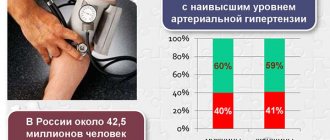
Regulation of normal blood pressure levels is carried out by the autonomic nervous system, due to the activation of compensatory mechanisms. So, the optimal blood pressure (blood pressure) indicators are 120/80 mm. rt. Art. A slight deviation from the norm can be observed as a result of physiological processes as a consequence of excessive emotional and mental stress, as well as after taking certain medications. However, a significant and constant increase in tonometer values indicates the development of pathological conditions in the body that are not amenable to regulatory mechanisms. A pressure of 150 to 110 is a sign of the initial stage of arterial hypertension, which requires urgent drug correction. What causes this disorder and what methods exist to correct it?
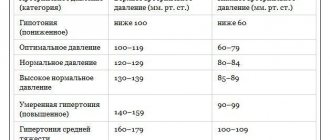
Indicators for measuring blood pressure
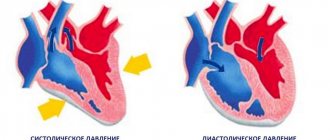
When measuring pressure, two values appear: the first is systolic pressure, the second is diastolic.
If the blood pressure monitor shows 140/60
- it means it has deviated from the norm. A person with such indicators needs to consult a specialist and undergo an immediate medical examination.
The difference between the upper and lower values is called the pulse. Its norm is 40 millimeters of mercury. This indicator is also influenced by physical activity and the psychological state of a person. However, even if this indicator changes, over time the pulse difference should return to the average value.
In an elderly person, such changes should not cause a feeling of malaise.
If blood pressure is 140 over 50
, the pulse difference is 80 mm. mercury column. This indicates that the body's cardiovascular system is not in order.
How to reduce blood pressure from 140 to 100
If you first saw the numbers 140 to 100 on a tonometer, you should think about the state of your health and rest. A number of simple steps will help reduce blood pressure from 140 to 100:
- Review your diet. Lose excess weight, limit your consumption of too salty, sweet, fatty foods.
- Increase your physical activity. Play sports, walk more, walk in nature.
- Give up bad habits. Alcohol and smoking are contraindicated in patients with hypertension.
- Get plenty of rest. Avoid overwork, normalize your sleep schedule, and do not give in to stress.
In cases where blood pressure rises regularly and does not normalize after rest, contact a medical facility. The doctor will analyze your condition in detail and prescribe effective medications that help lower blood pressure. It is not recommended to take any medications without a doctor’s prescription - incorrectly selected pills can cause a significant decrease in blood pressure and a deterioration in your well-being.
High blood pressure medications
Patients suffering from hypertension must take blood pressure medication regularly. Medicines that a doctor often prescribes for high blood pressure are:
- Bisoprolol is a drug that reduces the heart rate, which causes a decrease in the load on the myocardium.
- Carvedilol is a drug that reduces the rate and force of heart contractions and causes the arteries to dilate.
- Lozap - tablets that lower blood pressure, affecting vascular resistance, the level of aldosterone and adrenaline in the blood.
- Norvasc - tablets that lower blood pressure, increase the supply of oxygen to the myocardium, and reduce cardiac afterload.
- Noliprel is a potent medicine that prevents the occurrence of microvascular complications in people with high blood pressure.
- Ramipril is a drug that lowers blood pressure, facilitates the work of the heart and helps remove retained fluid from the body.
- Telmisartan is a tablet used to treat heart failure and hypertension due to its ability to dilate arteries.
Folk remedies for blood pressure
When wondering how to treat high blood pressure, people often overestimate the importance of pills and forget that there are folk remedies for high blood pressure. Traditional medicine will help cure blood pressure using harmless methods at home, including:
- Treatment with flax seeds, which are a source of unsaturated fatty acids. Taking 3 tablespoons of flax seeds per day as an addition to salads or in its pure form can strengthen the walls of blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
- Drinking tincture of red pine cones. One teaspoon of the distilled alcohol decoction should be drunk three times a day before meals.
- Treatment with garlic. Regular consumption of garlic or garlic infusion can reduce blood pressure by 7-8%.
- Freshly squeezed juices for hypertension. Beetroot, carrot, and cucumber juices thin the blood, cleanse blood vessels of calcium deposits, and prevent the formation of blood clots.
Risks of high blood pressure
With such blood pressure, it is recommended to immediately consult a cardiologist: the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations and make the correct diagnosis. It is important to remember that the greater the pulse difference when measuring pressure, the greater the load on the heart.
