31936 May 13
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only
General PSA (general prostate specific antigen): indications for use, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and normal indicators.
When is a PSA test prescribed?
The PSA test is the most reliable in diagnosing malignant prostate tumors and other pathological changes (inflammation or infections). The main goal of the study is to identify oncology. Manipulation is recommended annually for men over fifty - this is a risk group. Early screening is indicated for patients with a burdened medical history (first-degree relatives had cancer).
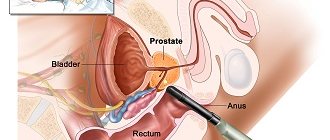
The prostate gland consists primarily of glandular tissue. It produces a secretion that is part of the seminal fluid. The prostate is sensitive to the concentration of male hormones - androgens. Abnormalities in the organ may be associated with a diet that increases cholesterol levels in the blood. Doctors also associate incorrect production of testosterone and its conversion to dihydrotestosterone.
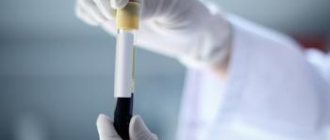
A referral for analysis may be given in case of complaints of painful and difficult urination, as well as in case of enlargement of the prostate and structural changes in its tissues. The therapist interprets the results together with the oncologist and urologist. Biomaterial—venous blood serum taken from the elbow vein at the bend.
Prostate cancer occupies one of the first places among possible oncological diseases among representatives of the stronger half of humanity. In the early stages, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms, so no one pays attention to it. Emerging complaints indicate progression of the diagnosis. In this case, we can already talk about stage 3-4 cancer. Screening will help protect yourself from a dangerous disease.
Indications
The main purpose of determining total PSA in plasma is screening for prostate cancer (PCa), including as an additional marker based on the results of a rectal examination.
The study is also carried out to determine the stage of the cancer process, the likelihood of relapse or remission, metastasis, general prognosis, which is important in the first 6-18 months of treatment, and making a decision on whether to perform a prostate biopsy. The test allows you to monitor the effectiveness of the chosen treatment regimen (chemo-, drug or radiotherapy, hormone replacement therapy, physical therapy, surgery, etc.).
In what cases is analysis prescribed:
- Suspicion of benign or malignant processes, inflammation of the prostate, structural changes in its tissues;
- Age over 50 years (mandatory screening);
- Age over 40 years (if there are close relatives with pelvic cancer);
- Prostatic hyperplasia;
- The patient complains of difficult, painful and frequent urination;
- An increase in the size, consistency and structure of the prostate gland according to rectal examination or ultrasound.
The interpretation of the analysis results is carried out by an oncologist, surgeon, urologist, and therapist.
Total PSA study
Total prostatic antigen levels are an important marker of prostate cancer. It is prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for prostate adenoma. The analysis is performed as part of a comprehensive examination together with the determination of general PSA.
In contrast, prostate biopsy is considered the “gold standard” in diagnosing cancer. Blood sampling is less painful, does not lead to complications and has a minimum of contraindications.
To examine the differences between benign prostatic hyperplasia and cancer, it is recommended to measure both total and free PSA.
Diagnostic triad of prostate cancer examinations
Is it possible to take pills before taking a blood test for biochemistry?
The role of the dog in solving clinical problems is great, but additional examinations are often required.
Dog analysis is only one type of prostate cancer diagnosis. In medicine, there is a so-called diagnostic triad, which allows an absolutely accurate diagnosis of a patient. In addition to testing for prostate-specific antigen, this includes an examination by a urologist and a TRUS.
Any formation in the prostate gland, whether benign or malignant, tends to grow. This allows the urologist to detect even the slightest compaction by palpation through the rectum when examining the patient. The method is very effective, as it can detect even a tumor about 5 mm in size. In 93% of cases, these two examinations (a blood test for the dog and an examination by a urologist) are sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis.
However, it is often necessary to resort to the last examination of the diagnostic triad. This is TRUS (transrectal echography of the prostate). The method is based on measuring the volume of the prostate and calculating the prostate density index: the value of the prostate level is divided by the volume of the gland. If the resulting density exceeds the value of 0.15, this will allow prostate cancer to be diagnosed. This type of examination is much more informative than a conventional ultrasound examination. TRUS allows the separation of benign hyperplasia and malignant formation, which guarantees the accuracy of the examination results.
All these three methods successfully complement each other and allow a man to be given an accurate and definitive diagnosis.
