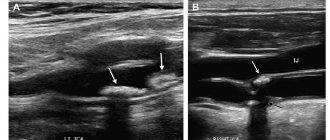
The brain is responsible for coordinating the work of the entire body. A reliable way to obtain information about the structure and functioning of the baby’s brain structures, to conduct NSG / neurosonography / of the brain with determination of the nature of blood flow in the vessels / Doppler ultrasound /
Currently, almost all children undergo NSG in the maternity hospital as a screening method.
To monitor the dynamics of the baby’s development and brain development disorders, repeated examination is recommended in order to exclude congenital or acquired abnormalities. This is especially true for children from the group of premature, low birth weight, immature for gestational age.
Dopplerography or duplex ultrasound scanning of blood vessels in children
Vascular ultrasonography is a major diagnostic field that uses duplex ultrasound scanning to see in real time how blood flows through the arteries and veins in different parts of the baby's body and organs.
Ultrasound examinations (ultrasonography) are a safe and informative method for modern diagnostics of the condition of the blood vessels of a newborn or older child. Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels can be performed without special preparation, right at the bedside. Such diagnostic studies are easily tolerated by the child.
Features of ultrasound examination of head vessels
Before starting diagnostic procedures, the diagnostician will ask the patient to remove any jewelry from the neck and take a supine position on the medical couch. Medical gel is applied to the areas of the skin located above the passage of the diagnosed vessels, which will ensure a tight fit of the ultrasound scanner sensor.
By moving it over the area under study and positioning it at different angles, the doctor receives an image on the screen that allows him to obtain the necessary information.
If necessary, functional tests can be performed, during which the diagnostician asks the patient, for example, to hold his breath.
Why is this ultrasound examination called duplex?
Duplex ultrasound scanning is used for visualization and differential diagnosis of various conditions and diseases of blood vessels. The term "duplex" means "double". The fact is that this study combines two types of ultrasound diagnostics: traditional sonography and Dopplerography. On the screen of a duplex scanning ultrasound machine, a double layer of image is simultaneously displayed in real time: visualization of the structure of the examined part of the body in shades of gray and a color Doppler image to visualize the movement of blood in the vessels. At the same time, the computer calculates the speed of blood movement, the volume of blood and the diameters of the vessels through which it flows.
How is it carried out?
It is possible to perform an ultrasound of the child’s brain only until the age when the fontanelles close. The examination is carried out through the anterior, lateral fontanelles or foramen magnum at the base of the child’s neck.
During an ultrasound, the diagnostician moves a special sensor over the baby's head. The resulting pulses are sent to the device and displayed on the monitor in the form of images. This is a comfortable procedure that can be done in the clinic, even while the child is sleeping.
You can sign up for ultrasound diagnostics by calling the reception at (495) 951 87 63 or
In our center, infants undergo comprehensive diagnostics (NSH, ultrasound of the hip joints, EEG/video-EEG monitoring) and consultations with a neurologist, orthopedist, geneticist, and ophthalmologist.
How does a Doppler ultrasound machine work?
Doppler ultrasound uses reflected sound waves to assess blood flow in different parts of your baby's body. It is important that ultrasound machines do not use any other type of radiation other than ordinary sound.
The mechanism for obtaining images during Doppler sonography is in many ways similar to the mechanisms that nature uses: with the help of ultrasonic waves, dolphins and whales search in the seas and oceans for schools of fish that they hunt. The tip of the Doppler ultrasound machine emits sound waves, like a dolphin, which are partly reflected from organs and tissues and partly absorbed by them. By analyzing the difference in reflected echo waves, the computer builds images of the structure of blood vessels. Structures that reflect sound well appear brighter on the screen, while organs and tissues that absorb most of the sound wave appear less bright than their surrounding environment. Body tissues that completely absorb sound waves (anechoic) appear black.
