“A disease of intellectual people”, “a royal disease” - hemorrhoids are called as many different names as possible. Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte, Boris Godunov, Russian Tsars Alexei Mikhailovich and Peter the Third suffered from this disease.
Currently, hemorrhoids have become especially common; both men and women are equally susceptible to it. Many people suffer from hemorrhoids, but are embarrassed to admit it to themselves, let alone see a doctor.
How to prevent the occurrence of this disease? How to choose effective remedies for hemorrhoids? How to treat hemorrhoids correctly? What methods of treating hemorrhoids are most effective today? We will answer all these questions in this article.
Hemorrhoids are a chronic progressive disease. To prevent the development of complications of hemorrhoids, you need to know the reasons for its occurrence. You can learn about this and much more from this video.
Hemorrhoids are a chronic progressive disease. To prevent the development of complications of hemorrhoids, you need to know the reasons for its occurrence. You can learn about this and much more.
Contraindications for carrying out
The procedure is minimally invasive with minimal tissue intervention, but there are limitations for the following conditions:
- acute inflammatory diseases
- exacerbation of chronic diseases
In addition, sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids has the following contraindications:
- inflammation of the hemorrhoid (the process should be stopped before surgery);
- thrombosis of the veins of the hemorrhoidal plexus;
- inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the rectum or in the surrounding adipose tissue (proctitis, paraproctitis);
- anal fissure
The traditional contraindication to surgery is pregnancy. Treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy and the postpartum period is carried out using conservative methods, since the enlargement of nodes is often associated with physiological changes in the body.
Modern technologies in the treatment of chronic hemorrhoids
Nechai I.A., prof., Goncharov D.Yu. Ph.D.
Hemorrhoids are one of the widespread diseases of the adult population of industrialized countries. It has been established that in people over 40 years of age, symptoms of hemorrhoids are found in 60-70% of cases.
Hemorrhoids account for about 40% of the structure of coloproctological diseases [2;5]. In recent years, minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids have become firmly established in the daily practice of coloproctologists . The advantages of these methods over surgical interventions are: the possibility of their use on an outpatient basis, without loss of ability to work; high efficiency in the initial stages of the disease; a small number of complications. The most commonly used minimally invasive methods are: - hardware ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings , - sclerotherapy, - infrared photocoagulation of hemorrhoids, - suture ligation of hemorrhoidal arteries under Doppler control, - electrocoagulation of hemorrhoids. The indication for minimally invasive surgical interventions is uncomplicated internal hemorrhoids of stages I – III. When choosing a method of treating patients with hemorrhoids, it is advisable to use a classification that subdivides chronic hemorrhoids into stage IV. I Art. Discharge of scarlet blood from the anus without prolapse of hemorrhoids. II Art. Prolapse of hemorrhoids with self-reduction into the anal canal (with or without bleeding). III Art. Periodic prolapse of hemorrhoids and the need for their manual reduction into the anal canal (with or without bleeding). IV Art. Constant prolapse of hemorrhoids along with the rectal mucosa, inability to reduce them into the anal canal using a manual aid (with or without bleeding). Contraindications include: a combination of hemorrhoids with an anal fissure, rectal fistula, inflammatory diseases of the anal canal and perineum, acute hemorrhoids.
Ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings is the most commonly used technique (32-82%), and sclerotherapy, due to the frequent development of complications (11-47%), is used less and less. Other minimally invasive treatment methods are used in less than 5% of cases [5].
Ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings . Blaisdell first developed and used a tool for applying a circular latex ligature to the pedicle of a hemorrhoid in 1954. Subsequently, other, more advanced models of ligators were developed. The use of this method is indicated for internal hemorrhoids II, sometimes III degree. Contraindications for performing ligation of hemorrhoids are: a combination of internal hemorrhoids with an anal fissure and rectal fistula; acute hemorrhoids; inflammatory diseases of the anal canal; treatment with anticoagulants. Direct ligation (clamping) of hemorrhoids occurs using a latex ring with an internal diameter of 1 mm, which has good elasticity and provides uniform, constant compression of the tissue. Rejection of the hemorrhoidal node along with the ligature occurs 5 to 9 days after the manipulation. During this period, as a rule, there is a slight discharge of scarlet blood from the anal canal, which does not require the prescription of medications, since it stops on its own. A connective tissue scar forms at the site of the rejected hemorrhoid. There are two main methods for ligating hemorrhoids. The first is based on drawing cavernous tissue into the sleeve of a mechanical ligator using a special soft clamp, after which one or two ligatures are dropped from the instrument onto the stem of the hemorrhoid. The ring should only compress the pedicle of the node, without capturing tissue located below the anorectal line. The essence of the second method is to use a vacuum ligator, which is connected to a suction device. The working part of the instrument should be pressed tightly against the hemorrhoid. After turning on the suction, negative pressure is created in the device cylinder, and the assembly is gradually drawn into the ligator coupling. When the pressure reaches 0.7 - 0.8 atmospheres, two latex rings are dropped from the instrument onto the stem of the hemorrhoid. During the first session, ligation of one or two hemorrhoids is performed. The next stage of treatment is prescribed no earlier than 15 days later. If the technique is followed correctly, the patient should not experience severe pain. After the manipulation, slight pain, a feeling of pressure, a feeling of a foreign body in the rectum, and tenesmus may appear, which may persist for 1 to 2 days. These sensations can be relieved by taking non-narcotic analgesics. Complications of ligation of hemorrhoids are: pain (noted if the manipulation is performed incorrectly), thrombosis of external hemorrhoids (occurs in 2-3% of patients), bleeding (observed in 1% of patients). The effectiveness of the technique is more than 80%.
Sclerotherapy . For the first time, sclerotherapy as a method of treating hemorrhoids was used by I.I. Karpinsky (Russia) in 1870, using iron persulfate and phenol for these purposes [5]. However, frequently developing complications after such sclerotherapy have led to the limitation of the use of this method. With the advent of new sclerosing drugs, anoscopes, and special needles, interest in this technique has increased again. In the Russian Federation, preparations from the detergent group are approved for use. These include: polidocanol-ethoxysclerol, thrombovar, fibrowein, sodium morruate, sodium tetradecyl sulfate [2]. Detergents are the most effective and safe phlebosclerosing chemicals. The mechanism of action of this group of drugs is based on the ability to cause coagulation of endothelial proteins and desquamation of the epithelium. Detergents have a local effect on vascular tissue and do not lead to systemic thrombus formation. The indication for sclerotherapy is internal hemorrhoids of stages I-II; continued bleeding from hemorrhoids. Contraindications to this method include: external hemorrhoids, paraproctitis, thrombosis of hemorrhoids, ulceration of the mucous membrane, anal fissure. The essence of the sclerotherapy technique is to introduce the drug into the thickness of the hemorrhoidal node, using a specially curved needle with a limiter. Depending on the size of the hemorrhoid, from 0.5 to 2.0 ml of detergent is administered. On the first day after the procedure, a tissue reaction to chemical coagulation occurs and pain may develop. A pronounced pain reaction may be associated with the introduction of the drug not into the thickness of the hemorrhoid, but into the muscular layer of the intestine, as well as with the introduction of a concentrated sclerosing drug in a larger volume. In this case, thrombosis and necrosis of the mucous membrane of the hemorrhoidal node may occur. In order to prevent the development of pain and inflammation, it is advisable to perform sclerosis of no more than two hemorrhoids in one session. The second stage of treatment is prescribed no earlier than after 2 weeks. During a follow-up examination on days 12-14 after the procedure, a flat, round, painless, sclerotic area of cavernous tissue with unchanged mucosa is determined in the anal canal.
Sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids is most effective for stage I hemorrhoids. As the stage of the disease increases, the number of good results decreases and the number of relapses increases. Sclerosing therapy does not allow achieving a radical cure of patients from the manifestations of hemorrhoidal disease, and good long-term treatment results are observed in only 20% of patients [5].
Infrared photocoagulation . With the beginning of the use of ultraviolet and infrared radiation in medicine, A. Neiger in 1978 proposed a technique for infrared photocoagulation of hemorrhoids. The method is distinguished by its simplicity and short exposure time.
It is used in the initial stages of internal hemorrhoids, as well as to stop hemorrhoidal bleeding. Contraindications are external hemorrhoids, thrombosis of internal hemorrhoids, combination with paraproctitis and anal fissure. The principle of operation of the photocoagulator is that the infrared light flux is focused and directed through the light guide into the cavernous tissue. The tip of the light guide transmits infrared light, which, penetrating the hemorrhoidal node, is converted into thermal energy. As a result, coagulation of submucosal structures occurs with the development of necrobiotic processes in the vascular endothelium, which leads to a decrease in blood supply to the cavernous tissue. The depth of necrosis depends on the duration of exposure. The technique is carried out as follows. A photocoagulator tube is inserted into the anal canal through an anoscope. The tip presses the mucous-submucosal layer against the muscle layer and photocoagulation is performed. This effect is carried out at 3-4 points, at the stem of the hemorrhoid, leaving gaps between the coagulation zones. In this case, a defect with a diameter of 4-5 mm is formed on the mucosa with a zone of local coagulation necrosis, the depth of which extends to no more than 5 mm. A week after photocoagulation, a scab forms at the site of exposure, which is gradually replaced by connective tissue to form a scar. It is advisable to carry out coagulation of no more than two hemorrhoids in one stage. The procedure is repeated after 2 weeks. Repeated courses of photocoagulation are possible. Observation of patients and analysis of treatment results showed that this method is most appropriate to use in stage I of chronic hemorrhoids, as well as to stop hemorrhoidal bleeding.
Cryosurgical treatment . One of the minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids is cold destruction. Cryotherapy is based on the rapid freezing of hemorrhoids with liquid nitrogen. The disadvantages of this method are: pronounced, uncontrolled swelling of the perianal tissues, a feeling of discomfort in the anal canal, pain, a weeping wound, as well as long recovery times. These manifestations are observed in more than 50% of patients [5]. The limited use of this method is also due to the difficulty of controlling the limit of spread of cryotherapy, the danger of deep tissue necrosis, and the possibility of bleeding. In this regard, cryotherapy, as a method of treating hemorrhoids, has practically not been used in recent years.
Suture ligation (disarterization of hemorrhoids) of hemorrhoidal arteries under the control of Doppler ultrasound. A relatively new minimally invasive technique, which has not yet become widespread in our service market, is suture ligation of hemorrhoidal arteries under the control of Doppler ultrasound. This method is attractive due to its ease of implementation and targeted impact on the etiological factor in the development of hemorrhoids. The method is based on the identification of hemorrhoidal arteries using Doppler ultrasound, followed by suturing and ligating them with a regular thread [11]. This method was developed and proposed by the Japanese surgeon Morigana R. (1996). For diagnostic Doppler measurements, an ultrasonic surgical device with a sound transducer and an anoscope with an ultrasound sensor built into it are used. After installing this sensor over the hemorrhoidal artery, a light and sound signal is heard on the device. Through the incisura in the anoscope, above the internal hemorrhoidal node, the distal branch of the hemorrhoidal artery is sutured and ligated with a figure-of-eight suture. The criterion for correct ligation of the artery is the disappearance of sound and light signals. In the same way, hemorrhoidal arteries are ligated around the entire circumference of the rectum. This leads to interruption of excess blood supply to internal hemorrhoids and their fixation in the anal canal. This technique is most effective for stages I-III of hemorrhoids. Contraindications are external hemorrhoids, thrombosis of hemorrhoids, inflammatory diseases of the anal canal, combination with paraproctitis and anal fissure. A small number of complications include short-term urinary retention and a feeling of discomfort in the anal canal for 2-3 days after the procedure [5;8]. However, it should be remembered that if the ligature is excessively tightened, the hemorrhoidal artery may erupt with the development of massive arterial bleeding. To prevent delayed arterial bleeding, it is advisable to stitch no more than 2 hemorrhoidal arteries in one session. Subsequent sessions are carried out 2 weeks after the first procedure. Suture ligation of hemorrhoidal arteries under Doppler ultrasound control may be a promising minimally invasive method for the treatment of hemorrhoids. However, to assess the effectiveness of this method, like other techniques, it is necessary to study the long-term results of treatment.