There are exceptions to any rule and PSA tests are no exception.
When undergoing an examination such as a dog analysis, you need to keep in mind that there are exceptions to any rule. So, for example, it happens that a man has prostate cancer, but at the same time has absolutely normal test results for his dog. In such situations, the cancer is diagnosed by a doctor who detects a lump when examined through the rectum.
There are also situations when a man has high PSA levels and the urologist discovers a lump during examination, but the man does not have cancer, but has prostate adenoma and similar diseases that are not malignant in nature.
There are also cases when the dog’s blood test is elevated, but a tumor biopsy shows the absence of malignancy. This happens when the tumor size is small. In such cases, it is necessary to repeat the biopsy after three months.
Naturally, such cases are very rare and are the exception to the rule, but they exist, and it is necessary to take this into account.
Conclusion
Despite the high mortality rate of humanity from malignant neoplasms, oncology has made great progress in the early diagnosis of tumors, especially prostate cancer. The role of the dog in solving such clinical problems is enormous. A blood test for this antigen allows you to identify dangerous prostate diseases at the very initial stages of their development. Therefore, every man needs to regularly take a blood test for his dog. Carrying out this procedure does not require a lot of time and effort, but in some cases it will allow the man to remain healthy and prolong his life.
Free PSA test
Free antigen is the active form that is not bound to blocking molecules. Some of the PSA protein that enters the blood binds to other proteins, the level of which can be measured. Prostate cancer cells (unlike soft tissue) no longer produce PSA. Therefore, in this situation, the percentage of free PSA is minimal.
Free PSA is a marker that has tissue specificity, not just cancer. The analysis is significant for screening examinations of large groups of patients. This is a safe and economical method.
To analyze total and free PSA, serum without foreign particles is used. The material can be stored at temperatures from +2 to +8° C for 24 hours. For longer storage (up to three months), the blood must be aliquoted and frozen. Secondary freezing and thawing should be avoided. After thawing, the samples are thoroughly mixed.
The biomaterial is placed in sealed tubes and sent for examination. Coagulation factors are first removed from the blood taken. Enzyme-labeled antibodies are then injected into the serum. They interact with free PSA and form a specific complex. The second step is the addition of a chemiluminescent substrate. A non-thermal glow is released, the intensity of which is recorded. The entire study takes a maximum of a few hours.
Decoding and what is normal
Without exception, all men who have reached the age of 40-45 are concerned with the question of what PSA level is normal for prostate adenoma, how to distinguish the disease from the normal state of the prostate? Assessing the normal level of tumor markers in the blood should be carried out comprehensively. The PSA level depends on the age of the man and for certain age categories there are different standards, above which the condition is considered a pathology.
Dog norms for prostate adenoma and other diseases and gland conditions are assessed differently for men before and after 40 years of age. This means that an increase in PSA in the blood is normal after forty years. This fact complicates the diagnosis of prostate pathologies when the results are slightly exceeded. High PSA requires additional diagnostics using instrumental methods.
PSA standards:
- For men under 40 years of age, the antigen level in the blood is less than 2.5 ng/ml.
- In men who have reached the age of 45, the marker norm is 4.0 ng/ml.
Based on these data, the borderline PSA level, which makes it possible to distinguish between normal and pathological conditions, is considered to be 4.0 ng/ml.
A particularly important criterion when assessing the level of antigen in a man’s blood is the rate of increase over time. These data make it possible to differentiate malignant and benign processes in the prostate gland.
Normal PSA readings in a man over 45 years of age should not increase by more than 0.75 ng/ml over the course of a year. If the values for prostate adenoma, prostatitis, or in the absence of prostate pathology increase annually by more than 0.75 ng/ml, this fact indicates the presence of prerequisites for cancerous degeneration of the epithelial tissue of the prostate gland.
If the analysis value shows an increase, a biopsy is required.
Elevated PSA in prostate adenoma, prostatitis, tumor and other processes, as well as in a healthy gland, can be distorted in the presence of the following factors:
- sexual intercourse with ejaculation (or masturbation) on the eve of the study;
- diagnostic studies performed in the area of the rectum or urethra on the eve of the test.
High tumor marker values are interpreted as follows:
- PSA results for prostate adenoma exceeding 50 ng/ml indicate prostate cancer with penetration of cancer cells into regional lymph nodes, surrounding tissues and organs with 80% certainty.
