Disease concept
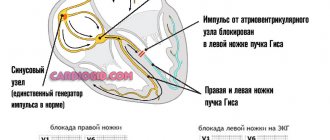
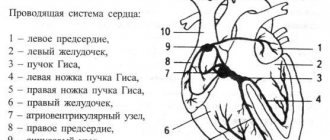
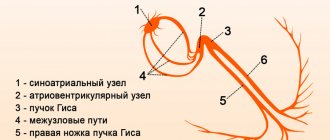
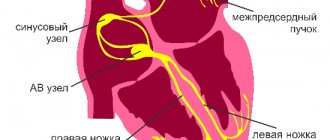
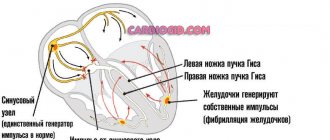
When doctors talk about a diagnosis such as incomplete or partial blockade of the right bundle branch, they mean an anomaly that occurs without visible symptoms in a child. When the disease occurs, the process of impulse transmission from the region of the right heart to the ventricular myocardium is disrupted. This impulse is transmitted by the so-called bundles of His. This is the name given to special cells connected to form muscle fibers. They are located in the interventricular septum. In turn, the bundles are divided into two branches - the right and left legs. Both legs are divided into anterior and posterior branches.
NBPBP has several variations. In young children, blockade of the right bundle or its branches is more often diagnosed. In this case, a slowdown in impulse transmission is observed. It is important to note that such a condition in a child is considered the norm of the child’s individual physiological development, and not a specific pathology.
Impaired impulse conduction is often observed in childhood. In the absence of various pathologies from the internal organs, this condition does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child.
What is right bundle branch block and how to live with it?
Every year, more and more people suffer from diseases of the cardiovascular system, which pose a serious threat not only to health and well-being, but also to life. Failures in the normal functioning of the heart are increasingly being identified in people of a younger age category, which is associated with lifestyle (the influence of cigarettes, alcohol, lack of sleep, stressful situations, etc.). Cardiac pathologies include disruptions in electrical conductivity; this process is called right bundle branch block, which provokes a slowdown in the contractile function of the heart.
Dysfunction of impulse conduction is not formed as a primary process; it usually acts as an addition to cardiac pathologies and manifests itself as a manifestation of the primary pathology. Right bundle branch blocks affect older men more than women. That is why all elderly patients should regularly visit the cardiology office at their place of residence.
The His bundle is the concentration of atypical fibers in the heart muscle. In the intracardiac septum, fibers form the right and left legs, along which excitation waves pass, responsible for normal contraction of the myocardium.
What are the risk factors?
Taking into account the variants of the course in clinical cardiology, this process is conventionally divided into partial and complete.
With partial damage, the wave passes along the right leg, the work of the left or one of its branches is preserved, the waves pass through healthy fibers, but this process occurs with a delay - this is exactly what a first-degree blockade happens.
If excitation occurs in an incomplete volume, grade 2 is diagnosed.
When a condition such as complete blockade of the right bundle branch develops, the signals are completely blocked.
8
24/7
During an electrocardiographic test, pathology can occur as intermittent (periodic) or permanent. In some patients, blockade occurs only when the heart rate increases or decreases.
Blockade of the right bundle branch is always preceded by valvular disorders or pathologies of the coronary system; they are visible on the ECG. In clinical cardiology, it is customary to distinguish the following pathological factors:
- overdose or long-term use of certain medications: antiarrhythmic drugs;
- persistent increase in the number of thyroid hormones in the body;
- water-electrolyte imbalance;
- history of severe endocrine pathologies;
- alimentary (primary) obesity;
- iron deficiency in the body;
- prolonged use of alcohol in large doses;
- insulin-resistant syndrome;
- disorders of the functioning of the immune system (autoimmune processes);
- PE (blockage of the pulmonary artery by a thrombus or its branches);
- COPD;
- smoking for a long period.
The set of anatomical structures of the heart has a complex structure, which is why the disease occurs in the following types:
- conduction failure on one fiber;
- along two fibers (along the right and anterior left branches);
- All branches of the bundle are involved in the process.
Why does it happen?
Cardiac failures, as provocateurs of blockade along the right bundle branch, are as follows:
- congenital or acquired heart disease throughout life: stenosis of the atrioventricular orifice and aortic valve, coarctation of the aorta, valvular insufficiency, anomalies of the interatrial septum);
- diseases that result in structural and functional disorders in the myocardium, in the absence of pathologies of the coronary arteries and valve apparatus, as well as under conditions of normal blood pressure;
- cardiac ischemia;
- dystrophic processes in the myocardium;
- Brugada syndrome (gene mutation characterized by a high risk of sudden cardiac death);
- history of myocardial infarction;
- pathological hypertrophy of the left ventricular wall;
- fibrous changes in impulse conduction fibers;
- myocarditis.
