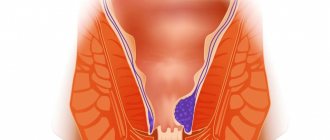
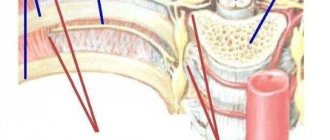
Hemorrhoids are a vascular disease in which dilation of the hemorrhoidal veins of the rectum is observed, causing the formation of characteristic hemorrhoids that cause pain and bleeding in patients.
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids is not difficult: more than 90% of cases are determined during a digital examination of the anus and do not require the use of instrumental research methods.
Types of hemorrhoids
The pathological condition of the rectum in women and men can be expressed in the following forms:
- external;
- internal;
- combined.
If nodes and seals are visible to the naked eye, then we are talking about external hemorrhoids. In the case when hemorrhoidal cones are beyond the reach of a person’s vision, inside the rectum, then this type of disease can safely be called internal. If there are formations of dense tissue both inside and outside, then this is a combined type. Let us dwell in more detail on internal hemorrhoids.
Thrombosis of hemorrhoids
Thrombosed hemorrhoids are more common than other complications and make themselves known by pain that is not associated with bowel movements and in some cases can completely deprive a person of any activity. Thrombosis is often accompanied by local inflammation, which sometimes becomes widespread. The cause of the formation of a blood clot is a violation of blood circulation in the cavernous bodies, due to congestion associated with physical inactivity, pregnancy, diet disorders and other factors. The prognosis of thrombosed hemorrhoids is questionable. In most cases, after a few days, the thrombosed node is replaced by connective tissue, but a more severe outcome is also possible, associated with necrosis, that is, death of the node and involvement of surrounding tissues in the purulent-necrotic process.
Internal hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids: symptoms in the initial stages are difficult for the patient to determine. There are no visible manifestations of this disease, and painful sensations can be attributed to other diseases or general malaise. The early period of the disease is not characterized by bleeding or prolapse of hemorrhoids. A slight discomfort during defecation, a slight burning sensation in the anus in the rhythm of constant time pressure can simply not be noticed or not given due importance. Of course, when the disease begins to progress, the symptoms also change. Nodes of enlarged hemorrhoidal veins do not allow stool to pass painlessly through the rectum. They squeeze it, narrowing the passage and making each bowel movement painful, and sometimes even excruciating. Itching and burning intensify; this can be facilitated by mucous discharge that accompanies the disease in more advanced stages. A person feels a terribly unpleasant odor when defecating, and underwear can also have a characteristic amber. This can lead anyone into a state of panic, especially women. In addition to the smell, mucous discharge irritates the anal area and can lead to inflammatory processes in this place. Any slightest movement can cause unbearable pain in a person; the feeling of discomfort does not go away either in movement or at rest. It always seems to a person that there is something foreign in the anus. This sensation is caused by swelling of the rectum and an increase in the size of the hemorrhoids. Both women and men may have blood in their stool during bowel movements. Representatives of the fairer sex may not attach much importance to this if such a phenomenon occurs during the period when women are menstruating. Bloody discharge may at first appear only as small specks in the stool, and then, as the disease progresses, even trickle down the toilet and leave marks on the underwear. Bowel movements may be accompanied by severe pain, and there are frequent cases of hemorrhoidal cones falling out. At first, a person can straighten these seals into the inside of the rectum himself, but a moment may come when only doctors can do this. Another symptom of internal hemorrhoids is the formation of cracks. As the cones grow, the rectal mucosa cannot stand it and bursts, leading to the appearance of cracked fragments. This is an additional source of pain, from which it is difficult to protect both women and men.
Causes of hyperthermia
Early diagnosis is important because many of the causes of fever and chills pose serious risks to health and even life. So, an increase in body temperature occurs in the following situations:
- Exacerbation of the disease
- Thrombosis and subsequent necrosis
- Sepsis and paraproctitis (pararectal abscess due to hemorrhoids).
During an exacerbation, a temperature of 37-37.5 °C is possible. The blood vessels of the terminal part of the intestine swell and increase in size, resembling the shape of a lump. A patient with hemorrhoids shudders, feels weak, and feels weak.
If nothing is done during an exacerbation of the pathology, inflammation develops. Bacteria and pathogens can penetrate from feces into the mucous membrane of the lower intestine. This leads to thrombosis and temperature up to 38 °C or more. After this, the process moves into the next stage - necrosis of thrombosed nodes. They are rejected from the mucous membrane and bleeding ulcers form. The temperature remains in the range of 37-39 °C.
Through cracks in the mucosa and ulcers resulting from necrosis, bacteria can enter the blood, which leads to sepsis. The skin in the perineum and genital area becomes deeply red in color, swelling and pain are felt. Temperatures can reach 40°C. This is a serious condition requiring immediate hospitalization and surgery. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
When infection penetrates into the tissue, paraproctitis develops. This proctological disease occurs more often in men than in women. Characteristic symptoms are fever, fever (temperature rises to 40° C), general malaise. After assessing the degree of threat, the issue of hospitalization is decided to prevent pus from entering the free abdominal cavity and the development of acute peritonitis against the background of hemorrhoids.
temperature with hemorrhoids
Features of internal hemorrhoids in women
Hemorrhoids can be called a “bisexual” disease, equally likely to affect both women and men. But the physiological characteristics of women can become a factor leading to hemorrhoids. This disease can manifest itself in the fairer sex for a number of reasons:
- Features of physiology. During menstruation, the vessels of the pelvic organs are filled with blood and this is an unfavorable moment for the appearance of hemorrhoids.
- Some gynecological diseases.
