The blood pressure value is expressed in two numbers. The first indicator is systolic pressure, which is popularly called upper, the second is diastolic, or lower. Systolic shows the level of blood pressure when the heart contracts, diastolic - at the moment of its relaxation.
Normally, blood pressure should not exceed 120/80 mm Hg. pillar If it is between 120/80 and 139/89, we are talking about prehypertension, higher values indicate hypertension, or hypertension. Most often, with elevated blood pressure, both indicators exceed the norm. A more rare occurrence is high lower blood pressure with normal upper blood pressure.
What is diastolic pressure?
It means the degree of blood pressure on the vascular walls at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle, when there is little blood in it. This indicator gives an idea of the tone of the vascular walls, since diastolic pressure is a reaction to their resistance. Lower blood pressure is considered normal if it is below 80 mm Hg. pillar
A sustained increase in diastolic blood pressure indicates a high resistance of the vascular walls, which means their constant spasm. If the vessels are always narrowed, blood flows poorly to the organs and tissues and they do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. This leads to disruption of organ function.
There are three stages of isolated increase in lower blood pressure:
- 1st – 90-100 mm Hg. Art.;
- 2nd – 100-110;
- 3rd - above 110.
Can the signs of hypertension be recognized?
The insidiousness of the disease is that it does not make itself felt for a long time. A person with hypertension that has not been diagnosed by a doctor may feel well for quite a long time, while his heart muscle is already working at high pressure.
At the same time, experienced hypertensive patients can easily name the signs that accompany increased blood pressure. Experts do not call them symptoms of the disease, because, strictly speaking, they do not signal an increase in blood pressure, but a complicated course of the disease.
- The patient's vision deteriorates, headaches, and tinnitus occur.
- Decreased strength and sensation in one or both limbs.
- At rest, shortness of breath and dizziness occur.
- The daily urine output inexplicably decreases.
In case of undiagnosed hypertension of II and III degrees or when stopping taking antihypertensive, blood pressure-lowering drugs prescribed by a doctor, the patient may experience a hypertensive crisis, sharply exacerbating the symptoms of the disease. A significant surge in pressure is accompanied by:
- severe headache and chest pain;
- shortness of breath;
- vomiting;
- disturbances of consciousness and convulsions;
- paralysis and even death.
The only way to detect increased pressure is to measure it with specialized devices, tonometers. The gold standard for diagnosing arterial hypertension is 24-hour blood pressure monitoring performed under the patient’s usual conditions. Diagnosis is carried out using a specialized device attached to the body. It measures blood pressure levels day and night at a specified frequency, identifying “daytime” and “nighttime” hypertension. Often, based on the diagnostic results, the patient is prescribed a consultation with a cardiologist.
Causes of increased diastolic pressure
Hypertension can be primary, that is, it is unknown why blood pressure has risen, and secondary (symptomatic), if it develops against the background of other diseases. Why does diastolic blood pressure increase?
Causes of isolated increase in lower blood pressure
If lower pressure is elevated for a long time, the reasons may be the following:
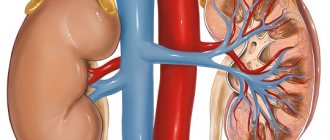
- Kidney disorders. The kidneys are one of the main organs involved in regulating blood pressure. The cause of increased diastolic blood pressure may be a narrowing of the renal artery, in which the volume of blood entering the kidneys decreases. An increase in blood pressure with a predominant increase in diastolic is observed in chronic glomerulonephritis, congenital anomalies in the structure of the renal vessels, and renal failure.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Cardiac pathologies: heart defects, tumor processes.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland.
- Spinal hernias.
- Changes in hormonal balance, for example in women during pregnancy.
The kidneys are directly involved in regulating blood pressure. If their work is disrupted, the pressure deviates from the norm
Reasons for increasing lower blood pressure simultaneously with upper blood pressure
- Increased lower pressure is usually observed in essential hypertension, which is also called essential hypertension (HD) or primary hypertension. The reasons for the increase in pressure in this case have not been established and it is in no way related to other pathologies. Hypertension with high diastolic pressure is more often observed in young people and can progress and take a malignant course. With this disease there is a high probability of developing complications, and the higher the pressure, the greater the risk.