- A PSA level in prostate adenoma exceeding 100 ng/ml indicates the presence of distant metastases of prostate cancer.
- If the value is 1000 ng/ml or more, then these figures indicate stage 3-4 cancer.
- A value of more than 30 ng/ml almost always means that the man being examined has an area of malignancy in the prostate gland.
According to various authors, a PSA level in the blood from 10 to 30 ng/ml with an 80% probability indicates the presence of a malignant tumor of the organ.
The greatest diagnostic difficulties are presented by cases when the PSA value for prostate adenoma is from 4 to 10 ng/ml. In such situations, a histological examination of the biopsy material is performed. Long-term studies show that with prostate adenoma, the PSA value ranges from 10-14 ng/ml; sometimes values up to 16 ng/ml are found with prostate hyperplasia.
If PSA after removal of prostate adenoma or cancer within 3 months does not decrease by more than 50% of the initial level, treatment is considered ineffective.
When determining the free PSA fraction in blood serum, the following features are taken into account:
- if, if prostate pathology is suspected, the level of free PSA is more than 10%, repeat studies are performed after six months;
- if the concentration of the free fraction is less than 10%, rectal ultrasound and biopsy are performed.
After removal of the prostate gland for cancer, a PSA test is the only and most accurate method for diagnosing recurrence. If the organ is completely removed, the prostate tumor marker approaches zero in its values. Its gradual growth indicates the return of the disease.
For prostate adenoma, partial removal of the gland or complete excision is performed, depending on the severity of the clinic. With incomplete removal, in particular after TURP of the prostate, PSA production continues, but growth dynamics are also determined throughout later life.
Preparing for analysis
The procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, but is not tied to a specific time of day. A PSA test can be taken in both public and private clinics. The reliability of the result largely depends on the patient’s preparation. The day before the procedure is necessary.
- Avoid everything fried, salted and smoked. Such food provokes the active production of substances similar to tumor markers.
- Eliminate physical and emotional stress. A stressful situation can radically change the functioning of the enzymatic system. You can't ride a bicycle.
- Do not smoke at least one hour before blood collection. Don't drink alcohol for at least a day.
- Medication intake is limited for two days. If this is not possible, be sure to notify the doctor about the names of the drugs.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for two days before the test.
- It is important that before the procedure at least 10 days have passed since the last prostate massage. After prostate surgery, PSA is taken no earlier than six months later.
In the referral for analysis, if necessary, indicate the presence of a confirmed diagnosis of prostate cancer, as well as information about previously performed medical procedures.
The study is carried out in a complete ELISA laboratory, which has a shaker-incubator, a washing device and a microplate photometer. Kits for PSA determination are produced by a number of Russian and foreign manufacturers. At the same time, domestic devices are not inferior to imported analogues in terms of accuracy. In terms of cost of analysis, they are many times more economical.
Volgograd Regional Uronephrology Center
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test
In order for the PSA test to be reliable, a number of rules must be followed before taking the test:
- Tell your doctor if you are taking finasteride (Proscar, Penester, Finast) or dutasteride (Avodart), which lower PSA levels;
- A PSA test must be carried out before DRE and TRUS (transrectal ultrasound), or catheterization of the bladder if these manipulations were carried out for medical reasons, a PSA test can be carried out no earlier than 2 weeks;
- 4-5 days before the examination, the following are undesirable: sexual intercourse, drinking alcohol;
- Examinations should not be carried out against the background of acute inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
Blood analysis
Preparing for the blood donation procedure
- A number of tests are done on an empty stomach. For example, biochemical (glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, etc.) and serological tests (syphilis, hepatitis B), hormones (TSH, parathyroid hormone), etc. “Fasting” is when at least 8 hours pass between the last meal and taking blood (preferably at least 12 hours). Juice, tea, coffee, especially with sugar, are also food, so you will have to be patient. You can drink water.
- Strictly on an empty stomach (after a 12-hour fast) you should donate blood to determine lipid profile parameters: cholesterol, HDL, LDL, triglycerides.
- If you have to take a general blood test, your last meal should be no later than 1 hour before donating blood. Breakfast may consist of unsweetened tea, unsweetened porridge without butter and milk, and an apple.
- It is advisable to exclude fatty, fried and alcohol from the diet 1 - 2 days before the examination. If there was a feast the day before, reschedule the laboratory test for 1-2 days. Avoid smoking an hour before blood collection.
