2965
Heart failure is one of the most frightening phenomena for a person. Heart rhythm disturbances have many causes, one of which may be extrasystole due to osteochondrosis. If arrhythmia that occurs in response to psychophysical overload goes away without treatment, then extrasystole from osteochondrosis has organic roots and requires medical supervision.
It is impossible to determine on your own how serious the heart failure is. To seek medical help in a timely manner, it is important to know how extrasystole manifests itself and how serious it can be.
What it is
Extrasystole is one of the features of cardiac arrhythmia, manifested by an impulse disorder of muscle contraction. Extrasystole manifests itself in a similar way with osteochondrosis in an advanced stage. Serious discomfort, pain, problems with other organs and body systems occur as a result of damage to:
- thoracic spinal column;
- cervical vertebrae;
- lower back.
Arrhythmic processes of the heart muscle as an independent pathology appear against the background of excessive physical activity. Impaired heart function occurs due to a lack of oxygen in the vessels that actively deliver blood flow to the internal organs. Extrasystoles, which are additional signals of an anomaly, act purposefully to eliminate the anomaly.
Reasons for needing therapy
Extrasystole often occurs due to osteochondrosis of the neck. The discs become thinner, and therefore the nerves that transmit impulses to the heart, as well as the vessels that supply it, are seriously compressed. Because of this, the heart begins to work worse, and pain appears at night. It happens:
- dull;
- bursting;
- burning.
There are several types of pain caused by extrasystole
Due to extrasystoles caused by osteochondrosis, the following complications often develop:
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- atrial fibrillation.
Both points can ultimately kill the patient. If the pain in the spine also causes heart failure, you need to consult a specialist. When treating, the doctor must consider:
- nature of extrasystole;
- mechanism of action of drugs;
- the effect of medications in each specific situation.
Emergence
Extrasystole and osteochondrosis are closely interrelated, since the pathology is caused by an advanced form of dystrophic disorders of the articular cartilages of the vertebrae. Destruction of the muscle tissue of the spinal column leads to the following problems:
- compression of the walls of blood vessels;
- abnormal conditions of nerve fibers;
- impulse disturbance of the heart muscle.
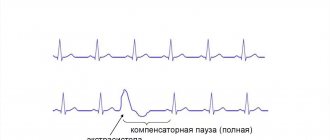
The manifestation of the disease is characterized by abnormal pulse beats. In this case, there is a pause before the next impulse, after which a short period passes before the next heart beat. This condition quite seriously alarms a person, since there is a fear of cardiac arrest.
The appearance of extrasystolic impulses is a compensating pause, due to which the general blood supply is restored. The location of the process can be observed in various areas of the lumbosacral region and other internal organs.
The occurrence of extrasystole in osteochondrosis is not uncommon, since it can be called the root cause of the disease. Lack of proper treatment leads to hypoxia of cardiac muscle cells.
Other reasons for provoking pathology are:
- Metabolic dysfunction in the body also leads to vascular dysfunction;
- Impaired activity of the heart muscle has a detrimental effect on the functioning of the nervous system, since the restriction of movements caused by pain causes serious discomfort. As a result of this, a person is in constant stressful situations, often leading to nervous breakdowns;
- Incorrectly distributed physical load on the parts of the spinal column can provoke displacement of the intervertebral discs, which also causes muscle tissue soreness;
- Taking certain medications prescribed for certain indications often causes extrasystole signals to appear.
The formation of pathology in different parts of the spine is characterized by certain differences.
Cervical region
Narrowing of the intervertebral discs caused by degenerative processes contributes to the risk of developing osteophytes, which exert mechanical pressure on the nerve roots. Moreover, the more nerve fibers are affected, the faster the disease progresses, causing severe pain spasms.
Compressed cervical vertebrae are characterized by pain spreading from the seventh to the second vertebra. In this case, the pain affects the inner area of the shoulders, reaching the tips of the upper limbs. A concomitant symptom is numbness in the fingertips.
Thoracic region
If muscle extrasystole occurs in the thoracic region, the patient often has heart disease, accompanied by pain in this area. Extrasystole of the thoracic spine is also characterized by disturbances in blood pressure and pulse. Painful symptoms are observed in the later stages of development of the pathology with increased physical activity.
