Interruptions in the functioning of the heart occur not only in sick people. Scientists have proven that it beats with different intensities throughout the day, so you shouldn’t worry about this when identifying one-time symptoms. It’s another matter if these symptoms become frequent during the day and for a long period of time. Many heart diseases are passed down and are considered to run in families. If there is an organ dysfunction, it is important to know whether your loved ones suffer from the same problems. Below in the article are the symptoms, causes and types of abnormal heart rhythms.
How does tachycardia manifest?
The state of the heart can be quickly determined by the heart rate (HR) - through the pulse, which can be easily felt in large peripheral arteries. Normally, its frequency coincides with the heart rate, since the pulse is the response of the arteries to the ejection of blood from the heart when it contracts. Indicators for a healthy person are 60–80 beats per minute. If your heart begins to beat faster, it may physically feel like it is jumping out of your chest.
However, this does not always happen, and then the presence of tachycardia can be suspected based on a number of other symptoms.
Different pacemakers (sources of impulse generation) are responsible for different types of tachycardia.
Clinical signs of tachycardia
- Pain or discomfort in the chest.
The chambers of the heart contract alternately: while some parts are filled with blood, others are resting. The stronger the tachycardia, the shorter the periods of myocardial relaxation. Working without rest causes pain in the heart.
- Dizziness and general weakness.
In the pulmonary circulation, blood oxygenation (oxygen saturation) occurs. With tachycardia, the time required for complete gas exchange decreases. Rapid contractions of the heart release blood into the vascular bed with a reduced content of O2, which is why the tissues do not have enough of it. To make it easier for organs to receive it, vascular resistance decreases. This results in a compensatory decrease in pressure in the blood vessels, accompanied by dizziness and general weakness. Sometimes it can lead to loss of consciousness.
- Dyspnea.
It occurs both during movement, since during physical activity the body requires more oxygen, and at rest - if tachycardia persists for a long time. The same oxygen starvation leads to the development of shortness of breath: increased breathing is an attempt to restore oxygenation.
- Cyanosis, or blueness of the skin.
With hypooxygenation (decreased oxygen concentration in the body), the blood contains a large amount of reduced hemoglobin, a substance responsible for binding oxygen. Low oxygenation leads to cyanosis of the lips, tips of the ears, or fingers.
Tachycardia can be expressed by less significant symptoms: cough, headache, nausea, sleep disturbances, decreased appetite and performance. These complaints are not typical for an increase in heart rate, but you should mention them when visiting a doctor
Diagnostics
When a patient contacts a doctor with a complaint of pulsation in the chest and heart area, the doctor initially performs a visual examination. To do this, the doctor slightly turns the patient on his left side and stands at chest level, so that the pulsation in the heart area is better visible.
The most interesting thing is that patients who complain of such symptoms have a history of myocardial infarction. Now the specialist’s task is to find out where exactly the source of the problem comes from: a hypertrophied apex of the heart muscle or an aneurysm.
To get a more accurate picture, your doctor may order an x-ray. It is usually not possible to detect an aneurysm on imaging, but in rare cases a pulsatile left ventricular aneurysm can still be seen. On fluoroscopy, you can track the paradoxical pulsation of the aneurysm, which does not coincide with the apex of the muscle. In addition, it is possible to detect protrusion of the left ventricular arch.
In general, there are three possible and most common causes of pulsation: tachycardia, atherosclerosis, and nervous tics.
Tachycardia at different times of the day
Since rapid heartbeat can occur due to physical activity, emotional reactions or behavioral habits (smoking, drinking too much strong coffee, etc.), an increase in heart rate only during the daytime is not considered a reliable symptom of heart pathology (although it should be alarming).
If tachycardia persists at night, this indicates the presence of pathology. At this time, the heart rate slows down due to physiology, and if the heart rate does not decrease during sleep, remaining consistently high throughout the day, it is necessary to visit a doctor.
At the same time, some pathologies are characterized by daily fluctuations in heart rate. For example, during the day a person may feel tachycardia, but when going to bed at night, they feel the opposite - the heart rate drops below normal, which also leads to problems with sleep, decreased oxygenation and shortness of breath. This condition may be a sign of sick sinus syndrome (SSNS), namely tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome. With this pathology, all symptoms of tachycardia, disturbing during the day, intensify at night due to a drop in heart rate below 60 per minute.
Attacks of tachycardia, related to the time of day, are potentially life-threatening: episodes of dizziness and fainting can result in injury, especially in children and the elderly. Such symptoms are a reason to visit a doctor
What is heart pulsation?
