Tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia characterized by an increase in heart rate above normal values. Typically, tachycardia is diagnosed when the heart muscle contraction frequency is more than 90 beats per minute.
Tachycardia is an objective characteristic (as opposed to the patient’s complaints of increased heartbeat). A person may complain of increased heart rate, and at the same time have a normal pulse rate. And vice versa: in some cases, tachycardia does not attract a person’s attention, and he does not notice that his heart is beating faster than normal.
How does tachycardia manifest?
It is important to distinguish between tachycardia:
- as a normal physiological phenomenon during physical activity, anxiety, anxiety or fear. Most often, the cause is the body’s normal reaction to external stimuli: time zone change, use of tonics or medications, stress;
- as a pathological phenomenon - increased heart rate at rest or increased heart rate that is not adequate to the load. The cause may be cardiovascular disease or dysfunction of other organs.
There are many types of tachycardia. Only professionals and highly qualified specialists can determine whether you have symptoms or a predisposition to the disease, and what type of tachycardia is bothering you. By making an appointment with a doctor at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, you will undergo a full examination using new high-tech equipment, receive advice and recommendations on preventing the occurrence of symptoms.
Medicines
In many home medicine cabinets you can find drugs to reduce heart rate. They are available without a doctor's prescription and will help you quickly restore your performance. However, before taking them, it is important to find out the cause of this symptom, since different groups of drugs have different compositions and are indicated for tachycardia of different origins. So, the doctor may recommend the following medications:
- Valocordin, Corvalol - drugs based on phenobarbital and plant extracts, available in the form of drops that need to be diluted in water;
- valerian officinalis - comes in the form of drops and tablets, it helps well with tachycardia caused by nervous tension;
- rosehip or hawthorn fruits, motherwort root - raw materials for the preparation of soothing decoctions, useful for calming the heartbeat;
- if necessary, medications to replenish potassium or magnesium deficiency (Asparkam, Panangin).
There are contraindications, you need to consult a specialist!
Related posts:
- Left side hurts Pain is a complex process, the occurrence of which is not fully understood. She…
- Not enough oxygen - why and what can help Hypoxia (literal translation from Greek - “little oxygen”) is a condition...
- My head is spinning, how to deal with the problem of VSD When the world “floats”, it becomes uncomfortable and frightening: you have to not...
- Neuralgia: causes, symptoms Neuralgia is damage to the peripheral nerves, accompanied by intense pain in…
Forms of tachycardia
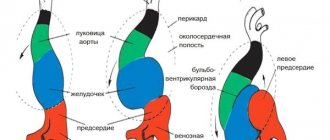
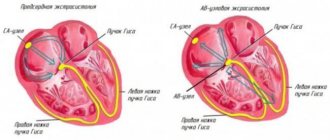
Our heart consists of several sections. As it contracts, it pumps blood throughout the body. When a person is excited, the heart beats faster. The pulse generator, the so-called, controls the work of the heart. sinus node. In normal mode, an impulse originates in the sinus node, which subsequently spreads to other chambers of the heart. When the nervous system affects the sinus node (for example, in diseases of the thyroid gland), it can generate a rapid heartbeat. In some diseases, the role of the pacemaker moves to the cells of the conduction system of the heart, which are located in the atria, atrioventricular node or ventricles. Tachycardia can be classified based on where the electrical impulse originated.
Experts identify several forms:
- Sinus – fast heartbeat with normal pulse, i.e. The heart rate exceeds the norm of 90 beats per minute, but the pulse is rhythmic with equal intervals between pulse fluctuations. This condition is normal and can occur under the influence of physical or emotional stress. Often this is a functional impairment. But sinus tachycardia may indicate heart failure, anemia, or intoxication.
- The atrial form of tachycardia, which can be asymptomatic, is characterized by a strong heartbeat. Occurs in any small area of the atrium. It is episodic and manifests itself as a sudden onset of palpitations. It can be unstable, but repeated, or continuous and stable;
- Atrioventricular - known as nodal tachycardia, because. the ectopic focus (voluntary contraction) is located in the atrioventricular node. It occurs quite often, especially in people under 45 years of age, mostly in women. This is due to greater susceptibility to emotional influences or congenital characteristics of the conduction system of the heart.
