Hypertension is a symptom of significantly increased blood pressure. Bradycardia is a symptom in which the heart rate decreases to sixty beats per minute. The combination of the two is rare because with high blood pressure, the heart is more likely to speed up to supply oxygen to the entire body rather than slow down. Therefore, it is difficult to choose drugs for hypertension and bradycardia - most drugs, on the contrary, slow down the heart rate in people with hypertension.
General information
Bradycardia is a condition of the heart muscle in which its contraction frequency is less than 60 beats per minute. This deviation is not always pathological (in many athletes, bradycardia is a type of normal). However, in most cases, such a disease is rarely independent and indicates the presence of problems in other body systems.
IMPORTANT! A slight decrease in heart rate is usually rarely pronounced. The patient may not even notice such a deviation.
General recommendations for bradycardia and high blood pressure
Usually, a slow heartbeat is observed with a decrease in blood pressure - hypotension, but many hypertensive patients also note dangerous symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances. A deviation, when the main organ of the human body with elevated tonometer readings (from 140/90 mm Hg) begins to beat slower than 60 times per minute, is provoked by many reasons.
General recommendations on how to treat bradycardia with high blood pressure depend specifically on the provoking factors:
- Taking too high a dosage of drugs from the group of beta blockers, which were prescribed to a hypertensive patient by a doctor to get rid of arterial hypertension, causes bradycardia. You may need to adjust dosages or stop taking certain medications after consulting your doctor.
- Suppression of the sinus node due to the use of drugs with a high content of calcium and potassium - while the pulse rate noticeably decreases. After assessing the existing changes, drug doses should be adjusted and symptomatic therapy should be carried out.
- The painful condition that occurs when hypertension passes into a chronic advanced stage must be prevented. To do this, hypertensive patients should undergo regular examinations, especially if a low pulse is regularly recorded during periods when the pressure has increased.
- Timely cure heart diseases - ischemia and cardiomyopathy, diagnose congenital defects.
- Pay attention to and treat pathologies of other systems and internal organs that affect high blood pressure during bradycardia. Inadequate production of thyroid hormones, kidney and liver failure, diabetes mellitus - all these diseases increase the risk of underestimating the heart rate in hypertensive patients.
- Timely identify the abnormal structure of the capillary system, which manifests itself at the genetic level.
- Prevent, if possible, age-related changes in blood vessels, during which they lose their elasticity, become fragile and lead to exacerbation of existing diseases.
A decrease in the heart rate is often observed after a severe course of viral infections; this condition is perceived as a complication of the disease. In addition, low pulse, which accompanies high blood pressure, is observed in people who abuse alcohol and smoke. Therefore, it is necessary to increase immunity to prevent severe colds and give up bad habits.
Frequent stress, lack of sleep, chronic fatigue, and a tendency to depression contribute to the aggravation of the condition.
Problems with the cardiovascular system are most difficult for people with obese body mass. Here, high blood pressure, accompanied by a slowdown in heart rate, is aggravated by swelling, breathing problems, constant rushes of blood to the face and neck, and increased sweating.
How to increase heart rate with normal blood pressure?
Hypertensive patients who lead a sedentary lifestyle, do not follow a diet, and abuse salty, spicy and smoked foods are almost all prone to pathological changes in the functioning of the heart.
Based on the above, if the pulse decreases against the background of high blood pressure, the factors provoking this syndrome should be eliminated. First of all, limit stressful and conflict situations. It is necessary to provide the body with proper rest, sleep at least 8 hours a day.
For chronic fatigue and problems with sleep, a vacation is necessary; if necessary, the doctor can prescribe sedative medications, preferably of herbal origin. What diet is necessary for a hypertensive patient who regularly has a low pulse? You definitely need to give up table salt or limit its amount.