The myocardium does not receive the required volume of oxygen. Additional extrasystoles in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region activate the movement of blood flow through the veins, accelerating the work of the heart muscle, which is accompanied by rapid pulse beats.
Lumbar
Extrasystole of the lumbar spine provokes the release of a large amount of toxic substances from the adrenal cortex, which leads to spastic vascular conditions. At the same time, like pathologies of the thoracic region, lumbar problems are accompanied by pressure surges and increased heart rate. The tonometer numbers can be so high that the patient is diagnosed with a hypertensive crisis.
Symptoms
It is easy to recognize extrasystole. The symptoms of the phenomenon are quite specific:
- Slowing of the pulse (when palpated, it is felt very rarely and weakly);
- Heart pounding (sometimes it even interferes with sleep, it seems as if the organ is jumping out of the chest);
- Blueness in the corners of the lips;
- Severe paleness of the skin;
- Pain in the chest area that is burning, bursting, dull or aching in nature;
- Increased sweating;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Fainting (with very intense extrasystole).
During an attack, the patient needs to be provided with free access to fresh air, a stable position (it is better to let him lie down) and rest. Usually, if the heart is healthy, the person's condition will stabilize within 5-10 minutes. Mild disturbances in heart rhythm in some cases go unnoticed.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the pathology is characterized by the fact that extrasystoles in osteochondrosis are manifested by a constant feeling of muscle tension and tissue soreness. Such symptoms significantly limit the patient’s motor activity; discomfort interferes with the natural movements of the body, upper and lower extremities.
Since the pain syndrome at the onset of the disease is not pronounced, patients rarely seek qualified medical help, believing that the pain will go away spontaneously. Ignoring symptoms can lead to their intensification, which becomes a frightening factor.
Additional signs of extrasystole in osteochondrosis are the following conditions:
- sudden shocks of the heart, accompanied by periodic freezing for several seconds. After this, the heart muscle begins to contract rapidly;
- discomfort, tension in the subscapular area;
- disorientation in space, accompanied by fainting;
- sudden hot flashes, sweating, chills;
- feeling of lack of air to take a deep breath;
- general weakness, blue lips;
- pale skin;
- irregular pulse, sudden jumps in blood pressure.
The occurrence of such symptoms should alert a person and prompt them to seek the necessary medical help. Otherwise, an increase in discomfort in the spine and other areas of the body can lead to serious psychological problems, which will require consultation with a psychotherapist and the prescription of appropriate treatment.
What types of extrasystole caused by osteochondrosis exist?
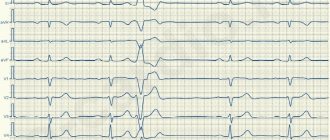
It is enough to take a cardiogram to notice irregularities in the pulse. You can get an even more accurate result using a Holter examination.
At this stage, in order to determine how to treat the patient further, it is necessary to find out how often extrasystoles occur. The frequency of attacks is divided into three types:
- rare - dozens per day;
- average - hundreds per day;
- frequent - thousands per day.
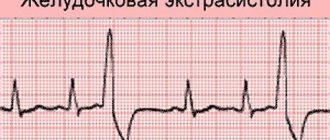
Important! Extrasystole caused by osteochondrosis may well manifest itself as constant paired attacks. Two in a row is called bigeminy. Three is trigemy. The most difficult thing to treat is ventricular extrasystoles. The severity of the condition and the complexity of treatment are proportional to the frequency of such attacks.
Diagnostics
To exclude serious pathological changes in the body, osteochondrosis and extrasystoles must be diagnosed in a timely manner. Initially, the therapist conducts a survey of the patient, facilitating a preliminary understanding of the clinical picture. His pulse is also felt and blood pressure is measured. After this, he is sent for examination to a cardiologist, who carries out the following measures:
- by palpation determines the location of the extrasystole and its type;
- studies the individual parameters of the patient’s body;
- prescribes pulse diagnostics;
- analyzes the frequency of heart contraction;
- conducts laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods;
- a halter is attached to the patient’s body for a day;
- ultrasound, ECG, MRI of the heart are prescribed;
- Treadmill testing and bicycle ergometry are carried out.
