Therapy during pregnancy is calculated according to an individual scheme and may include a variety of drugs with an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and laxative spectrum of action. The treatment algorithm takes into account the timing, complexity of the disease and associated complications. Complex procedures can be postponed to a later date - after the birth of the baby and in the absence of breastfeeding.
What are hemorrhoids - types, symptoms, features in pregnant women
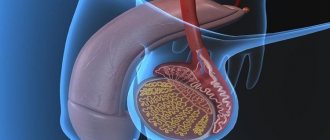
Hemorrhoids are a disease in which the vessels in the anus dilate and form hemorrhoids - inside the anus or outside under the skin.
Internal hemorrhoids form inside the anal canal. Internal hemorrhoids are often painless, but they can prolapse and bleed. External hemorrhoids form near the anus. If a blood clot develops in one of the external hemorrhoids, severe pain may occur. External hemorrhoids feel like a painful, hard hemorrhoidal lump. Hemorrhoids develop under the influence of certain factors. Pregnancy, along with other risk factors, contributes to the development of hemorrhoids. The incidence of the disease in pregnant women increases in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, as well as immediately after childbirth.
A growing uterus with a fetus and a sedentary lifestyle lead to impaired blood flow from the pelvis; chronic constipation in pregnant women contributes to excessive straining during bowel movements, which in turn contributes to the prolapse of nodes from the anus.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary: bleeding after bowel movements, pain, prolapse of nodes, sensation of a foreign body in the rectum. In addition, hemorrhoids can be characterized by a chronic course (chronic hemorrhoids): with minor, mildly expressed symptoms; and acute, in which there is a sharp pain in the anus and a rapidly swelling painful node or several nodes appear, which thrombose under the influence of certain factors. Thrombosis of the hemorrhoid is an indication for surgical treatment (if the disease is no more than 3 days old). This is also an indication for the treatment of exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids. Other symptoms of acute hemorrhoids can be treated by adjusting the treatment regimen and prescribing medications.
Removal of hemorrhoids with laser
After this small operation, which is performed on an outpatient basis and without pain, during pregnancy there is a more than 90% chance that hemorrhoids will not bother you. In 5-10% of pregnant women, slight swelling appears in the anus (there is still living tissue there, and swelling also occurs on the legs). Sometimes small veins, up to several millimeters, may appear and become inflamed. This is not at all comparable to inflammation of an entire hemorrhoid. But this is my reinsurance.
For almost 5 years of practice, not a single patient I operated on came during pregnancy with large inflamed nodes, wrote to me in the messenger or called me.
Yes, 5-10% may have small nodes after childbirth. We will remove it with a laser again and live in peace.
A phrase I have repeatedly heard from patients: “It’s good to be without hemorrhoids!” speaks for itself.
How is the operation performed?
We remove hemorrhoids with a laser through small punctures of the skin near the node. The operation is painless and is performed under local anesthesia. After it, sometimes half of the patients experience discomfort for up to 30 minutes. You go home 1 hour after the operation and go about your business, but without much stress.
If someone is in fitness, then in 2-3 weeks, please train.
A small but important point - all this applies to small or medium-sized hemorrhoids.
If the hemorrhoids are large enough or old (several years), or in those who have had surgery before, the recovery is a little more uncomfortable in the first week or two after surgery. A little - actually a little. Don’t be afraid, you took the Nise tablet if necessary and nothing bothers you.
With long-term hemorrhoids, the skin around the anus may stretch and anal fimbria may form. At the request of the patient, we will make the butt beautiful - we will remove these fringes.
How to cure hemorrhoids in pregnant women
The main difficulty in treating hemorrhoids in women during pregnancy and after childbirth is choosing drugs that can most effectively cope with the symptoms and are safe for the woman and child.
The pharmaceutical market offers a wide range of effective drugs with different trade names, many of them are made from natural substances and are safe for pregnant and lactating women. However, before prescribing any drug, consultation with a doctor is necessary to discuss the advisability of its use, the risk-benefit ratio and obtain recommendations.
Conservative (medicinal, non-surgical) methods often do not cure hemorrhoids, but only temporarily relieve unpleasant symptoms.
However, in some cases (ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, stage III-IV hemorrhoids, thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, complicated course, subjective complaints and patient desire), surgical treatment is necessary. Currently, there are minimally invasive techniques, low-traumatic methods that can relieve the disease for a long period of time without the need for the use of strong analgesics.
Until recently, pregnancy was a relative contraindication to surgical removal of hemorrhoids. This is primarily due to the need to use anesthesia during surgery, as well as prescribe painkillers. As is known, many medications are not recommended for use during pregnancy and lactation due to a possible toxic effect on the developing body of the child.
Our clinic provides both conservative and surgical treatment of hemorrhoids in pregnant women. If the task is to cure external hemorrhoids, the matter is often limited to drug therapy. For internal hemorrhoids, surgical methods are used.
The need for treatment of hemorrhoids in an expectant mother
External and internal hemorrhoids
All the above reasons are favorable factors for the development of hemorrhoids in the body. Therefore, their occurrence is not subject to the activities of a pregnant woman. No matter how much she wants to have them, they will still appear and manifest themselves in her condition. But enduring constant pain when going to the toilet is also not an option. It is imperative to treat them. Treatment of hemorrhoids is complicated by the fact that many of the components included in the medications will necessarily enter the circulatory system, circulating not only in the mother’s body, but also in the baby’s body.