Electrocoagulation of hemorrhoids . One of the modern minimally invasive techniques is electrocoagulation of hemorrhoids. This method of treating patients with hemorrhoids was first proposed by A. Gain in 1939. The literature reports on coagulation of hemorrhoids using various devices such as AKM, Bicap, Ultroid, WD-II. All these devices are based on the principle of diathermic action of electric current, by conducting it through a conductor to the mucous-submucosal structures. Through thermal and chemical effects on cavernous tissue, necrosis occurs, followed by fibrosis and the formation of scar connective tissue. The manipulation technique is quite simple. Depending on the type of device used, application electrocoagulation of the mucous membrane near the stem of the hemorrhoidal node (Bicap device) is performed, similar to the photocoagulation method. When using the WD-II device, the mucous membrane of the hemorrhoidal pedicle is pierced with the two-point electrode included in the kit to a depth of 0.5 cm, and when the device is activated, electrocoagulation of the cavernous tissue gradually occurs. The current strength is adjusted individually. The disadvantage of this method when using this device is the long exposure time of the electrode in one hemorrhoidal node (10-15 minutes). During this period of treatment, both the patient in the corresponding position and the doctor performing the procedure become tired. Therefore, in one session, it is possible to coagulate only one hemorrhoid. Indications for this technique are internal hemorrhoids of stages I – II, and contraindications are acute hemorrhoids, paraproctitis, anal fissure. According to domestic and foreign researchers, treatment of hemorrhoids using electrocoagulation allows one to obtain good results only in patients with stages I–II of hemorrhoids [5]. In conclusion of this section, it should be said that the accumulated personal experience of using various minimally invasive techniques, observation of patients and analysis of long-term results of treatment of such patients has shown that these techniques are most effective in the initial stages of hemorrhoids. In stages IV and III of the disease, it is advisable to use a surgical treatment method. Minimally invasive techniques in late stages of hemorrhoids can be used to stop hemorrhoidal bleeding, which can be the first stage of further radical treatment of such patients, as well as in elderly, somatically burdened patients with palliative purposes. In our opinion, no more than 10-15% of patients diagnosed with chronic hemorrhoids can be radically cured using minimally invasive methods. However, the combination of various methods makes it possible to expand the indications for their use. Of course, the positive side of minimally invasive techniques is their ease of use, a small number of complications, low trauma, good tolerability of the procedure, and the possibility of using them on an outpatient basis, which is economically beneficial in modern conditions of insurance medicine.
