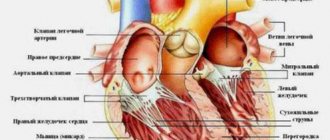
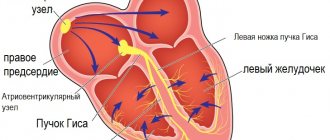
Supraventricular extrasystole (SVES) is a deviation of the heart rhythm from the norm, in which additional cardiac impulses occur. As a result of this process, extraordinary and defective contractions of the heart occur. Most often, this pathology occurs in patients with heart problems. In the article we will understand what it is, why frequent manifestations are life-threatening, and what consequences follow from ignoring the symptoms.
What does it represent?
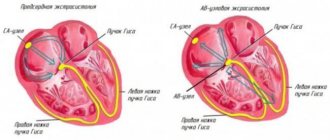
With supraventricular extrasystolic arrhythmia, the source of the spread of extraordinary contractions is localized above the ventricles. With such a deviation, a center of trigger activity is formed, sending periodic impulses out of turn. The ICD-10 code for this violation is 149.3.
Ventricular and supraventricular extrasystole can be determined by the severity of symptoms.
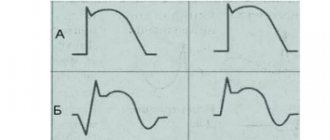
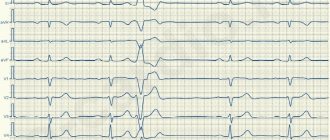
In the first case it will be more intense. To identify characteristic criteria and diagnose signs, it is enough to conduct a standard ECG (pictured). Diagnosis of supraventricular disease is complicated because the ECG will show a wide QRS complex.
Diagnostics
The first thing you should pay attention to when diagnosing supraventricular extrasystole is the clinical signs. This pathology is characterized by unpleasant sensations in the chest, which cause significant discomfort, but cannot be called pain.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient must undergo an ECG and 24-hour Holter monitoring.
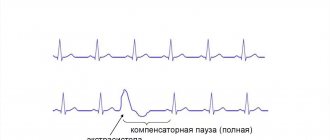
On the ECG, supraventricular extrasystole looks like this:
- expansion and deformation of the atrial P wave ahead of time;
- the P wave is followed by the normal ventricular complex;
- the compensatory pause is incomplete;
- if the origin of the extrasystole is atrioventricular, the P wave may not be detected or may be observed after the ventricular complex.
Reference! Supraventricular extrasystole on the ECG manifests itself clearly and leaves no doubt for making a diagnosis.
Classification
There are several classifications of supraventricular extrasystole. At the location of the source of excitation, the following varieties are distinguished:
- atrial – upper parts of the heart;
- antrioventricular - the septum between the ventricles and the atrium.
Depending on the frequency of extrasystoles in 1 minute: single (single), multiple, group and paired. With a single type, up to 5 additional contractions are observed, with multiple ones – more than 5. The group type involves several extrasystoles at once, which come one after the other, the paired type – 2 extrasystoles come in a row.
Rare and frequent extrasystoles can be distinguished.
Causes
Most often, supraventricular extrasystole occurs against the background of heart disease. However, there are a number of other common reasons that can trigger the development of such a disease. These include:
- drug exposure - uncontrolled use or overdose of diuretic or antiarrhythmic drugs;
- problems with electrolyte metabolism - low concentrations of calcium, sodium and potassium in the blood;
- poisoning or intoxication - excessive alcohol consumption, negative effects of chemicals and smoking, infectious diseases;
- diseases of the nervous system – neurocirculatory dystonia;
- endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, increased or decreased activity of the thyroid gland, menopause or the onset of menstruation;
- unhealthy lifestyle – frequent stress, heavy physical activity, increased nervousness, low physical activity.
Reference! In some cases, the cause of the development of the pathological condition cannot be determined.
Sometimes extrasystoles of the supraventricular type occur as an independent disease, but this is very rare - about 5-10% of all cases. In 50% of cases, the reason for the development of such a deviation is the presence of cardiac pathology.
Causes
Pathology can occur for various reasons.
Cardinal (heart) causes:
- ischemic disease – lack of blood supply and oxygen starvation;
- myocardial infarction – a certain area of the heart muscle dies and is replaced by scar tissue;
- cardiomyopathy – damage to the heart muscle;
- myocarditis - an inflammatory process in the heart muscle;
- congenital and acquired defects - violation of the structure of the organ;
- heart failure - the heart cannot fully pump blood, that is, it cannot cope with its main function.
The disease can be caused by taking medications , especially those that are taken uncontrolled and for a long time, for example:
- anti-arrhythmia drugs;
- cardiac glycosides;
- diuretics.
Hormonal ailments can also provoke extrasystole:
- diabetes;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- thyrotoxicosis.
