Photo: courtesy of the CELT clinic.
Our heart is constantly working: in an adult, it pumps about 10,000 liters of blood per day. In addition, our “fiery engine” is constantly under pressure: overload at work, family problems, stress, abuse... Doctors tritely call it: “heart muscle,” which we ourselves put at risk, leading to a heart attack. For many years and even decades, cardiovascular diseases have consistently led the way.
Why does our heart hurt so often and what are the ways to save it? The answer to these and other questions from our readers and his advice during the direct telephone line “MK” is given by the chief cardiologist of the Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy (CELT), MD. Inna Arkadyevna BESPALKO.
Causes
The exact percentage of the prevalence of coronary vascular spasm, otherwise known as Prinzmetal's angina, among the population has not yet been established.
This indicates that there are not many patients with a similar diagnosis. However, due to the similarity of the clinical picture with other forms of coronary artery disease, you should always be aware of the possibility of this problem. The occurrence of heart spasms is based on two key factors:
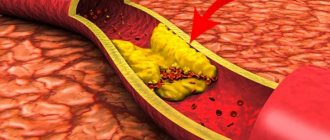
- The presence of atherosclerotic plaques inside the vessel. This appears as accumulations of fatty and inflammatory cells that are deposited in the inner wall of the coronary arteries.
- Spasm. When you are stressed, smoke a lot, or engage in strenuous physical labor, the lumen of the vessels that supply blood to your main “engine” in the body narrows. Given the presence of plaques in the arteries, the supply of oxygen to the muscle fibers of the heart sharply decreases, which provokes the onset of an attack.
These two factors remain key in the development of the disease.
Remember that the spasm rarely lasts longer than 5-10 minutes. This time is not enough for necrosis (infarction, death) of individual muscle fibers to occur, so there is no need to panic. However, a lack of cell nutrition develops with the addition of characteristic symptoms.
Now I will list the factors that provoke spasm of the heart vessels:
- Age. Traditionally, patients over 45-50 years old suffer from variant angina.
- Floor. Men are more susceptible to various types of IHD.
- Atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels of the heart and the whole body. The more plaque there is in the arteries (and the thicker it is), the higher the chance of developing typical signs of the disease.
- Smoking. Nicotine is a substance that stimulates arterial spasm throughout the patient’s body. Due to the presence of plaques in the vessels, an attack can occur virtually after every cigarette smoked. It all depends on the severity of the atherosclerotic process.
- Stress. Under the influence of emotional stress, the muscular lining of blood vessels contracts, reducing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the heart cells.
How to relieve heart spasms
First of all, it is necessary to make sure that the causes of the pathology lie precisely in the arteries. Heart spasm can be diagnosed by performing a hardware scan. To confirm concerns, you will have to undergo an electrocardiogram (determining the ST interval), daily monitoring or echocardiography.
Bicycle ergometry and laboratory blood samples to identify cardiac troponins and other markers indicating severe myocardial damage would be useful.
Unfortunately, there is no clear answer to the question of how to relieve cardiac muscle spasm. Therapy is selected individually, taking into account the physical characteristics of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases. People at risk are advised to carry nitroglycerin with them. If pain occurs in the chest area, you should take this drug in the form of a tablet or a diluted alcohol solution. Usually unpleasant symptoms disappear after a few minutes.
Heart spasms can be the first sign of a dangerous vascular disease. If there are irremovable negative factors (bad heredity, age), a cardiologist or arrhythmologist can prescribe preventive treatment. The most commonly prescribed drugs are anti-ischemic drugs, calcium channel blockers, antioxidants, and anti-sclerotic substances.
What to do if heart spasm becomes a symptom of a serious illness? Surgical treatment is recommended when dangerous arterial defects are identified and when pharmacological effects are low.
- Angioplasty is an operation using a special catheter that expands the lumen of the ducts.
- Coronary bypass surgery is the restoration of blood flow by implanting a “bypass branch” of the circulatory system.
Today, the stenting method is increasingly used. If cardiac spasm occurs due to weakness of the vessel walls, then a special tubular mesh is installed in it, which ensures blood flow.
Symptoms
Some patients I have worked with have believed that symptoms are the same for everyone. That is why I had to explain to them that manifestations can vary depending on the individual characteristics of the body. Of course, a number of general points can still be identified.
The clinical picture of variant angina, the cause of which is precisely a sharp decrease in the diameter of the coronary vessels, is in many ways reminiscent of traditional angina pectoris. Most forms of IHD are similar to each other. My task, as a doctor, remains the differential diagnosis of pathological conditions. The approach to treatment directly depends on this.
Complaints with which people turn to me or another cardiologist for help:
- Pressing pain in the heart area, which can spread to the left arm, neck, jaw. I often hear it compared to a twisting, cramping sensation in the chest. Sometimes patients indicate a burning sensation, which may go away on its own within 5-10 minutes.
- Increased heart rate. Against the background of pain, the heart rate increases. Recently, a woman said that, in addition to chest discomfort, her “heart wanted to jump out of her mouth.” Agree, this is a very eloquent description.