Surgery . Currently in Russia, the most common method of treating hemorrhoids is hemorrhoidectomy. Most coloproctologists and surgeons in our country use a technique aimed at excision of the main collectors of cavernous tissue, proposed by Milligan E. and Morgan G. in 1937. This operation is used in two modifications. Some doctors use closed hemorrhoidectomy, when after excision of the hemorrhoid, suturing and ligation of the vascular pedicle, the mucous membrane is sutured tightly. Other coloproctologists use an open technique, without restoring the integrity of the rectal mucosa, leaving a solid mucocutaneous strip of tissue between the excised hemorrhoids. Each modification has its own advantages and disadvantages. In connection with the development of new technologies and the development of modern devices, they began to be used when performing hemorrhoidectomy, in order to reduce the number of postoperative complications and reduce the recovery time for patients after surgery. The most commonly used are the ultrasonic harmonic scalpel, the LigaSure electrothermal system, and the radio wave scalpel. In recent years, the method of circular resection of a section of the muco-submucosal layer of the distal rectum using a circular stapler (Longo method) has become widespread. Ultrasonic harmonic scalpel. This method in our country began to be used in the practice of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids relatively recently, but immediately attracted attention. The operating principle of a harmonic scalpel differs from other electrosurgical devices in that it is based on a high frequency of vibration of the working blade in the longitudinal direction. This allows for simultaneous coagulation and dissection of tissue through mechanical cutting, cavitation and temperature effects. The installation allows you to reliably coagulate vessels up to 5 mm in diameter. It is important to note that in this case, a strictly targeted effect on tissue occurs, and the depth of thermal damage to adjacent structures does not exceed 1.5 mm, which distinguishes this device from electrocoagulators. When performing hemorrhoidectomy using an ultrasonic scalpel, the first stage is dissection of the perianal skin using an electrocoagulator and separation of the external hemorrhoid from the fibers of the subcutaneous portion of the external sphincter. Then, using the coagulation and cutting mode, the external and internal hemorrhoids are excised en bloc. The vascular pedicle is treated only in coagulation mode. The remaining hemorrhoids are removed in a similar way. The wounds are not sutured, but left open. Reliable coagulation and virtually bloodless excision of hemorrhoids allows reducing the time of surgical intervention. Shallow thermal damage to tissue leads to a decrease in pain response in the postoperative period. All this has a positive effect on the incidence of dysuric disorders and reduces the time of postoperative rehabilitation of patients [6]. Hardware-controlled bipolar electrocoagulation. Designed for bipolar electrocoagulation and vascular division, the LigaSure electrothermal system delivers controlled energy to the jaws of the clamp. As a result, denaturation of collagen and elastin occurs in tissues with the formation of a zone of coagulation necrosis [3;7]. In addition, the clamp mechanically compresses the tissues, to which electric current is dosed. The strength of the treatment zone, consisting of partially denatured protein, is comparable to the strength of stitched fabric. In this regard, there is no need to isolate and additionally ligate the vascular pedicle of the hemorrhoid. The whole process takes about 5 seconds. The device allows you to coagulate vessels up to 7 mm in diameter. The depth of thermal effect on tissue, according to the characteristics, is 2 mm. The LigaSure electrothermal system allows hemorrhoidectomy to be performed almost bloodlessly, without using suture material. At the same time, the operation time is significantly reduced [3;4;7]. However, in some patients, in the immediate postoperative period, a fairly intense pain reaction develops, which may be associated with a deep thermal effect on the tissue of the anal canal. In this regard, this device, in our opinion, is most appropriate to use for hemorrhoidectomy of large hemorrhoids. Radio wave scalpel. Some researchers suggest using a radio wave scalpel for hemorrhoidectomy, which has proven itself in cosmetic surgery. The device emits a radio wave, which causes the formation of heat in the tissues, under the influence of which the breakdown of cellular structures occurs and tissue separation occurs. In this regard, the device has good dissection properties. Thermal damage to tissue is minimal, which creates optimal conditions for wound healing [1]. However, the hemostatic properties of a radio wave scalpel are low, especially in the presence of biological fluids, which does not allow the use of this device alone (without an electrocoagulator) to perform hemorrhoidectomy. Operation Longo. This operation differs from other methods of surgical treatment of patients with hemorrhoids in that the hemorrhoids are not removed. Due to circular excision of a section