Blood is a special type of human connective tissue, without which the functioning of all vital organs and systems would be impossible. It supplies cells with oxygen and necessary substances, performs protective, homeostatic, transport and other functions. Ferritin in the blood is an important indicator, the violation of which may indicate the development of various human diseases. Let's consider what this substance is and what its norm is depending on the gender and age of the patient.
Ferritin concept
What is ferritin in a blood test? This concept implies a complex protein complex, the main function of which is the transport of iron. The structure of ferritin is quite complex; it includes the protein apoferritin and an iron atom in the composition of phosphate hydroxide. One molecule of the complex can contain up to 4 thousand iron atoms.
Ferritin is very important for the normal functioning of the body. It is responsible for the metabolic processes that maintain Fe atoms in a soluble, non-toxic form.
Preparing to donate blood
For this test, blood from a vein is taken on an empty stomach (food should not be consumed for 8 hours). During this period, only clean water is allowed; tea, coffee and carbonated drinks must be excluded. For half an hour before donating blood, you should avoid significant physical activity and stop smoking. Taking medications that contain iron should be stopped three days before the test (you should consult your doctor before stopping taking them).
Recommendations for preparation may be provided by the attending physician or laboratory staff.
General recommendations:
- avoiding drinks that contain sugar and caffeine;
- blood is donated on an empty stomach in the first half of the day (the fasting period should be 8-12 hours);
- It is recommended to quit smoking an hour before taking blood.
On the day of blood collection, you can only drink plain water (carbonated drinks, including those without sugar, should be excluded).
Clinical value
The level of ferritin in the blood helps doctors determine the supply of iron in the tissues of the body, as well as carry out a differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia with anemia in other pathologies. A decrease in the concentration of this substance indicates the development of true iron deficiency anemia. Redistributed iron deficiency indicates the presence of chronic diseases, often accompanied by an increase in the amount of the protein complex. This must be taken into account when prescribing medications that include Fe. In patients with redistributed deficiency, the administration of these drugs can provoke hemosiderosis - pathological deposition of hemosiderin in the tissues of the body.
Important! The amount of ferritin in a blood test means the level of iron, and a deviation from the norm indicates the development of various disorders in the body.
Additional Information
Ferritin is one of the important elements involved in iron synthesis. The lack of high molecular weight protein affects the functioning of the cardiovascular, nervous, and respiratory systems. Ferritin production affects iron levels. With a deficiency of the latter, an anemic state develops, up to chronic anemia.
Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle will help prevent the development of the disease. It is worth adding buckwheat, liver, prunes and hazelnuts to your diet. It is recommended to increase the consumption of clean water, eliminate snacks and eat three full meals a day. Low ferritin can be caused not only by diet, but also by a number of diseases.
The doctor has the right to prescribe medication. The choice of drug is based on its effectiveness and the desired result. The dosage is calculated based on the gender, weight and age of the patient. The level of hemoglobin in the blood also plays a role. The difference between drugs lies in cost, active ingredient, restrictions, and the risk of negative reactions.
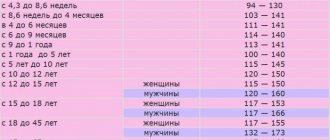
The norm depending on the gender and age of the person
Ferritin levels have great diagnostic value. Monitoring the amount of this substance is very important, because iron deficiency causes complex diseases, including anemia and hemochromatosis.
There are certain norms for men and women of different age groups. Let's look at them in more detail:
- children under 12 months – from 25 to 200 micrograms per liter (mcg/l);
- children from one year to 15 years – from 30 to 130 mcg/l;
- in men, the normal level is from 30 to 200 μg/l;
- in women – from 15 to 110 mcg/l.
There are certain standards for adults and children
During pregnancy, a ferritin test shows different numbers, depending on the trimester of pregnancy. From the first to the twelfth week, indicators should be in the range of 55–90 mcg/l. During the second trimester, the norm ranges from 25 to 75 mcg/l. From the 6th to the 9th month of pregnancy - from 10 to 15 mcg/l. If a deviation from the norm is detected, the doctor usually prescribes additional examination. This is usually a general and biochemical blood test.
Causes of elevated ferritin
An increase in ferritin in the blood is a signal of serious disorders that require additional diagnostics. Iron is a vital, but at the same time toxic element. Its excess is deposited in the joints, liver, heart, causing lasting harm to the body. That is why, if an increased concentration of this substance is detected, efforts should be directed toward identifying and treating such a deviation.
Medicine knows a number of diseases that provoke an increased content of a biological complex in the blood.
Hyperthyroidism
The disease is accompanied by an increase in the production of thyroid hormones. As a result, all metabolic processes in the body are severely disrupted, including iron metabolism. The pathology causes an increase in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, which entails symptoms such as irritability, nervousness, sleep disturbance, changes in heart rate, tremors of the limbs, weight loss and others.