- The content of many blood tests is subject to daily fluctuations, so for some studies blood should be taken strictly at a certain time of day. So, blood tests for some hormones (TSH and parathyroid hormone), as well as for iron, are given only before 10 am.
- When donating venous blood, it is necessary to exclude factors that influence the research results: physical stress (running, climbing stairs), emotional arousal. Therefore, before the procedure you should rest for 10-15 minutes in the waiting room and calm down.
- Blood is taken for analysis before starting to take medications (for example, antibacterial and chemotherapy) or no earlier than 10 to 14 days after their discontinuation. The exception is when they want to study the concentration of drugs in the blood (for example, valproic acid, anticonvulsants). If you are taking medications, be sure to tell your doctor about this.
- Blood should not be donated after X-rays, rectal examinations, or physical therapy procedures.
- During hormonal studies in women of reproductive age (from approximately 12 to 13 years of age and before the onset of menopause), the results are influenced by physiological factors associated with the stage of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, when preparing for examination for the hormones FSH, LH, prolactin, estriol, estradiol, progesterone, the phase of the cycle should be indicated. When conducting a test for sex hormones, strictly adhere to the recommendations of your doctor about the day of the menstrual cycle on which you need to donate blood.
- When performing tests for the presence of infections, it should be taken into account that depending on the period of infection and the state of the immune system, any patient may have a negative result. But, nevertheless, a negative result does not completely exclude infection. In doubtful cases, re-analysis is recommended.
- Different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement. To ensure that the assessment of your results is correct and the results are acceptable, do the tests in the same laboratory, at the same time. Comparison of such studies will be more correct.
Analysis of urine. General urine analysis
- On the eve of the test, it is recommended not to eat vegetables and fruits that can change the color of urine (beets, carrots, etc.), and not to take diuretics.
- Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform a thorough hygienic toilet of the genitals.
- Women are not recommended to take a urine test during menstruation.
- Collect your morning urine in a container. To properly conduct the study, during the first morning urination, release a small amount of urine (the first 1 - 2 seconds) into the toilet, and then, without interrupting urination, place a urine collection container into which to collect approximately 50-100 ml of urine. Close the container tightly with the screw cap.
- A specialized plastic container is the optimal means of collecting and transporting urine for laboratory research. Ask at pharmacies. The container is a wide-neck graduated translucent glass with a capacity of 125 ml with a hermetically screw-on lid. The container is sterile, does not require pre-treatment and is completely ready for use.
X-ray examination and magnetic resonance imaging
Preparation for the procedure:
On the day of the study, you should limit yourself to a light breakfast. And if you suffer from constipation, then the night before it makes sense to take a mild laxative (regulax, bisacodyl, senade). The patient must inform the medical staff about past illnesses, operations on the chest organs, and the presence of foreign bodies in the area of study.
General rules for cleansing the digestive tract before a diagnostic test
Goal: to free the digestive system from contents and gases as much as possible.
Indications: preparation for examination: sigmoidoscopy, irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, pyelography.
Contraindications:
- Intestinal bleeding
- Anal fissures
- Intolerance to radiopaque (iodine) drugs
Irrigoscopy (X-ray examination of the colon)
Purpose of the study: diagnosis of diseases of the large intestine: determination of the shape, position, condition of the mucous membrane, tone and peristalsis of the sections of the large intestine.
Preparation for the procedure: exclude gas-forming foods from the diet (vegetables, fruits, dairy, yeast products, black bread, fruit juices) 2-3 days before the study. Take 30-60 ml of castor oil at 12-13 noon the day before the test. give 2 cleansing enemas - the evening before the study and in the morning, with an interval of 1 hour.
Performing the procedure:
1. Introduce into the intestines through the anus using an enema a suspension of barium sulfate (36 -37 ° C) up to 1.5 liters, prepared in the X-ray room. 2. A series of photographs is taken.
Intravenous urography (x-ray examination of the kidneys and urinary tract)
Purpose: diagnosis of kidney and urinary tract diseases
Contraindications to the study: pregnancy (X-rays can negatively affect the development of the fetus), X-ray examination with a barium suspension within the last four days, the patient’s inability to remain still for even a short period of time, obesity (images with excess body weight are uninformative and unclear) .
