Pyelonephritis
Diabetes
Hepatitis
Rheumatism
52098 October 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Urea in the blood: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
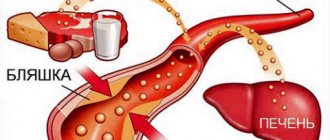
Urea cycle
The urea cycle is a chain of metabolic reactions in the human body. As a result, the toxic substance ammonia is packaged as urea and then released in a safe manner. In the human body, organic substances are constantly formed, broken down or converted into each other. Amino acids play an important role in this process.
Amino acids are part of proteins. Therefore, they are the most important building material of the body. In other words, amino acids are formed by the breakdown of proteins. When amino acids break down, many different substances are formed.
Some of them have a carbon skeleton and therefore can provide the body with energy. However, the other main part of the decomposition products is nitrogen. It turns into:
- ammonia – NH3;
- ammonia – NH4 + combined with hydrogen.
To prevent ammonia from building up in the body, it must be removed continuously. Since the substance is excreted by the kidneys and is toxic, it must first be well packaged.
This occurs during the urea cycle. The urea cycle occurs partly in the mitochondria and partly in the plasma cells of the liver and consumes a lot of energy.
The resulting urea is carried in the blood to the kidneys, filtered and added to the urine. In this process, urea shows its second function - it helps the kidneys produce urine, creating a concentration gradient. Therefore, not only is it permanently excreted only through the kidneys, but it also plays a crucial role in kidney function.
Reasons for low uric acid
Low uric acid levels can result from a low-purine diet. However, doctors often associate this deviation with the presence of one of the following diseases:
- Konovalov-Wilson pathology.
- Fanconi pathology.
- Hodgkin's pathology.
- Pathologies of the kidney tubules.
Uric acid in the blood also decreases during pregnancy. In addition, this deviation is typical for patients with extensive burns, tumor diseases, congenital liver pathologies, and when taking certain medications. If this deviation is detected, the patient is prescribed a series of diagnostic procedures to identify the true cause of low uric acid levels.
In what cases does a doctor prescribe a test?
Urea is used to diagnose various kidney and metabolic diseases. Urea determination is widely used to assess renal function. This test is often ordered along with a creatinine test to diagnose:
- diseases of the adrenal glands - cardiac decompensation, dehydration, increased protein catabolism;
- kidney diseases - glomerulonephritis, polycystic kidney disease, nephrosclerosis, tubular necrosis;
- adrenal hyperemia – urinary tract obstruction).
What to pay attention to before taking the test?
No special patient preparation is required.
The research material is blood.
Some medications may affect test results. Tell your doctor about the medications you are taking. You should not cancel treatment on your own.
The analysis time is 1 business day.
Indications for the study
A blood test for urea is prescribed if the doctor suspects that the patient has kidney or liver pathologies. It is also used to monitor the progress of treatment for such diseases. The test can be administered to patients of any age, including newborns. Kidney problems can be suspected if the patient complains of swelling, sleep disturbances, weakness, decreased appetite or diuresis, pain in the lumbar region, or high blood pressure.
If indicated, the test is usually prescribed independently. In some cases, it is included in a set of studies to obtain the most complete assessment of the patient’s condition.
What do the results mean?
Normal urea values
in blood serum: from 17 to 43 mg/dl or 2.8-7.1 mmol/l.
Increased values:
- acute and chronic renal failure;
- decreased renal perfusion due to heart failure, hypovolemic shock, severe hypotension;
- obstruction of the urinary tract;
- dehydration due to decreased fluid intake, excessive fluid loss - sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, diuretics, etc.;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- catabolic state: trauma, severe infection, fasting, some drugs with a catabolic effect, such as corticosteroids;
- high protein diet;
- aging.
Reduced values:
- liver disease;
- low protein and high carbohydrate diet;
- parenteral nutrition is intravenous nutrition through a catheter inserted into a vein;
- low protein diet;
- overhydration;
- pregnancy;
- advanced liver disease – cirrhosis, liver failure;
- inherited defect of the enzymes of the “urea cycle” - decreased synthesis of urea.
Norms
Urea, like uric acid, is constantly formed in our body. If the patient does not have any diseases that contribute to the accumulation of these substances in the blood, his analysis will show their content within normal limits. And the standards for these substances are as follows:
- Urea in women is normal from 0.15 to 0.45 mmol/l.
- Urea in men is normal from 0.23 to 0.51 mmol/l.
- Uric acid is normal in women from 0.14 to 0.46 mmol/l.
- Uric acid is normal in men from 0.17 to 0.54 mmol/l.
How can you reduce urea levels?
To reduce urea levels:
- avoid heavy physical activity;
- Avoid taking supplements containing creatine;
- eat less protein;
- drink more water;
- follow a diet - eat less meat and poultry, but more fish, nuts, vegetables and fruits, cereals, olive oil.
- limit your salt intake;
- Reduce your intake of bad fats – saturated and trans fats – found in processed meats, cakes, biscuits and pastries;
- Avoid obesity and lead an active lifestyle.