When the doctor sees on the screen a vessel in which he wants to evaluate the blood flow, he presses a button to turn on the Doppler function. To measure blood flow parameters, an ultrasound machine uses the Doppler effect, which consists of changing the length of the echo wave when reflected from a moving object (moving blood). In this case, the computer measures the change in the wavelength of the echo signal and calculates all the necessary parameters of the heart, blood vessels and blood movement, while building a color image of the blood movement in the vessels on the screen.
Decoding the results
The results are deciphered by the sonologist who conducts the examination. Usually he reports what he sees on the monitor to his parents and enters the findings into the conclusion. Subsequently, the conclusion must be transferred to the attending physician. It is worth noting that deciphering the results of an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck and making a diagnosis are not the same thing; the final conclusions about the child’s health are made by the attending physician. If necessary, a more in-depth study, such as an MRI, may be prescribed.
Why is duplex scanning of blood vessels performed?
Doppler ultrasound is used to evaluate blood flow through the chambers and valves of the heart. Spectral Doppler ultrasound can measure the size of the holes through which blood flows. In addition, Doppler ultrasound of the heart can accurately detect abnormal blood flow in the heart, which may indicate a hole in the heart septum or insufficiently functioning heart valves.
Vascular Dopplerography allows you to assess the quality of blood flow through central and peripheral arteries and veins. Using duplex scanning, you can identify blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques, underdeveloped vessels, anomalies in position and branching, tortuosity, damage and compression of their walls, narrowing of blood vessels (stenosis) or complete blockage of blood flow (vessel occlusion), assess changes in the course of the vessel, and abnormal tortuosity. Dopplerography helps to identify abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, determine the pathological expansion of the vessel walls (vascular aneurysm), the failure of the valves in the veins, assess the elasticity of the vascular wall and the condition of their internal surface.
Using diagnostic information obtained through duplex scanning of blood vessels, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the child that will prevent the development of possible complications associated with impaired blood flow (up to and including cardiovascular accidents: heart attacks and strokes, which, unfortunately, occur even in young patients).
Duplex ultrasound scanning can detect hemangiomas in a baby - congenital vascular lesions in newborns, most often occurring on the head and neck.
Duplex scanning is also performed before more serious diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in order to accurately determine the position, nature and probable cause of blood flow disturbance in the vessel.
Headache and cerebral hemodynamics in children
Table 3
. Indicators of cerebral hemodynamics in children with headache of unknown origin.
| Vessel | Before treatment | After treatment |
| Internal carotid artery: IR Q, l/min | 0,79+0,02* 0,45+0,01* | 0,77+0,03 0,44+0,01 |
| Vertebral artery: IR Q, l/min | 0,68+0,03 0,036+0,003 | 0,69+0,02 0,039+0,001 |
| Jugular vein: wave-like shape, ribbon-like shape Q, l/min | 85% 15% 0,21+0,02* | 71% 29% 0,25+0,01 |
Note. IR - resistance index, Q - indicator of volumetric blood flow, * - reliability with the norm (p
Discussion
The problem of headache, which in many cases is a harbinger of vascular diseases of the nervous system, must be studied from early childhood, since with untimely and insufficiently effective medical care for children, the diseases will progress and become the cause of disability in adults [3,4]. One of the main conditions for timely therapy is establishing the correct diagnosis, which is currently partly solved using Doppler ultrasound methods.
Three groups of children suffering from headaches of psychogenic and vascular origin were examined. Psychogenic headache is the most common type of headache in children. One can think of such a cause of pain when a complete examination does not reveal any pathological abnormalities [5].
In children with psychogenic headache, the average indicators of cerebral hemodynamics practically did not differ from age norms. However, individual analysis demonstrated multidirectional changes. In almost half of the patients, there was an increase in volumetric blood flow through the internal carotid artery and its decrease through the jugular vein, i.e. inflow prevailed over outflow. In the other half of the children, there was a decrease in volumetric blood flow through this artery, while the outflow through the vein remained close to normal. This pattern made it possible to speak about the presence of venous stagnation in the brain and a deficiency of cerebral blood flow. As a result of general restorative and pathogenetically based treatment, cerebral hemodynamic parameters (individual analysis) were practically normalized, which was confirmed clinically. The identified changes suggest that in psychogenic headaches there are vascular disorders associated primarily with congestion in the brain.
