plays an important role in the treatment of dementia, since brain cells have an increased metabolism, so even a slight deficiency of any elements can lead to serious consequences. For this reason, it is worth taking foods seriously, as they can not only help improve the condition of patients with dementia, but also help prevent the onset of pathology.
According to statistics, residents of eastern countries, in particular India, rarely suffer from diseases that cause mental impairment, as they attach great importance to the quality of food and its composition. For example, daily use of seasonings contained in oriental dishes (curry, turmeric, cinnamon and others), according to research, can prevent the formation and accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain, which cause damage to neurons and lead to the formation of Alzheimer's disease, accompanied by dementia. Based on these observations, it is worth concluding that for therapeutic and preventive purposes it is necessary to formulate a diet in such a way as to reduce the degree of manifestations and the likelihood of the formation of diseases leading to dementia.
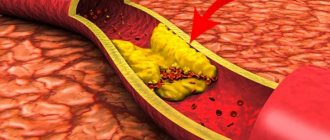
Vascular dementia often develops against the background of atherosclerosis, which is formed due to elevated cholesterol levels, which leads to the appearance of plaques and blockage of blood vessels. As a result, the brain experiences oxygen starvation, which ends in the destruction of neurons. For this reason, it is worth monitoring your cholesterol levels, in particular, avoiding foods with high cholesterol content and eating those that lead to a decrease in its levels.
Foods that lower cholesterol:
- dry red wine;
- almond;
- beans;
- blueberry;
- avocado;
- vegetable oils;
- barley, etc.
Also, if you have dementia, you need to drink enough water, and your diet should include dishes that improve the functional activity of the brain, which contain:
- fish;
- seafood;
- nuts;
- seeds;
- dairy products;
- dietary meat;
- seasonings (cinnamon, sage, saffron, lemon balm, etc.);
- vegetables;
- sauerkraut;
- fruits
What's harmful about dementia?
In addition to using healthy foods, you should exclude those that worsen the patient’s general condition, enhance the process of neuronal destruction, and negatively affect hormonal and metabolic processes and cerebral blood supply. In case of dementia, it is necessary to completely eliminate foods that increase cholesterol levels: egg yolks, animal fats, offal, sour cream, cheese, mayonnaise.
Excessive consumption of confectionery products is also harmful for dementia, so it is worth limiting or completely eliminating the use of white bread and sugar, pastries, chocolate, cakes, and ice cream. It is also worth reducing the amount of salt in food, eating less fried and fatty foods. It is especially important to give up alcohol, as it only enhances the processes of destruction in the brain.
Choice of therapy
Regardless of the type of dementia, researchers have found psychological and social therapy to be very effective. Treatment must be tailored to the patient. Simple memory training or word games, for example, can support mental performance. Occupational therapy—preferably at home—helps keep all activities under control. Music therapy can help reduce anxiety and fear. Research shows that physical activity stimulates the brain and helps prevent side effects of dementia such as depression. And the best recommendation is to stay in the center of life.
Life expectancy with dementia
It is impossible to give an accurate forecast of how long a person with dementia will live. Dementia comes in different types and can be slow and gradual, or it can progress and be fatal very quickly. Much depends on age, health status, care and adequate therapy.
Life expectancy with vascular dementia
Vascular dementia is a severe form of the disease. Dementia is caused by vascular disease, often develops after an ischemic cerebral infarction or hemorrhagic stroke, with atherosclerosis or hypertension; factors in the development of this form of the disease can be heart defects, high lipid levels and other disorders. Vascular dementia affects men more often.
In dementia accompanied by Parkinson's or Huntington's disease, the prognosis depends on adequate treatment of these diseases. Most often, dementia with such concomitant diseases is not characterized by rapid progression; the life expectancy prognosis is several years, with Huntington's disease - up to 10-15 years. Dementia with Lewy bodies is a rapidly progressive disease with a life expectancy of about 7 years.