Herbal remedies to reduce urea levels:
- Punarnava or burhaavia spreading
from the umbrella family. This herb helps get rid of excess fluid in the kidneys, reducing swelling without any side effects. - Prickly capers
are from the caper family. Preparations from this plant are used to break up kidney stones and as a cure for urinary tract infections. This herb helps remove elements blocking the urinary tract, removes excess fluid - Gokshura or Nerinjil or devil's weed is native to India. This is a diuretic. It is also used as an herbal tonic to restore kidney cells.
Diagnostics
Both substances under consideration belong to the group of residual nitrogen compounds. Their concentration in the blood is determined during biochemical analysis. In this case, urea on average makes up 45% of the total residual nitrogen, and uric acid only about 20%. In addition to these indicators, experts also evaluate the content of other substances belonging to the group of residual nitrogen, including creatinine, amino acids, ammonium, creatine, etc.
In total, this fraction includes more than 15 substances, but these are the most significant for diagnosis.
In order for the analysis of residual nitrogen components to be as accurate as possible, you need to follow the basic rules for donating blood. The most important of them is taking the test on an empty stomach. It is also necessary to avoid taking alcohol and any medications a few days before the test.
Only a specialist should decipher the analysis. Only a doctor will be able to correctly evaluate the results of your analysis and make a preliminary diagnosis, which will later be confirmed or refuted by additional diagnostics. Quantitative determination of the components of residual nitrogen is not a means of accurate diagnosis, but is only a reason to suspect a disease.
Forecast
Excess urea can lead to serious consequences: uremia up to coma, severe slagging, intoxication of the body, development of heart failure, hypertensive crisis, coronary artery disease, hepatitis or cirrhosis, lifelong dependence on an artificial kidney, death. The reason for the increase in urea levels in the blood is diagnosed within two days from the moment of treatment, so the development of complications depends entirely on the patient’s responsibility for his health. The faster the reaction to the first symptoms or identified pathology, the more favorable the prognosis. It is only necessary to correct the provoking factor. The question of interpretation of results and further tactics is the prerogative and responsibility of the doctor.
Prevention
Prevention of deviations of substances in the residual nitrogen fraction consists primarily of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. If we look at the statistics, we can see that initially deviations develop against the background of poor nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle. The situation is further aggravated by weak immunity and the emergence of chronic diseases.
It is especially important to monitor urea and uric acid levels in children. Deviations in these indicators can result in the development of severe and intractable pathologies for them. It is for this reason that children need to have blood biochemistry done at least once a year.
Every person should understand that any blood component is an indicator of the health of internal organs and systems. Never neglect donating blood for analysis, because it is this substance of our body that first of all reacts to the presence of a disease. In this case, indicators deviate even before the appearance of symptoms of the disease. Monitoring the level of urea and uric acid will allow you to promptly identify abnormalities and receive adequate treatment before dangerous pathologies develop.
Treatment of abnormalities
Now that it has become clear that urea and uric acid are two completely different substances, although similar in some ways, it should be noted that the treatment of abnormalities cannot be the same. Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the root cause of the deviation. It is generally accepted that an increase in uric acid is much more dangerous for the body, but the damage from an increase in urea cannot be underestimated. Each of the deviations carries a threat to humans. For this reason, self-medication is unacceptable. Only a doctor can prescribe adequate therapy for you.
Menu for the week
You can create a sample menu for the week yourself, using the above recommendations and studying the list of desirable and undesirable foods.
As already indicated, meals should be fractional, so the diet consists not only of specific products, but also the time of their consumption. The daily diet contains breakfast with a snack, lunch, afternoon snack and dinner.
- Monday.
Breakfast – weakly brewed coffee with croutons. Add cream to the drink, top the croutons with berry jam. Have a snack by drinking a glass of yogurt without fillers. For lunch, cabbage soup without meat with fresh cabbage, fry potatoes and brew weak herbal tea. For an afternoon snack, baked milk, in addition, if desired, eat a couple of crackers. Dinner - stew zucchini, add any fresh vegetables to it. Also make scrambled eggs. Drink a glass of fermented baked milk.
- Tuesday.
In the morning - cheesecakes and lemon tea. Snack on a pear. For lunch, vegetable soup-puree, as well as cabbage rolls and oatmeal jelly. Before dinner, have a fruit salad snack. Have dinner with vinaigrette, a couple of sandwiches with cheese and wash down with berry juice.
- Wednesday.
For breakfast - cottage cheese with berry tea. Afterwards, eat a couple of small apples. The next meal will consist of milk soup with noodles, barley porridge and a piece of chicken breast. Wash it down with currant juice. For an afternoon snack, prefer toast with jam and fermented baked milk. Dinner with compote and vegetable stew.
- Thursday.
Have breakfast with an omelet with fresh dill. Eat a couple of pieces of black bread. Wash it down with freshly squeezed orange juice. Snack – a handful of walnuts. For lunch, okroshka seasoned with kefir, rice casserole and cranberry juice. As a snack, biscuits with jam. Dinner – stewed potatoes with minced lean meat, green tea.
- Friday.
Breakfast – 2 soft-boiled eggs, cottage cheese casserole and blueberry tea. A couple of tangerines for a snack. For lunch, potato casserole and noodle soup, washed down with compote. Enrich your afternoon snack with a fruit smoothie. For dinner, carrot cutlets seasoned with sour cream. Drink a glass of fermented baked milk.