The subtitle of the article may seem somewhat provocative. “How to save your legs...” Unfortunately, this is the question that those who are faced with a diagnosis of “diabetic foot” have to look for answers to.
THE INSANE OF DIABETIC FOOT
I have no doubt that the name of this terrible syndrome is well known to all those suffering from diabetes. Doctors probably talked about precautions and warned about symptoms. But unfortunately, diabetes is difficult to control, and diabetic foot syndrome can take decades to develop. Slow changes do not attract attention until the development of the pathology enters the “high” stage.
A FEW NUMBERS
I don’t want to scare anyone, but I think that every person with diabetes should know these statistics. This is an excellent incentive for strictly following the rules of prevention. So
- The diagnosis of “diabetic foot” confidently ranks first in the number of amputations in non-war times.
- Diabetes mellitus greatly (up to 47 times!) increases the risk of amputation.
- After amputation, patients are at risk of amputation of the second limb within three years with a probability of up to 30%.
- The risk of repeat amputation within five years increases to 51%.
These numbers are too eloquent to be ignored.
DIABETES DESTROYS VESSELS
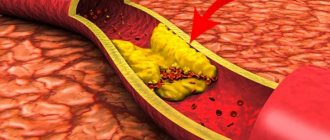
The peculiarity of human anatomy is such that surges in blood sugar have a destructive effect on the blood vessels of the lower extremities. Irreversible damage to small-diameter arteries occurs and, accordingly, circulatory impairment. The so-called ischemic form of diabetic foot occurs - due to insufficient nutrition, tissues on the legs degrade, non-healing wounds form and grow, bone tissue, nerves, joints, and tendons are destroyed. There is a growing serious risk of developing gangrene, sepsis, and amputation.
DIABETES KILLS NERVES
High blood sugar levels lead to decreased conductivity of nerve fibers located in the feet. As a result, sensitivity is lost and the risk of accidental injury increases dramatically. The patient simply does not notice the damage to the legs, and ischemia does not allow the wounds to heal. The disease is progressing.
DIABETIC FOOT: DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of diabetic foot syndrome is a complex medical task. A hardware examination of the condition of the arteries is required, the condition of the bones of the foot is determined, and sensitivity is analyzed - tactile, temperature and vibration. A bacterial analysis and, of course, a detailed blood test are required.
The vascular surgery clinic has installed the most advanced equipment to date, which allows you to quickly and accurately determine the condition of the limbs and create an adequate treatment strategy.
TREATMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT: REMEMBER ABOUT DIABETES!
I must emphasize that when treating diabetic foot, you must always remember the root cause of the disease - diabetes. Qualified observation by an endocrinologist, strict adherence to recommendations and prescriptions, as well as constant monitoring of glucose levels are required. Normalization of carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental condition for successful treatment.
Your name:
Your phone number:
Send
Description of the manifestations of “Diabetic foot”
Diabetic foot syndrome (diabetic foot or DFS) is a complex of complications of diabetes mellitus. This is a dangerous disease that develops in people with diabetes and involves the process of damage to the epidermis, dermis, bones, and nerve endings on the feet; With untimely or absent treatment, loss of a leg is possible.
According to statistics, every tenth person diagnosed with diabetes mellitus is diagnosed with diabetic foot disease; 50% of diabetics are at risk.
Diabetes mellitus implies a malfunction in the functioning of the nervous and vascular systems, which leads to disorders associated with blood supply and nervous regulation of the limbs. These violations are the cause of the disease DFS.
In the initial stages, the main symptoms of the disease are superficial ulcerative lesions on the feet; in later stages, the ulcers penetrate deeper, affecting the muscles, tendons, and bones. In the final stages, limited and then extensive gangrene forms.
The main methods of treating diabetic foot are normalization of blood sugar, local treatment of the skin and nail plates, drug therapy, and surgical measures.
Diabetic foot belongs to the category of those diseases whose treatment absolutely cannot be delayed! Gangrene, general blood poisoning, amputation, death of the patient - these are the real consequences of inaction. Therefore, you should contact specialists immediately.
