Blood pressure consists of systolic and diastolic, or, as people call it, upper and lower. Diastolic, or lower, is also called cardiac. It is formed at the moment of complete relaxation of the heart muscle. Ideally, it should be 70 mmHg. If this value exceeds 80 mm, then high cardiac pressure occurs. If it increases from excitement or during physical work, then there is no reason to worry: this is a normal phenomenon. We can talk about pathology if there is a persistent increase in lower pressure.
Causes
Elevated heart pressure is most often a concern for various diseases:
- Heart diseases. Common causes of high lower pressure are cardiovascular pathologies. It increases with deterioration of the contractile function of the left ventricle. This happens with myocardial infarction, myocarditis, myocardiosclerosis. If the return of venous blood to the heart is impaired, as a rule, only diastolic pressure increases, while systolic pressure remains normal.
- Diseases of other organs. The reasons for increased blood pressure are some kidney pathologies, thyroid disorders, obesity, spinal diseases, and hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms
With cardiac hypertension at the initial stage, symptoms are practically not expressed, so it is difficult to notice the disease with the naked eye.
The symptomatic picture with increased diastolic pressure is similar in its symptoms to ordinary fatigue. During an attack, the patient has:
- slight loss of strength;
- mild headache;
- mild dizziness;
- during critical surges - nausea and vomiting.
Most often, hypertension is detected during the diagnosis of other diseases. This is due to the fact that the symptoms of cardiac hypertension are not pronounced and the patient does not have specific complaints that would indicate the development of the disease.
Treatment
High blood pressure requires examination and treatment. Lowering blood pressure leads to an improvement in general condition and reduces the risk of developing dangerous diseases. For this purpose, antihypertensive drugs are used. People often use methods such as mustard plaster on the back of the neck and hot foot baths. You can massage the ears for a minute.
But treatment will be effective only when the causes of this condition are found. To do this, it is necessary to undergo an examination and determine why the lower pressure is high, that is, to diagnose the primary disease.
If it is not possible to find out what pathology caused the increase in pressure, we are talking about essential arterial hypertension. In this case, symptomatic treatment is carried out, that is, medications are prescribed to reduce blood pressure.
Dangers
The absence of symptoms with increased diastolic pressure makes the disease dangerous, since its complications contribute to the development of serious illnesses and fatal attacks.
When diastolic pressure increases, the heart is unable to relax, so during attacks it continuously works at an increased rhythm. These failures provoke disruption of blood flow in the heart muscle, which leads to a change in the structure of the vascular walls: loss of elasticity and impaired permeability. After some time, these pathological changes begin to progress.
Against the background of arterial hypertension, blood clots can form, which can lead to the development of myocardial infarction or stroke.
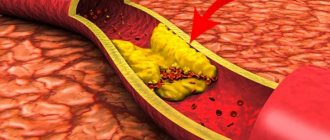
- Vessels suffer from a regular increase in diastolic pressure, which provokes the development of atherosclerosis. Disturbances are observed both in large arteries and in medium and small ones. After the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, the lumen of the blood vessels narrows, which over time threatens their blockage.
- High blood pressure is bad for your kidneys. Because of this reason, nephropathy may develop, which over time turns into renal failure.
- Cardiac hypertension leads to a disorder of the blood supply to the brain, which contributes to the development of stroke, hypertensive intracranial pressure, ischemia or cerebral edema.
- Also, increased diastolic pressure negatively affects vision: unhealthy changes occur in the small vessels of the retina, arterial walls thicken, bleeding into the retina occurs, and blindness occurs.
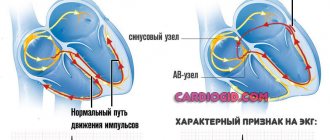
Arterial hypertension also contributes to the occurrence of other hypertensive conditions that affect the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. The heart consists of 4 chambers (atria and ventricles) that work in perfect harmony. At the moment of the systolic mode of the atria, the cardiac ventricles relax, that is, they are in a state of diastole. With an increase in diastolic pressure, the tension of the cardiac ventricles increases, their function weakens, and this contributes to the occurrence of pathologies, among which hypertrophy is pronounced.
General recommendations
To maintain normal blood pressure, you not only need to take medications, but it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle.
If you have high heart pressure, you need to get rid of bad habits
Daily regime
If you have high blood pressure, proper rest is important. Without this, treatment will not be effective. You need to set aside enough time for sleep. It’s good if you have the opportunity to sleep during the day or at least take a nap for a quarter of an hour. Instead of a quiet hour, you can take a walk in the fresh air. Rest has a beneficial effect on the entire body and overall well-being.
Nutrition
To maintain normal heart pressure, you should eat right. It is important to reduce weight and keep it in optimal condition. Nutrition should be balanced and include all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Doctors recommend sticking to a plant-based diet. You need to eat more vegetables, berries, and fruits. Be sure to include buckwheat and oatmeal porridge and wholemeal products in the menu. Meat and dairy products should be low-fat. Spicy, smoked, fatty, sweet, rich foods should be excluded from the diet, and the amount of salt should be reduced.
Physical exercise
Moderate physical activity has a good effect on the heart and blood vessels and overall well-being. If you have high blood pressure, you should exercise only after consulting a doctor who can prescribe a course of therapeutic exercises. It is useful to take walks in the evenings. If possible, you should walk to work.