If the pulse difference remains high for a long time, this may indicate internal bleeding or heart failure.
signs of pressure 140 to 60
Symptoms of low blood pressure
Physiological (primary) or secondary hypotension should be considered as a pathology if the condition is accompanied by the development of characteristic symptoms. These are:
- morning weakness for no apparent reason;
- migraine attacks;
- pain in the heart area;
- attacks of suffocation (lack of air);
- sleep disorders (insomnia);
- lethargy, depressed state;
- periodic causeless disturbance of health;
- poor appetite;
- tachycardia (increased heart rate above 100/120 beats per minute).
The symptoms discussed may occur periodically, but can be observed constantly. This significantly worsens the patient's quality of life. For this reason, if a person feels unwell due to low blood pressure, it is necessary to consult a doctor and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment.
At normal heart rate
At the initial appointment with the doctor, the patient will have their blood pressure measured. In addition to the obtained indicators, heart rate is of diagnostic interest for a physician. Normally, a person’s pulse should fall within the range of 60–80 beats per minute.
What does blood pressure 90/60 mean against the background of the permissible myocardial contraction frequency? In this case, the doctor will advise the patient to reconsider his usual lifestyle: rest more, get better sleep, eat well and give the body feasible physical activity.
Important! Low blood pressure is dangerous if it is accompanied by a deviation in the number of heartbeats up or down.
High heart rate
The combination of low pressure and increased frequency of myocardial contractions is quite rare. An accelerated heartbeat is called tachycardia and is one of the types of arrhythmia. Blood pressure of 90/60 with a pulse of 90 beats per minute or higher may be accompanied by the following conditions:
- soreness in the temple area;
- sensation of heart contractions;
- chest pain;
- unreasonable anxiety;
- increased sweating;
- attacks of nausea.
Tachycardia in combination with hypotension often indicates diseases of the heart and blood vessels, but can also be a sign of other serious pathologies. In particular:
- infectious diseases;
- blood loss;
- low hemoglobin level;
- dehydration;
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation);
- varicose veins;
- atherosclerotic disease, etc.
If the tonometer shows blood pressure 90 over 60 and pulse 110 and such measurements are repeated frequently, then you need to consult a doctor.
No ads 2
Low heart rate
A weak pulse is typical for hypotensive patients. But if the number of heart contractions drops below 60 beats per minute, then we are talking about the development of bradycardia. The condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- attacks of morning sickness and vomiting;
- headache;
- fainting;
- increased fatigue even after a good night's rest;
- apathy, weakness;
- cold extremities.
Bradycardia due to low blood pressure is a serious danger
In young people
In healthy young people, a decrease in blood pressure can be considered an acceptable norm and does not require treatment. But if the condition is accompanied by weakness, dizziness, fatigue, then you need to consult a doctor.
In old age
People over 60 years of age should monitor their blood pressure more carefully. Reducing its level to 90/60 mm. rt. Art. should be considered a serious deviation from the age norm. As a rule, it indicates the presence of a serious illness.
During pregnancy
If a pressure of 90 to 60 is detected during pregnancy, a woman is prescribed an ultrasound examination. If the condition does not affect the development of the fetus in any way, then it does not need correction. If during the procedure symptoms of fetal developmental delay or signs of hypoxia are diagnosed, then the pregnant woman is prescribed adequate treatment for the condition.
No ads 3
High blood pressure during pregnancy
Experts point out to patients that low blood pressure during the first trimester is normal during pregnancy. The closer the moment of birth, the more often high blood pressure is observed.
If a pregnant woman has a blood pressure of 140 over 40
, you must immediately consult a doctor: high blood pressure can cause fetal hypoxia.
If the pressure is 140 over 50, what does this mean?
? It is possible that high blood pressure is a short-term phenomenon caused by a stressful situation or physical activity. The doctor will prescribe sedatives and evaluate the pregnant woman’s diet.
However, situations often occur when the pressure does not return to normal: it is necessary to begin drug therapy. In this case, only a specialist can prescribe treatment, taking into account all possible risks to the health of the unborn child.
blood pressure during pregnancy
Causes of high blood pressure
One of the common causes of high blood pressure is genetic predisposition. For example, if blood pressure levels in parents were often elevated, then children are likely to be diagnosed with blood pressure that is higher than normal. Diastolic pressure of 100 and systolic pressure of 140 may be due to reasons not related to diseases:
- age-related disorders of the functioning of the body;
- bad habits;
- lack of sleep;
- obesity;
- chronic fatigue;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress, emotional instability;
- unhealthy diet (excessively salty or fatty foods, alcohol).
Often, high blood pressure is a consequence of existing diseases in the body. These include:
- Kidney diseases: chronic urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, acute renal failure.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels: atherosclerosis, heart disease, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Intestinal diseases: irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, colitis.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland: enlarged lymph nodes, cystic formations.
Causes of isolated systolic hypertension
This disease indicates that adverse changes are occurring in the cardiovascular system that require the intervention of specialists. Timely treatment will help avoid complications.
