What is low blood pressure anyway?
Blood pressure is the force with which blood pushes against the walls of the arteries. At the moment when the heart contracts, the pressure is highest - it is called upper, or systolic. In the interval between heartbeats, the pressure in the vessels drops - it is called lower, or diastolic.
Normal blood pressure ranges from 90/60 to 120/80 mmHg. The numbers 90 and 120 indicate systolic pressure, and 60 and 80 indicate diastolic pressure. If the readings are less than 90/60, the blood pressure is considered low. This condition is called hypotension.
Rules for measuring blood pressure
To get a reliable picture of a person’s health, it is important to measure blood pressure correctly; it’s not difficult:
- for an hour (at least 40 minutes) do not smoke, do not eat anything spicy, fatty, salty, do not drink strong drinks, coffee, tea;
- do not engage in physical labor;
- the position for measurement should be comfortable, in a sitting position, the hand for tonometry should be on a hard surface;
- two measurements are carried out, with an interval of several minutes;
- the cuff is placed above the elbow to make it comfortable when using a stethoscope.
Is low blood pressure dangerous?
Many people - most often thin women - live with hypotension for years and feel great. Doctors believe that these people are lucky: they are less likely to suffer from cardiovascular diseases.
However, if your blood pressure suddenly drops below normal levels, unpleasant symptoms may appear:
- blurred vision;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- nausea or vomiting;
- drowsiness;
- feeling of weakness.
As a rule, at a young age, the health risk is associated not with low blood pressure itself, but with the reasons due to which it falls. The exception is fainting. “This is the most alarming symptom, since it often leads to injuries and accidents,” says Oksana Dikur, general practitioner, cardiologist at the Rassvet clinic. “If hypotension is accompanied by loss of consciousness, you should definitely consult a doctor.”
But for older people, low blood pressure can be really dangerous. Moreover, a drop in diastolic pressure is more dangerous than a decrease in systolic pressure.
“This can lead to deterioration of blood supply to the kidneys and brain, increasing the risk of stroke and kidney failure,” explains Oksana Dikur.
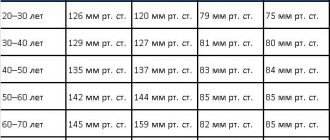
Normal blood pressure and pulse
Indicators of blood pressure and pulse allow you to assess the general state of a person’s health already at the first examination. Their fluctuations and arrhythmia indicate dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and make it possible to assess the severity of the disorders and the level of nutrition of each cell of the body.
Pulse and pressure are markers of myocardial contractility. It is no coincidence that the difference between SBP and DBP is called pulse (normally it is 30-50 units). It is by the pulse that the first symptoms of cardiovascular problems are recorded. Fluctuations of no more than 15 units are permissible, otherwise headaches, fainting, and anemia develop.
This may indicate that a person has:
- VSD;
- atherosclerosis;
- myocarditis.
The pulse difference is important for determining the condition of the aortic valves, myocardial function, and blood flow through human arteries.
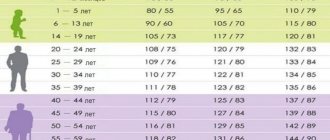
Pressure and pulse indicators by age for men and women are presented in the table.
| Men, age | Norm SBP/DBP in mmHg. Art. | Heart rate |
| From 20 to 30 | 123/75 | 51-91 |
| Up to 40 | 127/78 | 61-91 |
| Up to 50 | 130/80 | 62-82 |
| Up to 60 | 134/83 | 64-84 |
| Up to 65 | 137/84 | 72-91 |
| Over 65 | 135/89 | 75-90 |
| Women, age | Norm SBP/DBP in mmHg. | Heart rate |
| From 20 to 30 | 125/75 | 60-70 |
| Up to 40 | 128/79 | 70-75 |
| Up to 50 | 131/81 | 74-82 |
| Up to 60 | 135/82 | 79-83 |
| Up to 65 | 137/85 | 81-85 |
| Over 65 | 135/87 | 82-86 |
What causes hypotension?
If you suddenly change your body position
Get up quickly or, for example, sit up sharply in bed. This is called orthostatic hypotension. When a person assumes a vertical position, blood, under the influence of gravity, rushes to the legs and abdominal area, and the pressure in the vessels drops. In order to raise blood from the legs and normalize blood pressure, the autonomic nervous system increases the heart rate and constricts blood vessels.