Flow
When the development of diabetic foot begins, diet and control of sugar levels, proper foot care, periodic examination of the feet and timely monitoring by a doctor are extremely important. In this case, complications rarely develop. In European countries where podiatry services are developed, the development of diabetic gangrene is very rare. The number of amputations due to diabetes in Europe has decreased tenfold, but in Russia diabetic gangrene is the main cause of high amputation rates.
Causes of the disease
Impairment of normal blood circulation is the main cause of the disease. In patients with diabetes, the level of glucose in the blood is increased, which inevitably causes metabolic disturbances, which leads to damage to the blood vessels of the extremities and deterioration of blood supply to tissues. First of all, the blood supply to the distal parts of the lower extremities is disrupted. There is insufficient nutrition of the cells of the nerve endings, so irreversible changes occur - the nerve cells die, the lower limbs lose sensitivity. The feeling of pain weakens, as a result, small wounds, calluses, abrasions that appear on the feet do not cause pain, so they may not heal for a long time, grow and increase in size, and invading bacteria and viruses cause suppuration.
Thus, the main causes of DFS are impaired blood supply due to high levels of glucose in the blood (hyperglycemia) and nerve damage (neuropathy) of the lower extremities. Further development of the disease is caused by causes associated with damage to the skin of the feet:
· wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes, which can lead to the formation of calluses, corns and other skin damage;
· injuries, scratches, abrasions, insect bites and other mechanical damage to the skin;
· small cuts and wounds received during pedicure;
· ingrown nails;
· cracks on the feet;
· fungal diseases.
Classification
In world medicine, several classification options for diabetic foot syndrome (DFS) are accepted:
- according to the depth of distribution of the ulcer according to Wagner. This classification describes only irreversible changes in tissues;
- severity of the infectious process - threatened or not threatened amputation of a limb;
- the depth of the lesion and the presence of signs of infection in 12 gradations depending on the causes of occurrence.
In domestic neuropathology, three main forms of diabetic foot are distinguished:
- neuropathic - changes in peripheral nerves. The sensitivity of the foot decreases, the skin of the foot and lower leg dries out and becomes thinner, rough calluses and non-healing cracks in the interdigital space form. With this form there is a high risk of rapid development of phlegmon;
- ischemic, which occurs when blood vessels deteriorate, occurs in 5–10% of cases. In this case, small vessels of the lower extremities are damaged, the tissues do not receive enough oxygen, which leads to edema. In this case, the sensitivity of the foot is not impaired, calluses are not formed, the foot is not deformed, but a violation of the blood supply leads to the formation of blisters, which, if left untreated, progress to the stage of ulcers;
- neuroischemic, caused by diseases of the nerves and blood vessels. This form affects 25–40% of patients. The difficulty of treatment lies in the high risk of surgical intervention, which in some cases is caused by the impossibility of anesthesia due to concomitant diseases.
Each case has a fundamentally different approach to diagnosing and treating the disease.
Diabetic foot symptoms. Stages of the disease.
People with diabetes need to be as attentive and scrupulous as possible to their own health. At the first changes in your health and well-being, it is advisable to consult a specialist. Feet are a part of the body that also requires increased attention.
It is recommended to consult your doctor if the following symptoms occur:
· feeling of goosebumps in the legs
Numbness of the lower extremities, tingling
burning sensation in the legs
the appearance of cramps in the calves
hair loss in the shin area
· appearance of pigmentation on the legs or changes in color (blanching, redness, blueness)
darkening of the nail plate (bruising under the nail plate)
formation of cracks in the feet
formation of weeping eczema between the fingers (small blisters with clear liquid inside)
· injuries on the legs heal slowly or do not heal at all
· appearance of itching
formation of edema
peeling, dry skin
Symptoms of DFS may also include increased fatigue, as well as pain in the legs at night and during walking.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy - damage to sensory nerves occurs in 70% of patients with diabetes. Nerves in the legs are particularly susceptible to damage because poor diet and high sugar levels destroy the myelin sheath. In the neuropathic form, where a diabetic patient loses sensation in the legs, any microtrauma may go unnoticed until serious ulcers develop.