Cardiovascular disorders
With a persistent increase in the protein complex, a person may develop cardiac hemochromatosis. At the same time, the organ increases in size, its tissues become denser, and acquire a brownish, rusty color. The condition is accompanied by the development of cardiosclerosis. During this disease, a dystrophic change in the structure of muscle fibers and proliferation of fibrous tissue are noted.
Excess iron is a common cause of cardiac abnormalities
Polycythemia
This pathology involves a blood disease that causes an increase in the red blood cell count in the bloodstream. The disease in most cases affects males and is extremely rare (no more than 5 cases per million population). The main reason for its occurrence is a change in the structure of a special enzyme in the human bone marrow. There are true polycythemia and false type.
In some patients, it manifests itself in the form of bleeding gums, gout, enlarged spleen, itchy skin and other symptoms. A blood test reveals high levels of ferritin and red blood cells.
Important! Often the disorder occurs without visible manifestations and is discovered accidentally during a laboratory study of blood composition.
Liver diseases
The ferritin level increases in pathologies such as hepatitis, hepatoma (primary liver cancer), cirrhosis due to alcohol intake, obstructive jaundice, necrosis of organ tissue. In such patients, a moderate or significant increase in the amount of protein complex in the blood is diagnosed.
Inflammatory and infectious diseases
High iron levels are often triggered by various infections, accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process. These include:
- rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic pathology affecting connective tissue, affecting mainly small joints;
- osteomyelitis – purulent-necrotic changes in the structure of bones, bone marrow and surrounding tissues caused by pathogenic microorganisms;
- pneumonia – inflammation of lung tissue, provoked by the negative influence of various pathogens;
- diseases of the urinary system of infectious origin.
A ferritin test allows you to suspect many diseases.
In addition to the diseases described above, an increase in ferritin can be provoked by systemic lupus erythematosus, burns, lymphogranulomatosis, hereditary pathologies characterized by impaired iron storage in the body, leukemia and other conditions. Often an increase in the concentration of the protein complex is diagnosed in alcohol dependence.
Provoking factors for decreased iron levels
Low levels of ferritin are no less dangerous for human health. Iron deficiency anemia occurs due to a variety of reasons, among which the most common are the following:
- serious kidney problems. Nephrotic syndrome occurs against the background of many diseases, including pyelonephritis, nephropathy in pregnant women, diabetes mellitus, primary amyloidosis and many others;
- Low ferritin is often a consequence of massive internal and external bleeding. These could be injuries, fractures, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, liver, ovarian rupture due to ectopic pregnancy, intra-articular fractures, etc.;
- malabsorption - impaired absorption of microelements by the gastric mucosa;
- Celiac disease is a disorder of the folding of the cereal protein gluten due to damage to the villi of the small intestine by certain foods.
Symptoms of iron deficiency in the body include weakness, malaise, increased heart rate even with little physical activity, headaches, hair loss, brittle nails, dry skin, decreased memory, and frequent viral and infectious diseases.
Anemia leads to the development of many negative symptoms
Important! If there is no treatment for this condition, anemia progresses and poses a great danger to human life and health.
An example of a daily diet: today is my “iron” day...
How to create a menu that will help cope with iron deficiency? It's actually not difficult. Foods rich in iron and the vitamins necessary for its absorption are neither rare nor particularly expensive. Here is an example of an “iron” diet for one day:
Breakfast: 2 soft-boiled eggs or scrambled eggs, fresh cabbage salad, a slice of black bread with butter and hard cheese, orange juice:
Second breakfast: curd mousse with dried apricots and prunes or oatmeal with dried fruits, rosehip infusion. :
Lunch: chicken soup or borscht with mushrooms, stewed liver with onions or baked turkey with vegetable stew, fruit salad and dried fruit compote. :
Dinner: steamed beef patties or mackerel baked in foil, pea puree or stewed carrots, soothing herbal tea:
This menu is not only rich in iron, vitamins C, B9 and copper, it also fits the definition of dietary, contains a sufficient amount of fiber and will not harm your figure.
Heart Health Linked to Decreased Protein Complex
A lack of ferritin in a biochemical blood test often indicates the development of heart failure. At the same time, there is also a significant decrease in hemoglobin levels. When examining red blood cells, their decrease and poor hemoglobin saturation are diagnosed. In most cases, ferritin acts as a cause, not a consequence, of pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
Possible cardiac abnormalities:
- carditis is an inflammatory process of various parts of the heart due to infectious and allergic lesions. In this case, a person experiences pain in the chest area, fatigue, shortness of breath and other symptoms;
- changes in the thickness and structure of blood vessels;
- disruption of myocardial metabolic processes;
- attacks of arrhythmia (tachycardia, bradycardia).
Due to a deficiency of essential nutrients, the heart begins to function in an unusual mode, which means that it wears out prematurely. An increase in load on an organ provokes its structural changes, hypertrophy, and tissue proliferation. A persistent and long-term decrease in ferritin causes oxygen starvation of myocardial tissue and the appearance of areas of necrosis. The patient has a heart murmur and impaired functioning of the aortic and mitral valves.
If the described condition is not treated in a timely manner, a person may experience severe heart failure, stroke, or heart attack.