- Dyspnea. A sign that can sometimes be the only clinical manifestation of the pathology.
- Cold sweat. The symptom occurs in severe forms of the disease.
- Nausea, vomiting, confusion are rare but common companions of variant angina.
It will be useful for you to know that variant angina is not associated with physical activity. Most forms of IHD are characterized by an increase in pain during active walking, heavy lifting, and the like. With Prinzmetal's angina, sensations occur spontaneously, often at the same time of day. 55-65% of attacks occur in the early morning hours.
First aid and self-help for a heart attack
A heart attack is a serious pathological condition caused by an acute lack of blood supply to the heart muscle with the subsequent development of death of a section of this muscle. Necrosis
heart muscle is called myocardial infarction.
The most common symptoms of a heart attack are:
- Localization: in the chest area (behind the sternum), pain can radiate to the left arm to the forearm, hand, left shoulder blade, left half of the neck and lower jaw, as well as to both shoulders, both arms, upper abdomen
- Nature of pain: pressing, squeezing, burning or aching intense pain
- Stitching, cutting, aching pains that intensify with changes in body position or when breathing are not characteristic of a true heart attack
- Pain is usually accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness, severe sweating
- Duration of pain more than 5 minutes
What should you do if you have a heart attack?
- Sit (preferably in a chair with armrests) or lie in bed with the head of the bed raised
- Free your neck and provide fresh air (open the vents or window)
- Take 0.25 g of aspirin (chew the tablet, swallow) and 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin (put the tablet/capsule under the tongue, first bite the capsule, do not swallow)
- If, after taking nitroglycerin, severe weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, or a sharp headache appears, then you need to lie down, raise your legs (on a bolster, pillow, etc.), drink 1 glass of water and then you should not take any more nitroglycerin
- If after taking aspirin and nitroglycerin the pain has completely disappeared and the condition has improved, you need to call a doctor at home
- If the pain persists, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin a second time and urgently call an ambulance
- If pain persists 10 minutes after taking the second dose of nitroglycerin, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin for the third time.
ATTENTION! If nitroglycerin or aspirin is not available and the pain persists for more than 5 minutes, call an ambulance immediately.
- A patient with a heart attack is strictly prohibited from standing, walking, smoking or eating until specifically authorized by a doctor.
- Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is contraindicated if you are intolerant to the drug (allergic reactions in the past), or if you have already taken it that day, as well as with a clear exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers
- You should not take nitroglycerin if you have low blood pressure, severe weakness, sweating, as well as severe headache, dizziness, acute impairment of vision, speech or coordination of movements.
- If you have been diagnosed with coronary heart disease or, according to your doctor, you have an increased risk of developing a heart attack, you need to be well aware of the rules of first aid for a heart attack and always have aspirin and nitroglycerin in your pocket
How to give first aid to yourself?
There are different situations in life. What to do if a person cannot seek help, finding himself alone with a heart attack, when it is impossible to reach the phone to call an ambulance, and there is no medicine nearby?
In the event of a heart attack, you cannot waste precious time and you must start... coughing! And as strong as possible!
Before coughing, be sure to take a deep breath. The cough should be deep, “chest”.
The frequency of “inhale-cough” is approximately every 2 seconds. You should do this until you feel a little better so that you can take medicine, if you have one, and call a doctor.
The mechanism of action here is very simple. Taking deep breaths brings oxygen to the lungs, and coughing compresses the heart muscle and causes blood to circulate better. This helps the heart restore its normal rhythm.
What else is important to know?
- Keep your heart medications with you, even if you don't consider yourself a heart patient. By the way, a person with heart failure who constantly carries nitroglycerin or valocordin with him is in a better position than someone who considers himself healthy and does not take medications with him
- Learn the rule: heart medications should always be on hand! Keep them in your desk drawer, your nightstand drawer, and your clothing pockets. If you don’t need them personally, they may be useful to someone else who feels ill with their heart in your presence.
- You should always have a phone at hand - landline or mobile. Of course, it’s not a fact that in case of a sudden deterioration in your health you will be able to use it, but still it is at least some kind of safety net
- If you are experiencing severe stress, try to breathe deeply (even if there are no signs of a heart attack)
- If possible, avoid driving
- Take anti-anxiety medications as prescribed by your doctor
Take care of your health!
Valeologist of the prevention department of the healthcare institution “40th GKP” M. Vereshchagina
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose variant angina, according to modern recommendations and protocols, I use an integrated approach to assessing the patient’s condition. Much in the process of identifying the underlying disease depends on the quality of the first conversation with the patient.
The key features that allow me to diagnose coronary artery spasm are:
- Episodic symptoms that are not associated with physical activity. Patients may suffer from chest pain in the morning, but go to the gym in the afternoon and do a full range of exercises.
- The appearance of discomfort at approximately the same time of day.
- The short duration of the attack, which goes away on its own with further normalization of the person’s condition.