- Ventricular – rapid heartbeat from 100 to 220 beats per minute, characterized by an increase in the number of contractions in the ventricles. This occurs due to the disturbed structure of the myocardium, resulting in difficult transmission of electrical impulses to other parts of the heart. The work of the organ at such a pace can lead to ventricular fibrillation - complete disorganization of cardiac functions and cessation of blood circulation. It is important that ventricular tachycardia is always of organic origin, it is not functional;
Identification of one of the forms of tachycardia may indicate dysfunction of the endocrine, autonomic nervous and other systems of the body. For an accurate determination, you should contact a specialist. Doctors at the Cardiology Center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency will conduct a full examination of your heart in order to determine the form of tachycardia with 100% accuracy and give recommendations or prescribe treatment.
When should you see a doctor?
Alarming symptoms include constant heartbeat at rest with a heart rate of more than 80 beats per minute, different time intervals between pulse beats when counting the pulse, different pulse values on the left and right arms.
You should also consult a doctor in case of fainting, episodes of loss of consciousness, chest pain, a feeling of “interruptions” in the heart, tachycardia after blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, when tachycardia is combined with shortness of breath, dizziness, insomnia, frequent headaches, increased blood pressure. pressure, increased sweating, trembling hands.
In addition, it is important to inform your doctor if tachycardia occurs even with minor physical activity and does not go away within 5 minutes, as well as if an attack of tachycardia begins suddenly or there are repeated attacks.
An attack of tachycardia is manifested by the following symptoms: within a few minutes, the heart rate increases sharply and can reach 150-200 beats per minute, accompanied by sweating, weakness, and a feeling of fear.
Causes
The causes of tachycardia can be divided into two blocks:
- Intracardiac - the cause should be sought in the heart. These may be congenital or acquired heart diseases. Among them:
- cardiac ischemia;
arterial hypertension;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart failure;
- heart defects;
- cardiosclerosis;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- idiopathic - primary.
- Extracardiac - the cause of an increased heart rate can be various factors not related to the heart: disease of other organs or systems of the body, or exposure to external factors. In this case it could be:
- physiological reasons - physical activity, severe anxiety, emotional stress;
neurogenic - disruption of the cerebral cortex and subcortical nodes, disorders of the autonomic nervous system (neuroses, psychoses);
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- acute blood loss;
- severe pain attack;
- taking medications that affect the functioning of the sinus node;
- fever due to infectious diseases;
- consumption of tonics - coffee, energy drinks;
- bad habits – smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Determining the causes of tachycardia is extremely important for prescribing the correct treatment. It is not enough to simply eliminate the pathology; it is important to understand what causes it.
What factors affect heart rate?
The most common non-infectious pathology in all countries of the world is diseases of the circulatory system. Based on the results of epidemiological studies dating back to the late 90s of the 20th century, WHO experts came to the conclusion that an increase in heart rate (HR) at rest is one of the risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases in healthy people.
According to the national recommendations of the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiology, the resting heart rate of a healthy adult should be no more than 80-85 beats per minute and correspond to the pulse rate. The optimal heart rate for an adult at rest is from 60 to 80 beats per minute, while the specific heart rate is individual for each person and depends on a number of factors.
The first is gender. Women have higher normal heart rates than men. This is explained by the specific characteristics of hormonal and emotional backgrounds.
The second is age. In adults, the normal heart rate increases with age: at the age of up to 50 years, the average normal value is 70 beats per minute, at the age of 50-60 years - 74 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute in people over 60 years of age.
In addition, heart rate depends on lifestyle, including physical activity: trained people have a lower heart rate than those leading a sedentary lifestyle. Bad habits also have an impact - smoking, alcohol abuse.
And finally, this indicator correlates with external factors: heart rate increases with lack of sleep, nervous tension, after a heavy meal, increased ambient temperature, etc.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary depending on the form of tachycardia and how severe it is (what causes it, how long it lasts). Often, tachycardia can be asymptomatic or accompanied by ordinary malaise.
Among the most common:
- cardiopalmus;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- shortness of breath;
- insomnia;
- feeling of lack of air;
- fatigue;
- decreased appetite;
- decreased performance;
- worsening mood.
