The heart, as the most important organ of the human body, allows it to function normally by pumping a large amount of blood. But if there are problems with the heart and you have to undergo surgery, your quality of life can decrease significantly.
For example, after bypass surgery for coronary heart disease (CHD) or other pathologies, health difficulties may arise, so the issue of assigning beneficiary status, obtaining a certificate and corresponding preferences becomes relevant.
What diseases give the right to disability
According to experts, due to heart abnormalities, restrictions in the usual lifestyle are inevitable. Therefore, disability due to problems with this body based on the results of the ITU is given quite often. Moreover, the list of ailments is enshrined in law. Below we will look at some diseases that allow you to become a disability beneficiary.
Cardiac ischemia
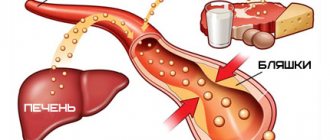
As experts note, approximately 25% of cases of ischemia end in the death of the patient. In addition, high cholesterol levels, which interfere with normal blood flow, are now detected even at a young age.
However, thanks to modern treatment methods, heart damage can be minimized. Although this does not exclude the problem from becoming chronic. And here you should contact the ITU Bureau for information so that specialists can assess the extent of the restrictions that have arisen and establish one of the groups:
First group
is established, as a rule, when coronary heart disease is combined with other pathologies.
To the second group
can be counted after a complex operation with resection. In addition, this category can be obtained in case of serious heart rhythm disturbances.
Third group
It is intended for those who have heart problems that are mild enough and do not significantly worsen their lives.
Attention
! Often the group is given to patients with coronary artery disease for a year or two. During this time, many undergo rehabilitation and can recover.
Hypertension
According to diagnostic data, about 20% of the population lives with high blood pressure, suffering not just from headaches, but at risk of encountering more global anomalies.
It is noteworthy that the risk of the disease depends on the current condition. For example, grades 3 and 4 are accompanied by other problems - often diabetes mellitus with neuropathy. If such a combination is identified, it makes sense to undergo an ITU. Experts examine and interview the patient to determine:
Third group
, if the ability to work and vital functions are slightly impaired.
Second group
with difficulties in self-care due to damage to internal organs.
First group
as a result of the inability to organize one’s life independently, not only due to high blood pressure, but also a lot of complications and other developed abnormal conditions.
In addition, hypertension can cause a stroke. To avoid this, it is recommended to take preventive measures and keep your blood pressure under control.
Heart disease
An abnormality affecting the valves or myocardium is:
— congenital, associated with a failure in prenatal development;
- acquired, developed as a consequence of autoimmune disorders (say, against the background of lupus or rheumatism in complex stages).
If a change in the structure of the heart is detected, this is a reason to assign a category:
| Group | Patient's condition |
| I | The operation is impossible. The basic functions of the heart muscle (contractility and excitability) are practically not performed. Any stress on the body is not allowed. |
| II | The heart rhythm is disturbed and severe tachycardia is observed. Organs of parenchymal origin are subject to serious dystrophy. Intrapulmonary pressure is abnormally high. |
| III | There is moderately high pressure in the lungs and muscle dystrophy. It is possible to perform surgery to reduce the pathological effect. |
By the way, doctors do not rule out the spontaneous disappearance of heart defects in the first years of a child’s life if the problem is detected at birth.
Arrhythmia
The rhythm of the heartbeat can be disturbed by one of the following types:
- bradycardia - the heart beats less frequently than usual;
- tachycardia - when over a certain period of time the organ contracts more often than necessary;
The question of establishing a special status comes up in most cases if the rhythm is seriously disrupted according to the first type. In particular:
First group
placed against the background of arrhythmia, which provoked a persistent disturbance of blood flow and, as a consequence, a lack of oxygen and nutrients in various organs (including the brain);
Second group
assigned for atrial fibrillation not corrected by medications;
Finally, the third group
prescribed to those suffering from weekly attacks of arrhythmia.
Important
! To make life easier, patients are advised to install a pacemaker.
Angina pectoris
This problem is severe pain, which is often accompanied by ischemia. Angina is characterized by:
- pain throughout the upper body;
- “return” of pain to the left hand;
- localization in the epigastric region.