Other reasons:
- electrolyte imbalance – change in the ratio of sodium, magnesium, potassium salts;
- the toxic effects of alcohol and nicotine on the human body;
- failures in the functioning of vegetation ;
- prolonged oxygen starvation - observed with apnea, anemia, bronchitis;
- idiopathic - the disease occurs without any specific cause or there is no way to find out.
Symptoms
With supraventricular extrasystole, the patient feels “interruptions” in the work of the heart. A healthy person does not feel his own heartbeat at all. Other symptoms include:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- constant feeling of anxiety;
- feeling of lack of air;
- panic;
- fear of dying.
The exact signs of the pathological condition will depend on the underlying disease. For example, with neurosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia, the patient's sweating increases and the feeling of anxiety increases. If the cause of the disease is cardiac pathology, then heart pain is observed.
Extrasystole
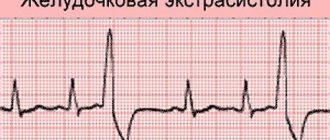
The heart consists of two “pumps” (left and right ventricles) and “chambers” (atria) that store blood. In general, in most cases, atrial arrhythmias are less dangerous than ventricular arrhythmias.
- Types of extrasystoles
Extrasystole is the most common type of arrhythmia, in which there is untimely excitation and contraction of the heart muscle. Ecstasystoles are felt as interruptions in the functioning of the heart, as pauses and extra beats. Complaints about extrasystoles are even more frequent than complaints about increased pressure. Among the different types of extrasystoles, there are those that pose a threat to life and those that are relatively safe. It is difficult for the patient, and sometimes also for the doctor, to determine which arrhythmias are dangerous and which are not.
- Examinations for suspected extrasystole
A person who comes with complaints about interruptions in the work of the heart must tell in detail about his complaints and undergo an examination - electrocardiography and, in some cases, Holter ECG monitoring. These studies allow you to accurately determine the type of extrasystole.
- Atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia
Atrial fibrillation is an extrasystole originating from the atria. This is the most common sustained arrhythmia and poses a certain risk. The second type is a rhythm disorder originating from the ventricles of the heart (ventricular tachycardia). An additional focus of electrical excitation appears inside the ventricles, like a certain group of military personnel, which “does not listen” to the “main” driver, but decides that it will act autonomously. This is how extraordinary heart contractions are triggered.
These arrhythmias are very different. The real danger is ventricular tachycardia when the focus inside the ventricle is powerful. It can be compared to the fact that there is no longer one group of military men, but a huge military unit with nuclear weapons that wants to achieve autonomy inside the left ventricle. Sustained ventricular tachycardia, which cannot be confused with anything on the ECG, is often accompanied by very poor health and fainting.
- Treatment of the most dangerous extrasystoles
Cases at high risk of sudden cardiac death
require special treatment in the form of installation of an electrical device - a cardioverter-defibrillator. That is, a person can “carry” a small defibrillator inside himself, which, if such an arrhythmia develops, will restore the rhythm by delivering an electric shock. At the Ilyinskaya Hospital we install such cardioverter-defibrillators for our patients.
Another treatment method used at the Ilyinskaya Hospital is radiofrequency ablation of the focus of the pathological rhythm. This is a minimally invasive endovascular surgery. Through a puncture in the femoral artery, a special catheter is inserted into the vascular bed and passed into the cavity of the heart. The surgeon determines the zone of the heart muscle in which the pathological source of excitation is located and destroys it with a high-frequency electric field.
- Treatment of non-life-threatening ventricular extrasystole
There are less dangerous arrhythmias, which also originate from the ventricles, but do not cause life-threatening tachycardia, however, the patient feels interruptions in the functioning of the heart and this significantly reduces the quality of his life. The situation is difficult, since drug therapy that eliminates arrhythmia does not prolong the patient’s life. The patient may be under the false impression that if there is no arrhythmia, then the risk of cardiac death is minimized. By removing one arrhythmia, an antiarrhythmic drug can cause another, more dangerous one. Therefore, the general approach to the treatment of ventricular extrasystoles that are not related to ventricular tachycardia is to try to find and eliminate the cause, if there is one. In particular, it may be myocardial ischemia.
If there is a focus inside the myocardium that causes arrhythmia, but the arrhythmia itself does not threaten death (although it interferes with life), then the patient must understand that medications will not add years to his life. Such patients should be recommended cardiac rehabilitation - various methods that will help improve the tolerance of this arrhythmia.
If a person is completely unable to live with arrhythmia, then he is prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs or undergoes radiofrequency ablation. It is important to understand that this is done to eliminate the subjective feeling of interruptions, and not to prolong life.
- Supraventricular extrasystole and its treatment
There is a much safer and more common type of arrhythmia - supraventricular extrasystole. Most often, this arrhythmia is not associated with any serious heart disease. Subjectively, supraventricular extrasystole can be felt by a person in the same way as ventricular extrasystole; it is almost impossible to distinguish them. Supraventricular extrasystoles originate from the atria and are quite safe, but they reduce the quality of life, since the anticipation of interruptions can be associated with the expectation of death. This is a special psycho-emotional state in which people begin to listen carefully to themselves. The phenomenon of somatosensory amplification appears, when a person becomes more sensitive and feels even those interruptions that a large number of healthy people have.
