Creatine kinase (CK) is an enzyme found in the heart, brain, skeletal muscle and other tissues.
It is also present in small quantities in the blood. An increase in creatine kinase in the blood indicates muscle damage due to physical activity, injury or pathological processes.
The causes of increased creatine kinase in the blood can be myopathies, muscular dystrophy, rhabdomyolysis - accelerated breakdown of muscle tissue. In this disease, the increase in CPK levels will be especially significant. Intoxication, taking certain medications (statins) and drugs can also lead to damage to muscle fibers. During myocardial infarction, CK in the blood also increases, and for a long time a blood test for creatine kinase was one of the main diagnostic markers, but currently a more specific marker is used to diagnose a heart attack - a troponin test. CPK analysis for suspected heart attack is now used as an auxiliary test.
What is creatine kinase?
Creatine kinase is an enzyme whose main function is to catalyze various chemical processes in the human body. It increases the reaction rate of creatine phosphate synthesis from adenosine triphosphate and creatine, which is used during heavy physical activity. This enzyme is found in the cells of muscles, brain, various glands and lungs.
The creatikinase molecule is divided into two parts, each of which can be considered a separate subunit:
- M (from the English “muscle” - muscle).
- B (from the English “brain” - brain).
These particles can be combined with each other, creating three isoforms of the enzyme: MM, MB, BB.
As their name suggests, they are located in different parts of the body:
- the MM isoform is predominantly found in skeletal muscles and myocardium;
- the MB isoform can be found exclusively in the heart muscle;
- the BB isoform is found in brain cells, the structure of some tumors, and some glands.
If you know where the process is located, then you can find out which isoform of creatine kinase is elevated, and vice versa.
Norm of creatine kinase MB
The level of this enzyme in the blood depends on many factors, including the age, gender of the child, as well as body type and type of physical activity.
In childhood, the nervous and muscular systems actively develop, which affects the increase in creatine kinase levels. The concentration of this enzyme in women is slightly lower than in men. In a newborn, a CK level of 650 U/L can be observed. Six months later, it drops by 2 times, and a year later - by another 100 units. But then there is a short-term increase, which is associated with the child’s first steps. Further, the level only decreases, periodically experiencing short-term increases in concentration.
Reasons for increased enzyme levels in children
If creatine kinase levels are elevated, there may be several reasons for this.
These include:
- myocardial infarction (increased concentrations after 2-4 hours, normalization after 2-3 days);
- all kinds of muscular dystrophies (a striking example would be Duchenne muscular dystrophy, which is a neuromuscular disease with severe heredity);
- coronary heart disease (lack of oxygen can cause starvation of the heart muscle, which leads to an increase in the level of creatine kinase MB in the blood);
- rheumatic inflammation;
- blood supply disorders;
- high physical activity;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- states of shock and hyperthermia;
- poisoning with substances containing alcohol;
- radiation.
It is also worth considering that the level of creatine kinase MB in the blood may increase during the use of drugs, the list of which includes:
- statins;
- drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis;
- drugs that are used in the treatment of gout;
- some antibiotics: Cyclophosphamide, Cephalosporin, Ceftriaxone;
- ascorbic acid;
- corticosteroids;
- psychotropic drugs: Clozapine, Phenozepam, Haloperidol;
- immunosuppressants.
When is the test prescribed?
CPK is found in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, heart and brain. Therefore, if an increased result is obtained, serious diseases such as myocardial infarction, chronic muscle diseases and even oncology can be suspected.
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) - 250 rub.
Urgent analysis - 500 rub.
Deadlines
Normal – 1 day.
Urgent – 1.5 – 2 hours.
Taking blood from a vein is paid separately - 300 rubles.
(If several tests are performed simultaneously, the service for collecting biomaterial is paid once)
Indications
- Comprehensive diagnosis of diseases associated with muscle cell damage.
- To confirm myocardial infarction and during the recovery period to assess the condition of the heart muscle.
- If oncology is suspected as part of a comprehensive diagnosis and to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
- To assess the severity of muscle injury.