You also need to forget about baked goods, carbonated drinks, fast carbohydrates, fatty, smoked and spicy foods. The ideal option is to eat lean meat and steamed fish, vegetables, fruits, grains and fiber. If necessary, the specialist prescribes a course of vitamin therapy.
Classification
Bradycardia is usually divided into several subtypes depending on its location:
- sinus (manifests itself when the sinus node is malfunctioning);
- caused by heart block (with such a deviation, sinus-atrial or atrioventricular contraction of impulses is usually disrupted).
In turn, sinus bradycardia is divided into several more subtypes depending on the reasons that caused its appearance:
- Organic . Manifests itself as a result of any cardiac abnormality, for example, dystrophy or myocardial infarction, cardiosclerosis or myocarditis.
- Neurogenic (it is not associated with heart disease). This form of pathology can develop due to a number of reasons, for example, due to increased intracranial pressure, the presence of tumors in the brain or hemorrhage in it, with neuroses, VSD, after head injuries, with frequent wearing of a tight collar or tight tie. By the way, bradycardia often occurs in people with reduced thyroid function; usually the cause of the appearance in such cases can be a stomach or duodenal ulcer.
- Medicinal . This type appears when taking certain medications, for example, cardiac glycosides, morphine, calcium channel blockers, etc.
- Toxic . Develops in the presence of severe intoxication due to sepsis, typhoid fever, uremia, hepatitis. Phosphorus poisoning can also cause a toxic form of bradycardia.
IMPORTANT! But often the exact cause of the reduction in heart rate cannot be established. And in this case, the doctor diagnoses idiopathic bradycardia.
Advantages of treating bradycardia in hypertension with medications
Many older people are afraid to take blood pressure pills. They all seem to be made up of terrible chemicals and have devastating side effects on the body. In fact, it is almost impossible to treat hypertension with bradycardia without medications.
They have several positive effects:
- Inotropic effect - under the influence of the drug, the heart begins to contract more strongly, and thus the effect of bradycardia is reduced;
- chronotropic effect - as a result of taking drugs, the heart begins to beat faster
- dromotropic effect - provides a higher speed of impulse that travels through the nervous system from the brain to the heart and signals the need for contraction
- butotropic effect - increases the sensitivity of the heart to nerve impulses.
There are also additional effects. For example, strengthening blood vessels or increasing oxygen levels in the blood. Although a different lifestyle can achieve a lot, pills are necessary.
Symptoms of bradycardia
Minor changes in heart rate (45-55 beats per minute) usually do not cause any discomfort in the patient. He may not even notice changes in his body. More severe symptoms, manifested in the form of dizziness, general weakness or even fainting, appear when the heart rate decreases to 40 beats per minute.
In addition to the listed symptoms, a patient with bradycardia may complain of:
- constant fatigue, which develops into chronic;
- shortness of breath;
- cold sweat;
- chest pain;
- regular surges in blood pressure;
- difficulty concentrating, problems with memory and thinking;
- to “floaters” before the eyes.
If the pathology has been advanced, then fainting and even moments of loss of consciousness are not excluded.
Characteristic symptoms and signs
The patient's diagnosis of a combination of bradycardia and arterial hypertension can be identified by symptoms. This includes:
- chronic fatigue - constant craving for sleep;
- dizziness - intermittent, usually due to physical exertion;
- general weakness - it is difficult for the patient to concentrate, it is difficult to perform actions that previously did not cause problems in a healthy state;
- shortness of breath - initially occurs only during physical activity, progresses over time and even occurs at rest.
Occasionally, the patient experiences attacks that are accompanied by an increase in blood pressure along with bradycardia. The pulse slows down and breathing becomes difficult. Sharp stabbing pain in the left side of the chest may spread to the arm.
She may be confused and may not respond if asked how she is doing.
A blood pressure diary, which is recommended for everyone over the age of 50, can also be used to track disease combinations. If measurements show that your blood pressure is constantly or frequently elevated, consult your doctor.