Due to this, they can have a negative impact on the child’s body. Taking medications orally, as a result, is not the most successful way to get rid of the problem. Other treatment methods should be considered. The best method of treatment in this situation is the use of special medicinal ointments, which have minimal harm to the health of the unborn baby. The pharmacy chain is simply replete with a variety of ointments for hemorrhoids, which are prescribed to pregnant women.
It is best to get rid of hemorrhoids before childbirth, so that the hemorrhoidal node does not become pinched during pushing. And as you know, if such pinching occurs, the woman will experience additional pain during childbirth, which is extremely undesirable. The use of conservative treatment has the most favorable positive effect on the body of the unborn baby. Before using any ointments, you should definitely consult with your doctor, and sometimes undergo appropriate tests.
In addition to the well-known ointments for hemorrhoids, there are special suppositories, the use of which will also not harm the baby developing in her body.
Surgeries to remove hemorrhoids in pregnant women in our clinic
The department has the technical equipment to perform all types of surgical intervention for hemorrhoidal disease, ranging from latex ligation to ultrasonic removal of hemorrhoids.
- Ligation of hemorrhoids. This method is used to treat internal hemorrhoids, when the manifestations of hemorrhoids include prolapse of self-reducing hemorrhoids and moderate bleeding during bowel movements. The essence of the method is that a small latex ring is placed on the hemorrhoidal node, which compresses its base with the vessels passing through it, stopping the blood flow in the node. After several days, the knot and the ring fall off, and the resulting wound heals within 1-2 weeks. This procedure is most often virtually painless.
- Sclerotherapy and infrared photocoagulation. These methods are suitable for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease, manifested only by bleeding without prolapse of nodes.
- Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical operation aimed at removing hemorrhoids. This is the best way to achieve complete disappearance of all symptoms. Surgical removal of internal hemorrhoids is used for prolapsed and non-reducible nodes, or when the effect of outpatient treatment is not observed, or when outpatient treatment is impossible. During surgery, excess tissue that is a source of bleeding is removed. To make the patient more comfortable, the operation is performed under spinal anesthesia with sedation.
Photo of hemorrhoids in a pregnant woman BEFORE
Photo of hemorrhoids in a pregnant woman AFTER
Taking into account the conducted research, standards for the management of patients with hemorrhoids during pregnancy and lactation have been developed, allowing for the safest possible surgical intervention and ensuring adequate postoperative pain relief. The Clinic of Coloproctology and Minimally Invasive Surgery is located in the same institution as the Clinic of Obstetrics and Gynecology. This allows us to monitor patients after surgical treatment together with gynecologists.
You should always remember that pregnancy is a special condition that requires careful monitoring and an individual approach. Therefore, even drug treatment and regime correction require consultation with a qualified specialist.
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy and after childbirth
Unfortunately, the risk of developing hemorrhoids increases during the second half of pregnancy, as well as during and after childbirth.
During the period of bearing a child, the uterus significantly increases in volume, and by the time of birth it occupies most of the abdominal cavity. The intestine is compressed by the enlarging uterus, the rectum changes its position, its venous vessels are pinched, which leads to blood stagnation. In addition, during pregnancy, the susceptibility of the intestinal muscles to nerve impulses and substances that stimulate its work is significantly reduced. This is no coincidence: the intestines and uterus have a common innervation (their work is regulated by one nerve plexus), therefore any excessive activation of the intestines can stimulate the contractile activity of the uterus. Such a positive protective reaction aimed at maintaining pregnancy also has its downside: bowel movements become more or less difficult, and the woman begins to suffer from constipation, requiring straining during bowel movements. During childbirth, during contractions and pushing, intra-abdominal pressure rises sharply, and the fetal head, pressing tightly against the walls of the pelvis, compresses the vessels, including the veins of the rectum. The existing nodes increase in size and acquire a denser consistency. During contractions, and especially pushing, they protrude and turn blue; in the period between pushing, when intra-abdominal pressure decreases, they decrease and take on a calmer appearance. The longer the labor process, the higher the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Statistics show that hemorrhoids occur in pregnant women quite often: they affect 7.7% of non-pregnant women, 25.7% of pregnant women and 49.8% of those who have just given birth. However, many pregnant women are in no hurry to tell the doctor about it, believing that hemorrhoids - normal state of a pregnant woman. But neglected, untreated hemorrhoids can cause anemia (decrease in the amount of hemoglobin), diseases of the musculoskeletal system (for example, arthritis - inflammation of the joint), genitourinary system (chronic inflammatory processes). The presence of hemorrhoids is not taken into account when choosing a method of delivery (natural birth or caesarean section), however, it cannot be ignored when determining the management of pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Prevention of hemorrhoids. How to avoid a “delicate problem”?
- A pregnant woman should pay special attention to the treatment of any disease. What is not contraindicated in a normal lifestyle can have a negative effect on the fetus during pregnancy. Therefore, during this period you should never self-medicate. The use of any medications must be strictly agreed with your doctor. Considering the variety of stages of hemorrhoids and the particular course of the disease, the selection of treatment should be individual and carried out by a proctologist (a specialist in the treatment of diseases of the rectum). In the first stage of the disease, it is enough to follow the following rules:
- Never strain during bowel movements.
- If possible, you should avoid prolonged work in a standing or sitting position, and if this is not possible, you should change your body position more often and take breaks.
- Follow a diet to prevent constipation. The diet should be rich in vegetables and fruits with a moderate amount of meat and carbohydrates. The diet is important (frequent, fractional, at least 5-6 times a day), drinking enough water (up to 1.5-2 liters per day). Fermented milk products, bran bread, vegetables (except legumes) are healthy. Depending on the time of year, it is necessary to eat beets, prunes, sauerkraut, pumpkin, carrots, watermelons, and melons daily. It is necessary to limit the consumption of black bread, legumes, fruits and berries, which can cause constipation. For hemorrhoids, any alcoholic drinks, salty, hot, spicy, pickled foods are strictly prohibited: these products increase blood flow to the pelvic venous plexuses. You should not eat fatty foods: it slows down the passage of food through the intestines, thereby creating the preconditions for the development of constipation.