of the mucous membrane of the distal rectum, using a circular stapler, the hemorrhoids are proximally tightened and fixed in the anal canal. In this case, the terminal branches of the hemorrhoidal arteries are crossed, which leads to a significant decrease in the blood supply to the cavernous plexuses. All this determines the relief of clinical manifestations of hemorrhoids after this operation. The method was proposed in 1998. Italian surgeon A. Longo. Indications for this type of surgical intervention are grade III-IV hemorrhoids. with loss of nodes, but without a pronounced external component, as well as relapse of the disease. Contraindications: inflammatory diseases of the anal canal and perineum, rectal fistula, prolapse of only one hemorrhoid. The advantage of hardware hemorrhoidopexy is low trauma and short duration of the operation, mild postoperative pain syndrome, and short rehabilitation time for patients [10]. However, it should be mentioned that in some patients, intense hemorrhage was noted in the postoperative period, requiring reoperation. Despite the widespread use of this technique abroad, in Russia this operation is performed relatively rarely. Limiting factors are the high cost of the device and the lack of data on long-term treatment results. Of course, it is necessary to have information about what happens to the remaining hemorrhoids in long-term follow-up. It remains unclear whether revascularization of the remaining cavernous tissue occurs after a few years, whether the fixation of hemorrhoids in the anal canal is reliable, or whether the clinical manifestations of the disease will return in the long-term follow-up period. So, the modern possibilities of surgical treatment of patients with chronic hemorrhoids are significant. The arsenal of methods for treating this common disease is large. It is impossible to adapt any one treatment method available in the clinic to all stages of hemorrhoids. It is necessary to skillfully determine the indications for treatment and, depending on the stage of the disease, choose the most appropriate method. It should be remembered that minimally invasive treatment methods, which patients readily agree to, especially those used on an outpatient basis, are most effective in the initial stages of hemorrhoids. When the stage of the disease increases, as well as when hemorrhoids are combined with other diseases of the anal canal and pararectal tissue, surgical treatment is indicated.
REFERENCES : Blagodarny L.A., Kuzminov A.M., Abdulaev I.A. The use of radio wave surgery in the treatment of non-tumor diseases of the anal canal and rectum in elderly and senile patients. Coloproctology, 2003, No. 3 (5), pp. 13-17. Vorobyov G.I., Shelygin Yu.A., Blagodarny L.A. “Hemorrhoids” M., “Mitra-Press”, 2002, 192 p. Soboleva S.N. Comparative characteristics of surgical methods for treating hemorrhoids. Abstract of dissertation. Ph.D. St. Petersburg, 2004, Timerbulatov V.M., Mehdiev D.I., Fayazov R.R., Gallyamov A.Kh., Akhmerov R.R., Bagautdinov F.Z. Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids using the “Ligasure” electrosurgical generator. Current issues in coloproctology: Abstracts of reports of the 1st Congress of Coloproctologists of Russia with international participation. – Samara: State Enterprise “Perspective”, SamSMU, 2003, p. 134-136. Tsarkov P.V. “Hemorrhoids” Educational and methodological manual for students of the Faculty of Fundamental Medicine of Moscow State University “Moscow University Publishing House”, 2006, 50 p. Shelygin Yu.A., Blagodarny L.A., Poletov N.N., Khmylov L.M. Open hemorrhoidectomy with ultrasonic scalpel. A manual for doctors. Moscow, 2002, 24 p. Chung YC, Wu HJ Clinical experience of sutureless closed hemorrhoidectomy with LigaSure. Dis. Colon Rectum, 2003, 46:87-92 Kolbert GW, Raulf F. Evaluation of the results of haemorrhoidectomy with Longo's technique by Doppler ultrasound of the arteria rectalis superior. 8 Biennial congress European council of coloproctology. Abstract book, Prague, 2001, p.37. Kosorok P., Mlakar B., Velikonja T. Complications after rubber band ligations of internal hemorrhoids. 8 Biennial congress European council of coloproctology. Abstract book, Prague, 2001, p.28. Kirsch J., Staude G., Herold A. The Longo and Milligan-Morgan haemorrhoidectomy. A prospective comparative study of 300 patients. Chirurg., 2001, 72(2), p.180-185. Morinaga K., Hasuda K., Ireda T. A novel therapy for internal haemorrhoids: ligation of the haemorrhoidal artery with a newly designed instrument (Moricorn) in conjuction with a Doppler flowmeter. Am.J.Gastroenterol., 1995
Advantages of the method
Sclerotherapy is affordable, popular and easy to perform. In addition, the advantages of the method include:
- absence of a difficult preparatory period;
- safety;
- no need for anesthesia;
- no pain;
- the procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis, there is no need to go to the hospital;
- short rehabilitation period not associated with strict restrictions;
- can be used to treat elderly people for whom other methods are contraindicated due to the fragility of blood vessels;
- the ability to consistently get rid of all hemorrhoids;
- affordable price.
