ECG is the first test on the diagnostic path
A patient who complains of chest pain to a therapist is almost immediately given an ECG, that is, an electrocardiogram. This is a test that can be performed very quickly in any clinic, hospital, or even at the patient’s home. An ECG is usually the first test to diagnose cardiovascular disease. An ECG should be performed on every patient visiting a cardiologist or with cardiac disease or chest pain. It is also recommended to perform an ECG for healthy people involved in sports professionally and as amateurs. To perform this test, you will need an electrocardiograph that records the functional currents of the heart muscle. Each muscle, including the heart muscle, produces electrical impulses that are recorded by the machine and transferred to paper. A special printout of electrical impulses is an electrocardiogram. An ECG test can detect dangerous cardiac arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, conduction block, tachycardia), as well as a recent heart attack. However, the diagnostic value of the test is limited, because even a correct ECG recording does not clearly exclude serious heart disease, and then a more accurate diagnosis is necessary. An at-home ECG is a safe and quick test. The patient, lying on his back, has electrodes glued or attached to his chest, arms and legs. The test itself takes up to 5 minutes and does not require special preparation. The patient receives the test result immediately after it is performed.
Why do a cardiac MRI?
We wrote about the principle of MRI in the material “CT or MRI: what to choose?” The method is used as often as Echo CG or Holter monitoring, but it gives particularly clear results in the study of heart tissue, and not its work.
- It is necessary to assess the extent of myocardial damage and impairment of its contractility after a heart attack.
- Consider whether atherosclerotic plaque or stenosis has accumulated in the blood vessels
- Check how recovery is going after treatment
All four types of research are absolutely safe. But even if you have thoroughly understood the information, only a doctor can select a diagnosis and analyze the results.
Find a cardiologist
Heart Echo - evaluates the anatomy, functions and changes in the structures of the heart!
Another test that cardiologists order when they need more information is an echocardiogram, more commonly known as a cardiac echo, simply an ultrasound of the heart. The specialist uses an ultrasound scanner to examine the heart, most often using the transthoracic method. It is non-invasive and does not require special preparation. Usually lasts from 15 to 30 minutes. During the examination, the doctor can evaluate the anatomical and functional aspects of the heart, i.e. confirm or rule out the presence of birth defects, leaks, and structural defects of the heart. He can also evaluate the condition and function of the heart valves, that is, recognize valve defects. Cardiac echo helps evaluate contractility and function of the heart muscle, which are associated with myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and ischemia.
IMPORTANT! An echocardiogram is a repeatable test, but its diagnostic value depends on the experience and skill of the treating physician. In case of diagnostic doubt, the diagnosis should be expanded to include, for example, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT). Transthoracic echocardiography allows you to determine the state of the disease, the degree of its development and the effectiveness of the treatment. An indication for its implementation is also a suspicion of pulmonary arterial hypertension. After this, if in doubt, transesophageal echocardiography can be prescribed.
Diagnosis of the heart using ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the heart is a fairly new method in cardiology, which in medical practice is called echocardiography. The procedure is carried out using a special device - an electrocardiograph; it generates ultrasound, the rays of which penetrate through the chest, determining the condition of the soft tissues and the thickness of the myocardium. The technique is safe for the patient and has high information content and reliability of the results obtained.
The method allows you to determine not only the condition of the vessels and walls of the myocardium, but also the speed of blood movement in a given period of time
Indications for the procedure:
- congenital heart pathologies in children;
- acquired heart disease in adults;
- the presence of symptoms of infectious damage to the heart muscle;
- clarification of the diagnosis of “heart attack”;
- assessment of the state of the myocardium after a heart attack;
- detection of intracardiac artery thrombosis;
- neoplasms in the chest cavity;
- monitoring the state of the myocardium in the postoperative period.
Ultrasound of the heart is recommended in situations where a person has a high risk of changes in the anatomical structure of the internal cavities of the organ.
Using ultrasound of the heart muscle, the following pathological conditions can be determined:
- identification of hidden heart defects;
- violation of the integrity of the outer and inner membranes of the organ;
- enlargement and thickening of the myocardium;
- pathological changes in the contractility of the organ;
- accumulation of fluid in the heart cavity;
- establishing the nature and speed of blood flow through the chambers and aortas of the organ.
The disadvantage of the procedure is the inability to establish possible disturbances in the passage of electrical impulses
Modern techniques make it possible to identify the slightest disturbances in the functioning of the organ, which are difficult to establish using a cardiogram.
Holter ECG - if a heart rhythm disorder is suspected!
Many patients who go to the doctor report that their heart rate is fast or slow, but the ECG is normal. Then the doctor decides to perform a Holter ECG. Holter is nothing more than an ECG, but its duration is 24 hours and sometimes 48. The patient usually has five electrodes attached to the chest, connected to a special device that contains a memory card on which the daily ECG image is recorded. The device is compact and can be attached to a belt. An ECG recorder is most often performed when cardiac arrhythmia, that is, supraventricular arrhythmia, is suspected:
- atrial fibrillation,
- increased heart rate (tachycardia),
- slow heartbeat (bradycardia),
- heartbeat,
- conductivity blocks.