- It is necessary to carry out an external toilet with cool water after each bowel movement; in case of severe hemorrhoids, it is better to completely abandon toilet paper. You can have a short (15-60 seconds) ascending shower (just turn the shower over and direct its jets upward) or apply tampons with a cold infusion of chamomile or oak bark (brew 1 tablespoon per glass of water and cool).
- 2-3 times a day, it is recommended to lie on your back for 15 minutes with your pelvis elevated, for example on a small pillow.
In addition to following the rules of prevention, women with the second and third stages of the disease are treated with special medications, warm sitz baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and infusions of medicinal herbs. Such women are strictly prohibited from heavy physical labor and certain types of housework (long hand washing, washing the floor by hand without using a mop).
In the fourth stage of the disease (excessive bleeding, strangulation and necrosis of prolapsed hemorrhoids), emergency hospitalization is necessary. In these cases, there is a need for surgical treatment. Such patients undergo hemorrhoidectomy (excision of nodes) or minimally invasive (small or bloodless) operations. More gentle interventions include:
- sclerosing injections (introduction of special “blinding” drugs into the node walls);
- ligation (the node is pinched with a latex ring, which causes rejection (death) of the node after 7-10 days, followed by the loss of the affected tissue);
- infrared photocoagulation and laser coagulation (exposure to laser or high temperature at the base of the node).
If the pregnant woman’s condition allows, then doctors try to postpone all these interventions until the period when the woman recovers after childbirth, i.e. after 2-3 months.
Table of antihemorrhoidal ointments allowed during pregnancy
For the convenience of pregnant women, all the ointments presented above are summarized in a table that will help you understand in which trimester of pregnancy this or that medication is allowed.
| Means | Trimesters | ||
| I | II | III | |
| Ichthyol ointment | + | + | + |
| Heparin ointment | – | + | +/- |
| Gepatrombin G | – | + | + |
| Vishnevsky ointment | + | + | + |
| Levomekol | + | + | + |
| Fleming's ointment | + | + | + |
| Posterisan | + | + | + |
| Troxevasin | + | + | + |
| Troxerutin | – | + | + |
| Relief | In consultation with the doctor | ||
| Bezornil | According to strict indications | ||
| Procto-Glyvenol | – | + | + |
| Relief Advance | In consultation with the doctor | ||
Ointments against inflammation and infection
Medicines in this category are usually prescribed for exacerbation of the hemorrhoidal process, for severe inflammation and/or prolapse of enlarged cavernous formations.
The active ingredients contained in the preparations quickly relieve swelling, accelerate tissue regeneration and destroy pathogenic bacteria that are present in the intestines and can infect damaged areas in the anorectal area. What ointments can be used for hemorrhoids?
The active ingredients contained in the preparations destroy pathogenic bacteria present in the intestines.
Ichthyol ointment
This drug is made from processed peat containing fish remains. The active ingredient is ichthammol, a substance containing sulfur.
The active component gives ichthyol ointment multiple beneficial functions, including pain relief, inflammation relief, disinfection, tissue drying and suppuration prevention, and improvement of local blood circulation.
Ichthyol ointment prescribed at any stage of gestation helps:
- from external hemorrhoids;
- from rectal fissures;
- from ulcers in the rectum.
Contraindications. The medication is prohibited for use only if a pregnant woman has intolerance to the active or auxiliary ingredients.
Application. A small amount of ointment is applied to the skin of the anus before going to sleep for 2 weeks. In the morning, excess drug can be removed with a napkin and the perineum can be washed with water. Before lubrication, hygiene procedures should be carried out.
Ichthyol ointment for hemorrhoids relieves inflammation and accelerates healing, but is not able to cure the disease, so it is used as part of a complex treatment of hemorrhoids with other medications.
Price. You can purchase the product at any pharmacy for 70-90 rubles.
Ichthyol ointment for hemorrhoids relieves inflammation and accelerates healing.
Heparin ointment
The main ingredient responsible for the effect of the drug is the anticoagulant heparin. It is thanks to this substance that heparin ointment for hemorrhoids effectively and quickly relieves inflammation, prevents the formation of blood clots and resolves existing blood clots.
Other active components - benzocaine and benzyl nicotinate - additionally anesthetize hemorrhoids and increase the penetration of heparin into tissues.
Heparin ointment for hemorrhoids is indicated for:
- inflammatory processes;
- enlarged external nodules;
- high risk of thrombosis formation.
Contraindications. Heparin ointment is prohibited for use if a pregnant woman has:
- increased bleeding (the drug reduces blood clotting, which leads to bleeding);
- rectal fissures;
- erosive damage to the anus;
- risk of spontaneous abortion.
Application. Since the medication has limitations and side effects, expectant mothers are allowed to use it only after consulting with their doctor. And in the first trimester it is better to avoid using it altogether.
For internal hemorrhoids, Heparin ointment is applied to a cotton swab, which is inserted into the rectum.
The dosage and duration of treatment is determined by a specialist; usually the product is applied to the external nodules twice a day for 10-14 days. For internal hemorrhoids, the drug is applied to a bath tampon, which is inserted into the rectum.
Price. The average cost of a medicine in Russian pharmacies is 50 rubles.