The listed signs are a good reason to visit a cardiologist, who, if necessary, will refer you to an ITU to obtain a special status for the patient. Moreover, angina pectoris is on the list of heart pathologies that allow you to become a beneficiary. Moreover, periodic examination is not required.
| Group | Characteristics |
| 3 | The appearance of pain if the patient walked more than 200 meters in a stable rhythm. Arrhythmia is observed. The condition is stabilized with the help of an installed pacemaker. |
| 2 | The installed stimulator is not able to stabilize the heart rhythm. Requires medication. |
| 1 | The attack appears even with minimal exertion or in a state of complete rest. |
Chronic heart failure
This diagnosis is relevant for 2% of Russians (mostly aged 55+). It is prescribed when the myocardium is weakened, and the key signs are fatigue and shortness of breath. In addition, insufficient myocardial functionality can cause:
- high swelling;
- oxygen deficiency in organs;
- decrease in blood circulation.
Although heart failure alone does not provide preferential status, its presence together with another disease or risk of development is taken into account on the ITU.
Indications for disability in adults and children
There are no clear indications and a complete list of diseases for which a child or adult can become disabled. Each case is individual and is considered separately. And this is a very pressing issue in our country, because absurd situations happen when a person who can barely stand on his feet has to go through several authorities to prove his inability to work.
If we talk about heart diseases and cardiac operations, then everything here is also quite blurry. In Soviet times, people with the third stage of hypertension and pathological changes in target organs became disabled people; with a pronounced deterioration in the functioning of the heart muscle; with vices; with severe heart failure and associated lung diseases. Everything seems clear, but it is impossible to say for sure whether a person who has suffered, for example, severe myocarditis will be given disability. First you need to conduct a full examination, and then draw conclusions.
By the way! Disputes about the assignment of disability often arise precisely on this basis. When one person is given a group, but another, who has exactly the same diagnosis, is not recognized as disabled.
When receiving disability, the patient's age also matters. For example, children with heart defects or after severe cardiac operations become disabled from childhood. This is a stable status that gives the right to certain benefits. Disability can be canceled or a group assigned only upon reaching 18 years of age. Then the size of payments will change, and the person will be able to decide his future fate in terms of study and future work.
Previous operations that give the right to a disability group
In some cases, you can secure your disabled status after heart surgery, which requires long rehabilitation. For example, if during a surgical intervention it was necessary to open the chest, stop the heart and perform other complex manipulations. In these situations, for the purpose of social protection and state support, the patient can be examined by medical examination.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
In case of complex ischemia, when medications do not bring the desired result, radical treatment is necessary - surgical replacement of diseased vessels. Since sometimes such operations involve a complete opening of the sternum, after the intervention the patient’s bones take a long time to recover.
In general, several results of radical surgery are possible:
- improvement of the condition so much that after orthocoronary bypass surgery (CABG), when the group is lowered or completely canceled;
- lack of the expected effect after the first operation and the need to perform it again, or there is a gradual replacement of blood vessels.
Important
! Failure to comply with the cardiologist’s recommendations may result in refusal to perform the second operation.
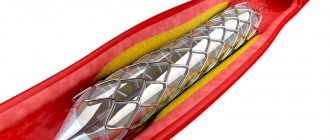
Stenting
A stent (a special exoskeleton) is necessary if, after a heart attack, the lumen of the vessels is critically narrowed and it is important to normalize blood flow. The implantation is done through a puncture in a vein, after which the results of the operation are expected to improve blood flow. But the procedure does not eliminate myocardial damage. Therefore, under certain conditions, it is possible to assign a specific category.
Options for aortofemoral bypass surgery
Aortofemoral bypass surgery can be performed in two options:
- Bilateral aortofemoral bypass surgery (aorto-bifemoral). This option involves restoring blood flow to both legs when both iliac arteries are blocked. The main branch of the prosthesis is sutured to the aorta, the branches of the prosthesis are sutured to the femoral arteries. 3 accesses are performed, two of them in both groin areas, one large on the left side.
- Unilateral aortofemoral bypass surgery is performed when one of the iliac arteries is blocked. Accordingly, only two accesses are required. One is carried out in the groin area on the affected leg, the other on the left side to the aorta.
For the operation to be successful, it is necessary to ensure good blood flow from the prosthesis; sometimes the arteries in the thigh are severely affected. In these cases, our clinic uses two-story bypass methods, when a connection is created in the groin area between the prosthesis and the most suitable artery, after which a shunt is launched further from the prosthesis from the great saphenous vein into the underlying arteries on the leg. Thus, the blood flow from the prosthesis is distributed throughout the leg and there is no stagnation of blood, leading to thrombosis and blockage of the prosthesis. If there is severe damage to the arteries in the groin, it is possible to perform femoral artery replacement. This made it possible to restore blood flow in poor condition of the peripheral vascular bed.