To obtain an accurate result, you must strictly follow the preparation tips. Laboratory equipment is no less important, so it is recommended to contact only those clinics that are equipped with modern equipment.
Material for analysis
venous blood serum (avoid hemolysis)
Preparing for the study
As a rule, before taking the analysis you need to do the following:
- Tell your doctor about the medications you are taking; they may need to be stopped temporarily. If it is impossible to cancel, then you need to donate blood before taking the medicine in the morning.
- Avoid eating 8 hours before blood sampling. Therefore, it is best to take the test in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- The day before blood sampling, you must avoid fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods. Alcohol and kvass are strictly excluded.
- It is worth telling your doctor about a recent ultrasound or x-ray. These examinations may affect the results.
- It is important to avoid intense physical activity - after exercise, muscle cells are damaged, which leads to an increase in enzyme levels. This may make it difficult for your doctor to interpret the results.
- It is recommended to avoid emotional stress before donating blood.
Enzyme level control
It is known that creatine kinase comes from destroyed cells where it was contained. For this reason, it is important to know the level of this enzyme in the blood for the most effective and rapid diagnosis of various diseases, such as heart attack.
But with the help of analysis, you can not only diagnose the disease, but also monitor the existing disease, which allows you to choose the right treatment.
When monitoring the concentration of creatine kinase in the blood, several important factors should be taken into account:
- Intense loads. This factor includes people who actually rarely do this and their creatine kinase levels may increase at this point.
- Previous operations or injections that were administered intramuscularly. After these actions, the level of creatine kinase increases significantly, which makes it difficult to give an adequate assessment of the analysis.
- Having suffered an accident or falling from a height. If a child has muscle damage, this will affect the level of creatine kinase MB.
- The Negroid race has more muscle mass. If the child is a member of this race, then his creatine kinase level will be much higher than that of Caucasian children.
- Newborn babies have greater concentration. This is due to the fact that they still have remnants of creatine kinase from the placenta.
- Alcohol. Children may accidentally mix up a water bottle or medicine bottle and drink some alcohol. If alcohol is detected in the child’s body, the enzyme level will be higher.
What to do if your child’s creatinine level changes
To return creatinine in children to normal limits, it is necessary to determine the root cause of changes in indicators: poor nutrition, low or overweight, exhaustion, chronic diseases, shock, lack of protein in the body, blockage of the urinary tract, etc. If creatinine in children has changed not due to For serious illnesses, you need to reconsider your diet. When nitrogen compounds in the blood increase, it is recommended to increase the amount of fresh fruits and vegetables. For boys and girls with low body weight, parents should encourage weight lifting. Along with it, creatinine in children rises to normal levels.
When to see a doctor
Changed creatinine in the blood of children indicates pathological conditions of the body. Pediatricians of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in the Central Administrative District are ready to help if the following symptoms appear: constant fatigue and fatigue, shallow difficulty breathing, disturbances of consciousness, pain in the heart, failure of the intestines. You need to sign up for an examination after being injured or in a state of shock. If creatinine is low in a child’s blood, no significant symptoms appear. If necessary, the pediatrician will refer you to specialists to prescribe treatment. An increase to 200 µmol/l poses a danger to health and life. In this case, you need to urgently undergo dialysis. This development of the situation is possible with kidney failure.
Diagnostics of blood parameters
Biochemical analysis is the main diagnostic method that shows creatinine in the blood and whether the norm in children is maintained or not. Laboratory tests check creatinine to nitrogen ratios and creatinine clearance. For the second analysis, an additional 24-hour urine sample is taken. For creatinine, the norm in children can vary +/- 15%. This is not an indicator of pathology. We can talk about its presence when there are sharp jumps in indicators to high numbers. 48 hours before the analysis, it is not recommended to consume meat and protein products in order to avoid correlation of analysis parameters. If your child plays sports, eliminate physical activity one day before.
