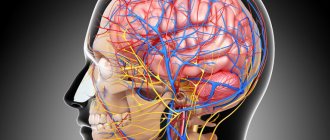
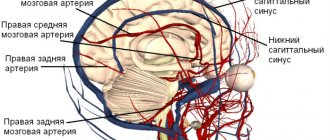
In infants, cystic formations are quite often recorded, resulting from anomalies of the arteries of their plexuses. They are not dangerous, but there is a possibility that the pathology that influenced their appearance may have a certain danger to the child’s health.
This article and the attached video will discuss choroid plexus cysts in a newborn, their types, causes and likely consequences.
Choroid plexus cyst in the brain in an infant
general information
A cyst is a benign formation that is round in shape, filled with fluid inside and surrounded by a capsule of glial or epithelial tissue. In the vast majority of cases, it is small in size and does not have a negative effect on the activity and functioning of the brain, so the formation is considered harmless.
Most often, the neoplasm forms in the lumen of the choroid plexus. If it is detected between 14 and 22 weeks of fetal development, then this is considered one of the acceptable norms, because it usually disappears on its own by the time the child is born.
Important. The phenomenon is considered dangerous when the cyst is large or grows uncontrollably.
Classification
Some types of cysts
There are several types of choroid plexus cysts in newborns:
- Choroidal - formed in the 3rd and 4th ventricles, often of infectious origin. Another reason may be hypoxia of brain tissue during childbirth. Its growth is accompanied by cramps, headaches, tremors of the arms and legs.
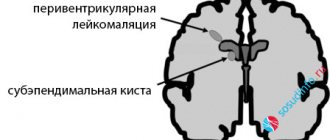
- Subependymal . Presented in the form of bubble formations with cerebrospinal fluid, it is formed under the membranes lining the brain cavities. Presumably appears due to trauma to the capillary walls during childbirth. When 2-3 small vessels rupture, a hematoma is formed; special cells filled with cerebrospinal fluid take part in its resorption. As a result, a cyst is formed, which usually goes away on its own if there are no abnormalities.
- Periventricular - formed during pathogenesis in the white medulla, when necrotic processes occur there, which begin in the prenatal period; similar processes are also possible in infectious diseases. In this case, therapy has certain difficulties, much depends on individual characteristics. Treatment is complex - conservative and radical.
- Arachnoid. It is quite rare (the probability of formation is no more than 3%). Neoplasms are more often diagnosed in boys. Characteristic signs: cramps in the muscles of the arms and legs, tremors, headaches. These are intracranial thin-walled cysts, which are divided into two types:
- primary - detected before or immediately after childbirth;
- secondary - formed as complications during surgery or when there is an inflammatory process.
Note. Periventricular cysts rarely resolve on their own.
Causes
Birth trauma is one of the reasons for the formation of cysts
The main factor is tissue degeneration followed by necrosis, which leads to the formation of internal exudate.
In newborns, among the main reasons it is important to name the following:
- birth injuries;
- pathologies during the development of the central nervous system;
- herpes virus;
- encephalitis and meningitis, and other inflammations of brain tissue or their membranes;
- ischemia and hypoxia;
- violation of intracranial circulation.
Important. Under unfavorable circumstances, an existing choroid plexus cyst may begin to grow uncontrollably, putting pressure on the tissue, which poses a certain danger.
Most often, increased intracerebral pressure can provoke an increase in neoplasia. Dangerous are injuries and concussions, as well as bacterial or viral infections of various kinds.
General information about pathology
A cyst is a fluid-filled cavity located in the substance of the brain or its membranes. When the pathology is small in size, it has a subclinical course and is diagnosed accidentally during a neuroimaging examination of the head. Since the intracranial space has limited dimensions, with a significant increase in the volume of the formation, intracranial hypertension develops.
The size of the cavity with liquid is largely determined by the compensatory capabilities of the formation and its localization. Due to the pliability of the skull bones in children at an early age, the cyst may not manifest itself for a long time.
The formation can be found in people of different ages, both in infants and in elderly patients. Even if the fluid cavity is congenital, it can make itself felt only by the age of 30-50.
According to generally accepted practice, treatment is prescribed only in the case of a pronounced clinical picture and when complications develop. If the cavity with fluid is frozen or slowly progressing and its volumes are insignificant, a wait-and-see approach is chosen, which involves regular monitoring of the patient.
Clinical manifestations
Frequent crying and a child’s bad mood is a reason to consult a neurosurgeon
As a rule, if cysts do not disappear on their own, they do not interfere with life and for a long time do not in any way remind of their existence. Brain tissue can be affected in the presence of infectious pathogenesis, trauma, or late appearance of a neoplasm.
