Pulse fluctuations have physiological and pathological causes. In the first case, an increase in heart rate can be triggered by emotional and physical stress, drinking large amounts of coffee or energy drinks, a hangover, general fatigue, and sleepless nights.
Pathological causes are more extensive - from cancer to infectious processes with a latent course. Therefore, you need to consult a doctor for diagnosis if pulse surges occur regularly and other symptoms such as dizziness, increased blood pressure, and hand tremors are present.
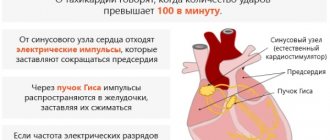
If the pulse fluctuates between 50-110 beats per minute during the day, then this is a clear confirmation of tachycardia of pathological origin, and this condition is fraught with strokes and heart attacks.
Pulse jumps: causes in adults
The most common causes of pulse surges in adults are physiological factors:
- excessive stress on the body associated with work, inadequate night rest;
- overeating, especially when fatty foods and any “heavy” foods such as kebabs and salted fish were consumed;
- psycho-emotional disorders, frequent experiences;
- excessive physical activity.
In addition, fluctuations in heart rate may be present in those people who drink energy drinks, drink large quantities of coffee and strong tea. Uneven heart rate is characteristic of hangover syndrome.
All these conditions are not dangerous and do not require any specific treatment. But if the pulse jumps from 50 to 110 beats per minute, and this happens several times during the day, there are symptoms of a clear deterioration in health (nausea, headache, trembling of the upper limbs, and so on), then you need to contact a cardiologist for diagnosis - these are signs tachycardia, which can be caused by various pathologies.
Panic attack in a dream
In the middle of the night, people with a disorder of the autonomic nervous system are often disturbed by sudden awakenings, which seem to “throw out” a person from sleep – “like a jolt.” Sudden awakenings can be accompanied by so-called “nightmarish” dreams, which are often perceived by the patient as the main cause of fear, rapid pulse, chills, sweating and other symptoms, which are actually direct symptoms of a panic attack at night.
“Nightmares” often accompany a panic attack during sleep and are direct evidence of an autonomic nervous system disorder. This phenomenon is also associated with the excessive production of adrenaline in the blood even at a time when our body is trying to tune in to rest: the harmonious unity of the chemical processes occurring in our body is disrupted, and sleep is abruptly interrupted.
Why does a teenager's pulse fluctuate?
In adolescence, the pulse fluctuates almost every day, and not only against the background of physical activity and any emotional experiences, often the causes of a rapid pulse are:
- active growth of the body - puberty is characterized by uneven growth of muscles, bones and blood vessels;
- hormonal changes in the body - too active production of hormones necessarily affects the heart rate, and the vessels are simply not able to cope with the sudden surge of blood;
- strain on the organs of vision – we are talking about long periods of time at the computer or on the phone.
If pulse fluctuations do not occur regularly, the frequency quickly normalizes, there are no chest pains or headaches, nausea, tremors (trembling) of the limbs, decrease/increase in body temperature, then parents and the teenager himself do not have to worry - this is how the period of active maturation of the body manifests itself.
Diagnosis of tachycardia
At the Cardiology Center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, the diagnosis of tachycardia and its forms is carried out by qualified specialists. During the initial visit, the doctor collects the necessary data about the patient: complaints, lifestyle, bad habits. Next, an examination is carried out: the patient’s skin color (with oxygen deprivation it looks pale), the heart rate and respiration rate are calculated. At this stage, heart murmurs may be detected, which will suggest certain causes.
Afterwards, the doctor gives a referral for the collection of laboratory tests and instrumental examination methods, such as ECG, ultrasound of the heart, monitoring, etc.
The FSCC FMBA has several heart examination programs. You can find out more about each by following the link.
A sharp jump in blood pressure and pulse: reasons
If, simultaneously with a surge in blood pressure, an increase in blood pressure occurs, this is most often a sign of tachycardia. It may be present on a daily basis or appear from time to time; in any case, consultation with a cardiologist is required, because this condition is provoked by pathologies:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- low level of hemoglobin in the blood (anemia);
- lack of potassium and magnesium in the body;
- cardiac ischemia;
- disorders of the thyroid gland.
It is interesting that the listed pathologies in the initial stage of their development are practically asymptomatic and surges in pressure/pulse are the only sign.
What causes your heart rate to fluctuate at rest?
If your heart rate fluctuates at rest, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- age of the person - in the elderly, an increase in heart rate is considered normal if it is not accompanied by pain and shortness of breath;
- ambient temperature - if it is high, then vasodilation will certainly lead to an increase in heart rate, thus the body simply cools down;
- lack of fluid in the body - banal dehydration makes the blood thick, reduces the amount of plasma, and the heart has to work with redoubled force to maintain blood circulation;
- stressful situations - even at rest a person is able to worry, remember, look for solutions to problems and an increase in heart rate against the background of stress is also possible;
- excessive physical activity - if a person is specifically involved in sports and his pulse increases at rest, then he needs to either reduce the time of training and its intensity, or increase the rest time between them;
- emotional state - even slight excitement automatically leads to an increase in heart rate.