To confirm the appropriate diagnosis, I always additionally prescribe a number of instrumental and laboratory tests.
Instrumental
Traditionally, the first step is to record an ECG. This method allows you to assess the electrical function of the heart, which changes against the background of various forms of coronary artery disease. It is important to note that there may not be any abnormalities on the ECG outside of an attack. This speaks in favor of spasm of the coronary arteries. However, for the reliability of the study, it is necessary to “catch” the patient during the period of pain, which is sometimes extremely difficult, given the night attacks. The film will record ST segment elevation, which is typical of decreased myocardial blood supply.
For the convenience of the patient and to simplify my task, I use Holter monitoring. The technique involves round-the-clock recording of an ECG in a specific patient with further interpretation of the results. With the help of this study, I can easily determine the time of the episode of coronary artery spasm.
Additional Methods
To fully assess the patient’s condition, the following procedures are also used:
- Angiography of cardiac vessels. The essence of the method is to visualize the patient’s coronary arteries on the monitor after introducing a contrast agent into the bloodstream. This allows me to pinpoint the location of the spasm. However, again, you need to “catch” the patient at the moment of the attack.
- Echocardiography. The technique is based on ultrasound examination of the heart. On the screen you can see the cavities of the organ, and I evaluate its functional activity. With Prinzmetal's angina, no special pathological changes occur.
- Test with dosed load. You are asked to exercise on a stationary bike or treadmill in a controlled environment. At this time, an ECG is recorded, pressure is measured and the general condition is assessed. If pain occurs in the heart, the procedure is stopped. However, with variant angina, patients traditionally tolerate the load well.
Based on the results of diagnostic procedures, individual treatment is selected.
How dangerous is this?
The prognosis for patients with coronary artery spasm is relatively good. The pathology does not cause critical damage to the myocardium, but in the absence of adequate treatment, the risk of developing disturbances in the rhythmic activity of the heart remains. This problem can cause a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition or even death.
Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time. Compliance with his recommendations in 90% of cases contributes to the complete elimination of the clinical picture and stabilization of a person’s well-being with a return to normal life.
Expert advice
The simplest and most effective advice that I give to all patients is to quit smoking. Nicotine causes a sharp vascular spasm, provoking a worsening of the disease. In some cases, eliminating tobacco may be sufficient to minimize symptoms. It is important to understand that the more negative factors simultaneously affecting you, the higher the chance of developing heart spasms. You cannot change your gender and age. However, the basic desire to quit smoking and the initiation of adequate therapy contributes to the complete elimination of the unpleasant symptoms of this disease.
Heart spasms - possible causes
The sources of the pathological condition characterized by problems with the functioning of the heart muscle have not been fully studied. Young women and adolescents are more often at risk. It should also be noted that there is an increased risk of an attack for people suffering from blood disorders (poor clotting).
In addition to capillary angina, spasm of the heart vessels can be caused by:
- vascular changes resulting from syphilis, rheumatoid diseases;
- various infections and allergic reactions to external irritants;
- some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
A separate group can be divided into a cause such as atherosclerosis. The disease negatively affects the patency through the coronary arteries, thereby significantly increasing the likelihood of cardiovascular spasm.
Clinical case
A 46-year-old man came to our clinic with complaints of pressing pain in the chest, which arose at rest, mainly at night, and spread to his left arm.
The patient suffers from the problem for 3 months. During the day the symptoms disappear. Exercising in the gym does not aggravate the patient's condition. The disease is associated with stress. The man smokes 1.5 packs of cigarettes per day and suffers from hypertension (160/100 mmHg). ECG at rest without abnormalities. We decided to use Holter monitoring. At three o'clock in the morning an ischemic attack lasting 4 minutes was recorded.
In the morning, when the ECG was re-registered, no pathological changes were detected. Other laboratory and instrumental tests are normal. The patient was diagnosed with IHD. Vasospastic angina, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Arterial hypertension stage II, degree 2, risk. I was prescribed Amlodipine (10 mg orally once a day), Nitroglycerin (1 tablet under the tongue during an attack), Aspirin (75 mg once a day), Rosuvastatin (20 mg per day), lifestyle correction - quitting smoking, minimizing stress. When re-examined 2 weeks later, the patient noted a complete absence of new attacks of chest pain. Feels good, exercise tolerance without restrictions.
I will be glad if this article was useful. Share your experience about episodes of compressive pain in the heart in the comments: how you saved yourself and what helps better. Our experts will help you understand the situation.
Prevention of angina
It is important to understand that spasm of the heart muscle can cause myocardial infarction. Probably everyone knows that such an attack often becomes fatal. What to do and how to avoid danger?
People at risk due to congenital pathologies and age will have to take special medications that support general health.
If no irremovable provoking factors are found, then you just need to give up bad habits (especially smoking), normalize your weight if necessary, and limit your consumption of fatty and starchy foods. Periodic physical activity (walks in the fresh air, active sports) and monitoring of your psycho-emotional state will not be superfluous.