What is the role of hemoglobin in the body
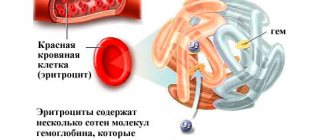
Hemoglobin is a physiological protein compound, a coloring substance present in red blood cells. Hemoprotein molecules contain iron atoms, which bind oxygen, are responsible for cholesterol and oxygen metabolism, and participate in the hematopoietic process. A healthy body contains about 4 g of iron. In the spleen, brain and liver - 1.5 g, in hemoglobin - 2.5 g.
Based on the results of a blood test for hemoglobin, the attending physician can
- establish the cause of weakness, fatigue, decreased metabolic rate;
- assess the quality of oxygen supply to cells;
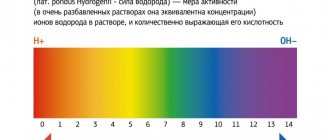
- determine the level of acid-base balance - pH;
- recognize signs of developing anemia.
A person’s well-being is negatively affected by both increased and decreased levels of iron-containing hemoprotein. With a deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood, metabolic processes slow down, health worsens, and a whole bunch of ailments develops. A hemoglobin test that exceeds the norm may indicate the development of cardiovascular diseases or the presence of serious pathologies in the body.
As long as all indicators are within normal limits, a person feels cheerful and full of energy. The hemoprotein resource is sufficient to deliver oxygen to each cell and remove carbon dioxide through the lungs, preventing acidification of the body.
Find and neutralize: how to identify anemia and find out its causes
Anemia may not manifest itself for a long time, and the person has no idea that he has low hemoglobin. But anemia always has a reason, which is important to find and eliminate!
Signs of anemia include frequent fatigue, physical weakness, pale skin and mucous membranes. Iron deficiency anemia can also manifest itself as shortness of breath, dizziness, tinnitus, and a sudden increase in heart rate. The skin may become dry, nails brittle and layered.
True, people, especially those leading a sedentary lifestyle, often attribute these symptoms to the fact that they move little, have gained weight, and do not spend time in the sun.
Common causes of anemia
There are quite a few factors for the development of anemia. Let's list the most common ones.
Chronic blood loss is a common cause of iron deficiency anemia in young women with heavy periods. For treatment, doctors prescribe either iron supplements during, before and after “critical days,” or oral contraceptives, which reduce the intensity of bleeding. However, blood loss can also occur due to frequent nosebleeds or gastrointestinal bleeding. Here diagnosis and treatment can be more complex.
Lack of iron, vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin), vitamin B 9 (folic acid) individually or all together can occur due to the lack of foods with these substances in the diet - this is typical for followers of very strict diets or constant food restrictions. We usually get enough vitamins from food if we eat a varied diet, but there may be difficulties in absorbing vitamins.
Often the cause of iron deficiency is constant and unnoticeable blood loss, vitamin B 12 - disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis, enteritis usually lead to anemia.
Increased blood destruction (hemolysis) also leads to anemia. At the end of their life (about 120 days), the red blood cells are destroyed in the spleen. In the presence of hemolysis, the destruction of blood cells occurs prematurely, which leads to a decrease in the lifespan of red blood cells. Anemia develops when the bone marrow does not have time to synthesize enough red blood cells to replace the destroyed ones.
How to check?
A set of laboratory tests “Hematology, diagnosis of anemia” will not only determine whether you have anemia, but will also help determine its cause. It includes several complexes and indicators.
A clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula will show the number of all blood cells. It will be clear whether you have anemia, whether there is an inflammatory process in the body, blood loss, or whether there is a suspicion of allergies or helminthic infestation.
Reticulocytes are the precursor cells of red blood cells. Their number shows how well the process of hematopoiesis is proceeding in the bone marrow.
Common and direct bilirubin is a bile pigment, the end product of hemoglobin breakdown.
Iron, vitamin B 12, vitamin B 9 are substances necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin.
Transferrin is a protein that transports iron from the intestine to the sites of blood synthesis and storage (bone marrow, liver, spleen). Its increase or decrease indicates different causes of anemia.
Ferritin is an indicator reflecting the supply of iron in cells and tissues.
The latent iron binding capacity of serum is the ability of transferrin to bind iron. Indicates iron deficiency.
If your stomach hurts often...
With age and with chronic gastrointestinal diseases, problems with the absorption of vitamin B 12 often begin. This can lead to B 12 deficiency anemia. It may be accompanied by decreased thinking abilities, depression, tingling of the fingers or periodic numbness.
The laboratory test “Determination of antibodies to Castle factor—intrinsic factor (AVF)” will help identify the cause. Intrinsic Castle factor is a protein produced by stomach cells. It is he who ensures the absorption of cyanocobalamin in the intestines. With autoimmune gastritis, the body's own immunity synthesizes antibodies that destroy the internal Castle factor. Most often this happens with atrophic gastritis.