Preparation for the procedure:
Exclude gas-forming foods (vegetables, fruits, dairy, yeast products, black bread, fruit juices) from the diet for 3 days before the test. For flatulence, take activated charcoal as prescribed by your doctor. Avoid eating 18-20 hours before the test. Ensure that you take a laxative as prescribed by your doctor the day before lunch, and limit fluid intake from the afternoon before the test day. Give a cleansing enema in the evening at about 10 pm and in the morning 1.5-2 hours before the test. Do not eat, take medications, smoke, do injections or other procedures in the morning before the test. Empty your bladder immediately before the test.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI examinations generally do not require any special preparation. However, there are cases when you need to prepare for an MRI in advance:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity is one of the most accurate, informative and safe diagnostic methods. It is based on the use of high radio frequency pulses and a magnetic field. This method does not use harmful ionizing radiation. MRI can successfully replace much more painful, complex and time-consuming procedures.
Abdominal organs that can be diagnosed by MRI include:
- liver,
- pancreas,
- kidneys and adrenal glands,
- gallbladder, bile ducts of the liver,
- spleen,
- organs of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach, large and small intestines),
- soft tissues of the peritoneum, retroperitoneal space, abdomen, lymph nodes, blood vessels of a given anatomical region.
Preparing for an MRI of the abdominal cavity:
- During the day, you must avoid foods that increase gas formation (carbonated drinks, fermented milk products, brown bread, fruits, vegetables);
- when performing MRI of the spleen, liver, pancreas, a low-carbohydrate diet is sometimes recommended 2-3 days before the procedure; on the day of diagnosis, it is advisable to eat light food and avoid coffee and tea;
- at least 6-8 hours should pass after the last meal;
- you should refrain from drinking for 4-6 hours before the examination;
- in case of increased gas formation, it is recommended to take a tablet of Espumisan or activated carbon;
- 30-40 minutes before the procedure, it is advisable to take an antispasmodic tablet;
Preparing for an MRI of the brain
Special preparation for an MRI is only necessary in some cases. For the rest, it’s enough to keep a few aspects in mind:
- When going for an MRI, you should not wear clothes with metal fittings (zippers, rivets, etc.). Otherwise, you will have to change into a hospital gown;
- During an MRI examination, you will have to do without watches, glasses, jewelry, or piercings. Also, on the day of the examination, it is better not to use cosmetics, because some cosmetics contain metal;
- It is in the patient’s interests not to bring electrical appliances and plastic cards into the room with the tomograph - they can be damaged by the magnetic field.
- The doctor must be told about the presence of metal or electronic objects in the body (implants, prostheses, pins, etc.). In addition to the fact that they can malfunction and distort the results of the study, these items can also cause injury.
- You should also notify your doctor if you have tattoos, as some inks contain metal and will cause irritation on an MRI. Sometimes patients are examined by nurses using a hand-held metal detector.
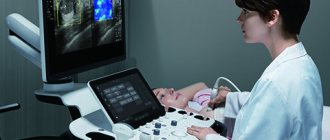
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Necessary conditions include:
- preliminary adherence to diet and water load;
- correctly follow the regimen of prescribing different studies on the same day, aimed at identifying the pathology of the abdominal organs;
- The attending physician must know about the medications that the patient constantly takes, about his bad habits, and correlate these data.
What factors can lead to distortion of the picture obtained during ultrasound examination.
- Bad habits or preliminary endoscopic examination can lead to a reflex spasm of intestinal smooth muscles.
- Excessive gas formation.
- If an X-ray contrast agent was previously injected, its undetected residues may give false information.
- Ultrasound waves penetrate less well (to a shallower depth) in overweight individuals, since they have an overly pronounced layer of subcutaneous fat.
- High physical activity of the patient (young children, excitable patients).
- The presence of scars or extensive skin damage at the sites where the sensor is installed.
Diet
The minimum period for which a diet is prescribed in order to prepare for the examination of the abdominal organs is 3 days. If you can start a slag-free diet earlier, this will only improve the result and make the work of the diagnostician easier.
The goal of nutrition is to reduce gas formation. These are priority measures; in second place is reducing the amount of toxins, normalizing peristalsis and cleansing the intestines with the help of medical means.
Products not recommended for consumption before an ultrasound:
- any legumes;
- all carbonated drinks;
- black breads;
- dairy products;
- fresh baked goods, confectionery;
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- fatty varieties of meat and fish products;
- alcoholic drinks;
- strong drinks such as tea and coffee.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed only on an empty stomach, so the last meal before the morning examination should be the evening before. If the procedure is scheduled in the afternoon, a light breakfast of approved dishes and products is allowed.