Price
| Name of service | Old price, rub. | New price until 12/31/2021 |
| Repeated appointment with a proctologist | 2000 | 1500 |
| Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids 3 nodes | 9000 | |
| Sclerosation of hemorrhoids 1 node | 3500 |
Specialists
Zinina Alina Anatolyevna
Surgeon, proctologist
Kovaleva Yulia Yurievna
Surgeon, proctologist
Muradov Shakhobiddin Narimanovich
Surgeon, ultrasound doctor, proctologist
Features of preparation for the procedure
In order to prepare for the procedure, you do not have to seriously limit yourself in anything or change your usual rhythm of life. However, the following requirements must be met:
- follow a diet that will limit the process of gas formation;
- in the morning before sclerotherapy, cancel breakfast, the procedure should take place on
- empty stomach;
- on the eve of the operation, before going to bed, you need to cleanse the intestines with an enema;
- a day before the procedure, you need to do a skin test for sensitivity to the drug;
Briefly about the main thing
Sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids is a minimally invasive non-surgical treatment method, the essence of which is chemical cauterization of the vessels feeding the node.
The procedure is indicated for the early stages of chronic internal hemorrhoids and is characterized by a short list of contraindications and a minimal risk of complications.
The procedure is performed without anesthesia and does not require hospitalization of the patient. For it to be successful, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines before the procedure and follow all the doctor’s recommendations during the recovery period.
Sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids radically eliminates the pathology, but in order to avoid relapses it will be necessary to follow the rules of prevention. Read more about the advantages and disadvantages of the method in our article.
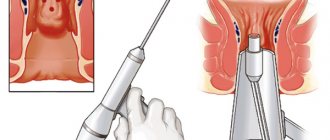
How is sclerotherapy performed?
The procedure takes place in a specially equipped room, where there is an anoscope, a proctology chair, devices for administering sclerosant and providing emergency medical care. Administration of the drug takes no more than 10 minutes, and the patient remains under medical supervision for about an hour.
Sclerosis occurs in the following order:
The patient is in a gynecological chair or on the operating table in a supine position, while pulling his legs to his chest or taking a knee-elbow position.
The doctor treats the hands, anus and intestinal lumen with a disinfectant solution.
An anoscope is inserted into the anus and is used to view the hemorrhoids.
Sclerosants are administered through a syringe. First, the internal node is sclerosed. The needle penetrates to a depth of approximately 10 millimeters. The volume of the drug is selected taking into account the size of the node.
Similar actions are performed for each hemorrhoid. In the case of stage 4 hemorrhoids, sclerosants are first injected into the bleeding area.
The needles are gradually removed after the injection is completed. This way you can avoid leakage of the drug and bleeding. The needle is removed after it has been in a calm state for several minutes.
The injection is performed at the point where the blood supply to the hemorrhoid occurs. After administration of the drug, the vessels lose their patency, thrombose, and aseptic inflammation begins. As a result:
- the size of the nodes decreases;
- the tone of the anus decreases;
- the swelling that causes hemorrhoids is eliminated.
