Emerging pain in the heart with osteochondrosis can be reflected or true. In the first case, a person experiences unpleasant sensations spreading along the pinched nerve fiber of the roots responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles on the left side. In the second case, the situation is much more serious and develops against the background of damage to the radicular or cranial nerves responsible for the innervation of the heart muscle, pacemaker, coronary blood vessels or the formation of the vagus nerve.
More often, pain in the heart is recorded with thoracic osteochondrosis, since the radicular nerves responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles and sternum are subject to compression in this type of disease. Also, if the intervertebral disc is damaged in the thoracic region, an inflammatory process may occur that affects the intercostal muscles. The second factor of negative influence is the static tension of the muscular frame of the back, which tries to compensate for the shock-absorbing load that the damaged intervertebral disc cannot cope with.
The pain in the heart that occurs with cervical osteochondrosis is dangerous because it is often associated with damage to the paired cranial nerves. One of these pairs is responsible for the parasympathetic nervous system, which ensures the performance of the myocardial muscle and regulates the work of the pacemaker. The second pair is responsible for the formation of the vagus nerve, which also regulates cardiac activity and controls the volume of arterial blood released into the systemic circulation. If this work is disrupted, a primary form of vascular heart failure may develop.
Damage to the radicular nerves in the lower structures of the cervical spine leads to disruption of the innervation of the coronary vascular bed. This can contribute to the development of coronary heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, etc.
Pain in the heart area that occurs with osteochondrosis is a reason to urgently seek medical help. It is necessary to get an appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist as soon as possible. Only an experienced doctor will be able to exclude the development of cardiac pathology and prevent negative consequences, such as aortic thrombosis, acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery stenosis, etc.
In Moscow, you can make an initial free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. To do this, just call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit. During the free consultation, the doctor will conduct a full examination, make a preliminary diagnosis, and give individual recommendations for subsequent examination and treatment.
Features of chest pain in various pathologies
A description of the discomfort will help distinguish heart pain from neuralgia and osteochondrosis. But the perception of pain is individual, so such a diagram can only provide approximate information.
| Osteochondrosis | Neuralgia | Angina pectoris | |
| Nature of pain | Stitching, aching, cutting, lumbago | Aching, burning, cutting | Stitching or burning |
| Conditions of occurrence | If you are in an uncomfortable position for a long time, sleep in an uncomfortable position, or undergo prolonged or sudden physical activity | With a deep breath, frequent breathing, being in an uncomfortable position, physical activity | During physical or emotional stress, less often in a stuffy room |
| Localization | Behind the sternum on the right or left | Behind the sternum or on the skin on the affected side | Behind the sternum on the left or in the center - in the region of the heart |
| Duration of attack | From a few minutes to several hours | A one-time outbreak of pain when inhaling, until shortness of breath ceases during physical activity, aching - constantly | 5-10 minutes, maximum duration – 30 minutes |
| Terms of termination | Changing body position, stopping activity, therapeutic exercises, massage, deep breathing, anti-inflammatory ointments | Reducing the depth of breathing, changing body position, stopping physical work, ensuring access to oxygen (open a window, go outside) | Stopping physical activity, calming techniques, taking nitroglycerin |
| Seizure frequency | Depends on the patient's physical activity | 1-2 times a month | Extremely variable - from rare attacks once a year to several a day |
| Additional symptoms | Decreased back flexibility, neck crunch, tinnitus, sleep disturbances, decreased cognitive function, back pain | Breathing disorders, shortness of breath, feeling of shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches | Weakness, palpitations, dizziness, fear of death, feeling of lack of air, tinnitus, darkening of the eyes |
Many signs are the same; it is difficult to distinguish pain caused by different causes. Typically, the patient thinks about heart pathology when a heart attack has already occurred. In other cases, angina becomes an incidental finding during examination for other diseases.
Lifestyle correction
After diagnosing thoracic osteochondrosis, the doctor necessarily recommends making certain changes to your usual lifestyle. If a patient shows signs of excess weight, he is advised to take measures to reduce it. But any diets for weight loss, especially monocomponent ones, are contraindicated. Nutrition must be complete and varied so that the body receives all the substances necessary for proper functioning, and metabolic processes in the intervertebral discs proceed properly. Therefore, it should comply as fully as possible with the principles of rational nutrition.
It is also recommended that all patients increase their level of physical activity, especially those who lead a sedentary lifestyle. This could be daily walking, swimming, yoga, or Pilates. But serious physical activity, in particular intense training on simulators, jumping sports, and weightlifting are contraindicated.