Clinical picture
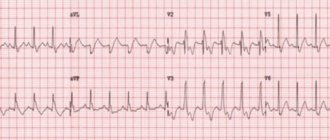
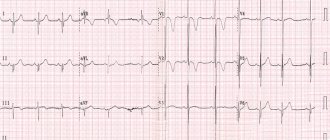
The disease can occur without symptoms or have changes on the ECG; blockade of the right bundle branch can be expressed by dizziness, even fainting, and a slowing of the heart rate (bradycardia).
At an appointment with a specialist, right bundle branch block is diagnosed based on changes detected during a preventive electrocardiogram or when looking for other cardiovascular diseases; usually this diagnosis is spontaneous.
In the absence of symptoms, the doctor’s main task is timely prevention of further manifestations.
A single-bundle lesion does not have specific symptoms. Clinical signs are observed as a result of three-fascicle blockade and manifest themselves in the form of severe bradycardia (with heart rate less than 30 beats per minute), disturbances in the frequency and depth of respiratory function in the absence of physical activity, arrhythmia, dizziness, short-term fainting and the appearance of cyanosis on the skin.
Diagnosis of pathology
Conduction disorders can be identified during an examination by a cardiologist based on complaints, most often on an ECG; long-term ECG recording is carried out, which is characterized by recording electrocardiogram indicators for 24 hours or more using a special portable device. This method makes sense if the disease was caused by cardiac diseases.
8
24/7
TEE is necessary to assess rhythm and cardiac contractility by applying small doses of electrical current to the area of the heart that is closest to the esophagus.
Laboratory tests are not very informative; they are not able to detect right bundle branch block; blood tests are prescribed to determine the underlying cause of the disease.
After making an accurate diagnosis, consultation with specialists in the field of cardiology and cardiac surgery is required.
Therapy at different stages
Treatment of people with right bundle branch block with drugs involves reducing the severity of the primary disease. If disruption of the electrical impulse is accompanied by heart failure, persistent hypertension or angina, maintenance therapy is indicated, for example: drugs of the nitrate group, antiarrhythmic and cardiotonic herbal drugs and antihypertensive drugs.
In the presence of a latent course, patient management tactics involve monitoring the condition with a cardiologist.
If atrioventricular (AV) or trifascicular block occurs, the cardiologist, together with the cardiac surgeon, offers patients the installation of a pacemaker, in other words, a pacemaker, which regulates the contraction cycle and normalizes the heart rhythm.
Forecast
Detection of the disease in the early stages allows for the necessary treatment and increases the patient’s chances of living longer.
How long do they live?
Why is right bundle branch block dangerous and what awaits the patient in the future? The prognosis of life is directly related to the root cause of development, an important place is occupied by the clinical variant of the course and the severity of the symptomatic complex. When diagnosing a single-bundle lesion, the prognosis is conditionally favorable.
Blockade of the right bundle branch without appropriate measures can lead to sudden death; life expectancy with such disorders does not exceed 4 years. If the causative factor is myocardial infarction, and during the course of the pathology angina pectoris, an increase in heart size, and atrial fibrillation are added, there is a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition and the risk of death increases.
Disease prevention
Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels have many symptoms that can worsen the quality of life and influence the development of severe conditions that pose a huge danger to life. By adhering to some recommendations, you can reduce the risk of developing CVS pathologies in the future:
- it is necessary to adjust the diet: include fresh fruits and vegetables in the daily diet, give up fatty, fried foods, smoked and pickled foods; It is preferable to choose lean varieties of meat;
- compliance with the drinking regime - at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day;
- adequate sleep, at least 8 hours a day;
- It is very useful to take daily walks in the fresh air and do gymnastics;
- give up alcoholic drinks and cigarettes;
- If possible, reduce stressful situations and nervous experiences.
Only timely confirmation of right bundle branch block will allow the necessary examination to be carried out and adequate treatment to be prescribed. At the first symptoms of cardiac disorders, you should immediately seek qualified medical help, often this can save a person’s life.
8
24/7
Why is this happening?
Having understood what incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch is, let’s talk about what causes this disorder may have. The following provoking factors can influence the development of such a diagnosis:
- Ischemic heart disorders.
- Development of tumor processes.
- Congenital anomalies of heart development.
- Transmission of infectious and inflammatory diseases affecting the myocardium and endocardium.
- Blockage of the pulmonary artery.
- Cardiosclerosis.
- Strong feelings and stress.
- Having a heart attack.
- Respiratory diseases leading to the appearance of the so-called cor pulmonale.
As for newborn babies, their right atrium is much larger than the left. Due to this feature, RBBB is considered a physiological norm.
By the age of 6 years, the difference in size between the right and left atria smoothes out and the impulse block gradually disappears. If by age 7 the defect is still detected, the patient is given a true diagnosis.