Dietary food may consist of:
- boiled lean meat (beef, veal, quail, chicken);
- lean fish. It is allowed to bake, boil, steam;
- hard-boiled chicken eggs. You can have one egg a day;
- from cereals: pearl barley, oatmeal and buckwheat; in the form of porridges;
- hard cheeses, not fatty.
In addition to the list of products, the patient is given recommendations to normalize his food intake: fractionally, in small portions approximately every 3 hours. Food should not be washed down immediately, so as not to disrupt its digestion and not contribute to the formation of toxins and gases. As for drinks, the diet allows sweet, weak tea and still water, which is drunk an hour before a meal or half an hour after a meal. The patient maintains a drinking regime - at least 1.5 liters of water per day. Other drinks (tea) are not included in this volume.
Preparation for ultrasound of children of different ages differs.
- For babies under one year old, it is enough to skip one feeding before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, this is approximately 3 hours before the examination. Drinking is prohibited one hour before the examination.
- Children from one to three years old can endure a four-hour fast and stop drinking an hour before the ultrasound.
- Children over 3 years of age fast for at least 6 to 8 hours before an abdominal ultrasound. Stop drinking liquids an hour before visiting the ultrasound room.
Using bowel preparation medications.
- Preparation is impossible without the use of medications that relieve symptoms of flatulence. The most commonly used drug that can be used by adults and children is Espumisan. In pediatric practice, “Bobotik”, “Infacol”, “Kuplaton” are allowed. Dosages according to age, course of administration - 3 days before the start of the study.
- If drugs containing simethicone (listed above) do not provide a full effect, or there are contraindications to them, it is advisable to use sorbents. This is “Smecta”, activated carbon, “white coal”. These medications need to be taken the night before and again 3 hours before the test. Activated carbon can only be taken by adults.
- To ensure that food components are completely digested and do not cause a fermentation process with the formation of gases, preparation can be supplemented by the administration of enzyme preparations such as Festal and Mezima, but only for adults, if there is no history of pancreatitis.
Use of Espumisan
With the help of drugs of this kind, you can simply and independently prepare for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. The drug is a surfactant, due to which gas bubbles in the intestines are destroyed and converted into water and free gas, which is easily excreted on its own or absorbed.
The drug is taken before the ultrasound, 2 capsules three times a day, and in the morning of the appointed day, 2 capsules once.
Purgation
This is a necessary component in order to qualitatively prepare for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Colon cleansing is carried out on the eve of the study day between 16-18 pm.
Preparation involves an enema, which is done using an Esmarch mug, the volume of water is 1–1.5 liters. The water should not be warm, as this promotes the absorption of toxins from the intestines. It is optimal to use cool, unboiled water. There is an alternative to a cleansing enema - these are laxatives.
- Senade. Take 1 tablet before bedtime. It is not advisable to increase the dose, as this may cause increased gas formation.
- Fortrans. Sold in bags for a weight of 20 kg, only for persons over 14 years of age. On average, you will need from 3 to 4 sachets, which should be dissolved in one liter of water and drunk within 3 hours. Preferred time is from 16 to 19 pm.
- Microclysters. These are Microlax and Norgalax.
Preparation may not be possible with some drugs. There are medications based on the use of lactulose. They are also aimed at ensuring easy bowel movements, but despite this, they cannot be taken for preparation, as they cause increased gas formation.
Nuances before ultrasound:
- Avoid smoking 2 hours before the procedure;
- do not eat candy or chew chewing gum;
- People suffering from diabetes should not starve! To do this, you should agree in advance with the doctor conducting or prescribing the study so that he reschedules the procedure for the morning.
- If you have had an x-ray examination using barium or other x-ray contrast agents in the last 2 days, warn the diagnostician about this before the examination.
- It is advisable to discontinue antispasmodic drugs if you are constantly taking them, after consulting with your doctor. These include: Papaverine, No-shpa, Spazmalgon, Papazol, Dibazol.
The material was prepared by the Deputy Chief Physician for Medical Affairs, Ivan Nikolaevich Dymkov.