Gepatrombin G
This is a combination drug that, in addition to heparin, also contains prednisolone and lauromacrogol 600. The combination of these ingredients allows you to dissolve and prevent the formation of blood clots in the veins, relieve swelling and stop inflammation.
In addition, the drug relieves pain, glues blood vessels together, which promotes the collapse and reduction of cavernous dilated veins.
In addition to external hemorrhoids during pregnancy, Hepatrombin G is indicated for the diagnosis of:
- internal hemorrhoids;
- thrombophlebitis of the anal veins;
- itchy sensations;
- eczematous lesions of the anus;
- anal fissures.
Contraindications. The drug is prohibited for use if the main or additional ingredients are intolerant.
Hepatrombin G relieves pain and glues blood vessels together.
You should also stop using the product if the skin or mucous membrane of the anorectal area is affected by bacteria, viruses or fungal organisms.
Due to the presence of heparin, the ointment is prohibited if there is a predisposition to bleeding and tumor formation of the skin.
Application. Hepatrombin G during pregnancy can be used only from the second trimester due to the content of a hormonal substance. Using the product is very simple - you need to apply it to the affected area 2-4 times a day. For internal hemorrhoids, the drug is administered into the intestine using an applicator.
Price. The ointment can be purchased without a prescription for about 170-190 rubles in any pharmacy chain.
Vishnevsky ointment
The composition of the ointment, or rather balsamic liniment, includes 3 main ingredients: xeroform, birch tar and castor oil.
It is their combination that determines the unique properties of the drug.
Vishnevsky ointment for hemorrhoids disinfects, relieves inflammation, kills pathogens, and also strengthens local immunity.
Vishnevsky ointment for hemorrhoids disinfects, relieves inflammation, and kills pathogens.
In addition, the ointment has an irritating effect on tissue, activating blood circulation in damaged areas and thereby accelerating regeneration.
Balsamic liniment is a universal remedy against many pathologies of the skin, purulent processes in the deep layers of tissue.
It can be prescribed to pregnant women when:
- acute external hemorrhoids;
- inflammation of the anorectal area;
- anal fissures.
Contraindications. The drug has a very short list of contraindications - it cannot be used only if you are hypersensitive to one or more ingredients.
Application. Expectant mothers can use the drug in any trimester; it is also allowed during breastfeeding. The product should be applied to the nodules and surrounding tissues in a thin layer, the procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day.
Price. Another advantage of balsamic liniment is its low cost. The ointment is sold in pharmacies for 30-40 rubles per package.
Levomekol
This is a combination drug, which is also called “the surgeon’s favorite drug.”
Levomekol is used to treat external hemorrhoids.
The drug Levomekol for hemorrhoids received this name for its pronounced antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and wound-healing qualities.
The combination of active substances (chloramphenicol and methyluracil) ensures rapid penetration of the product into the affected tissues and acceleration of recovery processes in the deep layers.
The drug is indicated for use when detecting:
- rectal fissures;
- external hemorrhoids;
- erosive and ulcerative damage to the anorectal area;
- inflammation of the anus.
Contraindications. Levomekol has a minimum of contraindications. The product is prohibited for use only in case of hypersensitivity to its ingredients.
Application. During the period of bearing a child, the drug is allowed, but it must be agreed with the gynecologist, since the ointment contains a local antibacterial ingredient.
For hemorrhoids, apply a small amount of ointment to the affected areas in the evening after hygiene procedures.
Price . You can buy Levomekol at any pharmacy at a very reasonable price - 100-110 rubles.
During pregnancy, Levomekol is permitted, but its use must be coordinated with a gynecologist.
Fleming's ointment
This is a homeopathic medicine that contains extracts of medicinal plants such as calendula, witch hazel, and horse chestnut. The drug also contains zinc compounds and menthol.
The natural components of Fleming's ointment can quickly and effectively relieve inflammation, destroy pathogenic bacteria, relieve pain, dry damaged areas, and strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
The drug is used for mild external hemorrhoids, which are accompanied by inflammatory processes and the release of venous exudate (the so-called weeping hemorrhoids).
Contraindications. Due to its naturalness, the drug has virtually no contraindications, with the exception of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Expectant mothers are prescribed this ointment in any trimester of pregnancy.
Application. The product is used in a short course – up to 7 days.
If symptoms do not go away, the doctor may extend treatment or prescribe a different drug. Apply the ointment 1-3 times a day, applying a thin layer to the inflamed areas.
Price. The price for a 25-gram tube is approximately 300-320 rubles. The drug is available without a prescription.
Fleming's ointment is used for mild external hemorrhoids, which are accompanied by inflammatory processes.
Posterisan
The drug, which is based on inactivated bacterial cells, has pronounced anti-inflammatory properties. Its use allows you to remove swelling, restore damaged tissue, accelerate the healing of cracks, and increase local immunity.
In addition, the ointment has a positive effect on the condition of veins and capillaries, increasing their tone, eliminating congestion, as a result of which itching and burning sensations in the perianal area disappear.
Hemorrhoid cream can also be used for problems such as:
- eczematous lesions of the anus;
- rectal fissures;
- itching in the anal area;
- perianal dermatitis.
Contraindications. The main contraindication for use is intolerance to the phenolic compound present in the composition. In other situations, the drug is approved for all categories of patients, including pregnant women.
Application. The drug should be applied to the affected area of the skin or mucous membrane in a thin layer in the morning or in the evening. For internal hemorrhoids, the product is injected into the rectal canal using the applicator included in the package.
Price. Prices for the drug vary, but the average cost of a 25-gram tube is 480 rubles.