The growth of neoplasia provokes the appearance of a certain clinic due to compression of neighboring structures. In addition, increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid is recorded, which causes the appearance of negative manifestations characteristic of hydrocephalus
A typical clinical picture in the presence of large or growing cysts in a newborn:
- attacks of nausea;
- constant regurgitation, vomiting is possible;
- decrease or increase in muscle tone of the arms and legs;
- convulsions;
- coordination disorders;
- strabismus.
The baby becomes lethargic, capricious, sleeps poorly, shows no interest and often cries, which is associated with constant headaches.
Brain cyst
The growth of the formation at the initial stage is in most cases accompanied by symptoms of intracranial hypertension. Patients constantly complain of nausea, which has nothing to do with food, deterioration in general health and decreased performance, constant cephalalgia and pressure on the eyeballs.
In some cases, the main symptoms include a constant feeling of pulsation in the head, sleep disturbance, mild hearing loss, dizziness, motor dysfunction, fainting and tremors of the limbs. Possible visual impairment, namely double vision, visual hallucinations, deterioration of visual acuity. With high intracranial hypertension, the patient is worried about constant vomiting.
There are cases when the first signs indicating a cavity with fluid are the first occurrence of epileptic paroxysm. Subsequently, epileptic seizures recur. Paroxysms can take the form of focal Jacksonian epilepsy or absence seizures and be of a primary generalized nature.
Compared to general cerebral manifestations, focal symptoms are observed in fewer cases. These may be sensory disorders, monoparesis and hemiparesis, brainstem symptoms. The latter include dysarthria, eye movement disorders, and swallowing disorders.
One of the complications of formation is cyst rupture. In this case, hemorrhage due to rupture of the vessel, compression of the brain, the formation of an epileptogenic focus and occlusive hydrocephalus are possible.
In the congenital form of the cyst, episyndromes and intracranial hypertension are recorded at an early age. Education in the brain can cause the child to develop mental retardation and mental development disorders.
Diagnostics
Doctors do not consider the formation of cysts to be an independent disease, but these formations can be the causes of various disorders. To identify, monitor and study neoplasms of the choroid plexus in infants, it is necessary to carry out the examinations given in the table.
Table. Diagnostic procedures for identifying cysts in the brain:
| Method | Characteristic |
| Can be performed without any harm to the mother or child. The method is accessible (low price) and informative. Helps doctors see the presence of an anomaly at the earliest stages of its development. |
| Taking cell cultures from the embryo and their subsequent cytogenetic analysis is a fairly accurate way to identify neoplasms of the choroid plexus. Indicated during the period of embryonic development up to 22 weeks. |
| This type of diagnosis is carried out on a one-year-old child or older, but it is important to examine a small patient before the moment when his anterior fontanelle begins to overgrow. |
| Tissue collection for histological examination. This invasive technique is indicated in cases of high risk of trisomy formation. |
Diagnostic measures
A neurologist may suspect the presence of an intracranial formation of significant size based on the patient’s neurological status and clinical symptoms. In this case, the patient is sent for examination to an ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist to check vision and hearing. Specialists perform ophthalmoscopy, audiometry, perimetry and visometry. With severe hydrocephalus, ophthalmoscopy reveals congested optic discs.
By referring the patient for echo-encephalography, it is possible to diagnose increased intracranial pressure. If the patient experiences epileptic paroxysms, he is additionally sent for electroencephalography.
It is extremely important to differentiate a cavity with fluid from a tumor, abscess and hematoma. It is not possible to do this on the basis of collected clinical data alone. Therefore, to make a clear diagnosis, neurologists use neuroimaging diagnostic methods.
By performing an ultrasound examination, it is possible to diagnose certain types of congenital cysts even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. After birth, until the baby's large fontanelle closes, neurosonography is performed to make the correct diagnosis. In adulthood, to visualize a brain cyst, the patient is sent to a magnetic resonance or computed tomography scan of the head.
MRI and CT are performed with contrast in order to differentiate a cyst from a tumor. A cavity with liquid is not able to accumulate a contrast agent, unlike a tumor.
After diagnosis, constant monitoring of the patient with a cystic formation is important. During regular examinations, the doctor monitors the volume of the cyst over time.
If the cyst is a consequence of a stroke, additional vascular examinations are carried out: ultrasound, MRI and CT of vessels, duplex scanning.
Basics of therapy
The choice of treatment tactics largely depends on a number of factors, the main of which will be: the type of neoplasia, its size and location features.
If prompt elimination of the problem is required, then several methods are possible, differing in the degree of invasiveness, but the effectiveness in any case remains at a high level:
- Radical is the most dangerous and traumatic way. A craniotomy is performed. This way the surgeon gets open access to the cyst and cuts it out completely. This operation is indicated in extreme cases, and also when other methods do not help.