Signs of foot neuropathy:
- Numbness of the skin
- Tingling
- Pain or burning of the skin of the legs (some forms of neuropathy may cause pain)
Stages of SDS
In medicine, several stages of the disease are determined:
Zero or initial stage
:
· deformation of the bone structure of the foot
formation of calluses
· pale skin color
Itching may occur without visible damage to the skin
The most important task of this stage is to prevent damage, because any wound on the feet is a risk of developing an ulcer. It is necessary to ensure maximum skin care and, if possible, not to put any strain on the feet.
First stage
:
formation of ulcers and cracks on the skin of the feet
darkening of the nail plate, possible ingrown nails
The bones of the thumbs are deformed
wounds, abrasions and cuts do not heal for a long time
The lesions are superficial - bones, tendons, and muscles are not damaged.
At this stage, it is necessary to prevent the wound from becoming infected. It is important to keep the wound clean and speed up the healing process.
Second stage
:
· wounds become deeper
The ulcer begins to affect the subcutaneous tissues, muscles, tendons
When a wound becomes infected, swelling, redness, and pus appear
Damage to deep tissues and bones at the second stage is not yet diagnosed. The wound can be either infected or uninfected.
The main task at the second stage is to remove dying tissue, thereby avoiding suppuration.
Third stage
:
· damage becomes deeper, bones and joints are affected
Osteomyelitis develops (an inflammatory process that affects all bone elements)
an abscess develops (purulent inflammation)
Fourth stage
:
· the process of formation of gangrene (death of living tissue) begins
First, the area of the fingers turns black (starts from the tips), then the supporting part is affected. The limb can be saved with surgery.
Fifth stage
:
· the spread of gangrene continues along the entire foot, rising to the lower leg.
The areas with the affected tissue increase in size; the only way out at this stage is amputation of the limb.
The fifth stage of the disease is extremely dangerous and poses a threat to life.
According to statistics, the diagnosis of SDS is the most common reason for amputation. It is important for diabetics to remember that they must follow the rules for preventing diabetes, and at the first suspicion, immediately consult a doctor.
Medical examination
Patients with diabetes mellitus and signs of DFS can be examined by an endocrinologist in Sergiev Posad at the Paracelsus clinic.
The center is equipped with expert-class ultrasound equipment. Our own laboratory quickly produces accurate results on the day of testing.
Reception is conducted by highly qualified endocrinologists with 11 years of experience in the specialty. In the department of endocrinology, appointments are conducted by a doctor of medical sciences with 37 years of experience in the specialty.
Patients at high risk of developing diabetic foot should be observed not only by an endocrinologist, but also by a vascular surgeon and orthopedic traumatologist. It is important to conduct self-examination for diagnosis, the purpose of which is to early detect signs of diabetic foot: changes in skin color, dryness, swelling and pain, crooked toes, fungal infections.
At the Paracelsus clinic, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, based on the results of which the doctor will select treatment. In the clinic, you can examine arteries and veins, identify vascular damage at an early stage and determine the state of blood flow.
Competent treatment from our doctors will prevent the development of complications. The doctor will help you adjust your lifestyle and diet.
Complications of diabetic foot
DFS disease is characterized by impaired blood supply and metabolism of foot tissues, which is a serious threat to the rapid healing of wounds. Often the resulting microtraumas go unnoticed, because do not cause inconvenience or pain. Calluses, abrasions, wounds from foreign objects caught in shoes or caused by nail treatment do not heal for a long time. A long-term non-healing affected area is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria, infections and fungi. Complications of diabetic foot can be extremely sad - there is a possible risk of developing trophic ulcers, the formation of gangrene and further loss of limb. According to statistics, this happens in 20% of cases of SDS.
Main complications of DS
: skin and bone necrosis, deformation of bones and joints, ulcers, gangrene.
Infections
Any abrasions take a very long time to heal, and there is a high risk of infection.
It is unacceptable to ignore doctor's appointments! At an early stage, you need to contact a podiatrist.