- Lower pressure can change throughout the day in healthy people, for example, it can increase during emotional or physical stress. As a rule, it quickly decreases on its own, and this is considered normal.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
Content:
- Why is hypertension dangerous?
- High blood pressure: causes
- Secondary hypertension
- Why does high blood pressure occur in a child?
- Brief conclusions
Hypertension is a leading risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disorders. It is characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure to 140/90 or more. It can occur at any age, but is more often diagnosed after 35-40 years. Found in 40% of people in the older age group. Of these, 58% are men, 42% of patients are women.
Danger
An increase in lower pressure often has no symptoms, and a person does not even know about it. They may be discovered during a routine examination or when visiting a doctor for other reasons. There is a misconception that only elevated upper blood pressure threatens health and life, but in fact, an increase in lower blood pressure is no less dangerous. The heart in this state is constantly tense and practically does not relax. The blood flow in it is disrupted, the disease progresses, structural changes begin to occur, which ultimately become irreversible.
It is important to know that high lower blood pressure cannot be ignored. It leads to organ dysfunction and, without treatment, can result in death within six months. There is a high risk of developing thrombosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
Prevention
The coherence of the heart and blood vessels is a key link in the health of the whole organism. Thanks to preventive measures, it is possible to maintain their harmony, thereby preventing the development of hypertension. These include:
- a measured lifestyle with adequate physical activity;
- weight loss to normal levels;
- balanced diet;
- quitting smoking, alcohol, drugs.
If the symptoms described above appear, you should begin to systematically measure blood pressure using a tonometer. Regardless of the reasons for high blood pressure, its long-term retention at high levels is a reason to contact a therapist or cardiologist.
Treatment
Treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. You should not do this yourself. First of all, you need to find out the reasons for the increase in lower blood pressure. If hypertension is secondary, treatment of the primary pathology is required. In any case, it is necessary to reduce the pressure, for which a set of measures is used, including:
- proper nutrition;
- loss of excess weight (if any);
- compliance with the daily routine (work and rest);
- physical activity (sports, physical therapy, walking);
- staying in the fresh air;
- taking medications;
- folk remedies.
Diet
Proper nutrition is of great importance for normalizing blood pressure. The diet should consist of:
- Fresh vegetables, herbs, berries and fruits.
- Lean meats.
- Dairy and fermented milk products.
- Lean fish.
- Bread made from wholemeal flour.
- Replace sugar with honey.
The following foods should be limited or avoided:
- salty (salt retains fluid in the body, which increases blood pressure);
- fatty and fried;
- sweet and buttery;
- alcoholic drinks.
All people with hypertension should limit salt in their diet
Medicines
You should only take medications prescribed by your doctor. Typically, medications from several groups are used to normalize blood pressure, including:
- Beta blockers are drugs that reduce the heart's need for oxygen, regulate its functioning and lower blood pressure.
- Calcium antagonists - increase the activity of renin, which is poorly produced in renal pathologies. Prescribed in severe stages of hypertension, for example, in renal failure, after heart attacks to prevent death.
- Diuretics (diuretics).
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers many remedies to lower diastolic blood pressure, but they should only be taken with the permission of a doctor. As a rule, these are decoctions and infusions that reduce nervous tension, help you relax and calm down.
Hawthorn
An infusion of the fruits of this plant relaxes vascular walls and relieves nervous excitability. A glass of water will require 20 grams of dry fruits. Boil for 30 minutes, then strain and add water to the original volume. Take a tablespoon three times a day.
Traditional medicine suggests treating hypertension with a decoction of hawthorn fruits
Motherwort
The infusion increases the strength of heart contractions, calms the nerves, and eliminates overexcitation. Two tables. Pour a spoonful of herbs into a glass of hot water and leave for an hour. Drink two per table. spoons every day before bed.
Diuretic collection
Pour a mixture of herbs (a tablespoon each of St. John's wort, oregano, motherwort and sage) with boiling water (two glasses) and leave for half an hour. Drink half a glass a day for a month.
Valerian
It has a relaxing effect on the central nervous system and helps lower blood pressure.