Why creatine kinase in the blood is elevated - the main reasons
In some people, creatine kinase in the blood is elevated; the causes of this condition are varied and lie primarily in damage to the skeletal muscles and myocardium. Total creatine kinase is an accurate and very sensitive marker of damage to muscles and the nerves innervating those muscles. Since this enzyme is very important in energy conversion processes, it is necessary to find out the reasons for the increase in its concentration in the blood mass.
Creatine kinase functions as an energy intermediary in cells and tissues. It is found in the muscles that most need energy replenishment. Found in the protoplasm of the heart muscle (or myocardium) and skeletal muscles. It has subunits M (muscle) and B (brain). In skeletal muscle, the MM of creatine kinase is 98 percent, and MV is about 1 percent.
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK): normal level in the blood, reasons for the increase
When a blood test is performed, a person may be found to have elevated creatine phosphokinase (CPK), often referred to simply as creatine kinase.
It will not be possible to find out immediately what the reasons may be. Most likely, the doctor will order additional tests. But still, some conclusions can be drawn after the first results arrive. If creatine kinase in the blood is elevated, there may be several reasons, but at a minimum this may indicate damage to the heart muscle, which can subsequently lead to myocardial infarction. Other skeletal muscles may also be impaired or abnormalities such as hypertension or angina may be present.
Decreased creatinine levels in the blood
Low creatinine in a child’s blood is a rare occurrence. It can be observed with insufficient body weight and poor or irrational nutrition. In cases of a vegetarian diet in children and adults, this is a characteristic feature that is subject to mandatory correction. Another reason is fasting. If creatinine is low in a child, liver disease may be a possible cause. The indicators are also reduced by the phenomena of hyperhydration (increased water content in the body) and muscle atrophy.
What should the creatine kinase level be?
The level of creatine kinase in a child and an adult will be different, since it directly depends on the person’s age. This occurs depending on the development of a person’s muscles and nervous system. What does it mean? In simple terms, the younger the person, the higher the level of enzymes in his body. Therefore, if creatine kinase is elevated in a child, this does not mean that he needs urgent treatment. To fully understand the situation, it is worth understanding what level of enzymes in a blood test is normal for people of different ages:
After 12 years, norms differ by gender
How to make an appointment with a pediatrician
Examination of children, collection of anamnesis and prescription of tests is performed by the pediatrician of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg). You can figure out why your child’s creatinine is low or high, and you can examine the current state of health at an appointment by making an appointment by phone: +7 (495) 995-00-33. The clinic is located at the address: Moscow, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10. This is the center of Moscow, so there are many metro stations nearby: Mayakovskaya, Chekhovskaya, Tverskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya. If you wish, you can make an appointment on the website of JSC “Medicine” by filling out the “Make an appointment with a doctor” form. You must provide your contact phone number and name. After this, a call will be received from the clinic to coordinate the date and time of the appointment.
Elevated creatine kinase levels
In most recorded cases of elevated creatine kinase in the blood, hypothyroidism is found, both in children and adults.
This disease negatively affects the structure of skeletal muscles. But such blood tests do not necessarily indicate the presence of any diseases. If creatine kinase has increased, this may be caused by ordinary alcohol intoxication. Scientists noticed that after drinking alcohol, an increase in creatine kinase in the blood will be observed for another 2 days. But this only applies to excessive use. Then the level of creatine kinase will be restored, even if we are talking about chronic alcoholism.
Another reason for the increase in CPK in the blood may be the possibility of a muscle injection. Also, when a doctor, for some reason, prescribed injections before blood tests, this is not the norm for the body in principle. Therefore, they can be attributed to another reason why there will be a deviation from the norm in the amount of enzymes in the human body.
Any surgical intervention will have a similar effect, since different muscle groups will be damaged during the operation. A blood test will show that creatine kinase in the blood is elevated for several more postoperative days.
If a deviation from the norm is noticed in the brain tissue, most often this concerns diseases of the central nervous system.
There are also certain types of medications that can cause an increase in the level of creatine kinase in the blood, these include:
What do the test results mean?