- Passion for diets. It's no secret that figure is very important for women. Throwing yourself into the loophole of certain dietary restrictions can lead to chronic constipation, which can negatively affect the condition of the rectum.
- Pregnancy. At this time, women’s motor activity decreases, the load on the entire body and on the vessels in the pelvic area also increases. Pregnant women often suffer from constipation. The enlarged uterus compresses the pelvic vessels.
- Childbirth. There is even a special term - postpartum hemorrhoids. During the birth of the baby, cracks may occur when pushing. Lumps in the anus and rectum.
Posthemorrhagic anemia
In patients who constantly lose blood, posthemorrhagic anemia occurs, which is accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin levels. In this case, the symptoms of acute vascular insufficiency come to the fore. The person is concerned about:
- shortness of breath with slight exertion;
- cardiopalmus;
- fainting.
At the same time, various tissues of the body experience oxygen starvation to varying degrees, and the heart is forced to work hard to compensate for the lack of oxygen, thereby increasing its own need for it, which can cause decompensation of cardiovascular diseases and other problems.
To prevent posthemorrhagic anemia in hemorrhoids, it is necessary to periodically take phlebotonic drugs, use hemostatic suppositories, and also promptly resolve the issue of surgical or minimally invasive treatment.
Possible complications
Due to the fact that internal hemorrhoids are much more difficult to diagnose than external hemorrhoids, you can skip the period of possible effective treatment. The effectiveness of all procedures aimed at combating the disease depends on the period in which the patient sought help at the hospital. It is very important for both women and men to pay great attention to their health and undergo regular, complete examinations whenever possible. If, nevertheless, the onset of the disease is missed, then this can lead to such troubles as anemia, strangulation of the node and the occurrence of thrombosis. Anemia occurs due to the fact that a person begins to lose blood with each bowel movement, and with each subsequent time more and more. A lack of hemoglobin will result in weakness, rapid fatigue, and a constant desire to lie down and rest. Thrombosis of hemorrhoids is formed due to the fact that blood stagnates in the area of the body responsible for emptying. Severe pain is the main characteristic of this problem. If inflammation is added to this, then you may encounter an even greater problem - damage to the perirectal tissue.
Therapeutic measures
In case of hyperthermia during hemorrhoids, measures should be taken to reduce the temperature. The list of antipyretic drugs is quite extensive. You can drink and inject the following:
- Paracetamol
- Panadol
- Efferalgan
- Aspirin
- Nurofen
- Ibuprofen
- Ibufen
- Analgin
- Nimesulide
Many of these drugs, in addition to reducing fever, also have an analgesic effect. The second step is to consult a doctor after taking an antipyretic. Doing something on your own or turning to traditional medicine is not recommended.
In case of necrosis, sepsis and paraproctitis, it is necessary to bring down the temperature only in a hospital setting. Doctors prescribe antimicrobial drugs (antibiotics), and local sanitation is performed. If there is a threat to life, it is necessary to perform surgery and excise the affected tissue.
An increase in temperature is a reason to contact a specialist. For any deterioration of the condition, it is important to determine the cause in order to prescribe appropriate medications, which is only possible after examination and a series of tests.
Timely diagnosis
To avoid hemorrhoids and possible complications, it is necessary to identify the disease at its earliest stages. Internal hemorrhoids can be detected by digital examination of the rectum, feeling for compaction of the hemorrhoidal veins. But such an examination is effective only when the nodes are located low. If the cones are located high up, then only modern equipment can help in diagnosing the disease. Anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are the most common techniques. In the first case, a special tube with an optical device is used, which allows one to examine the rectal mucosa over a ten-centimeter length. If the hemorrhoids are located even higher, then you cannot do without the help of a sigmoidoscope. The rectum at a distance of 25 cm will be “in full view” to the doctor. If the patient states that during defecation he himself observed the prolapse of nodes, then a diagnosis can be made based on this reliable fact. True, unfortunately, for the patient the stage of the disease in this case is later, and therefore less treatable.
Perianal pruritic dermatitis
Perianal dermatitis can be caused by various reasons, and hemorrhoids are far from the main cause of its occurrence. However, prolapse of nodes or mucus secretion contribute to irritation of the skin of the perianal area, which can cause inflammation. Clinically, this is manifested by itching of varying intensity, redness of the affected area of the skin and, in some cases, moderate pain.
Prevention of perianal dermatitis consists of careful adherence to recommendations on daily routine and diet, as well as daily hygiene procedures for the perianal area. Since scratching itchy skin further worsens its condition, it is necessary to take anti-itch medications.
Conclusion
I would like to draw a conclusion from all of the above - you should not delay going to the doctor if you notice at least one of the signs of internal hemorrhoids:
- itching;
- burning;
- pain during bowel movements;
- appearance of blood in the stool;
- mucous, odorous discharge;
- prolapse of hemorrhoidal cones.
If you find such signs in yourself, do not panic, but pull yourself together and find a good proctologist. Hemorrhoids can be treated successfully if all medical instructions are followed. You should not discount traditional methods (as an addition to the main treatment) or lifestyle changes. Start eating right, sign up for a fitness center, give up bad habits - success will definitely be on your side!
Mucus secretion
The following intestinal pathologies can lead to such discharge:
:
- haemorrhoids;
- Crohn's disease;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- anal fissures;
- fistula;
- neoplasms;
- proctitis;
- intoxication (usually the discharge is watery);
- herpes in the intestines;
- dysbacteriosis;
- peptic ulcer;
- condylomas, etc.
More often, mucus is released along with feces during bowel movements. However, there are also cases of discharge between trips to the toilet. This may be due to inflammation or low sphincter tone. In a number of pathologies, the mucus may have a pinkish tint, which indicates the presence of bleeding.