Diagnosis of bradycardia
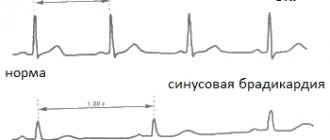
The first sign by which any doctor can suspect the progression of bradycardia in a patient is, of course, a rare pulse. With sinus bradycardia, heart contractions have a regular rhythm, their sonority remains unchanged, but some patients experience uneven breathing.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor will ask the patient to undergo additional examinations:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels;
- bicycle ergometry with additional load (in rare cases).
Diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must perform several diagnostic procedures:
- Obtain a medical history. The patient should be asked about symptoms, whether he has previously had high blood pressure, whether there are any concomitant diseases or allergies.
- Exam. The doctor listens and taps on the chest - if a person is sick, the sound will be different from normal.
- Echocardiogram and ultrasound. Allows you to get a complete picture of the condition of the heart.
- Cardiogram. Allows you to find out how the heart works, whether there are any malfunctions. It is there that the presence of bradycardia in a patient can be detected.
- Angiography. This allows you to find out the condition of the blood vessels.
In addition, if the doctor sees such a need, he can put a device on the patient that will monitor heart rate and blood pressure throughout the day. Test results will help make a diagnosis.
Treatment methods for bardycardia
First of all, it is important to correctly diagnose and find out the cause of bradycardia. Then, after collecting data and drawing up a detailed clinical picture, the doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment depending on the type of pathology.
All methods of treating deviations can be divided into two groups:
- Conservative therapy . Includes the use of medications that help increase heart rate, as well as medications that help eliminate the symptoms of the underlying disease. For hypothyroidism, for example, thyroid hormones are prescribed, for ischemia - antiplatelet agents, for infection - antibacterial and antiviral agents.
- Surgery . Involves implantation of a pacemaker. This is a special device that produces electrical impulses and, as it were, “imposes” the correct behavior and normal heart rate on the heart muscle.
IMPORTANT! In the case of heart disease of any type, it is extremely important to follow a diet and give up bad habits. Without these two points, recovery and a full healthy life will simply be impossible. No alcohol, fatty, salty, smoked foods, less salt, no cigarettes. You should also avoid wearing clothing that compresses your neck.
Cardiologist at the Stimul Clinic Grachev Sergey Aleksandrovich
Treatment of bradycardia. When does the heart need help?
Bradycardia is a slowing of the heart rate. Normally, an adult's heart rate is 65-80 beats per minute. In children, this figure is higher, the younger the child. A newborn's normal heart rate can be 140 beats.
Risk factors, what happens
In accordance with the generally accepted classification, there is no division of bradycardia. However, there is a conditional division that allows you to assess the severity of the violation.
Depending on the severity of the symptom, bradycardia is divided into:
- Light. It is said to occur when the heart rate is more than 50 beats/min and there is no discomfort in the patient. Treatment for bradycardia is not required.
- Moderate. The contraction frequency is in the range of 40-50 beats. In some cases, it may be a variant of the norm, for example, in athletes. Signs of oxygen starvation may occur.
- Severe bradycardia. A significant decrease in heart rate (below 40 beats/min) is accompanied by multiple disorders.
Causes
Bradycardia can be caused by a number of reasons.
Pathological causes that pose a danger are the following:
- increased tone of the parasympathetic nervous system;
- intoxication;
- hypothyroidism;
- a number of infections;
- heart diseases.
8
24/7
The appearance of bradycardia while taking medications is common and usually not dangerous. However, if this symptom occurs regularly, it is recommended to consult your doctor. Perhaps he will adjust the dosage or replace the drug.
The use of the following medications often leads to a slowdown in heart rate:
- Quinidine;
- Digitalis;
- Amisulpride;
- Adenosine;
- glycosides;
- beta blockers;
- calcium channel blockers;
- morphine
As a rule, bradycardia occurs due to an overdose of these medications.
