Patients often turn to cardiologists with complaints of chest pain. Such unpleasant sensations are easily distinguished by various manifestations; they cannot be relieved with the help of drug therapy. Instrumental research methods do not allow us to identify pathologies associated with the functioning of the heart. When additional studies are ordered, osteochondrosis is diagnosed. The founder of the “Club of Former Hypertensive Patients,” the chief physician of the “Doctor Shishonin Clinic,” Alexander Yuryevich Shishonin, talks about the effect of cervical osteochondrosis on the heart.
Causes and mechanism of development of osteochondrosis
To understand why your back hurts, you need to understand how our spine is structured, how it works, what functions it performs and what factors can lead to its damage.
The human spine consists of 32-34 vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 3-5 coccygeal), between which there is an intervertebral disc consisting of cartilage tissue. In the middle of the intervertebral disc there is the nucleus pulposus - a semi-liquid formation in the form of a “ball”, which performs the function of shock absorption and is surrounded by dense cartilage tissue (fibrous ring). The spinal canal, which contains the spinal cord and the nerves extending from it, runs through the entire spine. This entire structure is surrounded by muscles and ligaments. The main functions of the spine are musculoskeletal, shock-absorbing, and protective.
Imagine the Ostankino TV tower, which is held in a vertical position thanks to a whole system of cables stretched from the base to the top. Likewise, our spine is held in the desired position by a group of stabilizer muscles, which normally evenly distribute the load on the spine and joints. Unlike the Ostankino TV tower, our spine is more complex; it can bend in different directions and even twist, all this is possible due to the presence of an intervertebral disc, muscles and ligaments.
Every day a person makes some monotonous, repetitive movements associated with work or leisure activities. If the same muscles work for a long time, they become overstrained and spasm, while other muscles at this time do not experience any stress at all and atrophy. This leads to a change in the “geometry” of the body, the load on the intervertebral disc is redistributed, spasmed muscles tighten the vertebrae, and nutrition deteriorates. With monotonous hard physical labor, the same processes occur. In addition, the intervertebral disc does not have blood vessels, and its nutrition is provided by the surrounding muscles, and during movement in the intervertebral joint, nutritious synovial fluid enters it.
Cartilage tissue consists of 80-85% water, so the drinking regime is of great importance. During the day, a person should drink at least 2 liters of clean water. If not enough water enters the body, then dehydration (drying out) of the intervertebral disc occurs, the cartilage cracks and collapses.
In my practice, I have long noted that stress, anxiety, and worries often contribute to the occurrence of back pain. Our body perceives any stressful situation as danger. At the same time, the sympathetic part of the nervous system is activated, the adrenal glands “inject” stress hormones into the blood, blood pressure rises, the heartbeat quickens, and muscles tense. In nature, if an animal is frightened of something, it runs or defends itself, accordingly, stress hormones burn and the muscles, after working, relax. Man is a social being; he begins to worry more often and move less, so there is no relaxation. As a result, pain in the spine, headache, motor tics and more occurs.
In the literature you can find different formulations of osteochondrosis, but their essence is the same. Osteochondrosis is a “breakdown” of the motor segment, destruction, degeneration of cartilage tissue. The reason is an incorrect motor stereotype and, as a consequence, a malnutrition of the cartilage.
The progression of osteochondrosis is promoted by: a sedentary lifestyle, heavy physical activity, heavy lifting, obesity, carrying a bag on one shoulder, high-heeled shoes, too soft a mattress for sleeping, frequent hypothermia, bad habits, hereditary predisposition, stressful situations, insufficient drinking regime and other.
The mechanism of arrhythmias
Does osteochondrosis affect the appearance of heart pain and why?
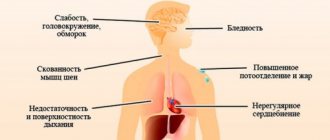
The clear answer is yes. The main cause is compression of the vertebral or vertebral artery, which runs along the entire spine and cardiac nerve. The vertebral artery supplies blood to 25% of brain cells. It can be compressed by spastically contracted muscles, osteophytes on the vertebral bodies as a result of spondylosis. At the same time, blood pressure increases, and subsequent pumping of blood from the atria to the ventricles occurs with increased effort and rhythm disturbances. In addition, cerebral ischemia develops, i.e. hypoxia, causing spasm of blood vessels and muscles. Because of this, the central innervation of internal organs, including the heart, is disrupted. Thus, a disturbance of cardiac activity occurs with interruptions in rhythm. In this case, tachycardia occurs more often.
The paravertebral tissues become inflamed, the anterior root nerve endings of the spinal cord are irritated. And if these endings innervate the heart, they can cause arrhythmia. Everything is very clearly interconnected. The number of impulses from the endings during inflammatory reactions increases and a zone of pathological impulses appears in addition to the normally functioning sinus node. In this case, the heartbeat with osteochondrosis with its frequency, rhythm and a certain sequence of contractions is disrupted.
Arrhythmias often occur with poor posture:
- scoliosis;
- stoop as a result of physical inactivity;
- long-term monotonous loads;
- sitting in an awkward position.
When such interruptions occur, it is not the heart that is treated, but the spine. Arrhythmias in osteochondrosis differ in some manifestations.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Manifestations of osteochondrosis will depend on the location and severity of the lesion in the spinal motion segment. At the initial stage, patients complain of dull, aching back pain, discomfort, slight limitation of movements in the spine, periodic numbness in the arms or legs, headache, and fatigue. By starting treatment and changing your lifestyle during this period, the result will not be long in coming and recovery will come quickly.