Peony
Pharmacy tincture from herbs and peony roots eliminates muscle spasms and has a calming effect.
Cedar cones
Tincture of pine cones helps lower blood pressure. To prepare, you need to take three whole cones, put them in a glass jar and fill them with vodka (1/2 liter), add ten pieces of sugar, a tablespoon of valerian tincture purchased at the pharmacy and leave for 10 days in a dark place. Strain and drink a tablespoon before bed. You can fill the cones two more times.
Beet
Freshly squeezed beet juice strengthens vascular walls and is used to lower blood pressure. You need to take two teaspoons of juice daily half an hour before meals.
Diagnostics
In case of newly identified pathology, it is advisable to examine the patient in a hospital setting. If not possible, during outpatient appointments. A cardiologist will help.
If necessary, an endocrinologist, neurologist and nephrologist are involved. Such a “consultation” is not always required, but in most cases.
Accordingly, the list of studies is as follows:
- Assessment of complaints, collection of anamnesis. To objectify symptoms. This is an important step that determines the diagnostic vector.
- Determination of blood pressure levels in both arms.
- Holter monitoring using an automatic programmable tonometer.
- Electrocardiographic study. To assess cardiac function and identify minimal abnormalities. Unfortunately, few people are able to read the result correctly.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasonography.
- Study of hormone levels in the blood.
- Biochemistry of venous blood.
- General analysis of hematological fluid (CFA).
- Study of neurological status, condition of the kidneys and excretory system.
How exactly to examine the patient is decided by specialists.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment is mixed, systematic. It is aimed both at eliminating the root cause of the development of the hypertensive process and at relieving the symptoms that inevitably arise during the course of the disease.
Lowering the lower pressure if it is 100-110 or more must be done carefully, using selective drugs. Rough exposure to classical medications will not work. A complex of medications is needed. Combinations are determined only by a cardiologist.
Since the problem is complex, only an experienced doctor can help. Errors are possible and even probable. But you can’t do anything on your own. It is recommended that all efforts be directed towards finding a competent specialist.
During treatment, and even after therapy, you need to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Don't drink, don't smoke, move more, but within reason, eat right, drink enough fluids, reduce salt intake to an acceptable minimum. These simple recommendations may help save your life.
Lifestyle change
Speaking about how to treat high blood pressure, it should be said that in the complex treatment regimen for this pathology, considerable importance is given to lifestyle changes.
First of all, this concerns diet. You should eat food 4-5 times a day in small portions. Chocolate, coffee, table salt, marinades, fatty and spicy foods are excluded from the diet (or severely limited).
The development of arterial hypertension is indicated in cases where three control measurements recorded blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. Art.
The daily menu should include fresh fruits and vegetables, herbs, dried fruits, foods rich in potassium (nuts, cabbage, tomatoes, baked potatoes, dried apricots), magnesium (buckwheat, fish, dairy products, strawberries, bananas) and B vitamins (yeast , liver, meat, pears, apples, oranges). It is advisable to contact a nutritionist to develop a detailed menu that takes into account the energy needs of the body, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
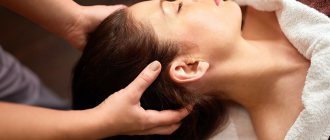
Physical activity. To improve blood circulation, it is necessary to devote sufficient time to physical activity every day. The level of permissible loads is determined by the attending physician, based on the general condition of the patient. Preferably swimming, walking, cycling. General massage is very useful.
Massage is useful for high blood pressure, as it helps normalize vascular tone.
Rejection of bad habits. The patient is advised to completely quit smoking. Nicotine promotes spasm of blood vessels, and hence an increase in diastolic pressure. It is equally important to give up the abuse of alcoholic beverages (it is permissible to drink no more than 50 ml of cognac or 200 ml of red wine per day).
Normalization of sleep and rest patterns. Night sleep should last at least 8-9 hours. You should try to go to bed no later than 10 pm. It is important to adhere to a daily routine, alternating work and rest.
Spa treatment. It is based on the use of climatic and physical factors that normalize the state of the cardiovascular system and thereby stabilize blood pressure.
An increase in diastolic pressure in older people is especially dangerous, since their blood vessels are significantly altered.