Disability group assigned after heart surgery
Because of an unhealthy heart, you have to make adjustments to your usual lifestyle, and if the problem is complex, then restrictions apply to almost all areas. For this reason, the beneficiary needs support in the form of:
— special medical services;
- good rehabilitation;
- medicines (not cheap);
— reducing labor loads;
- resort and sanatorium holidays.
The implementation of the listed items requires funds, and in case of a disability group, the state guarantees these types of assistance free of charge or with the opportunity to receive a discount or compensation depending on the group.
A person with a heart condition is given a group according to the degree of health restrictions encountered:
| Group and degree of loss of abilities | Condition Characteristics |
| 1 (>80-90%) | The patient is unable to care for himself. Requires assistance from an outsider when performing basic operations. The condition cannot be rehabilitated or restored. |
| 2 (60-80%) | Serious lesions, but the patient is able to perform some actions without help. |
| 3 (40-60%) | The restrictions are minor. |
Often, “core patients” need to confirm the presence of concomitant pathology to obtain the status. As doctors note, in groups 2 and 3 the likelihood of recovery remains, but in category 1 it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease and its consequences.
Important
! A disability certificate is proof of its holder’s right to financial assistance and benefits.
Where disabled people do not work
Having a disability group, a person works with certain restrictions. Of course, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s profession and work schedule.
Important! Like any other employee of the organization, a disabled person cannot be limited in labor rights.
After heart bypass surgery, a person is given a disability group, and he will not be able to work in hazardous industries, on night shifts or daily work, unload cargo or lift heavy objects. Restrictions also apply to military service and work in the police department.
It is possible to reach agreement with the employer on the work schedule and duration of work. However, disability relief does not apply to the quality of work performed.
The procedure for registering disability for heart disease
The procedure for establishing the status of a disabled person due to myocardial abnormalities is similar to that implemented for other diseases.
Required tests and diagnostics
To register a disability, a current extract from the outpatient card must be provided to the ITU office. Data should report results:
— blood tests (biochemical, general);
- X-ray and ultrasound of the chest organs;
— electro- and ecocardiograms
— angiography and MRI (if necessary).
Collection of documents
Among other things, a standard package of documents is required with:
— passport of the beneficiary;
— outpatient card;
— SNILS;
- a copy of the work book.
The listed and other documents (taking into account the specific situation) are attached to the doctor’s referral for medical examination and the application for a medical examination.
Passing the ITU
After submitting the requested papers, the examination will take place on the appointed day.
Important
! Seriously ill patients who are unable to come to the office will be examined at home, in the hospital, and in absentia.
The commission usually includes three specialists, and the procedure itself consists of a number of stages:
1) study of the presented documents;
2) assessment of the health status of the subject;
3) questioning the patient in various areas, for example, about social status, etc.;
4) meeting of experts;
5) announcement of the decision;
6) filling out the IPR and issuing a “pink” certificate (if the result is positive).
Do they give special status after a heart attack?
You can get disability after myocardial infarction and stenting if there are complications of the disease. To confirm them, you need to undergo an examination and submit an application to an expert commission, which makes the appropriate decision.
In theory, obtaining status is not difficult, but you need to be prepared to visit doctors and get tested. It can be difficult to do this on your own due to a heart attack. It’s good if there is a friend or relative nearby who is ready to help. It is better to make an appointment in advance to avoid tiring waiting in lines.
To avoid wasting time on paperwork, first consult with your doctor. Let a specialist assess your current condition and prospects for rehabilitation. Be also prepared for the fact that members of the expert commission may require additional examination and include narrow specialists in the list.
Surveillance program
Repeated examinations by a vascular surgeon and ultrasound are performed 3 months after discharge, and then annually. During follow-up examinations, the function of the shunt, the adequacy of blood flow in the legs, and whether the patient is taking the prescribed antithrombotic therapy are assessed correctly.
The most commonly prescribed medications are antithrombotic drugs - Plavix, ticlopidine, aspirin. Of the physical therapy methods, the most effective is therapeutic walking 3-5 km per day or cycling. It is important to protect your legs from various microtraumas and abrasions, especially if you have diabetes.
The basis for a successful life after aortofemoral bypass surgery is physical activity, taking antithrombotic drugs and regular examination by the attending physician with ultrasound monitoring of the function of the shunt. If narrowing of the shunt is detected, endovascular correction must be performed. When you follow these instructions, you will forget about the risk of gangrene from atherosclerosis.