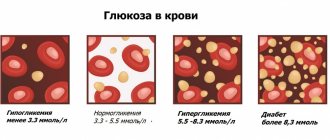
PSA norm
Standard values have been developed for tumor markers. However, they are for general information purposes only. Independent interpretation of the obtained laboratory data is not allowed. This can lead to worsening of the condition (even death).
| Patient age | Free PSA norm | Norm of bound PSA |
| 20-30 | Up to 0.4 | Up to 0.4 |
| 30-40 | Up to 0.4 | Up to 0.4 |
| 40-50 | 0,5-1,5 | 2,5-3 |
| 50-60 | 0,7-2,1 | 3,5-4 |
| 60-70 | 1,1-3,2 | 4,5-5,0 |
| Over 70 | 0,7-3,4 | 6,5-7,0 |
Standards may vary depending on the reagents and equipment used in each particular laboratory. A reduced level of a specific antigen indicates a minimal level of risk of malignant neoplasms. In overweight men, PSA levels may be lowered due to a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the plasma due to an increase in its total volume.
If the prostate biopsy does not reveal cancer and PSA continues to be high, a repeat biopsy will be required. As a rule, no earlier than after 3 months. If a patient is receiving hormonal treatment for metastatic cancer, follow-up tests are required once every 3 months.
Based on the test results, the dynamics of the development of the disease is assessed, so PSA is determined several times and must be combined with other examination methods.
PSA analysis as a tumor marker and its disadvantages
Controversial issues
The thought of diagnosing prostate cancer through a blood test was unimaginable until recently. The discovery of PSA was big news, giving doctors and patients hope that early, non-invasive screening and diagnosis could be possible. ()
However, the discovery of this antigen was controversial from the very beginning. Many scientists have studied PSA independently since the 1960s, finding it in both the prostate and semen, and they have all given it different names. Some even considered semen antigen to be a significant forensic marker for identifying rape victims. ()
A number of scientists have come to understand the potential of PSA for prostate cancer screening. However, only one scientist received fame for his discovery, while the others were unfairly forgotten. ()
The controversy doesn't end there. Prostate specific antigen has quickly become the most widely used marker in the diagnosis and follow-up of any type of prostate cancer. But in fact, PSA does not have the qualities of an ideal tumor marker. ()
When should you get your PSA level checked?
Until recently, professional medical organizations recommended annual screening for this antigen in all men as soon as they turned 40 years old. Some have advocated for even earlier screening for high-risk groups such as African Americans or men with a family history of prostate cancer. ()
However, recent findings have changed these guidelines. Studies have shown that some men with normal PSA levels (below 4.0 ng/mL) have prostate cancer, while many men with higher PSA levels do not have prostate cancer. ()
New research suggests that widespread use of such tests has led to overdiagnosis of prostate cancer in the United States. In turn, many medical professional associations have revised their guidelines, eliminating routine screening in most cases - and especially in men under 55 or over 70 years of age. (, 13)
The overall usefulness of PSA testing for detecting prostate cancer in men aged 55 to 69 years is low. Ultimately, men in this age group must decide whether they want to have this test or not, even if they are in a high-risk group. ()
Before you decide whether you want to undergo testing, you should be fully aware of its limitations in order to make the best decision.
NEW BIOMARKERS FOR PROSTATE CANCER, EXCEPT PSA ANALYSIS, SHOULD HELP IN THE TREATMENT OF PROSTATE CANCER AND BE USED IN CASES OF HIGH RISK DISEASE WITH LOW PSA LEVELS(I)
Limitations of the analysis
You may not benefit from knowing you have prostate cancer
The test can help detect small tumors that may be relatively harmless. It can also produce false-positive results, leading to overdiagnosis and unnecessary treatment. ()
Even if you have prostate cancer, you are probably not at high risk of dying from it. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and do not cause serious symptoms. About a third of older men die from other causes without even knowing they have prostate cancer. ()
You may receive treatment you do not need and experience side effects
Overtreatment and the psychological stress of a cancer diagnosis are likely to be more harmful to your health than most forms of prostate cancer. ()
Common side effects of prostate cancer treatment include erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, and bowel problems. ()
The harms of screening in men over 70 are even greater, as older people are more likely to receive false-positive results, suffer complications from biopsies, and experience more serious side effects from treatment. ()
You may get a false negative result
An antigen test can also give a false negative result, convincing you that you don't have cancer when the opposite is true. This is because some men with prostate cancer have low PSA levels. ()
PSA screening in men aged 55 to 69 years can prevent approximately 1 death from prostate cancer per 1,000 men screened over about 13 years. This is considered a slight advantage, and if you fall in this age range, you may want to consider getting tested. ()