Causes
Diseases such as:
- congenital and acquired heart defects - stenosis of the aortic and mitral valves, pulmonary artery stenosis, stenosis and coarctation of the aortic mouth, aortic valve insufficiency, atrial septal defect;
- cardiomyopathy, myocardial dystrophy of various origins - endocrine (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus), metabolic (anemia), nutritional (alcoholism, obesity), autoimmune (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis);
- cardiac ischemia;
- cardiosclerosis, as the outcome of many cardiac diseases, leads to the replacement of part of the muscle fibers with scar tissue, including atypical muscle fibers;
- myocarditis of viral or bacterial origin;
- heart damage due to rheumatism - endocarditis, myocarditis;
- myocardial infarction;
- long-term arterial hypertension, leading to myocardial hypertrophy;
- intoxication with cardiac glycosides;
- pulmonary embolism;
- chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema, severe bronchial asthma), leading to the formation of cor pulmonale - stagnation of blood in the right atrium and ventricle with their hypertrophy and expansion.
In young children and adolescents, incomplete single-fascicle right blockade may accompany minor anomalies in cardiac development, and in the absence of organic heart damage is considered a normal variant. One- or two-fascicular left blockade is almost always associated with acquired rather than congenital heart diseases and cannot be regarded as a normal variant.
Signs of blockade in children
Practice shows that in most cases, blockade of the right bundle branch in children 1-4 years old occurs without visible symptoms. The violation is determined only during an examination using a cardiograph. More often this happens during routine examinations. Sometimes the symptoms may be mild. This usually applies to children 8-10 years old with an already confirmed diagnosis. In this case, the child experiences the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath, breathing problems.
- Periodic mild pain in the chest area.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
- Dizziness.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Headache.
Such signs often indicate a complete block of the right bundle branch and require proper treatment. The examination must be carried out necessarily, since such symptoms often occur in the presence of other dangerous diseases in the patient.
Incomplete blockade in children under 7 years of age does not require specific therapy, since the condition is considered the normal limit.
4.Treatment
As shown above, the detection (even accidental) of blockade of the legs or branches of the His bundle requires clarification, but does not necessarily require treatment. In general, such blockades themselves are, strictly speaking, a symptom and not a disease. Therefore, further therapeutic strategy will be completely determined by the results of in-depth diagnostics. When a pathological process or dangerous anomaly is detected, the goal of treatment is to eliminate or relieve the symptoms of the underlying disease, and there are too many options for the therapeutic regimen to list them even briefly. In other, non-pathological cases, no special treatment is required or prescribed.
However, in conclusion, we emphasize once again: normally there should be no decreases, inhibitions, asynchronies, and even more so a complete absence of conduction in the His bundle, and if any blockade occurs, consultation with a cardiologist is strictly required in any case.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that RBBB in young children is considered a peculiar norm, it is important to identify the disorder as early as possible. This will help you choose the right supportive therapy. The fact is that conduction disturbances over time lead to a decrease in the number of ventricular contractions. The patient should undergo an ECG and a blood test for hormones.
On the cardiogram, RBBB in children manifests itself as the presence of a wave, indicating atrial contraction, and the absence of a wave, indicating ventricular contraction. At the same time, characteristic notches appear on the S wave.
In addition to an electrocardiogram, to confirm the disorder, the patient should undergo the following procedures:
- Laboratory testing of blood and urine.
- Carrying out an ultrasound examination of the heart.
- KTR. This technique is usually used in severe cases of the disease.
- Electrocardiography, which is performed through the esophagus (transesophageal echocardiography).
- Monitoring of cardiac activity throughout the day.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed appropriate therapy. It will depend on the severity of the disorder and accompanying symptoms in the child.
Methods to combat the disease
So, we found out that if, against the background of partial blockade of the right bundle branch, the child does not have any other pathologies, and the clinical picture is not accompanied by various negative signs, specific treatment is not required. In this case, doctors choose observational tactics.
If signs of pathology are present, treatment methods may include the following:
- Let's take medications that have a sedative effect. Pediatricians often prescribe medications based on natural plant extracts.
- Taking vitamins, in particular group B.
- Taking medications that thin the blood.
- For heart failure, diuretics may be required.
- Therapy that helps normalize division and heart rhythm.
- To prevent pulmonary diseases and the appearance of the so-called pulmonary heart, the patient is prescribed treatment with hormonal drugs.
- When an inflammatory process develops in the area of the heart muscle, the child is prescribed medications that have an antibacterial effect.
Complete blockade of the right bundle branch requires surgical treatment. During the operation, an artificial rhythm conductor is installed for the patient. If such a device is in the body, it is important to avoid contact with electrical devices.