Life expectancy for other types of dementia
Dementia can be caused by various diseases. Very often, senile dementia is associated with Alzheimer's disease. In this case, the patient’s age plays an important role: the older the patient, the slower the disease progresses; The younger the patient, the more the disease progresses. The average life expectancy of a patient with Alzheimer's disease is about 6-10 years from the time of diagnosis. Much depends on the age and stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the body.
Adequate treatment prescribed at an early stage of the disease can significantly prolong life and alleviate the condition. Specialists from the neurology department of the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating dementia and many other related diseases. Modern diagnostic equipment makes it possible to determine the areas of brain damage and the degree of development of dementia. The use of innovative world-class techniques at the Yusupov Hospital can improve the quality of life for patients with dementia.
Life expectancy in early dementia
Life expectancy at an early stage of the disease largely depends on the age of the patient. The younger the patient, the more complex and faster the disease progresses. In older people, the disease does not develop as quickly. Detected dementia at an early stage allows you to remain in adequate condition for a long time and take care of yourself. Manifestations of dementia at an early stage are:
- forgetfulness,
- slight mood swings,
- slight decrease in intelligence.
Life expectancy of bedridden patients with dementia
Bedridden patients with dementia are most often people who are at an advanced stage of the disease. Bedridden patients with dementia often die from pneumonia and sepsis, concomitant diseases already at a severe stage of dementia. The prognosis for dementia in bedridden patients is unfavorable, the condition is complicated by physical inactivity, impaired mental activity, and circulatory disorders.
Patients in serious condition are completely dependent on outside care; dementia is complicated by other diseases due to the patient’s immobility. At the Yusupov Hospital, relatives of the patient are trained. Caring for bedridden patients is complex and requires patience and knowledge about the characteristics of the disease.
Life expectancy of patients with dementia with optimal treatment
Life expectancy with dementia depends on the adequacy of treatment and care. At the first stage, the doctor prescribes diagnostic tests to differentiate dementia from other diseases. Treatment of senile dementia is based on eliminating the symptoms of the disease and reducing the risk of dementia progression.
Dementia is an incurable disease, the course of which depends on many factors - age, gender, type of dementia, concomitant diseases, adequate treatment and care. A calm environment and lack of stress help reduce the risk of progression of senile dementia.
Doctors recommend a special diet, vitamin therapy, music therapy, aromatherapy, acupuncture and other methods that improve brain activity. The average life expectancy of a young patient with dementia can be about 7 years; older people with dementia live on average from 7 to 15 years.
Diagnostics
Treatment is prescribed in accordance with:
- clinical symptoms of dementia in older people;
- a history of transient ischemic attack, stroke, and other risk factors.
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist. The following must be fulfilled:
- neuropsychological study
– questionnaire, conversation with loved ones, assessment of symptoms according to basic criteria;
- instrumental examination
– magnetic resonance or computed tomography, rheoencephalography, electroencephalography;
- laboratory diagnostic measures
(in particular, a study of hormone levels).
The psychiatrist gives his opinion. Dementia is similar to depressive states, anxiety neurosis, psychoorganic syndrome, and some other conditions.
To make the correct diagnosis, differential diagnosis is carried out. The following factors are taken into account:
- time elapsed since the onset of symptoms;
- state of the emotional-volitional sphere;
- degree of mental degradation;
- the impact of the changes on the quality of life.
Benefits of treating dementia at the Yusupov Hospital
The Yusupov Hospital has created all the conditions for the treatment of patients suffering from dementia:
- Comfortable rooms equipped with forced-air ventilation and air conditioning;
- Complete high-quality nutrition;
- Competent medical staff;
- Highly qualified doctors;
- Modern equipment from leading global manufacturers;
- Individual approach to choosing a treatment method for each patient.
The neurologists at the clinic have extensive experience in treating patients with various types of dementia. If relatives do not have the opportunity to provide care for the patient at home, comfortable conditions for the patient’s stay have been created in the hospice at the Yusupov Hospital.
To make an appointment with a neurologist, you should call. Contact center specialists will offer a convenient time for consultation with a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of memory disorders.