Healthy people do not experience discomfort, since this mechanism works very quickly. But in some cases, the autonomic nervous system fails. As a result, the pressure drops, the blood does not have time to rise from the legs, the brain lacks oxygen, and symptoms of hypotension appear. This happens, for example, in pregnant women, in people with certain diseases such as diabetes, and in every fifth elderly person.
Sometimes healthy people experience similar sensations, for example due to heat, and there is nothing to worry about. But if you feel dizzy every time you change position, you need to see a doctor.
If you eat
After eating, blood rushes to the gastrointestinal tract, and to prevent pressure from dropping too much, the autonomic nervous system constricts blood vessels and increases the heart rate. However, in about a third of older people it cannot cope with such a load. This condition is called postprandial hypotension. If this happens, you need the help of a doctor.
If you grow too fast
As you might guess, the problem most often occurs in children and adolescents: due to rapid growth, a malfunction occurs in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. As a result, when you change your posture or bend over, symptoms such as dizziness and fainting appear. This is called nerve-mediated hypotension. Children usually outgrow the problem, and hypotension goes away on its own.
But sometimes neurally mediated hypotension is a sign of serious neurological diseases. In this case, the person needs the help of a doctor.
If you get sick
Blood pressure may drop in people who are dehydrated, those who have had shock, diabetics, and patients with arrhythmias and heart failure. In this situation, doctors seek to cure or control the disease that is causing hypotension.
If you take certain medications
Sometimes hypotension is a side effect of anti-anxiety medications, diuretics, painkillers, or blood pressure pills. In order to solve the problem, it is usually enough for the doctor to adjust the dose of the medication.
Prevention
Prevention of blood pressure deviations from normal values primarily consists of lifestyle modifications that can prevent the development of the disease. The recommendations must be followed by people with a family history who are at risk (excess weight, frequent stress).
To prevent hypotension, night sleep should be normalized - it should be at least 8 hours, include dishes with a high content of calcium, potassium and magnesium in the menu, eat often in small portions, limit animal fats and fast carbohydrates, and ensure sufficient physical activity.
To maintain normal blood pressure, people with a tendency to high blood pressure need to follow a clear daily routine, exclude fried, fatty, salty and spicy foods from the menu, reduce excess weight, and provide moderate physical activity.
In both cases, it is important to give up smoking and alcohol, avoid physical inactivity, night vigils, and reduce stress levels.
Recommendations
If the cause of arterial hypertension is any concomitant disease, the necessary set of measures is selected, including the use of medications and surgical interventions (if necessary). Nutritional correction is required. You must also follow the recommendations described below.
Every day you should do twenty minutes of gymnastics; daily walking shows good results. You can use a contrast shower; after a shower, it is useful to rub the skin with a towel until redness appears (in the absence of hypertension). Specialists can prescribe general, lymphatic drainage, and hardware massage.
Drinking caffeinated drinks should not increase your blood pressure. The maximum is two cups of coffee or tea per day. If this concerns pregnant women, it is better to add milk to coffee without overusing the quantity and strength of the drink. The same recommendations apply to elderly patients. Nutrition should be balanced, rich in essential vitamins and minerals. To normalize vascular tone, you can use decoctions of ginseng, golden root or elecampane. A good night's sleep is also important.
How to identify possible pathologies?
Just stating the fact of the presence of hypotension says little. This is not informative. Establishing the etiology of the condition is required, and this is much more difficult.
Lowering blood pressure is an interdisciplinary problem that is dealt with by specialists in different fields. Consultations with a neurologist, cardiologist and endocrinologist are necessary.
In most cases, the pathology is polyetiological in nature and requires the help of several doctors at once.
At the initial appointment, complaints should be recorded, and having determined the symptoms, it is necessary to establish an anamnesis.
Important information is character and lifestyle, age, hormonal status, presence of diabetes, history of hypothyroidism, bad habits. Diet, nature of professional activity, etc.
After the initial measures, special research needs to be carried out:
- Determination of blood pressure using a conventional tonometer. They measure it on two hands; there should not be a big difference.
- Daily blood pressure measurement using an automatic tonometer. The so-called daily tonometry. Helps identify persistent hypotension and determine peak values over 24 hours.
- Electrocardiography. Makes it possible to assess the functional activity and consistency of the heart.
- Encephalography. To assess the functioning of brain structures.