In medical terminology there is the concept of pulsation. It stands for: movements of the walls of the heart and blood vessels in the form of shocks, which is characterized by transmission displacements of soft tissues that appear during contractions of the heart muscle.
Ripple is a broader concept than pulse, because it refers only to the pulsation of the walls of vessels pumping blood, which is caused by the passage of a pressure pulse wave passing through the vessel and forming in the aorta.
Atherosclerosis
The aorta is the largest vessel in the human body, for this reason it is most often affected. It is divided into abdominal and thoracic segments, starting in the left ventricle of the heart and has many branches that feed all organs located near it. In most cases, it is partially affected and has symptoms that always depend on the specific case.
Quite often, atherosclerosis is the cause of many serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels. With this pathology, connective tissue begins to grow in the walls of medium and large arteries, as a result of which the inside of the vessels is saturated with fats, and their walls become denser and thicker. Thus, they lose their elasticity and lumen, and this leads to the risk of blood clots.
Atherosclerosis can develop in absolutely any part of the aorta. When the problem lies in the chest, it pulsates in the area of the heart, namely between the ribs to the right of the sternum. In addition, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- hoarseness of voice and difficulty swallowing;
- burning and squeezing effect behind the sternum and in the heart;
- increased blood pressure;
- radiating pain in the spine, neck, arms and under the ribs;
- paroxysmal pain;
- fainting;
- weakness and dizziness.
When a patient encounters damage to the abdominal aorta, he experiences the following problems:
- weight loss;
- aching pain in the stomach;
- bloating;
- frequent constipation;
- unevenness and hardness when palpating the aorta.
Why do people face this disease? It affects patients aged 40-50 years and older. Moreover, it occurs much more often among men than among women. Smokers are the most potentially dangerous group susceptible to atherosclerosis. In addition, there are other risk factors:
- gout;
- high blood pressure;
- overweight;
- sensitivity to stressful situations;
- genetic predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity.
Clinical picture of the disease
The functional manifestation of extrasystole does not cause concern. Organic tumbling of the heart muscle is considered dangerous. The patient most often complains of intense shocks from inside the chest, turning over of the myocardium in its place, as well as interruptions in the functioning of the main human organ - its periodic freezing.
Only the attending physician can identify the presenting symptoms:
- Increased activity of the sebaceous glands, causing excessive sweating;
- Oxygen starvation of internal organs;
- The occurrence of anxiety of an unreasonable type;
- Severe headaches of an intense nature;
- Frequent dizziness and periodic fainting;
- Manifestation of shortness of breath in a calm state and hot flashes throughout the body.
Treatment of fasciculation of intercostal muscles
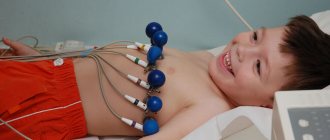
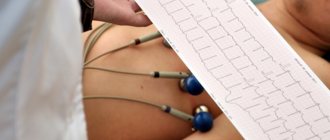
Advice that can be given to patients with similar fasciculations of the intercostal muscles is to simply not pay attention to them. If there is no pain, then you can simply check your heart as planned: do an ECG, ultrasound of the heart, take tests for cholesterol, blood sugar and atherogenicity index, and calm down. And for medicinal purposes, multivitamin complexes are used, which include potassium, calcium and magnesium, as well as B vitamins, which improve the function of impulse conduction along the nerve fiber.
Structure of the heart
In addition, such drugs as “Fitosedan”, “Novo-passit”, as well as glycine, which improves inhibitory processes in the central nervous system, have a good effect. This drug is completely harmless, since it is one of the simplest amino acids that make up any protein that we eat. In addition, glycine was found in gas and dust clouds surrounding cometary nuclei. This proves that glycine is widely distributed in nature and is non-toxic to humans.
Sometimes such fasciculations can be a consequence of intercostal neuralgia, especially after shingles, or herpes. At the same time, the nerve conduction of the impulse itself changes, and if the motor nerve has been exposed to herpes, then with a pathological impulse, instead of burning pain, a muscle twitching will be felt. Therefore, you need to ensure that any herpes that appears on the lips “from a cold” is treated in a timely manner, using antiviral agents, both locally and internally. The doses should be sufficient for all labial herpes to disappear quickly (within 2-3 days).
In addition, you need to arm yourself with medical knowledge in order to understand what is happening to your own body, at least at an “amateur” level, in order to avoid panic and unjustified actions.
Treatment of heart failure
The approach to treating heart failure is determined by the cause of the development of this symptom. In some situations, conservative therapy will be effective, in others, surgical intervention may be necessary (for example, stenting of the coronary arteries in severe cardiac ischemia), in others, doctors will limit themselves to observation and general recommendations (on regimen, diet, physical activity). What is clear is that without eliminating the cause, even the most modern antiarrhythmic treatment will not give a truly good result.