If the patient’s profession involves heavy physical labor, such as heavy lifting, it is recommended to try to change it. This is due to the fact that increased loads on the back in the presence of osteochondrosis can play the role of a trigger for the rapid progression of degenerative changes in the discs.
Absolutely all patients with thoracic osteochondrosis are recommended to change the mattress to an orthopedic one with medium hardness, as well as purchase an orthopedic pillow. This will ensure that the physiological curves of the spine are maintained and will prevent further disc degeneration.
How to distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis and neuralgia
It is possible to distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis of the thoracic region by a number of signs presented in the table:
| Diagnosis | Symptoms | How long does an attack last? | Associated symptoms | Where is it localized? |
| Angina pectoris | The appearance of severe pressing pain | About 4 minutes | Fear of dying, desire to empty the bladder | Left side of the chest, back, left upper limb |
| Heart attack | Begins with general weakness, then develops into angina pain | About 3 days | Pale skin, shortness of breath, feeling nauseous | Left hypochondrium, occipital region and abdomen |
| Pericarditis | pain in the heart area | Long-term | Frequent breathing, sudden increase in temperature, swelling of the facial skin and thickening of the blood vessels in the neck | Heart pain extending to the neck and lower jaw |
| Thoracic aortic aneurysms | Feeling of dull, piercing pain radiating to the left upper limb | Long-term | Convulsive cough, shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing | Pain in the heart area, radiating to the left shoulder blade |
| Intercostal neuralgia | Point pain | Over the course of several days | Hypersensitive skin | Along the costal arch |
| Psychosomatic chest pain | Penetrating pain that increases with movement | From several hours to several days | Increased heart rate, body tremors, shortness of breath | Under the chest and in the upper left limb |
| Extrasystole | Pressing sensation under the chest | Individually | Difficulty swallowing, belching | Under left breast |
| Thoracic osteochondrosis | Symptoms of angina pectoris that do not go away when taking Nitroglycerin | Long-term | Painful movements, sharp increase in symptoms when inhaling | Area of the heart and shoulder blades |
| Vegetovascular dystonia | The appearance of a dull aching pain | Less than an hour | The appearance of causeless tachycardia, tremor, poor sleep, increased fatigue | Chest, upper left limb |
Surgery
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is necessary in cases where conservative treatment for 6 months was ineffective. Surgical treatment for osteochondrosis is always selective, which means that the patient himself decides whether to undergo surgery or not.
It is recommended that all factors be taken into account before deciding to undergo surgery for osteochondrosis, including the length of the recovery period, pain management during recovery, and spinal rehabilitation.
Vertebral fusion surgery
The standard surgical treatment for lumbar spine degenerative disc disease is fusion surgery, in which two vertebrae are fused together. The purpose of fusion surgery (spinal fusion) is to reduce pain and eliminate instability in the motion segment of the spine.
All spinal fusion surgeries consist of the following:
- The damaged disc is completely removed from the intervertebral space (discectomy).
- Stabilization is carried out using bone graft and/or instrumentation (implants, plates, rods and/or screws).
- The vertebrae then fuse to form a solid, immobile structure. Fusion occurs within a few months after the procedure, and not during the operation itself.
After the operation, wearing a corset and taking analgesics are prescribed. Physical exercises are included very carefully, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the degree of tissue regeneration. Full recovery from fusion surgery may take up to a year while the vertebrae fuse together.
Surgical replacement with artificial disc
Replacing a damaged disc with an artificial implant has been developed in recent years as an alternative to fusion surgery. Disc replacement surgery consists of completely removing the disc damaged by degeneration (discectomy), restoring the disc space to its natural height, and implanting an artificial disc.
This procedure is designed to maintain motion in the spine similar to natural motion, reducing the likelihood of increased pressure on adjacent spinal segments (a common complication of spinal fusion).
Recovery from disc replacement surgery usually lasts up to 6 months.
The main characteristics of pain arising from cardiac pathologies
Heart disease is divided into several types of pathology: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pericarditis, myocarditis.
Each pathology is accompanied by specific signs, having an idea of which, a person can sound the alarm in time and seek help from a medical institution.
Angina pectoris
An attack of angina is an acute heart failure caused by vasospasm, resulting in insufficient oxygen reaching the heart. The heart begins to contract harder, causing unpleasant sensations such as:
- sudden pain like a prick;
- pain radiates to the upper limbs;
- appear: panic, anxiety, fear of death;
- lack of air, suffocation;
- increased sweating;
- pallor of the skin.
With angina pectoris, pain appears, similar to an injection.