- Tests for thyroid and pituitary hormones (TSH, T3, T4).
If necessary, other studies are prescribed. Everything is decided at the discretion of the treating specialist.
Symptoms of hypotension and the danger of the condition
Patients seek medical help with the following complaints:
- the appearance of drowsiness and loss of strength;
- cephalgia;
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- decreased performance;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting.
A headache with hypotension differs from the one that occurs against the background of elevated blood pressure numbers, which allows you to differentiate your own condition if you don’t have a tonometer at hand. With hypertension, the pain seems to compress the head, and pulsation occurs in the temples and crown. Against the background of hypotension, the pain is aching in nature and often appears in the back of the head. The danger of hypotension lies in the fact that blood flow slows down, that is, the brain and internal organs do not receive the required amount of blood, and therefore nutrients and oxygen.
How to choose blood pressure pills
IMPORTANT!
If you have hypertension, you should never self-medicate. Only a doctor can prescribe blood pressure pills, because all drugs have different principles of action, certain contraindications and side effects. And it’s far from a fact that the pills prescribed to your neighbor can be taken by you too.
When choosing a treatment regimen, the doctor takes into account a lot of nuances: the patient’s age, the presence of kidney or hormonal problems, diabetes, excess weight, high cholesterol, vascular condition, etc.
The following groups of drugs are used to reduce blood pressure:
- Beta blockers.
These blood pressure medications lower it by reducing the heart rate. When the heart works slower, it pumps less blood, which means the force of its pressure on the blood vessels decreases. Side effects: bradycardia (expressed as general weakness), skin rashes. - Diuretics (diuretics).
Such drugs remove excess water from the body, which reduces blood pressure. Side effects: decreased heart rate, nausea, dizziness, numbness of fingers, goosebumps, convulsions. - Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
With hypertension, the body produces an excess amount of the hormone angiotensin - it spasms blood vessels, causing fluid retention and a surge in pressure. Similar drugs reduce the synthesis of this hormone (spasm decreases, pressure decreases). Side effects: allergic reactions, coughing attacks. - Angiotensin antagonists.
Such blood pressure medications also affect the hormone angiotensin, binding to its receptors and inhibiting activity. Side effects: decreased vascular tone, dizziness, nausea, sharp decrease in blood pressure. - Calcium antagonists.
Calcium ions are responsible for the tone of arterial vessels. Such drugs relax the vascular walls, thereby reducing blood pressure. Side effects: rapid heartbeat, dizziness.
Often, not one drug, but several (from different groups) is used to treat hypertension. The dosage of blood pressure tablets is selected individually. This usually takes three to six months until the perfect combination is achieved.
In some cases, basic therapy is supplemented with emergency medications when a person experiences a hypertensive crisis and needs to quickly stabilize blood pressure. Here, too, it is important to choose the right dose.
For high blood pressure, several drugs from different groups are often prescribed
Photos from open sources
Read also: Top 10 best blood thinners Blood thinners
Why can pressure “jump”?
There are actually many reasons for high blood pressure, but here is a list of the most common:
- The heart does not work as before, its strength is reduced.
- The quality of the blood has changed. The older a person is, the thicker his blood is, which makes it difficult for it to pass through the vessels. Blood thickening can be caused, for example, by diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
- The vessels have become less elastic. Possible causes are poor diet, excessive exercise, and taking certain medications.
- Atherosclerotic plaques due to increased levels of “bad” cholesterol.
- A sharp narrowing of blood vessels due to hormonal imbalance.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- Hereditary factor.
In most cases, high blood pressure can be stabilized on your own by starting to eat right, eliminating bad habits and stress, and starting to move more. This will allow you to stay healthy for as long as possible and avoid the dangerous complications of hypertension (stroke, heart attack).
If lifestyle changes do not affect the situation, the doctor prescribes antihypertensive drugs that must be taken on an ongoing basis so that the blood pressure remains normal.
Correction of indicators and first aid
To increase the pressure, you must follow the following algorithm:
- Call a team of medical workers.
- Lie on a horizontal surface with the leg end raised or lay the victim down in this way.
- Open a window or direct a fan to provide fresh air.
- Drink sweet warm tea or give the victim something to drink. You can add 10 drops of tincture of eleutherococcus, ginseng or Rhodiola rosea.
- Rub your whiskey with lemon essential oil.