Timely testing and a subsequent visit to a therapist or gastroenterologist will help get rid of anemia without extra costs and take control of its causes.
When is it necessary to take a hemoglobin test?
In modern medical practice, a blood test for hemoglobin is considered basic. The study is prescribed when registering pregnant women, to clarify the diagnosis if anemia or the development of other pathologies is suspected. Living in a deteriorating environment and constant mental and physical stress require careful attention to your health. Chronic fatigue, frequent depression, loss of interest in life are serious reasons to visit a doctor and get a referral for a blood test.
Indications for prescribing a hemoglobin test are:
- frequent headaches;
- the appearance of dry mouth;
- lethargy, drowsiness or painful insomnia;
- paleness of the skin, long-lasting bruises;
- severe thirst and increased urge to urinate;
- deterioration of vision and memory;
- poor healing of cuts and wounds;
- instability of psycho-emotional state.
Clarifying the level of hemoprotein in the blood is especially important for pregnant women carrying a child, parents planning to replenish the family, and patients with persistent hyperglycemia.
A blood test for hemoglobin itself does not eliminate the problem, but it can prompt dramatic lifestyle changes. Giving up bad habits, a balanced diet and proper rest can protect against irreversible changes in the endocrine system. To improve your quality of life and calmly greet each new day, it is enough to periodically set aside a few minutes to submit biomaterial for research.
Transcription of analyzes online.
cost of service: 500 rubles
Order
General practitioner Khanova Irina Ivanovna will interpret your tests during an online call in the Zoom or WhatsApp application.
- detailed explanation from the general practitioner.
- an alternative opinion from a competent specialist in interpreting the analyses.
- the opportunity to ask questions to the doctor regarding test results.
The importance of determining hemoglobin levels
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein found in red blood cells. It performs an extremely important function, ensuring the delivery of oxygen entering the blood to the tissues and cells of the internal organs.
When hemoglobin levels drop rapidly, cells do not receive enough oxygen, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire body.
The protein compound captures oxygen in the lung tissues and transports it to the body’s cells, ensuring their full functioning. Hemoglobin also captures and removes carbon dioxide from the body, which is a waste product.
Carbon dioxide accumulates in tissues, which leads to a deterioration in overall health and the development of such unpleasant symptoms as severe headaches, weakness, loss of strength, and pale skin. It is very important to promptly detect a decrease in hemoglobin and begin treatment. In its absence, complications such as a weakened immune system, tissue hypoxia, chronic insomnia, and heart failure may develop.
How to take a blood test for hemoglobin
To donate blood, no special preparation is needed, but there are rules that should be followed. Obtaining the most reliable result depends on them:
- hemoglobin test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach;
- the last meal is taken 10-12 hours before blood sampling;
- on the eve of going to the laboratory, it is recommended to avoid heavy physical labor, strenuous training, and stressful situations;
- Fatty foods and alcohol, which distort the data, must be eliminated from the diet within 24 hours.
To carry out the procedure, venous or capillary blood (from a finger) is taken. For prevention purposes, it is enough to undergo a test for hemoprotein levels once every 2-3 years.
Determination of hemoglobin using the device
Today in the pharmacy chain you can find a wide selection of special devices designed to measure hemoglobin levels at home. Such a device is called a hemoglobinometer and is produced by several pharmacological companies.
Some of the most popular devices are MiniGem 540 and Easy Touch. Such hemoglobinometers allow you to determine protein levels in 10 seconds. Technique for performing home analysis:
- using a special needle from the set, pierce your finger;
- drop a few drops of blood into a test tube;
- add hydrochloric acid (included with the device);
- pour distilled water into the device - the liquid should take on the scarlet hue of blood;
- evaluate the result obtained on a special scale and compare it with the presented age norms.
The results of the study will be reliable only if you properly prepare for the procedure yourself. To do this, you must avoid any food or drink for at least 12 hours, and also stop taking any medications.
Norms and deviations of hemoglobin as a result of analysis
The normal level of hemoglobin in the blood is a guarantee of good health for adults and children. The indicator for each person up to a certain age is approximately at the same level. In 2-week-old babies it is 135-200 g/l, at 1 year old it is 100-140, and at 12 years old it is already 114-145 g/l. The concentration of hemoprotein in the blood of strong healthy children is always higher.
The norm is different for men and women. The strong half of humanity is characterized by a hemoglobin test value of 130-160 g/l, for girls and women over 18 years old - 120-155. During menstruation it can drop to a level of 100 g/l. After 45 years, the hemoprotein content in both sexes may change upward.