“Indicators of normal pressure are different for everyone”
Doctors often hear this statement from patients themselves. Some say that they feel great with a pressure of 180 over 110, while others complain of weakness and poor health with readings of 120 over 80. In fact, the boundaries of the acceptable corridor are strictly limited: pressure that does not fall below 90/60 mm Hg is considered normal. Art. and not rising above 140/90 mmHg. Art. For some diseases, the values of the upper acceptable corridor may decrease.
The top reading is called systolic pressure. It corresponds to the moment of contraction of the heart muscle. The lower one, diastolic pressure, is measured between heartbeats as blood flows toward the heart. The systolic pressure indicator is more important, as it demonstrates the peak load on the vessels with each heartbeat.
The World Health Organization has adopted a more detailed classification. Normal pressure indicators are divided into three categories: optimal - up to 120/80, normal - up to 130/85, and high normal - no higher than 130-139 mm Hg. Art./85–89 mm Hg. Art.
Arterial hypertension is diagnosed with the following indicators:
- mild hypertension (stage I) - 140–159/90–99;
- moderate (stage II) - 160–179/100–109;
- severe (stage III) - over 180/110 mm Hg. Art.
A patient with persistently elevated blood pressure should make an appointment with a good therapist, as he needs mandatory treatment.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of hypertension is based on monitoring blood pressure at home (during exercise and at rest). You can monitor your blood pressure using automatic or manual pressure gauges.
When diagnosing hypertension in the clinic, the following is carried out:
- detailed questioning of the patient, accurate recording of all risk factors, the doctor identifies predispositions to the disease;
- clinical examination (the doctor measures the person’s pulse and blood pressure);
- daily monitoring of blood pressure (prescribed if necessary);
- conducting Holter monitoring, performing an electrocardiogram;
- determining the stability of blood pressure levels, minimum and maximum numbers, the effects of medications, etc.;
- consultations with a nephrologist, neurologist, endocrinologist;
- laboratory diagnostics (general analysis and biochemistry of blood and urine, levels of sodium and calcium, phosphates and uric acid, plasma potassium, etc.);
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, heart;
- diagnostics using bicycle ergometry, load tests (if necessary).
How and with what is high blood pressure treated?
Pharmacists offer a range of effective antihypertensive drugs that not only reduce blood pressure, but also protect the heart, blood vessels, kidneys and brain suffering from high levels. A wide variety of pharmaceuticals of different classes allows doctors to select the optimal treatment regimen for a particular patient.
Self-administration of antihypertensive medications is strictly prohibited. After all, when prescribing medications and choosing their dosage, not only blood pressure indicators and the patient’s age are taken into account, but also the data of his laboratory tests and the presence of concomitant diseases. Therapy with modern drugs is lifelong and has several significant features.
- As a rule, several drugs are prescribed at once, acting effectively in combination.
- There is still an opinion among people that they should be taken only when blood pressure levels are elevated, and that when blood pressure levels are normal, they can be skipped. This approach completely eliminates the ongoing therapy. Blood pressure medications should be taken even on days when the patient feels well. After all, the indicators normalized as a result of treatment will immediately jump when the active substances of the medicinal formulas are completely removed from the body.
Methods for diagnosing the state of the cardiovascular system
Electrocardiogram (ECG) at rest. An ECG measures the heart rate and allows you to assess the condition of the heart muscle and the overall condition of the heart. This is usually a so-called screening examination - that is, one that is recommended to be performed regularly prophylactically, even in the absence of complaints. Unfortunately, it is not very informative due to its short duration, but we can “catch” the most serious pathological changes using an ECG.
If there are complaints or suspicion of diseases, it is recommended to perform more detailed, extensive tests.
ECG with physical activity (treadmill test). This procedure involves continuous ECG recording and blood pressure monitoring under conditions of stepwise increasing dosed exercise on a treadmill until a submaximal heart rate is reached (200 minus age). This makes it possible to identify possible ischemia (oxygen starvation) of the heart muscle, which is not detectable at rest, and to register existing heart rhythm disturbances (most often they lead to sudden deaths in athletes).
The study is carried out on a specially equipped treadmill. During the treadmill test, walking is actually simulated - a familiar type of exercise for any person. This is why most researchers consider the treadmill test to be a more physiological method of stress testing. Adhesive electrodes are attached to the chest and distal extremities to record ECG. Using a computer program, the slope of the track is adjusted, due to which the patient is given a certain physical activity with a gradual further increase. Simulates walking uphill. Along with the ECG, blood pressure is measured at certain intervals.
During the treadmill test, the patient must report the occurrence of pain and other unpleasant sensations. The study ends when a certain heart rate is reached, or due to a deterioration in the patient’s well-being. After stopping the procedure, the cardiogram and blood pressure readings continue to be recorded for about 10 minutes.
The value of any examination is characterized by the sensitivity and specificity of the method, which are quite high for the load treadmill test: according to various authors, the sensitivity of the treadmill test is 80–85%, the specificity is 83–88%.
The results of the treadmill test allow you to choose the most optimal treatment method - conservative or surgical, evaluate the effectiveness of therapy, give recommendations on household and professional physical activity, and create rehabilitation and training programs.