The listed factors relate to the physiological causes of pulse fluctuations at rest; they are quite easy to correct.
But if, against the background of the main symptom, a person is bothered by headaches, a feeling of pressure in the chest (the anatomical location of the heart), periodic increases in blood pressure, and dizziness, then it is worthwhile to undergo examination by a cardiologist. It is possible that pathologies such as microinfarction, heart failure, malignant neoplasms, infectious or inflammatory processes will be diagnosed - they may occur for some time without pronounced characteristic symptoms.
Treatment of tachycardia
Depending on the form of tachycardia, various treatment methods are used. Somewhere it is necessary to eliminate external factors, such as refusal of certain physical activities. Somewhere they resort to prescribing medications, as in cases of stress (sedatives), and in serious situations - surgical intervention.
In the therapeutic departments of the Cardiology Center, you will be examined and drug therapy will be selected. If you have a form of tachycardia that can be eliminated, then you may undergo catheter ablation (exposure to the source of the arrhythmia with radiofrequency or cold).
Blood pressure and pulse jump: reasons
If the pulse periodically quickens or slows down against the background of a decrease/increase in blood pressure, then the causes of this condition may be:
- myocarditis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- infectious diseases;
- hyperthyroidism (thyroid disease);
- heart defects;
- pathological changes in the upper chamber of the heart;
- obesity 2-3 degrees;
- pulmonary or heart failure;
- benign tumors;
- cardiac ischemia.
The listed conditions are exclusively pathological in nature; they require long-term and targeted treatment.
What are the dangers of sudden increases in heart rate?
Sudden changes in heart rate are dangerous because in this state the heart works at an increased rate, the blood vessels dilate greatly and then suddenly narrow. And if this happens regularly, the result will be:
- decreased heart function;
- stretching of the walls of blood vessels, reducing their elasticity;
- lack of oxygen;
- death of heart muscle cells;
- incomplete filling of the ventricles of the heart with blood;
- increase in heart size.
In people with sharp increases in pulse rate, acute myocardial infarction is often diagnosed, which in the absence of resuscitation care often leads to death.
Symptoms of change
Symptoms of pulse surges that occur for physiological reasons will only be a rapid heartbeat and a feeling of anxiety inside. They pass quickly, and the person manages to calm down on his own and get his pulse readings in order. But the signs of a pathological jump in pulse will be:
- pain in the sternum of varying intensity;
- dizziness;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of oxygen, inability to take a deep breath;
- clouding of consciousness, up to short-term fainting;
- general severe weakness;
- trembling (tremor) of the upper and lower extremities;
- a sharp increase in body temperature.
The listed symptoms, even if only one of them is troubling, indicate a pathological origin of pulse surges.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary depending on the form of tachycardia and how severe it is (what causes it, how long it lasts). Often, tachycardia can be asymptomatic or accompanied by ordinary malaise.
Among the most common:
- cardiopalmus;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- shortness of breath;
- insomnia;
- feeling of lack of air;
- fatigue;
- decreased appetite;
- decreased performance;
- worsening mood.
Without proper treatment, complications may occur, so you should consult a doctor if these symptoms are detected.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures aimed at stabilizing the heart rate will “work” only if they are followed on a regular basis:
- Lose weight - obesity is considered a direct danger to the heart and blood vessels. You need to adjust your diet and regimen, refuse or reduce the amount of fatty, smoked, salty foods and desserts/sweets you consume. You can’t start losing weight suddenly by following some strict diets - this will only worsen the situation, and there will be no results. The best option is to seek help from a nutritionist.
- To refuse from bad habits. We are talking not only about smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, but also about drinking coffee at night, excessive consumption of drinks with caffeine - these include energy drinks.
- Give your body regular physical activity. Doctors constantly emphasize that in trained people the pulse slows down, and this indicates the strength of the entire cardiovascular system. There is no need to engage in professional sports; even regular walking and simple morning exercises will be useful.
Jumps in pulse and blood pressure may be physiological in nature, but often they are the only symptoms of the development of serious pathological conditions. If your heart rate increases regularly, you should contact a cardiologist for examination, because the lack of qualified medical care can lead to heart attacks and strokes, coronary heart disease and myocarditis.
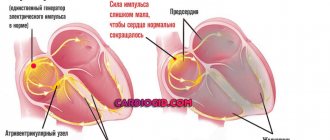
How does tachycardia manifest?
It is important to distinguish between tachycardia:
- as a normal physiological phenomenon during physical activity, anxiety, anxiety or fear. Most often, the cause is the body’s normal reaction to external stimuli: time zone change, use of tonics or medications, stress;
- as a pathological phenomenon - increased heart rate at rest or increased heart rate that is not adequate to the load. The cause may be cardiovascular disease or dysfunction of other organs.
There are many types of tachycardia. Only professionals and highly qualified specialists can determine whether you have symptoms or a predisposition to the disease, and what type of tachycardia is bothering you. By making an appointment with a doctor at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, you will undergo a full examination using new high-tech equipment, receive advice and recommendations on preventing the occurrence of symptoms.