With severe damage to the intervertebral disc, severe pain, persistent numbness and/or weakness in the arm or leg occurs (depending on the level of damage). These signs may indicate destruction of the intervertebral disc and the presence of a hernia, and it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
In the most severe cases, the pain syndrome can be extremely severe, possible dysfunction of the pelvic organs, severe weakness and numbness in the arm or leg. If these signs are present, urgent hospitalization in a hospital is necessary to resolve the issue of surgical treatment.
With cervical osteochondrosis, pain occurs in the neck, can radiate to the shoulder, arm or head, numbness or weakness in the arm, headache, dizziness.
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, pain occurs in the chest, radiates to the sternum or scapula, intensifies with breathing and movement, and sometimes there is a feeling of lack of air. Patients often confuse this condition with heart pain.
When the lumbosacral spine is affected, the pain is localized in the lower back, intensifies with movement, radiates to the leg or perineum, and numbness or weakness in the leg may occur.
It is necessary to remember that our body is a single whole, and the division of osteochondrosis into cervical, thoracic, and lumbar is arbitrary. As a rule, the disease develops throughout the spine, but manifests itself in the part that experiences the greatest load.
How does osteochondrosis affect the heart?
If there are several factors of how osteochondrosis affects the heart, they are divided into external and internal. An external factor of negative influence is the constant use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are necessary for pain relief and relief of acute symptoms of this disease. These pharmacological agents act negatively both on the hematopoietic system, triggering the production of defective red blood cells by bone marrow structures, and on the epithelial layer inside the vascular bed. Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases the aggregation (tendency to stick together) of platelets, which contributes to the formation of blood clots in the coronary blood supply (this is the main cause of the development of acute myocardial infarction). The ability of red blood cells to transport oxygen changes, so the tissues of the heart muscle suffer from constant oxygen starvation.
Internal factors of the negative impact of osteochondrosis on the heart are:
- disruption of the process of innervation of the vascular bed, resulting in its spasm, alternating with prolapse, which entails instability of the blood supply to the myocardium;
- compression of the radicular nerves responsible for the performance of the intercostal muscles - as a result, the breathing process is disrupted and a secondary form of oxygen deficiency may develop, the biochemical parameters of gas exchange change;
- development of posterior vertebral artery syndrome, which leads to a significant deterioration in the blood supply to the medulla oblongata, where the respiratory center is located;
- compression of the cranial nerves responsible for the formation of the vagus nerve and solar plexus - this entails disturbances in heart rhythm, dislocation of the ventricles and atria, disruption of hemodynamics within the heart muscle and in the pulmonary circulation.
Other negative factors include a forced sedentary lifestyle, as the patient tries to avoid increased physical activity in case of severe pain. A secondary change in posture due to static tension in the muscular frame of the back can lead to curvature of the spine and compression of the heart muscle due to deformation of the chest.
How to prevent the development of pathology?
Our doctors recommend the following prevention methods:
- during the day, lie down for 40-50 minutes - this will relieve the load on the spine;
- if you work a lot at the computer, change your position, get up from your chair every 2 hours, bend a couple of times in different directions, stretch, straighten your shoulders;
- engage in water sports: swimming, diving, water aerobics;
- do not get too cold, keep your back warm;
- Do the following exercise regularly: lying on your stomach, place your hands on the floor and bend back. Stay in this position for 5-10 seconds. Repeat the exercise 8-10 times.
Pain due to lumbar osteochondrosis
This species, according to statistics, accounts for half of the total diversity of the disease. And if with its thoracic variety the organs suffer less, since they are surrounded and held by the ribs, then the picture is completely different with the lower back. There are many nerve endings here, so the pain will be severe and sharp. Possible acute, subacute and chronic course. Acute pain syndrome in lumbar osteochondrosis is called lumbago or lumbago. At the same time, the person, as they say, cannot breathe or gasp, his lower back burns or goes numb. The duration can be up to a week, and from time to time, if a person is hypothermic, turns sharply, or physically works for a long time, it can come again and last a whole month. Irradiation is observed in the leg, buttock, and sacrum.
How is this pathology treated?
Experienced doctors work at the Noosphere clinic. They know how to get rid of the disease using conservative methods. The course of treatment includes:
- Resonance wave UHF therapy. Resonance wave therapy is a method of therapeutic effects on the aquatic environment of the body with low-intensity, high-frequency electromagnetic waves.
- Fermatron injections. Fermatron intra-articular injections are an effective method of treating various diseases of the musculoskeletal system by introducing a drug (chondroprotector) into the affected joint.
- Rehabilitation on the Thera-Band simulator. Treatment of the spine and joints using the Thera-Band simulator will restore limb mobility in a short period of time without expensive treatment in specialized sanatoriums.
- Blockade of joints and spine. Joint blockade is a type of drug treatment of the spine and joints aimed at relieving acute pain, inflammation and muscle spasms.
- Drug treatment. Drug treatment of joints and spine at the Noosphere clinic is used in a wide range and in combination with physiotherapy. Intra-articular injections, blockades and droppers.
As a result of using all methods in combination, the following effect is achieved:
- improves blood circulation and nutrition of intervertebral discs;
- stops the destruction of discs, restores their structure;
- relieves inflammation of nerve roots;
- relaxes tense back and chest muscles;
- restores the biomechanics of the spine;
- prevents complications such as protrusions and hernias;
- normalizes blood pressure;
- strengthens the muscles of the back, shoulder girdle, and respiratory muscles;
- straightens posture;
- stimulates the functioning of the immune system.
After treatment, it is very important to do home exercises. The attending physician will tell you how and when to do gymnastics. In each case, an individual course of treatment and home training program are selected.