An increase in total creatine kinase is observed with myocardial infarction, increased physical activity, trauma and burns, myocarditis and myocardial dystrophy, Duchenne myopathy, poliomyelitis, muscular dystrophies, tumor decay, taking statins, dexamethasone, NSAIDs, drugs, after surgical operations.
A decrease in CPK levels may indicate alcoholic liver damage, loss of muscle mass, pregnancy, rheumatoid arthritis, hyperthyroidism, or taking certain medications (vitamin C, amikacin, aspirin). It should be remembered that the CPK test is not specific enough for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and other pathologies, therefore, in case of deviations from the norm, additional studies must be carried out.
Elevated creatine kinase in blood test
7 minutes Author: Lyubov Dobretsova 1006
A biochemical blood test allows you to identify disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and diagnose diseases at an early stage of development. During the study, the amount of proteins, enzymes, lipids, glucose, and the state of nitrogen metabolism is determined.
One of the bioelements of the analysis is creatine kinase (otherwise known as creatine phosphokinase), the level of which evaluates the energy potential of the entire muscular system of the body, including the myocardium (heart muscle), and the nervous tissue of the brain. If creatine kinase in the blood is elevated, this indicates the destruction of the cellular structure of muscle tissue.
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) in the body
Creatine phosphokinase is an enzyme that accelerates the biochemical transformation of creatine and adenosine triphosphate into creatine phosphate. During this transformation, energy impulses are enhanced, ensuring full muscle contraction.
CPK contains two constituent molecules (B and M), which in different combinations form three isoenzymes, each of which is localized in a specific structure of the body and is responsible for its neuromuscular functionality. CPK isoenzymes:
- MM – isoenzyme of skeletal muscle cells (myocytes);
- VM is an isoenzyme of muscle fibers of the myocardium and skeletal muscles;
- BB is an isoenzyme of the nervous tissue of the brain.
CPK-BB is detected in the blood only in cases of vascular or cerebral pathologies. In a healthy state of the body, the isoenzyme is unable to overcome the barrier between the circulatory and central nervous systems (blood-brain barrier). CPK CM is an indicator of cardiac muscle contractions and the main diagnostic indicator of myocardial infarction. CPK MM makes up 98% of all creatine kinase.
Creatine kinase (Creatine phosphokinase CPK)
Creatine kinase is an enzyme that stimulates the conversion of creatine into creatine phosphate and provides energy for muscle contraction.
Research method
UV kinetic test.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Creatine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl residue from ATP to creatine to form creatine phosphate and ADP. The reaction, catalyzed by creatine kinase, provides energy for muscle contraction. There are creatine kinase contained in the mitochondria and cytoplasm of cells.
The creatine kinase molecule consists of two parts, which can be represented by one of two subunits: M, from the English muscle, and B, brain. Thus, in the human body creatine kinase exists in the form of three isomers: MM, MB, BB. The MM isomer is found in skeletal muscles and myocardium, MV - mainly in the myocardium, BB - in brain tissue, and in small quantities in any cells of the body.
In the blood of a healthy person, creatine kinase is present in small quantities, mainly in the form of the MM isomer. Creatine kinase activity varies with age, gender, race, muscle mass, and physical activity.
Creatine kinase enters the bloodstream in large quantities when the cells containing it are damaged. At the same time, based on the increase in the activity of certain isomers, one can conclude which tissue is affected: MM fraction – muscle damage and, to a lesser extent, heart damage, MV fraction – myocardial damage, BB fraction – cancer. Typically, tests are done for total creatine kinase and its MB fractions.
Thus, an increase in creatine kinase in the blood allows us to draw a conclusion about a tumor process, damage to the heart or muscles, which in turn can develop both with primary damage to these organs (during ischemia, inflammation, trauma, degenerative processes), and as a result of their damage during other conditions.
Muscle diseases in which cells are destroyed are myositis, myodystrophy, injuries, especially when compressed, bedsores, tumors, intense muscle work, including what occurs during convulsions. In addition, there was an inverse relationship between the levels of thyroid hormones and creatine kinase: with a decrease in T3 and T4, the activity of creatine kinase increases and vice versa.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of coronary heart disease.