Migraines are attacks of repeated headaches of varying intensity and duration, usually of unilateral localization, accompanied by autonomic disorders. All children were examined during the interictal period, since the available literature does not contain data on the state of cerebral hemodynamics during this period, although knowledge of them is important for carrying out appropriate targeted therapy and determining its effectiveness.
Children with migraine were characterized by a decrease in arterial vascular tone and a decrease in volumetric blood flow through the internal carotid arteries. Changes in blood flow through the jugular veins were associated with its pronounced asymmetry and a significant increase in vascular tone. In this case, the presence of hypertonicity could be indicated by recording the ribbon-like shape of the Doppler curve, which did not depend on either the cardiac cycle or respiration, which sharply distinguished it from the wave-like shape. Signs of venous discirculation during migraine in adults were noted by A.R. Shakhnovich, V.A. Shakhnovich [6,7], finding asymmetric retrograde venous blood flow through the ophthalmic veins. In all children with migraine, after a course of treatment with vasoactive and vasotropic drugs, cerebral blood flow normalized.
Cerebrovascular diseases often develop in childhood, with disorders localized in the vertebrobasilar region. Pathological changes in the cervical spine lead to discirculation in the vertebral vessels. All this was confirmed in the examined children with vertebrogenic headaches, since a sharp disturbance of blood flow through the vertebral arteries was noted, associated with pathological disorders in the osteoligamentous apparatus of the cervical spine. In addition, venous blood flow disturbances were observed in 50% of children. Despite intensive and targeted treatment, a stable asymmetry remained in hemodynamic parameters, indirectly confirming the congenital genesis of changes in the vertebral arteries. Timely identification of the causes of vertebrogenic headaches makes it possible to begin early targeted treatment, which serves as a real measure to prevent the development of more severe disorders with age.
Patients with headache of unknown origin comprised group 3. According to the 1988 International Classification of Headaches, these pains are characterized as unclassifiable. Provoking factors for the development of this type of headache can be coughing, sneezing, a tight collar, prolonged eye strain, and weather dependence. A characteristic feature of the headache was its intensification after a long stay in a horizontal position.
All indicators of blood flow in children of the 3rd group in the arterial vessels were increased, while in the jugular veins they were decreased, and in the latter, most children had pronounced hypertonicity, i.e. Doppler ultrasound data indicated venous congestion in the brain. Clinical confirmation of this was the positive reaction of children to all tests that contribute to a delay in venous outflow and, in particular, headaches after sleep. The use of vascular drugs and physiotherapy in treatment contributed to some normalization of blood flow, which was clinically expressed by a decrease in headaches.
Thus, summing up the work done, we can talk about the informativeness of the Doppler sonography method used for headaches in children to clarify their genesis. Analysis of the data obtained during the Doppler study allows us to suggest the cause of cephalgia, which makes it possible to clarify the nature of therapy. At the same time, it turned out that Doppler blood flow indicators obtained during a dynamic study during therapy are less sensitive than clinical signs, since in almost all cases they only tended to normalize, although the clinical effect of treatment was obvious. This discrepancy may be due to the primary effect of therapy on smaller vessels, as well as the relatively short follow-up period.
Literature
- Bondarenko E.S., Freidkov V.I., Shiretrova D.Ch. Headache in children. — M.: Medicine. - 1977. - P.30.
- Bondarenko E.S., Solomatina O.G., Shiretrova D.Ch. Vegetative-vascular dystonia. — M.: Medicine. - 1989. - P.37.
- Akimov G.A. Initial manifestations of vascular diseases of the brain. — L.: Medicine. - 1988. - P.222.
- Linkov V.V., Andreev A.V. About the clinic of cerebral strokes in children // Children's neurology. 1995. - N 2. - P. 64-67.