It is also recommended to perform a holter in case of frequent fainting or loss of consciousness.
This test looks for so-called silent myocardial ischemia in patients with suspected coronary artery disease. This is also a study conducted on patients with a pacemaker to monitor its performance. IMPORTANT! An ECG recorder is not invasive, but there are a few things to keep in mind! After putting on the device, the patient should lead a normal lifestyle. To do this, he must keep a special activity diary in which he records individual actions and the periods of time in which they were performed, for example: climbing stairs, eating, driving, rest and sleep times, as well as symptoms such as dizziness, rapid palpitations, fatigue or shortness of breath, etc. The heart rate monitor also monitors your heart rate at night, giving your doctor valuable information. During the test, remember that the electrodes should not come off, and if you notice this, stick them with adhesive tape. During the examination (24 or 48 hours), you should not swim or shower. After the examination, the card with the record goes to a specialist who, using a special program, downloads the data and analyzes it. Usually, after a few days, the patient receives a description of the examination from a cardiologist, with whom he goes for further consultations.
Holter: monitoring and analysis of heart function
A holter is attached to the patient, most often on a belt, in a special case and electrodes are applied. Doctors often use the phrase “hang up the Holter” or “make a Holter”, meaning that the device will be used for 24 hours, on an outpatient basis, in the patient’s usual living conditions - at home, at work, during night sleep. Patients are asked not to wet the device, but otherwise lead their usual lifestyle.
This process of taking readings is called Holter monitoring, named after the American research scientist Norman J. Holter, who first used this technique in 1961.
Performing an ECG - check the performance of the heart!
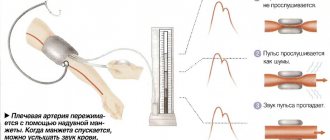
You can often hear the term “stress test”; this is nothing more than an ECG with stress, that is, it is performed under increased physical activity. The main purpose of a stress ECG is to check the performance of the heart muscle. The test is used in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease, as well as in monitoring patients after coronary angioplasty and myocardial infarction. They are often performed by people with a normal resting ECG but suspected of coronary artery disease. An exercise test is also performed to select the appropriate cardiac rehabilitation. Athletes regularly undergo exercise testing. Most often, the test is performed on a treadmill, less often with a bicycle ergometer. The patient undergoes physical activity on a treadmill in the form of walking and fast walking with variable load and inclination angle of the treadmill. During the examination, the patient is connected to an ECG machine, which constantly monitors the heart and regularly measures blood pressure. The entire test usually takes about 20 minutes. Unless the doctor advises otherwise, the patient should take medications that he regularly takes on the day of the examination. IMPORTANT! The patient for examination should come earlier and rest and be at least 2 hours after eating. Sports clothing and sports shoes are required for the examination. First, a normal resting ECG is performed. Then, in the presence of a doctor who monitors the patient’s heartbeat and condition, an exercise test is performed. The doctor may decide to stop the test when he notices abnormalities, or if the patient complains of chest pain or becomes pale. After the test, an ECG is performed, which shows the recording while the heartbeat calms down. The test shows the blood supply to the heart, blood vessels and the reaction of the heart muscle to increased oxygen demand. There are a number of contraindications to performing stress tests. Exercise testing is not recommended in the presence of infection, fever, resting chest pain, shortness of breath, aortic aneurysm, high blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmia, exacerbation of lung disease (asthma), uncontrolled diabetes, and certain valve defects. Due to the low diagnostic value of the test, especially for women, the stress test can only be an additional test, but not decisive in terms of the presence or progression of coronary heart disease. After the examination, the doctor writes a description of the examination. The patient receives an ECG recording along with a description and must return to his cardiologist for interpretation of the results and, if necessary, treatment.
Indications for the procedure
The examination is carried out only with a referral from a cardiologist. A visit to the doctor can be either planned or in case of complaints about heart function.
Frequent symptoms of impaired heart function include conditions such as:
- Compressive pain in the chest, as well as in the region of the heart, which radiates to the shoulder blade;
- Rapid pulse, which causes dizziness and increased heart rate;
- Shortness of breath with minor exertion;
- Periodic fainting;
- Dry barking cough;
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
Particular attention is paid to patients who have suffered a stroke, have congenital heart abnormalities or rheumatism.
Specialists conduct an examination and give a referral to see a doctor if they find:
- extraneous noise in the work of the heart muscle;
- with low or high blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
The following categories of citizens are subject to mandatory examinations, namely:
- Persons with congenital or acquired heart disease;
- Athletes who have a serious load on their heart function;
- Patients undergoing examination before surgery;
- Women who are pregnant.