- With symptoms of myocardial infarction, in particular with a blurred clinical picture, especially with a recurrent infarction, atypical localization, pain or ECG signs, difficulty in differential diagnosis with other forms of coronary heart disease.
- For hypothyroidism.
- For symptoms of myositis, myodystrophy, myopathy.
- When planning pregnancy by a woman whose family had Duchenne myopathy patients.
- For diseases that can lead to damage to the heart or muscular system.
What do the results mean?
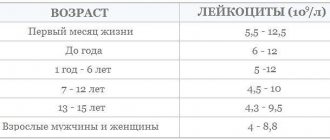
| Gender/age | Reference values |
| Male/ > 17 years old | |
| Female/ > 17 years old |
The results of the analysis indicate the presence or absence of damage to the myocardium, skeletal muscles, tumor process, and thyroid diseases. The correct interpretation of the obtained indicators allows us to draw a conclusion about the form of the lesion and the degree of its severity.
Reasons for increased total creatine kinase activity:
- myocardial infarction,
- myocarditis,
- myocardial dystrophy,
- polymyositis,
- dermatomyositis,
- muscular dystrophy,
- injuries, burns,
- hypothyroidism,
- tumor process in the body,
- tumor disintegration,
- taking dexamethasone, statins, fibrates, amphotericin B, painkillers, alcohol, cocaine,
- intense physical activity,
- seizures, status epilepticus,
- surgical interventions.
Reasons for decreased activity of total creatine kinase:
- decrease in muscle mass,
- alcoholic liver damage,
- collagenoses (for example, rheumatoid arthritis),
- hyperthyroidism,
- taking ascorbic acid, amikacin, aspirin,
- pregnancy.
Creatine kinase test
A blood test for CPK can be prescribed separately or as part of a biochemical study of biological fluid (blood) to assess all indicators. Emergency blood microscopy to check the level of creatine phosphokinase is carried out for acute pain in the heart and behind the sternum, radiating under the scapula, into the forearm and shoulder on the left side.
If, against the background of pain symptoms, a sharp increase in CPK is observed, it means that the integrity of the myocardium is compromised. In 100% of cases, an infarction or pre-infarction condition is diagnosed. Increased attention to CPK in biochemical blood tests is paid in the primary diagnosis and treatment of the following diseases:
- myositis – inflammation of skeletal muscle fibers of various locations (neck, chest, back, etc.);
- myopathy (chronic neuromuscular pathology);
- inflammatory heart diseases (pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis, etc.);
- IHD (coronary heart disease);
- hypothyroidism is insufficient synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Reference values for the CPK enzyme
The level of creatine phosphokinase in the blood depends on several factors:
- Age category of the subject. Due to the intensive growth of muscle mass and general development, children's normative CPK values are higher than those of adults.
- Muscle mass (not to be confused with the patient's overall weight).
- The presence of chronic pathologies or temporary damage to the muscle structure.
- Gender. Men have higher rates. This difference is associated with the weaker physical potential of the female body by nature. Graduation of results by gender begins at the age of six.
In women and men of reproductive age, the healthy percentage of isoenzymes is: BB:BM:MM=0:6:94. In the case when the amount of the CM isoenzyme is ⩾6% of the total creatine kinase indicator, the patient requires a detailed examination. A low level of CPK in older people is not a violation, because muscle activity (often muscle mass) decreases with age. High creatine kinase values should cause alarm.
At puberty (from 12 to 17 years), boys have an increase in creatine kinase levels to 270 U/L, and girls have a decrease to 123 U/L. The FDC norm for adult men is 190 units/l, for women – 167 units/l. A reduced concentration of the enzyme is recorded in women during the perinatal period, and may also indicate a disruption of the thyroid gland or be a consequence of a hypodynamic lifestyle.
An increased content of CPK is a clinical sign of destruction of the membranes of neuromuscular cells of a particular organ. Interpreting the results and making a diagnosis if abnormalities are detected is the responsibility of the doctor who referred the patient for blood biochemistry.