Posterizan ointment has a positive effect on the condition of veins and capillaries, increasing their tone and eliminating congestion.
Ointments with vasoconstrictor and venotonic properties
Ointments for external hemorrhoids for pregnant women are prescribed to improve blood circulation in cavernous formations. Venotonic drugs are designed to restore the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels and improve venous blood flow.
Also used are agents with a vasoconstrictor effect, which are intended to stop bleeding and relieve swelling of hemorrhoids.
Troxevasin
The drug, classified as a venotonic and angioprotector, increases the tone of the venous walls, increases their elasticity and reduces fragility, relieves inflammation and swelling.
In addition, Troxevasin reduces the severity of pain and prevents the formation of blood clots in the venous ducts. At the initial stages, the gel is able to completely restore blood circulation in the veins.
The drug not only relieves hemorrhoids during pregnancy, but also effectively fights conditions such as:
- venous insufficiency;
- varicose veins;
- spasms of the rectal valve.
Troxevasin reduces the severity of pain and prevents the formation of blood clots in the venous ducts.
Contraindications. The gel is prohibited for use if you are intolerant of the active or additional ingredients. Also, the product should not be applied to deep wounds and infectious processes in the anorectal area.
Application. Venotonic can be used at any stage of gestation with the permission of the treating doctor. The drug is applied to the damaged area or a compress soaked in the product is applied to the external hemorrhoids.
Price. The drug can be purchased without a prescription for 180-210 rubles.
Troxerutin
The drug acts similarly to Troxevasin, since it contains the same active ingredients. This venotonic helps normalize blood circulation, prevent the formation of blood clots, eliminate congestion in the anal veins and relieve inflammation and swelling.
Among the indications of the medicine are:
- external hemorrhoids;
- swelling of the anorectal area after hemorrhoidectomy;
- venous insufficiency.
Contraindications. The list of contraindications coincides with the restrictions that the previous venotonic agent has.
Troxerutin helps normalize blood circulation and prevent the formation of blood clots.
Application. But on this point there are some discrepancies. Troxerutin is prohibited in the first 12 weeks of gestation; its use can only be started from the third trimester. Apply the gel to the damaged external nodules in the morning and evening.
Price. The expectant mother may be pleasantly surprised by the price of the medicine. In pharmacy chains it costs approximately 35-40 rubles for a 40-gram tube.
Relief
The product contains a unique ingredient - shark liver oil, which helps stop bleeding, accelerate tissue regeneration, relieve inflammation and itching.
The second active component, phenylephrine, is a pronounced vasoconstrictor that prevents bleeding and relieves swelling of tissues.
In addition to external hemorrhoids, the drug is used to treat:
- internal hemorrhoids;
- rectal fissures;
- itching in the anus.
Contraindications. The ointment is prohibited for use in cases of intolerance to the constituent elements of the product, blockage of blood vessels with blood clots, or a blood disease in which the number of granulocytes is reduced. Due to the vasoconstrictor effect, the drug is prescribed with caution to hypertensive patients.
Relief is approved for use during pregnancy, but only under strict indications.
Application. The product is approved for use during pregnancy, but only under strict indications. Apply the ointment twice a day to the affected areas or inject it into the rectum using an applicator.
Price. The medicine can be purchased for 390 rubles per tube.
What medications for hemorrhoids can pregnant women take?
In the treatment of hemorrhoids, two types of drug treatment can be used: local and systemic. During pregnant women, local treatment is preferred to systemic treatment.
Local treatment. Today, there are a large number of different medications for the local treatment of hemorrhoids, which are available in the form of suppositories or ointments and creams. Local application of drugs reduces the risk of side effects, increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the negative impact of treatment on the fetus. The action of these drugs is aimed at rapid pain relief, limiting inflammation and swelling, normalizing blood circulation in the rectum, counteracting vascular thrombosis, relaxing the rectal sphincter, reducing intestinal motility (motor activity) and softening stool.
Rectal suppositories for hemorrhoids are inserted into the rectum after bowel movements. The suppository should be inserted while lying on your side, without pushing it into the ampulla of the rectum, but holding it in the anal canal for 1-2 minutes: this way it will dissolve and its insertion will be more comfortable.
Hemorrhoids - varicose veins in the anus, caused by hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies of the rectum, are the most common proctological disease. It is believed to affect more than 10% of the population aged 30 to 50 years. According to various authors [1, 2, 14], hemorrhoids occupy one of the first places in coloproctology, and its prevalence is high and amounts to 140-180 people per 1000 adults.
In women, hemorrhoids appear or worsen mainly during pregnancy and childbirth. According to statistics, hemorrhoids are 5 times less common in nulliparous women than in women who have given birth at least once. In this case, the age criterion also plays an important role: during pregnancy at 30 years of age, the disease occurs 3 times more often than during pregnancy at 20 years of age. According to N.V. Moon et al. [5], hemorrhoids occur in 7.7% of non-pregnant women, 25.7% of pregnant women and 49.8% of postpartum women. Pregnancy, although not the main pathogenetic factor of hemorrhoids, often reveals it and aggravates its clinical course. On the other hand, hemorrhoids in pregnant women often complicate the course of labor and the postpartum period [1, 10, 11].