Treatment
There is no special course of therapy to treat the pathology. A patient with right bundle block does not require treatment. To a patient who has a single-fascicle or double-fascicular blockade, the cardiologist prescribes antioxidants, vitamins, sedative herbal medicines, antihypertensive drugs for arterial hypertension, ananginal drugs for coronary heart disease, antiplatelet agents to prevent the formation of blood clots in the heart and blood vessels. In severe cases, surgical intervention is required - installation of a pacemaker. With complete right blockade, when myocardial infarction develops, temporary cardiac pacing is required. In this procedure, an electrode is inserted into the right ventricle through a central vein. Permanent pacing is required with a three-fascicular block in the event of a Stokes attack (loss of consciousness).
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of therapy should be used with extreme caution in childhood. Before using them, it is important to consult with your doctor. Drinks such as a decoction of hawthorn berries, rose hips, and tea made from lemon balm leaves will be beneficial for cardiac activity. As a sedative, you can add motherwort, valerian, viburnum leaves and lingonberry to tea.
Before using any herbs, you should first make sure that your child is not allergic to them. The medication should be started with small amounts. If at this time no negative symptoms arise, then you can safely carry out treatment.
Is there any danger?
Many mothers are interested in the question of what is the danger of incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch in children? Medical practice shows that if the patient does not have serious pathologies of the heart, respiratory system and other internal organs, the diagnosis for the child is usually favorable. More often, danger arises when there is a blockade of the left bundle branch. Despite this, this disorder cannot be treated negligently, since a right-sided disturbance in the transmission of impulses can cause some complications.
Often, patients with this diagnosis experience so-called ventricular tachycardia. The condition is accompanied by increased heart rate, which leads to various problems over time. In particular, we are talking about an increased risk of developing such a dangerous disease as ventricular fibrillation. In the absence of timely assistance, this condition is often accompanied by death.
Regular preventive examinations with a cardiologist will help to identify any heart problems in children in a timely manner. Parents should under no circumstances self-medicate if any anxiety symptoms develop in their children. This can lead to serious complications.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The possible clinical picture of the blockade varies over a wide range and is determined, firstly, by the localization of the conduction disorder, and secondly, by the degree of its reduction.
Thus, blockade of the right bundle branch is usually detected by chance, on a preventive or “commission” ECG, and is not accompanied by any symptoms. This phenomenon occurs both in absolutely healthy people and in well-trained athletes, but also in people who have suffered a serious cardiac disease in the past.
About the same can be said about partial blockades of one of the branches of the left bundle branch. However, a complete blockade of the left leg is much more often than a blockade of the right one, and is based on a serious pathology.
Finally, combined variants of blockade, especially complete atrioventricular block of the third degree (maximum severity) pose a real risk of developing life-threatening conditions - for example, ventricular and/or atrial fibrillation with sudden cardiac arrest and death within a few minutes in the absence of specialized emergency resuscitation.
The most common symptoms of clinically significant blockades are heart pain of varying nature and intensity, attacks of dizziness, arrhythmias, tachycardia, and syncope.
One of the diagnostic problems is that the presence of left bundle branch block makes it impossible to reliably diagnose (ascertain or exclude) myocardial infarction using an ECG. Blockade of the right bundle branch does not interfere with electrocardiographic diagnosis of a heart attack, but may itself be a symptom of a heart attack, or a symptom of thromboembolism, or simply an epiphenomenon that does not mean anything clinically.
In general, identifying any type of blockade in the structures of the His bundle automatically (regardless of the absence or presence of subjective complaints, their intensity, etc.) requires a more in-depth examination of the condition of the heart muscle and its functioning. For this purpose, various methodological modifications of ECG and EchoCG are prescribed, according to indications - MRI, MSCT, laboratory tests, etc.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Is it possible to serve in the army and play sports?
NBPBB is not considered a pathology for which military service is prohibited. This, of course, does not apply to cases of severe disease with various additional disorders of internal organs and systems.
As for sports, physical activity is allowed if the person is in good health, but it is still better to exclude too intense physical activity and strength sports.
Is there prevention?
The diagnosis of incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch in children is a disorder that in most cases does not interfere with a full-fledged lifestyle and often goes away on its own at an older age. Despite this, to prevent various complications, the patient should still avoid excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress. It is important to adhere to the following rules:
- Sleep at least 8 hours throughout the day.
- Eat properly.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Try to eliminate stress.
- Physical activity should be moderate. It is useful to walk, swim, cycle, horse ride and other non-strength sports.
- To maintain heart health, it is recommended to saturate your child’s diet with foods rich in potassium, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus and other beneficial components.
- If any alarming symptoms develop, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- You should undergo scheduled preventive examinations with a cardiologist and other specialists annually.
If the patient has a pacemaker installed, the doctor should be visited 2-3 times a year.
A child with the described growth should take any medications in a strict dosage and only as prescribed by a doctor. These simple rules will help preserve the life and health of your child. Take care of yourself and be happy.