Most often, hypertension is a short-term phenomenon, to eliminate which you just need to give up physical activity, review your diet, and give up coffee and other energy drinks.
Many people are at risk due to a sedentary lifestyle, hard work and poor diet. All these factors negatively affect health, and make themselves felt in old age.
Main reasons for development
Symptomatic hypertension is observed in chronic diseases of the kidneys, thyroid gland, blood vessels and myocardium.
The predominant increase in diastolic indicator is associated with high arterial spastic activity that occurs when the following organs are affected:
What to do if the pressure is 150 to 70
- Dysfunction of the periglomerular apparatus. Causes excess production of biologically active substances that provoke vascular spasm. As a result of the influence of vasospastic hormones, the tone of the smooth muscles of the arteries increases and the vascular lumen decreases. These pathologies include (glomerulonephritis, atherosclerosis of the renal vessels, nephropathy).
- Excessive production of thyroid hormones. The production of large amounts of thyroid-stimulating hormones provokes pronounced activity of the sympathetic nervous system. This serves as a provocateur of afferent stimulation of the vascular center in the medulla oblongata, which is expressed in the formation of arterial spasm.
- Increased circulating blood volume. It is observed when the activity of the renal tissue is impaired, when sodium and fluid retention occurs. It is registered against the background of endocrine dysfunction, manifested by fluid retention, which leads to hypervolemia.
An increase in blood pressure values against the background of cardiac and vascular pathologies is referred to as hemodynamic secondary hypertension. Its formation is caused by atherosclerotic processes in the aorta, some heart valve defects, chronic heart failure, and severe disorders of myocardial contractile activity. Atherosclerotic damage to regional vessels leads to a disorder of the heart rhythm, as a result of which the myocardium does not relax enough in the diastole phase.
Provoking factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- men over 40 years of age;
- women over 50 years of age;
- lipid and carbohydrate metabolism disorders;
- excess body weight;
- excessive consumption of sodium chloride;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- bad habits;
- low resistance to stress.
No ads 2
Kidney factor
The kidneys ensure the maintenance of normal blood pressure levels. When they are damaged, pressure levels increase, and they are also the target organ for essential hypertension. Secondary hypertension of renal origin is associated with damage to the vessels of the organ; thus, renovascular and renoparenchymal forms are distinguished.
With the renovascular form, the pressure of blood flowing into the vessels of the kidneys decreases, as a result of which mechanisms aimed at restoring blood circulation are activated, which leads to excess production of renin. This provokes an increase in vascular tone, their spasm, as a result of which the pressure level increases. In the clinical picture, the disease is manifested by an increase in the predominantly diastolic indicator, resistant to antihypertensive therapy.
Renoparenchymal hypertension is the most common type of pathology, developing as a result of chronic glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, and infection of the excretory system. In the clinical picture, high blood pressure is combined with characteristic renal symptoms such as swelling, pain in the lumbar region, and urinary disorders.
Important! A pressure of 150 to 120 may correspond to the renal form of the pathology, when the diastolic value increases significantly, and endocrine metabolic disorders provoke a proportional increase in the systolic value.
Preventing high blood pressure
In order to maintain normal blood pressure, you must:
- Maintain a daily routine.
- Avoid unhealthy foods, the consumption of which can lead to obesity and increased cholesterol levels.
- Stop drinking alcohol and tobacco products.
- Avoid stressful situations.
A healthy lifestyle is a great way to normalize blood pressure over the long term. Elderly people are recommended to undergo systematic examination by a cardiologist, as well as regularly take medications, the main task of which is to control vascular tone.
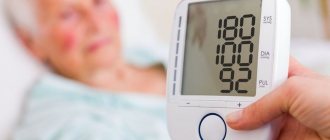
What does blood pressure 150/110 mean?
A pressure of 150 over 110 is not normal and in most cases signals the formation of the initial stage of arterial hypertension. A one-time deviation from normal values does not indicate the formation of pathology, since a temporary increase can occur as a result of excessive intake of salty foods, or an overdose of alcoholic beverages and medications. The diagnosis is established based on the systematic identification of abnormalities, when high values are recorded for 14 days, with episodes 2 to 3 times a week.
Classification of hypertension by blood pressure level
In most cases, blood pressure readings of 150/110 are considered a mild form of arterial hypertension. However, upon closer examination, the systolic indicator corresponds to the first stage of the disease, and the diastolic indicator indicates the transition of the pathology from the second to the third stage. This discrepancy between the lower value and the criteria may indicate a high peripheral resistance tone, as well as tension in the vascular walls during the period of myocardial relaxation. A violation may indicate the development of symptomatic (secondary) hypertension against the background of other organs involved in the regulation of blood pressure.
No ads 1