We do not have an ideal antiarrhythmic drug in our arsenal. With ventricular arrhythmia, we can talk about at least a zero balance of harm and benefit from prescribing medications. In the case of treating supraventricular arrhythmia, an antiarrhythmic drug can cause real harm to the heart. Therefore, the key method in treating such patients is psychotherapy. The psychotherapist’s task is to change the patient’s attitude towards the disease and explain to him that these interruptions are safe. In exceptional cases, when cognitive behavioral psychotherapy is not enough, an antiarrhythmic drug can be prescribed or radiofrequency ablation can be performed. But these are extreme measures.
- Alternative treatment for extrasystoles
If safe atrial extrasystole causes you serious anxiety and psychological discomfort, psychotherapy should be put first. Psychotherapists at the Ilyinskaya Hospital, in collaboration with cardiologists, will provide you with the necessary help.
If you have never been examined and do not know what type of arrhythmia you have, you need a high-quality examination with a daily ECG recording in order to exclude rare and dangerous rhythm disturbances, which can sometimes be observed against the background of ordinary extrasystole.
Features in children
If a child has been diagnosed with supraventricular extrasystole, then you should first of all monitor his lifestyle and follow a daily routine. It is important to explain to the child that if he does not follow all preventive measures, serious complications may arise that will negatively affect his health.
The child's diet should be varied and balanced. Food should be rich in amino acids, vitamins, proteins, fats, carbohydrates and minerals. The diet should include fruits, vegetables, dairy products, fish and meat. You should minimize the consumption of sweets and junk food.
In order to prevent further development of the pathological condition, it is necessary for the child to have rational physical activity and spend as much time as possible in the fresh air. The baby's condition may worsen due to a cold or infectious disease.
Important! If the child’s condition worsens, you should immediately contact a pediatrician or cardiologist. In some cases, hospitalization is required.
Treatment and recommendations
If the patient is diagnosed with single systoles and there are no other cardiac pathologies, treatment for supraventricular extrasystole is not carried out. Recommended lifestyle adjustments:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- moderate physical activity;
- proper nutrition;
- minimizing stress;
- a full night's rest;
- positive emotions;
- walks in the open air.
When diagnosing heart pathology, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root cause. It is possible to prescribe symptomatic therapy - drugs with a sedative effect, antiarrhythmic drugs.
Treatment
How to change your lifestyle?
If extrasystole of the supraventricular type occurs, you should especially carefully monitor your daily routine. For adults, this means that it is recommended to have a normal work schedule and work no more than 8 hours a day. Stress, psycho-emotional stress, and night work should be excluded.
It is necessary to give up bad habits. The body must have proper rest, so you need to sleep at least 8 hours, and it is recommended to spend your rest time as actively as possible.
To prevent the condition from worsening, the patient should review his diet. It is recommended to exclude foods high in cholesterol and animal fats from the diet. The basis of the diet is plant foods, dietary meat, nuts and dried fruits. Oils that are especially useful are sunflower, olive and flaxseed.
Drug therapy
Treatment of ventricular extrasystole begins with drug therapy - drugs are selected depending on the presence of additional disorders, the degree of deviation from the normal heart rhythm and the type of cardiac pathology. Therapeutic effect of antiarrhythmic drugs:
- prevention of the occurrence of organic systolic murmurs;
- decreased conductivity levels in the heart;
- decreased force of myocardial contractions;
- normalization of heart rate.
To monitor the effectiveness and correctness of therapy, an ECG is prescribed. This procedure allows you to see all the changes in the body, which gives the doctor the opportunity to timely adjust the course of treatment.
Antiarrhythmic drugs can cause problems with the respiratory system. Therefore, treatment should only be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. To minimize the risk of complications, the doctor periodically performs urine and blood tests. This is necessary in order to establish the concentration of medicinal substances in the patient’s body.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is prescribed only if conservative therapy has failed. To eliminate extrasystole of the supraventricular type, radiofrequency catheter ablation .
This procedure involves inserting a catheter through an artery. The doctor guides the electrodes through the catheter directly to the parts of the heart from which the impulse comes. This is a closed type of operation, sometimes open surgery is performed.
Open surgery is prescribed if there is a need for intervention in other parts of the heart.
The essence of surgical intervention for supraventricular extrasystole is to eliminate the focus, which generates additional cardiac impulses.
Consequences and complications
With timely detection of pathology, adequate therapy and lifestyle changes, the prognosis for supraventricular extrasystole is favorable. If the patient does not have concomitant illnesses, death from extrasystole cannot occur. But if the clinical picture is ignored and treatment is refused, the following complications may develop - coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation and other life-threatening diseases.
Important! Despite the fact that supraventricular extrasystole, as an independent pathology, does not pose a threat, consultation with a doctor should be mandatory.
LiveJournal