- Badalyan L.O., Berestov A.I., Dvornikov A.V. Headaches in children and adolescents. - M.: MP "Papor". - 1991. - P.60.
- Shakhnovich A.R., Shakhnovich V.A. Diagnosis of cerebral circulatory disorders (transcranial Doppler sonography). — M.: Medicine. - 1996. - P. 365.
- Shakhnovich V.A. Impaired venous circulation of the brain according to transcranial Dopplerography // Ultrasound Doppler diagnostics of vascular diseases / Ed. Yu.M. Nikitina, A.I. Trukhanova. - M.: Vidar. - 1998. - P.240-260.
Ultrasound machine RS85
Revolutionary changes in expert diagnostics.
Impeccable image quality, lightning-fast operating speed, a new generation of visualization technologies and quantitative analysis of ultrasound scanning data.
Preparing for the study
The key to the success of this diagnostic procedure is that the child can lie quietly during the examination. Therefore, it is necessary to feed him 2 hours before the test, and immediately before the study, take him to the toilet or change his diaper. On the day of the study, older children are not recommended to drink tea, coffee, energy drinks or take other drugs that may affect vascular tone.
Only duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta requires special preparation. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. 2 days before the test, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that stimulate gas formation in the intestines: black bread, raw vegetables, legumes, carbonated drinks, fermented milk products. 3 hours before the test, it is necessary to give the child (in agreement with the pediatrician) a drug to reduce gas formation, Espumisan.
Indications for use
The procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- narrowing of the great vessels;
- pathological tortuosity of arteries;
- aneurysms;
- birth trauma, asphyxia and hypoxia;
- difficult and protracted labor;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- intracranial pressure;
- prematurity;
- obesity, diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of infections in a pregnant woman.
Among the complaints of children and external signs, after which you should immediately consult a doctor:
- headache and migraine;
- decreased memory and attention;
- poor cognitive function;
- decline in academic performance;
- fast fatiguability;
- irritability and inattention;
- attacks of chills and numbness of the limbs.
High blood pressure is not just an adult problem. If cerebral circulation is impaired, hypertension is also observed in children, so all family members need to measure blood pressure. Regarding pain, with inflammation of blood vessels, children complain of pain in the neck muscles and an unpleasant burning sensation.
Conducting research
The doctor will place the child in a comfortable position on the couch and apply an acoustic gel, warmed to body temperature, to the surface of the area being examined, which helps sound waves penetrate the body tissue. The doctor will move the tip of the ultrasound machine along the gel, which will make pulsed whistling sounds. The doctor may ask the child to lie down in different positions, take a deep breath, and hold his breath. In some cases, a cardiogram can be taken and pressure in the upper and lower extremities (at the ankle and shoulder) can be measured at the same time. The duration of the study is 30-45 minutes.
How is the research going?
Ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the head and neck for children is done in ultrasound diagnostic rooms. In order to examine the vessels of the head, the child will be asked to lie on the couch, his neck and head should be freed from clothing and jewelry. Transcranial vessels of the head during ultrasound examination are examined with a sensor in the area of the back of the head, temples and eyes, which the child must be told about in advance. In order to examine the vessels of the neck, the patient must lie on his stomach. Doppler ultrasound of head vessels
and the neck of an infant is done with the help of parents who hold the baby in such a way as to ensure his immobility.
Dopplerography and ultrasound of a child’s neck in St. Petersburg
SM-Clinic offers to perform examinations of the brain and blood vessels using the latest Italian equipment. We employ high-class specialists who have extensive experience working with children. An individual approach and a friendly atmosphere guarantee that visiting the clinic will not cause stress.
Parents, remember:
- Ultrasound can be done at any age, starting from the first days of life;
- the method allows you to diagnose the disease and prescribe timely treatment;
- With timely assistance, the risk of developing cerebral palsy is reduced significantly.
Sign up for a consultation and examination in a convenient way: by phone or through our website.