The views of researchers on the etiology of this disease are very contradictory. If Hippocrates attributed the cause of hemorrhoids to bile and mucus, then in subsequent centuries many different theories were put forward and disputed. Congenital insufficiency of the venous system, venous congestion, and disruption of the mechanism of the rectal sphincter were mentioned as the main pathogenetic factor. At the same time, none of the hypotheses based on the pathology of the venous system could explain the origin of the main symptom characteristic of hemorrhoids - the discharge of scarlet blood. The answer to this question was given relatively recently, in 1963, when cavernous vascular plexuses were discovered located in the submucosal layer of the caudal part of the rectum. Cavernous bodies are located in the area of the base of the anal columns diffusely or, more often, grouped mainly in three zones: on the left lateral, right anterolateral and right posterolateral walls of the anal canal. It is in these areas that hemorrhoids most often subsequently form. It has been proven that, in addition to veins and arteries, these vascular formations contain elastic connective tissue and smooth muscle cells. By regulating blood flow in the anal canal area, hemorrhoidal plexuses provide the basic functions of the rectum: retaining feces and defecation, providing an effective immune barrier between the internal environment of the body and the outside world. A hemorrhoid is a hyperplastic change in the cavernous tissue of the rectum, caused by an increased influx of arterial blood into the cavernous bodies through arteries with obstructed outflow through the efferent venules. The development of dystrophic processes in the anatomical structures that form the fibromuscular framework of internal hemorrhoids contributes to their gradual displacement in the distal direction [6, 19].
A major role in the development of hemorrhoids is played by impaired blood outflow through the venules from hyperplastic cavernous bodies of the distal rectum and anus. These cavernous bodies are present normally and are formed at the 3-8th week of embryonic development and are located in the area of the base of the Morganian columns. Cavernous bodies differ from ordinary veins of the submucosal layer of the rectum in the abundance of direct arteriovenous anastomoses. This is precisely the explanation for the fact that in hemorrhoids bleeding is arterial in nature. Hemorrhoids usually occur in individuals with pronounced groups of cavernous bodies. Other factors in the occurrence of hemorrhoids are congenital functional deficiency of connective tissue, impaired nervous regulation of the tone of the venous wall, increased venous pressure due to constipation, prolonged work in a standing or sitting position, heavy physical labor, and pregnancy.
The main pathogenetic factors in the development of venous pathology during pregnancy are:
- dishormonal changes;
— functional state of the vein walls;
- increase in circulating blood volume;
- changes in the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure.
A certain role in the occurrence of hemorrhoids is attributed to the abuse of alcohol and spicy foods, as a result of which the arterial flow to the cavernous bodies of the rectum increases. With prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors, along with predisposing factors, hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies occurs and the hemorrhoidal node itself is formed [4, 10, 12].
There are internal hemorrhoids, located above the pectineal line under the mucous membrane of the rectum, and external, located below the pectineal line under the skin. Approximately 40% of patients have a combination of external and internal hemorrhoids - mixed hemorrhoids. External hemorrhoids are observed infrequently - in less than 10% of patients [3, 7, 20].
With external hemorrhoids, the nodes are localized on the outside, and they should not be confused with prolapsed internal hemorrhoids. Most often, external nodes manifest as thrombosis. As a rule, bleeding from external nodes does not occur, since they are not injured during defecation. But constant stagnation of blood in them can lead to the formation of blood clots in them. Externally, the external hemorrhoidal node can be of different sizes, from 3 mm or more, which depends on its blood supply. An external hemorrhoid is usually covered by skin, while a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid is usually covered by the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
With internal hemorrhoids, there are varicose hemorrhoidal veins, which are located deep in the anal canal, so such hemorrhoids are not visible during a normal examination. In order to see them, you have to resort to special research methods: anoscopy, rectoscopy. Also, such nodes can be identified during digital rectal examination.
There are three degrees of internal hemorrhoids:
1st degree - hemorrhoidal veins are located in the anal canal, may not be palpable, cause subjective complaints by maintaining inflammation or causing bleeding.
2nd degree - nodes protrude from the anus when straining and disappear on their own.
The 3rd degree is characterized by prolapse of hemorrhoids that cannot be reduced on their own.
Hemorrhoids can occur acutely or chronically, but essentially these are phases of the same process. In acute hemorrhoids, inflammation occurs in the nodes, which, in addition to other symptoms, leads to severe pain in the anus. Spasm of the rectal sphincter increases swelling, leads to stagnation of blood in the lower rectal plexus and thrombosis of external hemorrhoids. In some cases, acute inflammation is accompanied by swelling of the perianal area and necrosis of the nodes. The often occurring tissue swelling and inflammatory infiltration create the impression of pinched hemorrhoids [2, 21].
The acute course of hemorrhoids is divided into three stages:
Stage I is characterized by thrombosis of hemorrhoids without inflammation.
Stage II is characterized by the addition of inflammation.
Stage III is characterized by widespread thrombosis of external and internal hemorrhoids with inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, swelling of the skin of the perianal area, necrosis of the mucous membrane of the hemorrhoids.
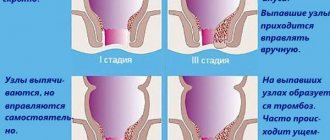
During chronic hemorrhoids there are four stages:
In stage I, minor changes are noted in the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum, which is responsible for holding hemorrhoids in the anal canal, i.e. There was no prolapse of hemorrhoids.
In stage II, changes in the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum are expressed to such an extent that prolapse of hemorrhoids is noted during the act of defecation, but they themselves are reduced into the anal canal. In this case, bleeding may or may not be observed.
Stage III is characterized by such changes in the rectum that the prolapsed nodes no longer correct themselves, and the patient is forced to reset them himself after each act of defecation.
In stage IV, there is already a constant prolapse of hemorrhoids, and it is almost impossible to set them back. This is due to pronounced changes in the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum.