The pain disappears in a short time, as unexpectedly as it appeared. Heart rhythm returns to normal.
The nature of the pain helps differentiate angina from thoracic osteochondrosis. Pain when nerve endings are pinched always occurs or disappears with body movement and does not go away after using heart medications (nitroglycerin). The pain that occurs with this cardiac pathology is provoked by stress, intense physical activity, sudden temperature changes, overeating and goes away after taking nitroglycerin.
The intensity of pain during angina pectoris does not increase with coughing or movement, but may reappear during exercise.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction occurs as a result of a blood clot formed in an artery, which clogs the lumen of the vessel. Blood circulation in this place stops, the integrity of the vessel is disrupted, which leads to bleeding and death of nearby tissues. All this is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sharp, sudden pain that occurs in most cases at night;
- inability to move due to pressing pain behind the sternum;
- panic attacks, resulting in an increase in the level of adrenaline in the blood. Due to the release of adrenaline, the coronary vessels dilate, the pressure drops, and the person loses consciousness;
- severe weakness, feeling of cold, vomiting, thready pulse.
During myocardial infarction, sharp, sudden pain appears.
Life-threatening pain is the main symptom that distinguishes a heart attack from osteochondrosis.
Heart attack pain generally does not arise out of nowhere, but is the result of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease.
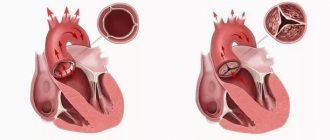
Pericarditis
Pericarditis occurs when the serous membrane of the heart becomes inflamed. Inflammation disrupts the contractile function of the heart, causing unpleasant symptoms:
- pain of increasing nature;
- hyperthermia;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- nausea and vomiting;
- When listening to the heart, a murmur is heard.
Inflammation of the lining of the heart during pericarditis
The main difference between cardiac pain during pericarditis and chondrosis is increasing pain, the intensity of which increases for several days.
- What you can’t do and what you can do at home if your heart hurts
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- slow heartbeat;
- low blood pressure;
- sensations of pain behind the sternum, pressing in nature;
- breathing problems, shortness of breath;
- pale skin with a bluish tint;
- swelling.
Inflammation of the heart muscle with cardiac myocarditis
Symptoms of pain of a pressing nature are a distinctive feature from pain with osteochondrosis.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic physical education plays one of the leading roles in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, since it allows:
- strengthen the muscle corset, which will ensure the creation of high-quality support for the spine;
- normalize muscle tone;
- activate blood circulation, which will improve the course of metabolic processes in the affected intervertebral discs.
But patients should understand that using general sets of exercises can negatively affect the course of the disease and well-being, since they do not take into account individual characteristics, the degree of osteochondrosis and existing concomitant diseases. Therefore, for effective treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, it is necessary to develop an exercise therapy program on an individual basis.
Initially, so that the patient can master the correct exercise technique, it is recommended to exercise under the supervision of an exercise therapy instructor. He will be able to correctly calculate the load in accordance with the level of physical development of a person and adjust his movements so that the exercises performed bring maximum benefit. The program will gradually become more complicated, and after it has been fully mastered, the patient can practice at home. But for classes to give good results, they should be carried out daily.
When performing all therapeutic exercises, it is important to avoid sudden movements.
Associated pain
Patients often make an appointment with a urologist and gynecologist due to pain in the lower abdomen. This is how osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine manifests itself. Formed osteophytes infringe on the spinal roots, causing disruption of innervation. Therefore, when patients ask whether osteochondrosis can cause pain in the lower abdomen, vertebrologists answer in the affirmative. The progression of the pathology is indicated by the absence in the clinical picture of characteristic signs of urogenital diseases - bleeding, the appearance of cheesy discharge, cutting and burning during urination. But difficulties with emptying the bladder and intestines due to disrupted innervation cannot be ruled out. With exacerbation of osteochondrosis, other specific symptoms may occur:
- pain in the mammary glands, requiring differential diagnosis to exclude benign or malignant tumors;
- pain in the hypochondrium, epigastric region, reminiscent of an attack of gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, hepatic colic, hepatitis.
There have even been cases of toothache occurring during relapses of cervical osteochondrosis. Also, a person’s condition can be complicated by increased blood pressure, headaches, and dizziness. The psycho-emotional state is often destabilized - sleep is disrupted, anxiety and fatigue arise.
Diagnostics
- The medical history includes a detailed study of the patient's symptoms, their intensity and the relationship of pain with exercise or body position. Information about regular physical activity, sleep habits, and past injuries is also needed.