- Endoscopic elimination of pathology. Several punctures are made in the bony vault of the skull, which are used to insert instruments and a micro-camera (the surgeon monitors all manipulations on the monitor, can take photos and record videos). The cyst is excised. The advantages of this technique are low invasiveness and a significantly shorter rehabilitation period. Complications and relapses are extremely rare.
- Shunting. A shunt is delivered into the cyst using a boat through large vessels, exudate is pumped out, and the cavity is filled with a special sclerotizing substance. The walls of the cavity stick together, and the tumor subsides. However, despite the safety of this procedure, there are risks of relapse or incomplete removal, which can cause the development of inflammatory processes.
Note. When a choroid plexus cyst is discovered in a newborn during its intrauterine development, it usually resolves on its own over time. Therefore, radical measures are not taken, but the child is under constant supervision of a pediatrician and specialists.
Surgical treatment is performed very rarely; more often the cyst goes away on its own or therapy can be carried out in less invasive ways
Features of treatment
As a rule, treatment for a vascular cyst is not carried out, since the body can cope with it on its own. However, there are cases when specialists are forced to prescribe medications to resolve the cyst.
Before using medications, you must consult your doctor.
Most often, neurologists prescribe the following medications:
- Cavinton. Used to eliminate cerebral circulation disorders.
- Cinnarizine. The product has a beneficial effect on the vascular system, which helps the body destroy pathological formations and stabilize.
In other cases, therapeutic measures are not carried out. For continuous monitoring of cysts, experts recommend undergoing ultrasound diagnostics of the brain once every 3 months until they are completely resolved.
Thus, the presence of a cystic neoplasm does not harm the baby’s health and does not affect his mental abilities in the future. It does not require the use of special treatment methods; it is only necessary to control the dynamics of education in a timely manner. The cyst is of great importance in assessing the risk of the formation of genetic mutations in the fetus, in cases where other pathological symptoms are also detected.
Complications
Cysts tend to spread and grow; often such processes pass latently. The result of a latent course will be the rapid manifestation of a pathological clinic; for example, the risk of a cerebral stroke cannot be excluded.
The growth of neoplasms is more often observed in adolescence, which is explained by active metabolic processes and hormonal changes, so at this time the sick child should be given as much attention as possible.
Without appropriate therapy, the following negative phenomena are possible:
- visual impairment;
- hearing impairment;
- the occurrence of seizures;
- difficulty functioning of the brain, which is associated with difficulties in thinking, learning and remembering;
- impaired coordination, disorder of the vestibular system, etc.
Early diagnosis and timely adequate therapy will help to avoid the development of complications. In this case, it is very important to distinguish between benign and malignant neoplasms.
Choroid plexus cysts in newborns are not capable of malignancy, that is, they never degenerate into cancer, and therefore do not pose a threat to life in this regard.
Classification
Classification by location:
- Cerebral (intracerebral). It is formed in areas of dead brain tissue in the internal structures of the brain.
- Arachnoid. It is formed as a result of the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in places of adhesions formed as a result of inflammatory processes and in places of their congenital duplication. The advantage is localized in the meninges.
The following types of brain cysts are distinguished separately:
- dermoid;
- colloidal;
- choroid plexus;
- pineal gland.
According to its genesis, a cavity with fluid can be congenital or acquired. In turn, congenital is divided into colloid and dermoid, and due to its formation into post-infectious, post-traumatic, post-stroke and echinococcal.
Forecast
In the vast majority of cases, everything ends well. Typically, choroid plexus cysts in a newborn, which are formed during embryogenesis, resolve themselves by the time of birth.
If the tumor still remains, then depending on the individual characteristics of the diagnosis, therapeutic tactics are chosen. As a rule, with timely removal of large or growing dysplasia, it is possible to achieve its complete cure.
The prognosis for choroid plexus cyst in a newborn is favorable
Possible danger
Signs of a cyst discovered during the examination should necessarily alert the doctor, although this is not dangerous. But its presence still increases the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities. If there are no abnormalities in clinical tests, the presence of a cyst does not give reason to suspect any abnormalities in the brain tissue. But in some cases, the mother's amniotic fluid is analyzed to check for the absence of genetic changes.
If the fetus has brain damage, the consequences can be quite serious, for example, Edwards or Down syndrome. However, this effect has not been proven by scientific research.
Types and times of examinations
To identify dysfunction of brain tissue, all babies undergo neurosonography. Such a study can be performed before the child reaches one year of age. In older children, the large fontanel, as a rule, is already closed, and it is like a window through which you can see the state of the brain. You can also perform an ultrasound when the baby reaches the age of 3, 6 and 12 months. Particular attention should be paid to premature babies, as well as to those born with weight problems. Newborns who were injured during childbirth or suffered from hypoxia in the womb should not be overlooked.