With chronic hemorrhoids, scarlet blood is released during bowel movements, prolapse of hemorrhoids, dull, incessant pain in the anus, and itching. A typical symptom complex of the chronic course of the disease consists of repeated bleeding, usually associated with defecation and prolapse of hemorrhoids from the anus. Bleeding as the leading symptom of hemorrhoids is observed in more than half of patients. Continuous bleeding from the anal canal is a complication of the disease. Prolonged bleeding from hemorrhoids leads to anemia. The second most common symptom characteristic of hemorrhoids is prolapse of hemorrhoids. There is a direct relationship between the increase in the duration of the disease, its stage and the frequency of prolapse of hemorrhoids. Anorectal bleeding, in addition to the main symptom of hemorrhoids, is a characteristic symptom of other diseases of the colon: malignant tumors, diverticulosis, nonspecific ulcerative and granulomatous colitis. Under the guise of hemorrhoids, especially when bleeding from the rectum, diseases such as polyps and colorectal cancer often occur. Therefore, for any manifestations of intestinal discomfort and, especially, when blood is released from the rectum, it is necessary to perform a digital examination, rectoscopy, colonoscopy or irrigoscopy. One rule must always be followed: at the slightest suspicion of a tumor, always take a biopsy and completely examine the colon [6, 9, 19, 21].
In modern conditions, the problem of hemorrhoids in pregnant and lactating women occupies a special place [1, 4, 13]. The clinical symptoms of hemorrhoids during pregnancy do not differ from those during the normal course of the disease. Most often these are pain in the anus, rectal bleeding and anal itching [5, 15, 22].
Often pregnant women are diagnosed with hemorrhoids in an asymptomatic stage. These women do not present complaints characteristic of hemorrhoids, but upon examination, hemorrhoidal nodes are found in typical places on the walls of the anal canal. Timely identification of pregnant women with clinically asymptomatic hemorrhoids and implementation of preventive measures in them makes it possible in many cases to prevent its development, which complicates the course of childbirth and the postpartum period [1, 13].
The clinical picture of hemorrhoids in pregnant women develops gradually. Initially, unpleasant sensations appear in the anus, especially after defecation. As the duration of pregnancy increases, more pronounced signs of hemorrhoids appear - pain, enlargement of hemorrhoids, bleeding, anal itching, tenesmus, etc. [1, 15, 22].
About half of women who have hemorrhoids during pregnancy experience an exacerbation of the disease after childbirth. As a rule, already with the onset of labor, pain in the anal area increases sharply. During the second stage of labor, when the fetal head passes the pelvic cavity, the vessels of this area, including the rectum, are sharply compressed. Venous outflow is disrupted, blood stagnation and tissue hypoxia increase. This creates additional conditions for the opening of arteriovenous anastomoses directly into the lumen of the cavernous cavities of the rectum. The longer the second stage of labor, the more pronounced these processes are. Hemorrhoids swell, increase sharply in size, and become tense. During pushing, the anal sphincter opens, the distal end of the rectum gapes, and both external and internal hemorrhoids are clearly visible. They enlarge before our eyes, become bluish and dense. After the end of the pushing, the internal nodes decrease somewhat, and with subsequent pushing, the picture repeats. When the fetal head erupts, internal hemorrhoids, if they are sufficiently pronounced, are squeezed out and sometimes their walls rupture. After childbirth, as the anal sphincter gradually contracts, the internal nodes become smaller and reduce on their own, but often, if the sphincter contraction occurs quickly, these nodes are pinched and acute hemorrhoids occur [1, 4, 13].
Conservative treatment, the main goal of which is to eliminate pain and inflammation and normalize blood circulation in the rectal area, is carried out for acute hemorrhoids and in the early stages of chronic hemorrhoids. Conservative drug treatment can be general - drugs that increase the tone of the veins, improve blood flow through small vessels and cavernous veins, and local - wound healing, analgesic and antipruritic ointments, suppositories, microenemas and baths [8, 16, 18].
Prevention of exacerbations is also of great importance, which includes:
- combating stool disorders (getting rid of constipation and improving bowel function without prolonged straining);
- proper nutrition (a diet rich in fruits and vegetables; a strict prohibition of any alcoholic beverages, salty, hot, spicy, pickled, peppered dishes, as these products increase blood flow to the veins of the pelvic floor and primarily the hemorrhoidal venous plexuses);
- proper hygiene after defecation;
- prevention of physical inactivity (physical therapy and hygienic gymnastics help improve the function of the large intestine, increase the tone of the muscles of the anal area and abdominal wall, and reduce congestion in the pelvic veins).
The development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy, as well as its complications, especially in the postpartum period, significantly affects not only the patient’s condition, but also her quality of life. When choosing a drug for treating a pregnant or lactating woman, one should take into account its safety both for the patient herself and for the fetus and newborn, which significantly limits the doctor’s choice [1, 10, 17].
For asymptomatic hemorrhoids, women are prescribed only preventive measures.
In stages I-II of the disease, treatment is carried out with suppositories and ointments, infusions of medicinal herbs, and the prescription of drugs taken orally. After defecation, it is possible to use rectal suppositories containing analgesic components. For spasm of the anal sphincter, it is possible to add suppositories with oil.
When hemorrhoids are combined with anal fissures, or acute hemorrhoids, conservative treatment is carried out in a hospital. It includes rest, diet, cleansing enemas, laxatives, novocaine blockades in the anus, local treatment with suppositories and ointments.
In case of prolapse of internal nodes, without symptoms of acute inflammation, they limit themselves to careful repositioning of the nodes after defecation (it is better to do this in a warm sitz bath). When there is a urge to defecate, small-volume cleansing enemas are recommended. Women are strictly prohibited from heavy physical labor and certain types of domestic work.