Increased tone of the parasympathetic nervous system is also dangerous by slowing the heart rate. It can develop against the background of:
- neuroses;
- depression;
- TBI;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- cancerous tumors in the mediastinum;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer.
Intoxication can develop not only due to medications, but also due to the effects of other substances on the body. Toxins can damage various organs and systems. This cause is determined quite simply, since in addition to bradycardia, intoxication is accompanied by many more symptoms.
Intoxication with substances such as:
- lead and lead compounds;
- organophosphorus substances;
- nicotine;
- some drugs.
Thyroid pathologies are another reason why your heart rate may slow down. A decrease in thyroid hormones leads to bradycardia, while an increase in their level leads to tachycardia.
Hypothyroidism is a hormone deficiency that occurs due to diseases of the gland itself or due to a lack of iodine.
Infectious diseases that provoke a decrease in heart rate:
- typhoid fever;
- sepsis;
- some forms of hepatitis.
It can also develop against the background of almost any infection in its protracted stage, when the body does not have the strength to fight the disease.
Cardiac pathologies are a logical reason why rhythm disturbances can be observed. The most dangerous processes in this case are sclerotization and inflammation that have spread to the conductive tissue. When this tissue is damaged, the impulse is delayed and cannot pass normally.
Symptoms
With mild bradycardia, no additional symptoms occur. Severe bradycardia significantly affects blood flow and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- dyspnea;
- general weakness;
- paleness of the skin;
- increased fatigue;
- chest pain.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment for bradycardia, a diagnosis must be made. Detecting bradycardia is not difficult and can be done by a person independently by measuring the pulse on the radial or carotid artery.
However, confirmation from a specialist is still required, since pulse and heart rate do not always coincide.
8
24/7
To confirm the diagnosis the following can be used:
- auscultation;
- electrocardiography.
Auscultation is performed by a doctor during the initial examination. The procedure involves listening to tones and noises using a stethoscope. The advantage of the method is the ability to evaluate the functioning of the heart valves, which allows one to suspect certain heart diseases.
Electrocardiography is a method for studying the bioelectric impulse. The differences from the cardiogram of a healthy person will be in the longer distance between the teeth.
Treatment
Treatment of bradycardia is carried out only when it is pathological and is aimed at the reason for which it developed.
The patient should not make his own decision about taking medications, since they are not always necessary.
Drug treatment of arrhythmia during bradycardia should be carried out in the following cases:
- the presence of dizziness, fainting and symptoms indicating circulatory disorders;
- decreased blood pressure;
- frequent attacks of slow heart rate, accompanied by a feeling of discomfort;
- the presence of chronic diseases that act as a provocateur of bradycardia;
- heart rate drops below 40 beats/min.
In these cases, treatment of bradycardia is necessary, since it is important to normalize blood circulation and prevent the development of complications. Hospitalization is required only for those patients who have serious concomitant pathologies.
Most often, only drug treatment for bradycardia is used to eliminate symptoms.
Bradycardia is treated with medication using the following medications:
- Atropine. A drug from the category of anticholinergics. It prevents overexcitation of the parasympathetic nervous system. While taking it, the tone of the vagus nerve decreases and the heart rate increases. It is administered by injection subcutaneously or intravenously.
- Analogs of adrenaline. Isoprenaline, Izadrine (intravenously), Isoprenaline (orally), Izadrine (sublingual tablets). The drugs act on special receptors in the myocardium, increasing the tone of the sympathetic nervous system and stimulating the heart rate.
- Eufillin. The drug is a bronchodilator drug, but has a good effect on bradycardia. It improves the transport of oxygen to tissues and accelerates heart rate. It is administered intravenously.
In cases where bradycardia is a consequence of another disease, medications are prescribed to eliminate the underlying cause.
Treatment of bradycardia in hypertension is carried out using the following medications:
- Prazoline;
- Terazosin;
- Artesin.