Foot deformity
Damage to the nerves of the lower extremities leads to a decrease in motor activity of the muscles and their atrophy. Muscle tone becomes weak, which affects the musculoskeletal system of the limbs - the fulcrum points change, the correct distribution of weight is disrupted; Such disorders lead to the development of flat feet and changes in the ankle joint. The patient experiences changes in gait – lameness appears.
A serious complication associated with foot deformity is Charcot arthropathy.
Charcot's foot is a rare, rapidly developing, severe complication of diabetes, which is associated with the destruction of the soft tissues of the feet and joints; there is deformation of the shape of the foot and the formation of trophic ulcers in places of high pressure on the foot; full support on the leg is impossible.
Ulcers
In 20% of people suffering from diabetes, a complication such as trophic ulcers occurs, and ordinary wear and tear from shoes can cause its development. Often, it is long-term non-healing wounds that become the reason for visiting a doctor and further diagnosing diabetes mellitus.
Ulcers are mainly the result of self-medication!
It is very important to start treatment on time, because... the wound does not heal on its own, spreads deeper, and necrosis begins.
Independent and timely diagnosis of ulcers is difficult, because Symptoms do not appear until infection occurs - until swelling, unpleasant odor, irritation and itching appear.
Gangrene
Gangrene is necrosis of the tissues of a living organism. Tissue cells die and the skin turns black. To stop the spread of infection throughout the body and to save lives, a limb is amputated.
According to statistics, within five years after amputation, amputation of the second limb is performed in 50% of cases.
In rare cases and in the first stages of the disease, the only way to save a leg is to restore blood circulation in the extremities.
For people with diabetes, regardless of the stage and form of the disease, self-monitoring and strict care are extremely important! Constant monitoring of blood glucose levels, thorough daily examination and foot care will reduce the risk of dangerous complications by half!
Loss of sensation
Diabetes mellitus “clogs” small vessels, starting from capillaries (microangiopathy). Vision is the first to suffer, then other small vessels join. The foot is the organ farthest from the heart, so the blood vessels in the foot are especially susceptible to blockage. Losing blood supply and nutrition, the foot begins to lose sensitivity due to a decrease in the functioning of nerve fibers. The feet no longer react to temperature and lose sensitivity even to light touches. It becomes easy to injure your feet even while walking. With constant high sugar levels, ulcers may develop on the plantar part of the foot in areas of greatest pressure. In diabetics, tissue healing is poorer and wounds require longer treatment because the body's recovery occurs more slowly.
Diagnostics and treatment methods for diabetic foot
First of all, doctors need to study the history of the underlying disease - diabetes; In addition to examining the medical history, a survey and examination of the patient is carried out.
To determine treatment tactics, a number of studies are needed:
· detailed collection of anamnesis (information about the patient and the development of the disease): duration of the disease, presence of ulcers, previous treatment, state of vision, presence or absence of pain, period of its manifestation, etc.
· examination of the feet: color of the skin and nails, presence of flat feet, deformities of the fingers, presence of swelling, cracks, thickening of the skin, etc.; Inspection of both extremities is mandatory.
assessment of the state of blood flow using palpation of the arteries
· study of diabetic neuropathy: assessment of subjective (character of pain, tingling, burning, chilliness, decreased sensitivity) and objective (muscle strength, reflexes, etc.) symptoms. To assess the functions of the peripheral nervous system, electroneuromyography (ENMG) is performed - a modern research method that allows you to diagnose the condition of the nervous system.
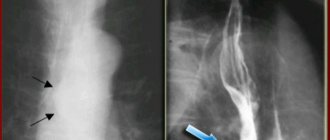
· study of macroangiopathy (changes in the arteries that develop against the background of diabetes mellitus): assessment of blood flow using ultrasound duplex scanning of blood vessels (USDS) and X-ray contrast angiography. Ultrasound scanning allows you to visualize a blood vessel, examine its condition and blood flow. Angiography is the main method for assessing vascular damage and blood flow status.