Pregnant women suffering from hemorrhoids with prolapse of internal nodes and frequent exacerbations of the disease are subject to hospitalization and surgical treatment. The timing of the operation is determined individually. Patients with such complications are treated with surgical (hemorrhoidectomy - excision of nodes) or minimally invasive treatment methods (minor or bloodless operations). These methods include sclerotherapy, ligation, infrared photocoagulation and laser coagulation. If the pregnant woman’s condition allows, all interventions are postponed to the postpartum period. Exacerbation of hemorrhoids, especially in combination with postpartum perineal trauma, is the most common disease that affects the quality of the postpartum period.
Currently, in obstetric practice for hemorrhoids, Procto-Glivenol is widely used, which is available in the form of rectal cream (1 g contains tribenozide 50 mg and lidocaine hydrochloride 20 mg) and rectal suppositories (1 suppository contains tribenozide 400 mg and lidocaine hydrochloride 40 mg).
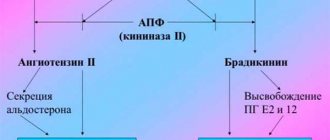
The therapeutic effectiveness of Procto-Glivenol for hemorrhoids is due to the combination of two components: tribenoside and lidocaine. Tribenoside has a venotonic and anti-inflammatory effect. The venotonic effect is manifested by improving vascular tone, reducing venous stagnation, reducing the permeability of capillaries and venules and improving microcirculation. The anti-inflammatory effect is manifested by an inhibitory effect on some endogenous substances (bradykinin, serotonin, histamine), which act as mediators in the development of inflammation and pain. Lidocaine has a local anesthetic effect.
The above properties of Procto-Glivenol allowed it to take one of the leading places among antihemorrhoidal drugs, which is explained by the optimal composition, high efficiency and safety of use, especially during pregnancy (starting from the second trimester) and during breastfeeding, since it is during these periods that safety drugs is especially relevant.
Material and methods
We assessed the effectiveness and tolerability of Procto-Glivenol (cream and rectal suppositories) in the treatment of hemorrhoids in pregnant women. 85 pregnant women with clinical signs of hemorrhoids were examined.
All patients were divided into three groups depending on the stage of the disease. The 1st group consisted of pregnant women with asymptomatic hemorrhoids, who underwent preventive measures, including a diet with limited spicy foods and a sufficient amount of plant fiber, physical therapy, walks, and using the anal toilet after defecation. Group 2 consisted of patients with complaints of bleeding, anal itching, and pain during defecation. These women, in addition to the above measures, were treated with suppositories and cream with procto-glivenol from the second trimester of gestation. Group 3 (4 pregnant women) included patients suffering from hemorrhoids subject to surgical treatment. These were women with prolapse of internal nodes and with a history of frequent exacerbations, with heavy hemorrhoidal bleeding, as well as with acute hemorrhoids in the stage of necrosis of the prolapsed strangulated nodes. Pregnant women of group 3 were consulted by a proctologist, together with whom general tactics for further management were developed. These patients were also prescribed Procto-Glivenol according to individual regimens for preoperative preparation.
Procto-Glivenol cream was used for external hemorrhoids, applied to the affected areas in a thin layer 2-4 times a day, and after the pain disappeared - once for 7 days. Procto-Glivenol suppositories were used for internal hemorrhoids 2 times a day for 5-7 days, after the disappearance of painful sensations, once a day for another 7 days.
Results and discussion
It has been established that identifying pregnant women with clinically asymptomatic hemorrhoids and carrying out the special preventive measures described above make it possible to prevent the development of the disease, which complicates the course of childbirth and the postpartum period.
Clinically, the symptoms of hemorrhoids during pregnancy were almost no different from those among other categories of patients with this diagnosis. Of 85 pregnant women with clinical signs of hemorrhoids, pain in the anus was observed in 40 (47.1%), bleeding of nodes - in 28 (32.9%), anal itching - in 26 (30.6%). 55 (64.7%) of the observed women had external hemorrhoids, which was characterized by the appearance of hemorrhoids in the form of warty formations or folds, dense to the touch and not decreasing in volume upon palpation. In internal hemorrhoids (30-35.3%), the nodes were located between the folds of the mucous membrane, could be either single or multiple, collapsed when pressed and filled when coughing. In addition, in 13 (15.2%) pregnant women, hemorrhoids were combined with an anal fissure. It should be noted that if in pregnant women aged 20 to 30 years, hemorrhoids are detected in approximately every fifth, then after 30 years - in every second.
When assessing the results of therapy, the severity of remaining clinical symptoms was assessed by patients as average by the 7th day of treatment and as weak by the 15th day. At the same time, such a clinical symptom as pain during defecation was observed in 9 (10.5%) patients by the 7th day of treatment, and was not observed in any pregnant woman by the 15th day, bleeding - in 5 (5.9%) and 2 (2.4%), anal itching - in 6 (7.1%) and 2 (2.4%) women on the 7th and 15th days of treatment, respectively.
Clinical tolerability was assessed by patients and doctors on a scale: excellent, good, average, poor. Tolerability of treatment with Procto-Glivenol was excellent and good in 96% of cases.
conclusions
1. Procto-Glyvenol is the drug of choice for the conservative treatment of hemorrhoids and the prevention of its complications during pregnancy. The use of Procto-Glivenol, both in the form of cream and rectal suppositories, is an effective way to treat pregnant women with hemorrhoids.
2. The speed of action and good tolerability make it possible to recommend Procto-Glivenol for widespread use in obstetric practice.