Computed tomography - helps diagnose heart defects
In a situation where the above tests are not enough or do not give results, the cardiologist may prescribe a computed tomography scan of the heart and coronary vessels (CT). This is a non-invasive examination, unlike coronary angiography, which is performed strictly in cases of acute coronary syndromes. Computed tomography allows preparation of cardiac imaging. The examination consists of assessing the anatomical structures of the heart, coronary arteries and aorta, as well as its branches. Tomography, unlike the above examinations, requires proper preparation and very detailed consultation with a cardiologist and radiologist. Tomography is performed with an iodinated contrast agent, which provides better visibility of the vessels. In order for specialists to prescribe contrast, the patient must first undergo a blood test, which will determine the level of creatinine and thus assess kidney function. If the patient is allergic to contrast, this should be reported to hospital staff prior to the examination. The patient should not eat 4-6 hours before the examination. During tomography, X-rays are used, which is a contraindication for examination of pregnant women. Before the examination, the patient will undergo a puncture - a cannula through which contrast will be injected. During a CT scan, the patient is also given an ECG, so electrodes are attached. Cardiac and vascular CT scans help diagnose heart defects, leaks, abnormal vascular connections, and aortic aneurysms. A separate study is the so-called MSCT examination - that is, computed tomography of the coronary arteries. Some patients in whom a doctor suspects coronary heart disease may have a CT scan of the coronary arteries to evaluate the risk of atherosclerosis. However, it should be remembered that this examination does not usually replace coronary angiography, that is, an invasive examination that is the gold standard in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and coronary atherosclerosis. On the other hand, MSCT has a proven role in assessing the patency of venous bypass surgery in post-bypass surgery patients. After the examination, the patient receives an examination protocol and a description made by a specialist doctor, who must consult with his cardiologist. It should also be remembered that computed tomography is performed only on the direction of a doctor.
Magnetic resonance imaging - recommended, for example, in the diagnosis of myocarditis In addition to computed tomography, there is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart and blood vessels, which uses the physical phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly specialized test that evaluates the heart muscle more accurately than echocardiography (heart echo). As with tomography, magnetic resonance imaging uses contrast. The patient should have a blood test to determine the level of creatinine and therefore the level of kidney function. People with an allergy to contrast should tell their doctor. The patient should be 4 to 6 hours after their last meal. During the examination, the patient has ECG electrodes glued to his chest. The test takes longer and can take between 30 and 90 minutes. In addition, it should be remembered that this examination involves the patient being in a strong magnetic field. The presence of metal prostheses, implants, pacemakers, etc. may be a contraindication to MRI. The condition after implantation of a coronary stent in most cases is not a contraindication to cardiac MRI, but detailed information should be provided by the treating cardiologist. Cardiac resonance allows, among other things, to evaluate:
- functions, thickness and vitality of the heart muscle,
- muscle damage after heart attacks,
- congenital heart defects,
- severity of leak defects and location of leaks.
Cardiac MRI is recommended for the diagnosis of myocarditis, storage diseases, cardiomyopathies, and coronary heart disease. After the examination, specialists prepare a CD with a recording, description and comments, with which the patient must return to the cardiologist who diagnosed him. The examination can only be carried out with a doctor's direction. All of the above studies are non-invasive. However, they are necessary for making the correct diagnosis in the diagnosis and treatment of various cardiac diseases. It is worth remembering that if you have any doubts before the examination, you should ask your doctor all questions. A good and very useful solution is to also prepare a list of questions in advance.
Comparison of both methods
The general objectives of conducting a survey do not mean the same quality of the study. Electrocardiography and EchoCG differ in the following types:
- by the method of conducting the survey;
- by type of violations detected;
- on the effectiveness of monitoring the circulatory system.
A cardiogram shows and records the electrostatic activity of the heart muscle in the form of a graph. It shows whether there is a stable pulse rhythm, its numerical indicators, and the presence of arrhythmias. Arrhythmias on electrocardiography are visible quite clearly, so this particular method of diagnosing the circulatory system makes it possible to detect deviations in time and take health-improving measures.
EchoCG is performed with a special-purpose device - an ultrasound sensor. The waves emanating from the sensor penetrate the intracardiac cavity, are reflected from the tissues and return back to the device, where the data is analyzed and displayed on the screen.
Unlike an ECG, the ultrasound method allows you to visualize the heart on a monitor. Ultrasound is performed using a special sensor and conductor gel
Holter or ECG?
They say ECG is a thing of the past. Better than a halter. Is it true? In what situations can you not do without an ECG?
Olga, Saratov
– ECG remains the leading method of instrumental diagnosis of heart disease. At the same time, with the development of other methods, the role of the ECG does not weaken, but increasingly increases. It is in recent decades that, based on ECG features, a number of new diseases with a high risk of sudden cardiac death have been described, such as long and short QT syndromes, Brugada syndrome and others. It is impossible to identify them without a traditional ECG.
An ECG will be the first to indicate the presence of heart changes that will require further examination and treatment by a cardiologist, so this method remains indispensable. I strongly advise anyone who, considering themselves healthy, has not had an ECG done on themselves or their children, to do so and repeat it periodically, even if there are no complaints.
Prohibitions with Holter monitoring
During monitoring, the following actions are prohibited:
- turning off the device during sleep;
- X-ray, CT or MRI;
- active sports;
- self-removal of electrodes.
When taking a shower, be careful not to get the device wet!
The study makes it possible to identify various disorders at an early stage. This is an important diagnostic procedure to evaluate heart function. If your doctor has recommended that you undergo such an examination, you should not postpone it.