After sclerotherapy of hemorrhoidal veins, the patient remains in a lying or sitting position for an hour. If there is no discomfort or any complications after this time, you can leave the clinic.
Diagnostic tests
The main diagnostic examination that determines the presence of indications for the sclerotherapy procedure for hemorrhoids is anoscopy.
During an endoscopic examination, the condition of the rectal mucosa is assessed, the number of nodes and their size are determined.
If there are indications for surgery, a standard examination is prescribed, which, as a rule, includes: • general laboratory blood tests, glucose level testing; • test for blood-borne infections (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis); • coagulogram; • electrocardiogram.
Attention! During a personal consultation, you must inform your doctor about cases of intolerance to medications. If you are forced to take any medications, be sure to notify your doctor.
Rehabilitation after sclerotherapy
The patient can leave the clinic on the day of the procedure. But at the same time, the doctor will explain in detail the rules of precaution and the need for attention to his own well-being.
For 2 to 3 days, patients with hypersensitivity may feel discomfort or mild pain at the injection site. Usually such sensations go away on their own.
The pain may intensify at the time of defecation - this is a short-term and expected reaction of the body. As soon as the nodes begin to decrease in size, you feel better.
There is no need for special treatment of the injection site. But in the morning and evening, as well as after each bowel movement, you need to wash yourself with cool water, a decoction of chamomile or calendula.
If you are prone to constipation, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe medications to soften the stool.
Recovery period
The duration of the recovery period after sclerotherapy depends on the number and size of the nodes treated and can range from 5 to 7 days. Therefore, during the first week, doctors recommend limiting physical activity (especially heavy lifting), visiting the bathhouse, and drinking alcohol.
It is necessary to monitor your stool, preventing constipation in a timely manner. A diet high in fiber is recommended. If the diet does not help, you need to take a mild laxative (Duphalac).
Pain after sclerotherapy is often absent or moderate and can be easily relieved with standard painkillers. If other unpleasant symptoms (fever, bleeding, weakness) appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In the vast majority of cases, the recovery period goes smoothly, and the patient returns to see the doctor 10 days after the procedure to evaluate the result of the operation.
Why you should contact the multidisciplinary clinic “Your Doctor”
Modern diagnostic equipment
Highly qualified specialists
High-tech medical care
The procedure is carried out by specialists with many years of experience, we care about our patients and are aimed at high-quality diagnosis and treatment.
Our multifunctional clinic has been operating since 2002. Over all these years of work, we have created all the necessary conditions, each patient receives professional medical services at the highest level:
Reviews from patients and recommendations from doctors
We analyzed reviews of sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids. Most patients characterize the procedure as unpleasant but painless.
One review complains of pain during the first two weeks after the intervention. This complication can occur if you violate the doctor’s dietary recommendations (spicy, salty or rough foods)
Attention! If the pain syndrome is not relieved by standard painkillers, then you should consult a doctor.
In negative reviews, patients complain about the short-term effect of the operation: after some time ( from 3 to 6 years ), the disease returns. These patients conclude that sclerotherapy is an operation that does not eliminate the causes of the disease.
From the point of view of doctors, the procedure prescribed according to indications is radical, but to prevent the occurrence of new nodes it is necessary to follow preventive measures.
Prevention of relapse
Hemorrhoids occur in people with a hereditary predisposition. If the patient has undergone surgery, this means that he has a genetically determined defect in the structure of the veins of the hemorrhoidal plexus.
To avoid relapse, you should follow simple rules:
• take care of regular bowel movements (ideally daily); • monitor your own weight; • limit the consumption of spicy and salty foods, as well as alcohol; • limit heavy lifting (more than 7 kg) and thermal procedures (bath, sauna); • promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; • avoid prolonged sitting.
To prevent recurrence of hemorrhoids, doctors have developed exercises that help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Dosed physical activity is very useful: morning exercises, industrial gymnastics, walking in the fresh air.