Increased creatinine levels
If creatinine is elevated in a child’s blood, this indicates a violation of the excretory system. Excessive accumulation of substance occurs. At sharp and high levels it can have a toxic effect. Nitrogenous substances are excreted from the body in urine. They should not linger because they are decay products. If the analysis shows that creatinine is elevated in a child, regardless of age, you need to look for the causes and place of development of the pathological process. Possible options:
- renal failure;
- thyroid diseases;
- liver dysfunction;
- adrenal hyperfunction;
- consequences of severe injuries, infections;
- history of intestinal obstruction;
- dehydration of the body;
- pathology of connective tissue, etc.
Increased concentration of the substance
Why are the numbers increasing? Due to mechanical damage or under the influence of pathological factors, the integrity of myocytes containing creatine kinase isoenzymes is disrupted, and they enter the blood uncontrollably. First of all, an increased level of CPK is associated with the development of ischemic necrosis of a portion of the heart muscle (myocardial infarction).
When diagnosing an acute condition, an increase in the reference values of creatine kinase by 6–20 times is recorded. Moreover, the larger the focus of necrosis, the higher the enzyme levels in the blood rise. They reach their maximum concentration within 24 hours after the onset of circulatory failure in the myocardial layer of the heart.
Factors influencing the increase in CPK can be divided into two categories:
- pathological, associated with the development of various diseases;
- non-pathological, caused by external influences or the physiological state of the body.
In addition to myocardial infarction, the first category includes:
- heart diseases: ischemic heart disease, cardiac decompensation, stable pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis, rheumatic carditis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS), psychopathology, brain damage, including epilepsy, meningitis. encephalopathy;
- endocrinological diseases: hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, etc.;
- chronic potassium deficiency in the body (hypokalemia);
- inflammatory diseases of muscle fibers: myositis, myopathy and rhabdomyolysis as its consequence;
- genetic pathologies of the muscular system: Pompe disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy;
- spinal compression syndrome caused by disc herniation, tumor, vertebral displacement;
- malignant neoplasms of the genitourinary system.
Non-pathological causes of increased creatine kinase:
- muscle injuries: sprain, rupture of muscle fibers, muscle avulsion, deep burns;
- medical manipulations: intramuscular injections, surgical interventions with dissection of the muscle layer;
- brain damage: concussion, compression, bruise, axonal damage, intracranial hemorrhage as a consequence of a blow;
- alcohol intoxication (with a single dose of a large dose, the CPK indicator will be increased; in chronic alcoholism, the values do not go beyond the normal range);
- excessive physical activity and sports activities that exceed the body's capabilities;
- incorrect use of medications: immunosuppressants (Azathioprine, Betamethasone, Triamcinolone, Methylprednisolone, Prednisolone), fibrates (Clofibrate, Gemfibrozil, Fenofibrate), ascorbic acid preparations.
Level stabilization methods
An increase in creatine kinase is not diagnosed as an independent disease. Changes in indicators are a consequence of pathological violations of the integrity of myocardial muscle fibers, skeletal muscles and nervous tissue of the brain. Initially, it is necessary to determine the reason that influenced the deviation of the values from the norm.
A history of diseases, against which the level of CPK rises, should be treated according to the accepted therapeutic regimen, which is recommended to be supplemented with diet therapy. Some chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, autoimmune and genetic pathologies) cannot be completely cured. In this case, the doctor who deals with the underlying disease. should adjust treatment tactics taking into account the results of a biochemical blood test.
Regardless of the cause, high creatine kinase levels can be reduced by following these guidelines:
- Avoid psycho-emotional overload. Distress (constant neuropsychological tension) is one of the causes of heart and central nervous system diseases.
- Observe the work and rest schedule. To restore energy resources, the body needs good sleep lasting at least 7–8 hours.
- Rationally plan sports and other physical activity. Loads on the muscular system (including the myocardium) should be moderate, but always regular.
- Review your daily diet. It is necessary to remove harmful foods from the menu, replacing them with healthy ones.