An increased level of hemoglobin, recorded as a result of the analysis, in some cases indicates the presence of cancer problems, heart and intestinal pathologies.
A low rate is often associated with malnutrition, low-carbohydrate diets, hidden blood loss and blood diseases. It is observed in people suffering from diabetes, pancreatic tumors, and occurs in pregnant women.
Important! Whatever the results of a blood test for hemoglobin, it is strictly not recommended to make a diagnosis on your own and self-medicate. An experienced specialist from the Health of the Nation medical center will conduct a thorough examination, determine the exact cause of the ailment, and prescribe competent treatment.
Health is the main wealth that nature has awarded to humans. It should be taken care of by professionals.
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration) - the average concentration of hemoglobin in a red blood cell
Parameter calculation
MCHC reflects the concentration of hemoglobin in the “average” erythrocyte (the ratio of hemoglobin content to cell volume) and characterizes the degree of saturation of the erythrocyte with hemoglobin as a percentage. This parameter can be calculated using hemoglobin and hematocrit indicators:
MCHC = Hb (g/dL) 100/Ht (%).
Genetically determined indicator
The average hemoglobin content in an erythrocyte is the most stable, genetically determined indicator and for adults does not depend on age, gender, or race. The coefficient of variation of this parameter in patients in the clinic is 4–5%.
Of all the erythrocyte indices, MSHC is the least susceptible to fluctuations under pathological conditions. Therefore, its reduction is of great value in diagnosis:
- iron deficiency anemia,
- thalassemia,
- lead intoxication,
- some hemoglobinopathies.
Error indicator
For the same reason, the parameter can be used as an indicator of instrument error or inaccuracy made when preparing a sample for research. The stability of calibrations, the correct functioning of equipment - all this is useful to monitor using the current average MCHC value. It should fluctuate within 34±2 units.
Clinical and diagnostic value
| Promotion | Decrease (to <31 g/dL) |
|
|
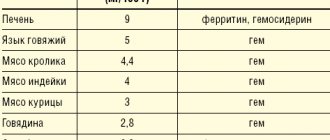
Proper nutrition to increase hemoglobin
If your hemoglobin level is low, you should include as many iron-containing foods as possible in your diet.
| Healthy foods | Variety |
| Meat and offal | Beef, chicken, beef liver, tongue |
| Cereals | Buckwheat |
| Fish and seafood | Red fish, red caviar, shrimp, crabs, mussels, oysters, kelp |
| Eggs | Egg yolk |
| Fruits | Pomegranate, feijoa, plum, persimmon, apples, bananas, apricots, peaches |
| Berries | Cranberries, wild strawberries, raspberries, strawberries, blueberries, black currants, rose hips |
| Vegetables | Beets, carrots, beans, lentils, peas, pumpkin, tomatoes, potatoes, onions |
Various dried fruits can be an effective way to quickly increase hemoglobin at home. Raisins, apricots, and dried apricots contain a significantly higher concentration of iron than fresh fruits.
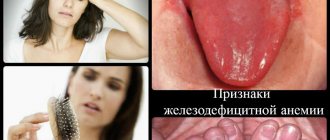
Main symptoms of iron deficiency anemia
You can determine a low hemoglobin level yourself, without special equipment. To do this, you need to pay attention to the characteristic signs that may indicate the development of iron deficiency anemia. The main manifestations of low hemoglobin:
- headaches accompanied by dizziness or fainting;
- noise in ears;
- pale or yellowing of the skin of the face and body;
- lethargy, weakness, loss of strength;
- loss of appetite;
- muscle pain;
- decreased immunity and frequent colds;
- cold extremities;
- change in taste preferences - the desire to eat chalk, raw dough, eggshells.
Iron deficiency anemia is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, constant shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and heart rhythm disturbances. Also, a decrease in iron-containing protein in the blood leads to indigestion, changes in the color and consistency of stool. A lack of hemoglobin can also be detected by a person’s appearance. His skin becomes dry, acquires a jaundiced or pale tint, the conjunctiva of the eyes turns red, hair and nails become brittle, and their growth slows down.
Consequences of low hemoglobin
Decreased immunity is a dangerous condition that cannot be ignored. It is accompanied by a serious deterioration in general well-being - a person is bothered by regular headaches, weakness, lethargy and loss of strength. In severe forms of iron deficiency anemia, severe dizziness and fainting may occur, attention disturbances, increased fatigue and muscle relaxation are often observed, which at an advanced stage can lead to urinary incontinence.
A decrease in hemoglobin below critical levels negatively affects not only a person’s well-being, but also his appearance.
As a result of lack of oxygen, skin, hair and nails dry out and become thinner, becoming dull and faded.
If iron-containing protein falls below normal, this negatively affects the immune system. As a result, a person is bothered by regular colds, as well as exacerbations of chronic diseases.