Diagnosis of extrasystole allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis, after which optimal treatment can be prescribed.
Treatment
Since the connection between extrasystole and osteochondrosis is pronounced, therapeutic measures are prescribed if the patient has more than 200 attacks per day. Effective monitoring is carried out by Holter. There are several therapeutic methods. Depending on the diagnosis, they consist of the following activities:
Medicines
Serious pain conditions require taking painkillers (usually Panangin is prescribed, which helps enrich the heart muscle with calcium, magnesium, and improve metabolism). Sedative medications are prescribed for a pronounced fear syndrome of heart failure, even to the point of cardiac arrest.
The development of arrhythmia can be provoked by taking certain medications. In this case, doctors review the treatment regimen and prescribe other groups of drugs.
If hypertension is a symptom of the pathology, the patient is prescribed medications that normalize blood pressure.
Manual therapy
Using this method, spastic conditions of muscle tissue are reduced, blood flow and metabolism are normalized.
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic exercises and massage significantly improve the patient’s general condition. The physiotherapeutic complex is selected based on individual characteristics.
Traditional therapy
To improve the patient's condition, folk remedies are used:
- 4 teaspoons of valerian should be added to 1 glass of water, the contents are placed in a water bath for half an hour. After filtering and cooling, the raw materials are taken 1 tbsp. spoon three times a day after meals;
- 5 – 6 cloves of garlic, 2 lemons are crushed in a meat grinder, placed in a three-liter container, filled with water. The product is taken once a day, half a glass. At the same time, heart function improves and metabolism is normalized;
- For 1 glass of water you need to add 1 tbsp. spoon of motherwort. Take a drug that improves the functioning of the nervous system, 1 tbsp. spoon before meals for 2 weeks.
Preventive measures and nutrition
To prevent extrasystole in osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, it is advisable to adhere to medical recommendations:
- avoid stress;
- supply the body with sufficient amounts of microelements and vitamins;
- follow an individually designed diet;
- promptly treat diseases of internal organs;
- monitor blood pressure;
- monitor the level of potassium and magnesium in the blood.
To normalize the general condition, the patient is advised to give up bad habits and not overuse strong coffee or tea.
Pathological heart function can be caused by diseases of the respiratory and immune systems, problems of the gastrointestinal tract, and negative processes in the spine leading to osteochondrosis. A serious approach to getting rid of extrasystole in osteochondrosis can effectively eliminate the problem.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
Treatment of arrhythmia resulting from osteochondrosis
If osteochondrosis caused the onset of extrasystole, it cannot be treated as usual: this will only worsen the disease.
Having found out the cause, you can begin therapy. It's best to proceed in stages. Here are the most important stages of treatment:
- return of metabolism to normal;
- correction of diet;
- if necessary, losing extra pounds;
- in advanced cases - the use of drugs designed to combat arrhythmia;
- a course of gentle manual therapy.
Usually it is not enough to cure a person of osteochondrosis just once. After all, even if such a disease is cured, it can strike again at any moment. So prevention of osteochondrosis must be done throughout your life. And sometimes it is recommended to use medications against arrhythmia for months after recovery so that it does not return again.
Treatment in each case must be developed by a doctor. Moreover, it is best to consult with several at once. Even chronic osteochondrosis may not be the main cause of extrasystole. It is often the result of a combination of several factors:
- certain volumetric processes;
- poisoning of the body due to chronic sluggish infections;
- poisoning of the body is unknown by what and because of what;
- hyperthyroidism;
- allergies;
- hypertension.
If extrasystole is not treated, other heart-related pathologies may develop.
During osteochondrosis, the severity of chest pain is always different. At first, the pain is sharp, and sometimes the neck, shoulder blades, and fingers go numb. Then the pain becomes dull, constantly aching. Usually older people get sick, especially those who work while sitting. So the best prevention of this is movement and sports.
Important! Chest pain caused by osteochondrosis can be recognized by the fact that it becomes stronger when the patient changes position, sharply turns his head, or actively moves his arms and legs.