· study of the condition of bone structures: assessment of the condition of bone tissue using radiography. If necessary, examination using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is possible.
· blood test and bacteriological examination of discharge from wounds. Research is necessary to determine the severity of the inflammatory process and select effective antibacterial therapy.
Treatment methods for diabetic foot
· antibacterial therapy: bactericidal agents, antibiotics, antiseptics. The choice of drugs and duration of treatment depends on the results of a blood test and bacteriological examination of the wound contents
· surgical treatment of ulcerative defects: removal of damaged tissue
· unloading of the affected limb: use of special devices and bandages
· therapeutic measures to improve blood flow
· physiotherapeutic methods: most often carried out after surgical treatment for the purpose of rehabilitation and involve magnetic therapy, light therapy, UHF therapy, etc.
The main rules that every patient with diabetes should know are refusal to self-medicate, timely consultation with a doctor and an integrated approach. Monitoring blood counts, treatment procedures and timely contact with a specialist will help avoid disastrous consequences.
Basic rules for foot care
Diabetic feet need to be cared for daily, following simple rules of prevention:
- careful hygiene, including the interdigital space;
- treatment of keratinized areas with pumice;
- moisturizing dry skin with cream;
- Regularly changing socks. Socks and stockings must be made of natural fabric and selected exactly in size so that folds and gathers do not form and the tissues of the foot and lower leg are not compressed;
- wearing loose, comfortable shoes.
In addition, it is important to carefully trim your nails in a straight line, not to use medicinal products without a doctor’s prescription, to do daily exercises to improve blood flow, and to undergo regular medical examinations.
What not to do:
- walk barefoot even after all ulcers and other injuries have healed;
- be exposed to hypothermia;
- warm your feet by rubbing, steaming and using a heating pad;
- cover the damage with a band-aid without consulting a doctor. You should only use special dressings prescribed by your doctor.
Symptoms
Everyone diagnosed with diabetes has heard the phrase “diabetic foot.” The endocrinologist always warns that this is an insidious disease, asymptomatic, but fraught with dangerous late complications. If you do not keep your sugar level, diabetes inevitably affects the kidneys, eyes, and legs. Unfortunately, not everyone understands how serious these complications are until they are faced with them.
It is very important to know the first symptoms of diabetic foot so that you can take action right away.
At an early stage, only small changes are observed, which many do not pay attention to:
- the skin becomes dry, begins to peel, crack;
- hyperkeratosis appears (thickening, keratinization);
- corns, calluses, ingrown nails form, and nail fungus may develop;
- sensitivity decreases slightly;
- Wounds, cuts, and abrasions take a long time to heal.
In the absence of proper glycemic control and treatment at the initial stage of diabetic foot, the disease progresses rapidly.
The signs of diabetic neuropathy depend on which nerves are affected. In some patients, nerve damage does not cause symptoms.
Others get:
- numbness, feeling of chilliness;
- burning, tingling;
- pain in the feet, legs, toes, hands;
- redness of the skin of the feet;
- increased sweating of the feet;
- reduction in the volume of the lower leg muscles;
- loss of temperature sensitivity.
When large nerve fibers are damaged, there is no sensitivity to finger movements, problems with maintaining balance, and pathological changes in the joints appear.
The following symptoms indicate impaired blood flow to the lower extremities with “diabetic foot”:
- the skin becomes pale and cool to the touch;
- swelling appears;
- toes become bluish;
- hair growth on the legs decreases;
- legs get tired quickly after walking for a short time;
- I am bothered by cramps in the calf muscles.
Why do my legs hurt with diabetes?
The main reasons why legs and feet hurt and go numb in diabetes are:
Significant reduction in foot sensitivity.
For this reason, a person often receives various foot injuries, but due to reduced sensitivity he does not feel them. Also, decreased sensitivity leads to hypothermia or overheating of the legs. Patients often complain that their legs burn in diabetes mellitus when it comes to simple overheating.
Problems with blood vessels.