Surgical intervention
Treatment methods for bradycardia are not limited to taking medications. Surgical treatment of cardiac bradycardia is performed extremely rarely - only in cases where the deviation significantly affects hemodynamics. As a rule, in the presence of congenital anomalies, the operation is performed in childhood.
Surgery is also indicated in cases where cancerous tumors affect the mediastinum area.
For persistent bradycardia leading to heart failure due to an unknown cause, implantation of a pacemaker is indicated. This is a special device that creates electrical impulses.
Forecast
If sinus bradycardia is not treated, the following consequences may develop:
- heart failure;
- thrombus formation;
- transition of bradycardia to a chronic form.
Heart failure is an extremely rare complication of bradycardia. It can occur with a strong decrease in heart rate. The pathology is accompanied by disruption of the left ventricle, in which it cannot supply a sufficient volume of blood to the tissues and maintain pressure at the required level. Against this background, the risk of ischemia and heart attack develops. It is important to control the level of physical activity, since increased load requires greater oxygen consumption by the myocardium.
The formation of blood clots occurs when heart blockades and slow heartbeat with rhythm disturbances occur. Blood is pumped slowly and a small volume of it is not pushed out of the ventricle, but stagnates. This is where clots form. The likelihood of this increases with prolonged or frequently recurring attacks.
The resulting blood clots can penetrate any vessel and lead to blockage. This increases the risk of serious complications such as heart attack and stroke. Confirmation of blood clot formation is carried out using echocardiography. It requires specific treatment for bradycardia. Surgery may also be performed to prevent congestion in the ventricle.
Chronic attacks of bradycardia are most often the result of physiological causes, so drug treatment will be ineffective.
Prevention
First of all, bad habits should be eliminated. One of the most dangerous is smoking. Constant poisoning of the body with nicotine has a negative effect on the functioning of the myocardium and the entire circulatory system.
Permitted physical activity should be discussed with your doctor.
Meals should be organized taking into account the following principles:
- limiting the consumption of fatty meat (especially pork);
- refusal of alcoholic drinks;
- control of water and salt consumption;
- inclusion of nuts and foods rich in fatty acids in the diet.
Some patients think that bradycardia is not such a terrible symptom and no measures can be taken. However, such a positive attitude is not always justified. To make sure that your life is safe, you need to contact a specialist. Only he can confirm the absence of dangerous diseases.
8
24/7
Prevention of bradycardia
To prevent bradycardia, doctors usually recommend monitoring your general condition. This means that all those factors that can lead to the development of the disease need to be identified at an early stage.
It is also important that, in fact, bradycardia is more of a pathological symptom rather than a full-fledged disease. Therefore, it is a consequence, not the cause of your poor health. In some cases, it may even be a physiological feature of the body. Therefore, it is extremely important to consult a doctor on time and monitor your well-being yourself.
Bradycardia is not always a sign of a serious illness, although most often this symptom indicates that something wrong is happening in the body. Don’t torment yourself with guesswork - consult a cardiologist for advice. The sooner the causes of unpleasant symptoms are identified, the higher the likelihood of complete relief from the pathology with the help of conservative treatment methods.
Emergency care for bradycardia
You need to act quickly, especially if several symptoms are present at once, and be sure to call an ambulance.
While you are waiting for an ambulance you need to:
- lay on your back, placing a cushion under your legs so that they are slightly higher than your heart.
- If symptoms include pain in the heart area, nitroglycerin can be given. This drug acts quickly, relief will come within 5 minutes.
- You can take some medications (belladonna extract). This drug is suitable for those who are experiencing symptoms of bradycardia attacks for the first time. Two tablets of the drug need to be crushed and poured under the tongue. But the effect will not appear as quickly as from nitroglycerin, and will appear only after 30 minutes.
- those who have frequent attacks and have cardiovascular diseases,
You can take isadrin - the drug acts for 10 minutes, but to take it you need to consult a doctor.