- A physical examination is necessary to examine range of motion and muscle condition. The presence of painful areas on palpation or physical abnormalities is also determined. In addition, neurological tests are performed to determine neurological deficits.
- The above diagnostic methods are usually sufficient to diagnose osteochondrosis, but an accurate diagnosis requires the use of imaging methods.
- CT
- Radiography
- MSCT
- PAT
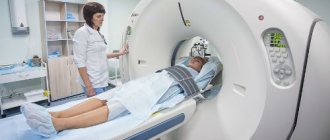
- MRI is a diagnostic method that allows you to clarify the degree of degeneration, the presence of fractures, herniated discs and stenosis. Often, an MRI examination is necessary in preparation for surgical treatment in order to accurately determine the location of the degenerated disc and plan the operation.
Studies have shown that MRI findings of moderate to severe disc degeneration are found in scans of patients with both severe pain and minimal or no pain. In addition, many disease conditions may not show up on MRI. For this reason, the diagnosis cannot be made solely on the basis of imaging results, and verification of the diagnosis is possible only on the basis of a combination of all clinical and instrumental examination methods.
Symptoms for various pathologies
The development of diseases of the central organ of the circulatory system is characterized by certain symptoms and varying degrees of pain.
Angina pectoris
Signs of discomfort that occur with angina pectoris due to acute lack of blood supply to the myocardium:
- pain is paroxysmal, occurs when walking, climbing, emotional stress, during physical activity after eating and disappears after 3-5 minutes in the absence of physical effort;
- 1-3 minutes after taking nitroglycerin, the discomfort in the heart area completely disappears.
Heart attack
With myocardial infarction, the pain is intense, burning and stabbing in nature, manifests itself most often in the morning and lasts several tens of minutes. The syndrome cannot be relieved with medications .
Inflammation of the outer membrane
Inflammation of the outer lining of the heart or pericarditis is characterized by a strong pain symptom, which turns into fever after 2-3 hours from the onset of the acute stage.
Discomfort increases with changes in body position:
- Heart scintigraphy in Moscow
- if a person stands , the pain radiates to the left shoulder;
- when lying down , it intensifies and radiates to the left hand.
Degenerative changes
Degenerative changes in the myocardium or myocarditis often do not have a clear clinical picture and are asymptomatic. In some cases, patients complain of:
- mild or severe pain in the heart, accompanied by shortness of breath;
- general fatigue;
- swelling;
- sweating
Thromboembolism and aortic aneurysm
Acute, stabbing pain in the heart area, aggravated by breathing, and the appearance of shortness of breath at rest may indicate blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus (in this case, pulmonary embolism). Symptoms may be localized in the right hypochondrium, accompanied by bloating and prolonged hiccups.
In some diseases, local expansion of the aortic wall occurs . The clinical picture of an aortic aneurysm depends on the location of the vessel and is often characterized by the absence of symptoms in the early stages. A person may complain of pain in the chest, back, lower jaw, and difficulty breathing.
What types of physical therapy are there?
Physiotherapeutic methods can be natural or artificial. Natural factors include exposure to natural factors - healing waters, mud, sun, sea bathing, etc. Artificial is a hardware effect that imitates the work of natural sources.
A person receives natural health treatments when undergoing spa treatment. Artificial - this is what, in fact, is called physiotherapy. Her patient has the opportunity to undergo treatment not only on vacation in a sanatorium, but also in a clinic at his place of residence. The most common methods of artificial or hardware physiotherapy are as follows:
- Electrophoresis. A procedure often prescribed for various lesions of the spine, during which the patient, under the influence of a weak current, penetrates the skin of medicinal substances.
- Magnetotherapy. The method is based on the effect of a magnetic field on the diseased area. Has a healing and analgesic effect.
- Ultrasound. The procedure provides micro-massage of the required areas using ultrasonic vibrations.
- Ultraviolet radiation. Simulates the effect of the ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight. Has an analgesic, bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect, promotes the synthesis of vitamin D.
- Shock wave method. It is the use of an acoustic wave of a certain length and intensity, which has an analgesic effect.
- Laser therapy. Laser treatment gives several effects at once - pain relief, inflammation relief, stimulation of metabolic processes, wound healing.
- Detensor therapy. During this procedure, special mats are used to stretch the spine.
- UHF. It is the use of ultra-high frequencies for deep heating of soft and bone tissues.
- Electrotherapy. The method is based on the direction of electric current of various frequencies to the affected areas, which is usually used in combination with electrophoresis and the use of therapeutic mud.