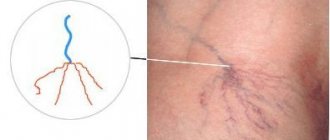
Blockage of the blood supplying vessels to the extremities leads to poor circulation; pain is associated with insufficient oxygen supply to the muscles. Spots appear on the legs in diabetes mellitus, looking like “stars”, swollen veins, the skin takes on a bluish-purple color.
Decreased muscle tone.
When pain occurs, a person tries to limit his activity and spends time mainly in a sitting or lying position. This leads to atrophy of the leg muscles and the pain becomes even more intense.
Of course, this does not mean that it is necessary to lead an active lifestyle when experiencing severe pain, but after completing a course of treatment and relieving acute pain, mobility should not be limited. It is important to wear properly fitted orthopedic shoes and use special insoles for diabetics to relieve stress on the feet.
Click on the picture below to learn more about diabetic foot insoles and order them for home delivery or mail.
Presence of calluses and ulcers.
Calluses, abrasions, corns, areas of rough skin, ulcerations, ulcers, and fungal infections are the causes of pain when walking and at rest. These symptoms require immediate treatment, which is aimed at suppressing the infection.
Excess weight and old age.
Patients over 55-60 years of age and obese people often experience swelling of the legs due to diabetes, which is accompanied by pain. The cause of pain in this case is the increased load on the legs due to excess weight and degenerative changes in bones and muscles that appear with age.
How to improve blood circulation in the legs?
To prevent diabetic foot complications, it is important to maintain good blood circulation in the extremities.
To do this, do leg exercises daily and maintain general physical activity:
- wiggle your toes throughout the day;
- make movements in the ankle joints, pull the toe away from you and towards you, rotate clockwise and counterclockwise;
- Walk more, swim, ride a bike, if there are no contraindications.
If you have a sedentary job, try to get up and walk around a little every hour. While you are sitting, keep your legs in a position that does not impede blood circulation. To do this, space them out slightly. At the same time, your feet should be completely on the floor, wiggle your toes. If possible, elevate your legs, for example by placing them on a stool. Never sit cross-legged for long periods of time. This way you compress the vessels and further reduce blood flow to the feet.
Smoking poses a major threat to your feet. If you suffer from this bad habit, be sure to quit. If you can’t quit on your own, seek professional help from a psychologist. Smoking has a bad effect on the entire cardiovascular system, reduces blood flow to the legs, and contributes to clogged arteries. Accelerates damage to small blood vessels in the feet and legs. Statistically, many people with diabetes who need amputation are smokers.
Treatment
The most effective treatment for diabetic foot is preventative. It will help protect your legs from developing severe complications. The main task is frequent monitoring and correction of glucose levels with sugar-lowering drugs or insulin. To check your blood sugar at home, it is convenient to use a glucometer.
If signs of diabetic foot appear (numbness, pain, burning, pallor, coldness), you should immediately consult a doctor. Among the drugs, medications can be prescribed to treat neuropathy, drugs that improve blood circulation, metabolic processes, and physiotherapy.
If it comes to ulcers and purulent complications, then how to treat diabetic foot depends on the degree and depth of tissue damage. To make sure that the bone is not infected, the doctor orders an x-ray. If detected early, leg ulcers can be treated. For treatment, infected tissues and dead particles are cleaned, and infected tissue is collected for a culture tank to identify the type of pathogen and determine its resistance to antibiotics.
Antibiotics are used in the form of ointments or injections. Dressings are also prescribed to keep the wound clean and dry, and medications that accelerate tissue healing and relieve pain. Until the ulcer heals, the person is advised to unload the foot, rest and a gentle regime. Do not put any weight on your sore leg, as the pressure from walking will aggravate the infection and expand the ulcer. To protect the wound surface, the doctor may prescribe special shoes and gauze bandages.
If the ulcer does not heal for a long time and there are signs of circulatory disorders, a consultation with a vascular surgeon is indicated to resolve the issue of revascularization. Restoring adequate arterial blood supply is necessary for wound healing and eliminating foci of infection. For this purpose, bypass surgery, stenting, and angioplasty are used.
Infections that cannot be treated may require amputation.