Without proper treatment, complications may occur, so you should consult a doctor if these symptoms are detected.
Clinical case
In my practice, there was a case of sinus tachycardia in a pregnant woman.
The woman constantly felt a rapid heartbeat, which was an adaptive reaction of the body: pressure decreased, heart rate increased; but the patient was also diagnosed with anemia. After correcting the hemoglobin level with iron supplements, her health improved and the feeling of palpitations disappeared. Although at first the woman was sincerely surprised when she was not prescribed drugs to slow down her pulse! Depending on the location of the source of excitation, tachycardias are divided into supraventricular and ventricular.
The first arise in the structures of the heart up to the level of branching of the trunk of the His bundle: in the atria, AV node, in additional conduction pathways. The source of origin of the latter is the His bundle, Purkinje fibers, and ventricular myocardium.
Based on the nature of the course, paroxysmal and non-paroxysmal types of pathology are distinguished.
According to the mechanism of occurrence - reciprocal, ectopic, with trigger activity, and so on.
Differential diagnosis of arrhythmias is a difficult and responsible task. In particular, when it comes to tachycardia with wide QRS complexes on the ECG. This may be a ventricular arrhythmia or tachycardia involving the accessory tract (accessory tract).
Ventricular tachycardia has a poor prognosis and occurs as a result of damage to the heart muscle. In contrast, arrhythmia involving the AP appears in a person without gross structural pathology of the heart.
To clarify the type of tachycardia, an ECG with an intrathoracic lead should be recorded or a transesophageal electrophysiological study should be performed. However, in real clinical practice, such an opportunity is rarely provided, and in these situations the doctor is guided by the following rule: assess the condition as the most dangerous to human health and life and begin appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of tachycardia
At the Cardiology Center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, the diagnosis of tachycardia and its forms is carried out by qualified specialists. During the initial visit, the doctor collects the necessary data about the patient: complaints, lifestyle, bad habits. Next, an examination is carried out: the patient’s skin color (with oxygen deprivation it looks pale), the heart rate and respiration rate are calculated. At this stage, heart murmurs may be detected, which will suggest certain causes.
Afterwards, the doctor gives a referral for the collection of laboratory tests and instrumental examination methods, such as ECG, ultrasound of the heart, monitoring, etc.
The FSCC FMBA has several heart examination programs. You can find out more about each by following the link.
Prevention
If you have diseases of the cardiovascular system or have symptoms of tachycardia, preventive measures should be taken.
Even if you are completely healthy, you need to follow some rules that will help keep your heartbeat normal.
For a healthy person it is enough:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle: move actively and regularly, follow a routine and keep your body in good shape;
- monitor proper nutrition and weight;
- refrain from bad habits.
Depending on your health condition, traditional medical care or surgery may be used.
Only professional diagnostics can determine preventive measures to prevent tachycardia. Therefore, it is necessary to contact the specialists of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, because Prevention includes the use of medications, such as sedatives.
Do not self-medicate, contact specialists of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency for professional help.
Tachycardia: norm and pathology
29.Sep.2021
WHO experts say: an increase in heart rate even at rest is one of the risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases even in healthy people
According to the national recommendations of the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiology, the resting heart rate in a healthy adult should be no more than 80-85 beats per minute and correspond to the pulse rate. The optimal heart rate of an adult at rest is from 60 to 80 beats per minute, while the specific heart rate is individual for each person and, first of all, depends on four factors - gender, age, lifestyle and certain external circumstances, such such as nervous tension, lack of sleep, changes in atmospheric pressure and others.
For example, women have a higher normal heart rate than men. This is explained by the specific characteristics of hormonal and emotional backgrounds. With age, heart rate also increases: up to 50 years of age, the average normal value is 70 beats per minute, from 50-60 years old - 74 beats per minute, and 79 beats per minute in people over 60 years of age.
Athletes or people leading an active lifestyle have a lower heart rate than those who are sedentary. Bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse also affect your heart rate.
WE COUNT BY OURSELVES
The most common way to find out your pulse is by palpation (palpation) of the radial artery of the wrist. You need to count your pulse at rest, no earlier than 2 hours after eating, bathing, or massage.