The second factor that determines the treatment tactics for irregular heart function is the nature and potential danger of rhythm disturbances. With some of them, the patient's heart may even stop. Therefore, doctors will take active therapeutic measures and, if drug therapy is ineffective, they will recommend surgical intervention (for example, radiofrequency ablation of an arrhythmogenic focus in the myocardium or installation of a pacemaker). As for the symptomatic treatment of heart failure, it is carried out with the following groups of drugs:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs. For each type of arrhythmia, certain medications from this group are indicated, so taking pills to help one of your relatives get rid of an attack is strictly prohibited.
- Sedatives - herbal or synthetic. Worry and anxiety are factors that provoke the appearance of heart failure, so they must be excluded.
- Metabolic drugs. Medicines in this group improve metabolic processes in the myocardium, which contributes to more efficient functioning of the heart muscle.
In addition, in case of interruptions in the functioning of the heart, it is very important that the patient stop drinking and smoking, start eating properly, enriching his diet with heart-healthy foods, give up heavy physical work if possible, and review his daily routine, devoting sufficient time to rest and sleep. Equally important is regular visits to a cardiologist with mandatory registration of an ECG and the necessary blood tests.
Causes of heart tumbling
Somersault of the heart varies depending on the cause of its occurrence. There are organic and functional extrasystole. In the latter case, the abnormal behavior of the myocardium does not arise due to problems with the main organ. The cause of the behavior of the heart muscle is a malfunction in the functioning of the nervous system. Factors that provoke fluttering in the gridy are due to the following:
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- Excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco products;
- A person's prolonged stay in a stressful situation;
- Effects of large amounts of caffeine on internal organs;
- Hormonal imbalance in women.
The first type of extrasystole is organic. It develops only during a pathological process in the heart muscle. The following diseases can provoke a feeling of tumbling of the main human organ:
- Heart attack;
- Long-term circulatory failure, recorded as chronic;
- Cardiosclerosis;
- Developmental defect;
- Ischemic myocardial disease;
- Cardiomyopathy;
- Pericarditis;
- Hemachromatosis;
- Sarcoidosis.
Pathology can also develop after surgical interventions on the heart muscle. In people involved in sports, the feeling of the heart tumbling is caused by dystrophy of the main organ. This process occurs due to excessive physical exertion.
Localization area
This is a rather interesting disease from a medical point of view, because it has several types of location in the heart muscle. Supraventricular is the result of arrhythmia, which is caused by foci of impulses in the heart muscle. They are usually located in the atrioventricular septum or supraventricular region. If a person encounters ventricular localization, it occurs due to the formation in the ventricles of the muscle of an absolutely independent source of contraction of impulses, which interferes with the stable functioning of the heart. This problem is more often encountered by older men.
In fact, the symptoms themselves are not pronounced, but as with other arrhythmic disturbances, there is a feeling of the heart tumbling, freezing or increased rhythm. This form of localization does not pose a threat to life, however, if the indicators are elevated, examination and treatment are necessary.
Atrial appears as a result of the occurrence of foci of electrical impulses in the atria. Atrioventricular is the result of the formation of a focus of pathology in the area of the ventricular-atrial septum.
Are heart failures dangerous?
Interruptions in the heart should be considered an alarming sign in the following cases:
- If the unpleasant sensations recur several times a week or bother you constantly.
- If the duration of attacks increases each time.
- If the irregularity of the heart is accompanied by severe pain, noticeable pallor, fainting or increasing shortness of breath.
It is also worth noting that the severity of the patient’s subjective feelings does not always reflect the severity of the disease. Often, severe and frequent interruptions in the functioning of the heart are the result of unpleasant but harmless diseases, such as autonomic dysfunction.
Really serious illnesses, for example, severe arrhythmias (flutter, atrial fibrillation, extrasystole) and myocardial infarction can only be detected by ECG. Therefore, the exact answer to the question of whether the described sensations in the heart are dangerous should be given by the doctor after a complete examination of the patient.
Symptoms
In most cases, the disease has no symptoms, especially if the occurrence of additional contractions is isolated and occurs very rarely. But in practice, patients faced with such a pathology simultaneously complain of the following symptoms:
- a feeling of overwhelming fear;
- heart sinking;
- anxiety;
- inability to take a breath;
- feeling of cardiac arrest;
- “gurgling” in the heart;
- more intense and pronounced heartbeats;
- a feeling that something has turned over in your chest.