First, you need to take a watch or stopwatch. Sit down with your hand on a horizontal surface, palm up. Place the index, middle and ring fingers of the opposite hand on the wrist approximately 3 centimeters from the base of the thumb;
When you feel the pulsation, you need to lightly press the artery to the inside of the radius. There is no need to press with force, as the pulse wave may disappear under pressure.
Then you need to count the number of blood pulses within 1 minute. Pulse waves should follow each other at regular intervals. The event should be repeated on the second hand.
An increase in heart rate at rest greater than 90 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
PHYSIOLOGY OR POTHOLOGY?
Depending on the causes of occurrence, physiological and pathological tachycardia are distinguished.
Physiological tachycardia occurs during emotional, physical stress, high temperature and humidity, being in hot and stuffy rooms, abuse of tonic drinks - strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, taking certain medications, smoking or drinking alcohol.
In healthy people, physiological tachycardia is an adaptive mechanism and, when the external stimulus is removed, returns to normal levels within 5 minutes.
Pathological tachycardia occurs in cardiovascular, endocrine, acute infectious, oncological and other diseases and accompanying conditions - dehydration, large blood loss, shock conditions, pain syndrome, etc. - or when the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted.
With tachycardia, the heart works under increased load and does not have time to fill with blood in the required volume, the blood supply to all organs deteriorates, and oxygen starvation develops.
The kidneys, organs of vision and gastrointestinal tract, central and peripheral nervous systems suffer, and the course of existing diseases is complicated.
The heart muscle gradually wears out, which can result in heart failure.
You should consult a doctor if you have fainting, episodes of loss of consciousness, chest pain, a feeling of “interruptions” in the heart, tachycardia after blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, if tachycardia is combined with shortness of breath, dizziness, insomnia, frequent headaches, increased blood pressure , increased sweating, trembling hands.
ATTACK OF TACHYCARDIA: practical advice
The attack is characterized by a sharp jump in the pulse. The rate can reach 150-200 beats per minute, accompanied by sweating, weakness, and a feeling of fear. To alleviate the condition you need to:
- unbutton the collar of your clothes. Open the window. Inhale deeply and exhale very slowly (for 5-10 minutes). Then hold your breath and, as it were, “push” the air into the lower abdomen - this stimulates the vagus nerve, as a result of which the heartbeat will slow down.
- Take Corvalol or Valocordin (dissolve 15-20 drops of the drug in half a glass of water at room temperature).
- Wash with cold water. Lie down on a high pillow and place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead.
- Close your eyes and simultaneously press on your eyeballs for 2-3 minutes (10 seconds press, 10 seconds break).
- Find the right carotid artery (directly under the jaw, at this point it connects with the cervical artery) and massage carefully, without pressure. This technique also stimulates the vagus nerve and slows the heart rate.
If there is no improvement, if you experience dizziness, a feeling of shortness of breath, or darkening in your eyes, you must call an ambulance.
PREVENTION
In addition to individual biological factors (gender and age), lifestyle and risk factors for developing cardiovascular diseases influence heart rate levels: high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, low levels of physical activity.
Therefore, prevention of tachycardia is a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits and medical supervision. It is important to control your body weight and undergo diagnostic examinations (ECG, blood glucose levels, cholesterol levels) at least once a year. Do not neglect medical examinations and preventive examinations.
Aibaniz Gyulverdieva, physician-therapist, Nyagan City Polyclinic
Treatment of tachycardia
Depending on the form of tachycardia, various treatment methods are used. Somewhere it is necessary to eliminate external factors, such as refusal of certain physical activities. Somewhere they resort to prescribing medications, as in cases of stress (sedatives), and in serious situations - surgical intervention.
In the therapeutic departments of the Cardiology Center, you will be examined and drug therapy will be selected. If you have a form of tachycardia that can be eliminated, then you may undergo catheter ablation (exposure to the source of the arrhythmia with radiofrequency or cold).
Attacks of palpitations
If a person experiences attacks of rapid and strong heartbeat, then he should fix his attention on the following manifestations of tachycardia:
- the frequency of occurrence of such a condition;
- duration of the attack;
- the cause of tachycardia (stress, food, physical activity, no apparent reason);
- typical time of onset of attacks (time of day);
- associated symptoms;
- pulse rate and rhythm;
blood pressure readings during an attack.